Abstract
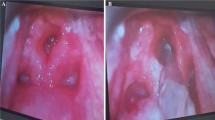
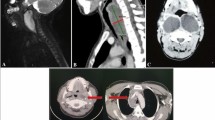
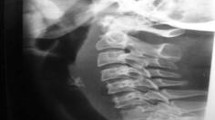
Retropharyngeal abscess (RPA) is a rare, potentially fatal condition found more frequently in young children usually who were having a history of Upper respiratory infection. RPA is an acute suppurative infection of the retropharyngeal space. In view of scarce literature availability and atypical presentation in infants, it poses a definitive diagnostic dilemma to the clinicians. Here, we are reporting a three-month-old male infant presented with feeding difficulty, obstructive sleep apnea and intermittent inspiratory stridor. Child was managed in a pediatric ICU with a multidisciplinary approach which involved pediatrician, otorhinolaryngologist pediatric anesthesiologist, microbiologist, and radiologist. With the recent advances, early radio imaging have a vital role in diagnosing the condition and also helps in planning of surgery. Prompt diagnosis and surgical management with appropriate antimicrobial therapy for this condition is imperative to prevent complications such as airway obstruction and mediastinitis. Timely surgical intervention, preferably intraoral transpharyngeal approach, to drain the abscess is recommended.





Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The data that support the findings of this study are available from Command Hospital Central Command Lucknow, but restrictions apply to the availability of these data, which were used under license for the current study, and so are not publicly available. Data are however available from the authors upon reasonable request and with permission of Command Hospital Central Command Lucknow.
References
Elsherif AM, Park AH, Alder SC, Smith ME, Muntz HR, Grimmer F (2010) Indicators of a more complicated clinical course for pediatric patients with retropharyngeal abscess. Int J Pediatr Otorhinolaryngol 74:198–201
Ukeba Y, Saita Y, Matsuzawa T, Wada T, Kanai N, Kobayashi I (2009) Apnea in a 2-month-old girl with retropharyngeal abscess. Acta Paediatr 98(2):210. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1651-2227.2008.01144.x. (Epub 2008 Nov 22 PMID: 19038013)
Singh I, Madan T, Rai A, Yadav A, Sivasankar R, Rajguru R et al (2020) Retropharyngeal abscess in a 3-month-old infant: a rare entity. J Mar Med Soc 22:241–244
Elsherif AM, Park AH, Alder SC, Smith ME, Muntz HR, Grimmer F (2010) Indicators of a more complicated clinical course for pediatric pa tients with retropharyngeal abscess. Int J Pediatr Otorhinolaryngol 74(2):198–201
Sanz Sánchez CI, Morales AC (2021) Retro pharyngeal abscess. clinical review of twenty five years. Acta Otorrinolaringol Esp 72:71–79
Vinograd AM, Zonfrillo MR, Pawel B (2017) Retropharyngeal abscess and mediastinitis in a well-appearing infant with prolonged fever. Pediatr Emerg Care 33:43–46
LeRiger MM, Miler V, Tobias JD, Raman VT, Elmaraghy CA, Jatana KR (2017) Potential for se vere airway obstruction from pediatric retro pharyngeal abscess. Int Med Case Rep J 10:381–384
Jain H, Knorr TL, Sinha V. Retropharyngeal Abscess. [Updated 2022 Nov 8]. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2022 Jan-. Available from: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK441873/.
RahmanM, SavageJR, LeeCA. Spontaneous descending retropharyngeal abscess. BMJ Case Rep 2009;2009. pii: bcr10.2008.1034]
Hasegawa J, Hidaka H, Tateda M, Kudo T, Sagai S, Miyazaki M et al (2011) An analysis of clinical risk factors of deep neck infection. Auris Nasus Larynx 38:101–107
Jain A, Singh I, Meher R, Raj A, Rajpurohit P, Prasad P (2018) Deep neck space abscesses in children below 5 years of age and their complications. Int J Pediatr Otorhinolaryngol 109:40–43
Showkat SA, Dar FA, Shaf OM, Patigaroo SA, Ahmed R (2020) Deep neck space abscesses in children and methicillin resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) as an emerging pathogen – a clinical study. Int J Curr Microbiol Appl Sci 4:1087–1097
Metin Ö, Öz FN, Tanır G, Bayhan Gİ, Aydın-Teke T, Gayretli-Aydın ZG et al (2014) Deep neck infections in children: experience in a tertiary care center in Turkey. Turk J Pediatr 56:272–279
Bagatell SJ, Weimer SM, van Dyke RB, Bracey SV (2007) Direct extension of an abscess and hematogeneous seeding are other pathways, Neck pain. Clin Pediatr (Phila) 46:280–281
Hay WW, Levin MJ, Sondheimer JM, Detering RR (2010) Lange current diagnosis & treatment pediatrics, 20th edn. McGraw Hill
Römer M, Mäkitie A, Nokso-Koivisto J (2015) University of Helsinki, Helsinki, Finland: pediatric deep neck infections: a 10-year retrospective single-centre study
Red Book: 2015 Report of the Committee on Infectious Diseases, 30th ed, Kimberlin DW, Brady MT, Jackson MA, Long SS. (Eds), American Academy of Pediatrics, Elk Grove Village, IL 2015
Hoffmann C, Pierrot S, Contencin P, Morisseau-Durand MP, Manach Y (2011) Retropharyngeal infections in children. Treatment strategies and outcomes. Int J Pediatr Otorhinolaryngol 75:1099–1003
Wilkie MD, De S, Krishnan M (2019) Defining the role of surgical drainage in paediatric deep neck space infections. Clin Otolaryngol 44(3):366–371
Wong DK, Brown C, Mills N, Spielmann P, Neeff M (2012) To drain or not to drain - management of pediatric deep neck abscesses: a case-control study. Int J Pediatr Otorhinolaryngol 76(12):1810–1813. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijporl.2012.09.006. (Epub 2012 Oct 22 PMID: 23089190)
Acknowledgements
None
Funding
None.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
LBR; Design, Conduct, Analysis, Presentation of research; SR; Design, Conduct, Presentation of research; HCB; Design, Conduct, Analysis, Presentation of research; ST; Design, Conduct, Presentation of research; OSC; Conduct, Analysis, OS; Conduct, Analysis
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing Interests
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
Ethical Clearance was taken from Institutional Ethics committee. The authors assert that all the procedures contributing to the present work comply with the ethical standards of the relevant national and institutional guidelines on human experimentation and with the Helsinki Declaration of 1975, as revised in 2008.
Consent for Participation
The authors certify that they have obtained all appropriate patient consent forms. In the form the patient(s) has/have given his/her/their consent for his/her/their images and other clinical information to be reported in the journal. The patients understand that their names and initials will not be published and due efforts will be made to conceal their identity, but anonymity cannot be guaranteed.
Informed Consent
Informed and written consent was obtained from legal guardian of patient.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Rajanna, L., Raina, S., Bayad, H.C. et al. A Rare Case of Retropharyngeal Abscess in a 3 Month Old Male Infant: Case Report and Review of Literature. Indian J Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 75, 4066–4070 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12070-023-04043-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12070-023-04043-2