Abstract
Background
Charcot arthropathy (CN) can ultimately lead to limb loss despite appropriate treatment. Initial conservative treatment is the accepted treatment in case of a plantigrade foot. The aim of this retrospective study was to investigate the mid- to long-term clinical course of CN initially being treated conservatively, and to identify risk factors for reactivation and contralateral development of CN as well as common complications in CN.
Methods
A total of 184 Charcot feet in 159 patients (median age 60.0 (interquartile range (IQR) 15.5) years, 49 (30.1%) women) were retrospectively analyzed by patient chart review. Rates of limb salvage, reactivation, contralateral development and common complications were recorded. Statistical analysis was performed to identify possible risk factors for limb loss, CN reactivation, contralateral CN development, and ulcer development.
Results
Major amputation-free survival could be achieved in 92.9% feet after a median follow-up of 5.2 (IQR 4.25, range 2.2–11.25) years. CN recurrence occurred in 13.6%. 32.1% had bilateral CN involvement. Ulcers were present in 72.3%. 88.1% patients were ambulating in orthopaedic footwear without any further aids. Presence of Diabetes mellitus was associated with reactivation of CN, major amputation and ulcer recurrence. Smoking was associated with ulcer development and necessity of amputations.
Conclusions
With consistent conservative treatment of CN with orthopaedic footwear or orthoses, limb preservation can be achieved in 92.9% after a median follow-up of 5.2 years. Patients with diabetic CN are at an increased risk of developing complications and CN reactivation. To prevent ulcers and amputations, every effort should be made to make patients stop smoking.
Level of Evidence
III, long-term retrospective cohort study
Similar content being viewed by others
Avoid common mistakes on your manuscript.
Introduction
Charcot arthropathy (CN) has first been described in 1868 by Jean-Martin Charcot [1]. As a chronic, often progressive disease, it affects mostly bones and joints, but also the surrounding soft tissues, and places the affected limb at an increased risk of lower extremity amputation [2, 3]. The incidence of CN is 0.12–0.3% in diabetic patients [3,4,5]. At the time of Charcot`s first description, tabes dorsalis was thought to be the reason for CN [1]. Today, presence of polyneuropathy is known to be the prerequisite for diagnosis of CN [6]. Diabetic neuropathy has become the main risk factor to develop CN aside of the alcoholic polyneuropathy, kidney failure, spinal cord injury or other neuropathies [7]. The Charcot foot appears clinically mostly painless, swollen, flushed and overheated [8]. On conventional X-rays, there is a bony destruction, which typically progresses and results in foot deformities [9]. Those deformities can cause a variety of complications such as ulcers, soft tissue infection or osteomyelitis, with subsequent surgical treatment including amputation [10].
Common classifications of CN exist for clinical stages and anatomical patterns.
The Eichenholtz classification describes three clinical and imaging stages merging into each other [11]. Stage 1 is the active stage with destruction and fragmentation. Stage 2 is the healing stage with coalescence, sclerosis und sintering. Stage 3 is the chronic disease with completed bone remodeling. The original classification was later modified by Shibata et al. with an overheated, swollen, flushed foot with normal radiographic findings, but bone edema and stress fractures in MRI [12].
The Sanders and Frykberg classification defines five anatomical types of [13]. Type I involves the forefoot joints, Type II involves the Lisfranc’s joints, the tarsometatarsal joint, including the metatarsal bases, cuneiforms, and cuboid, Type III includes Chopart’s joints or the naviculocuneiform joints, Type IV contains the ankle with or without subtalar joint involvement and Type V involves the calcaneus [13].
The diagnosis of CN is made based on clinical signs supported by radiological imaging [8, 14]. Presence of polyneuropathy or small fibre neuropathy is an indispensable condition to diagnose CN [6, 15]. In case of ambiguity or to exclude differential diagnoses such as infections, ulcerations, osteomyelitis, joint instability or fractures, MRI is recommended because of the highest diagnostic accuracy [8]. Laboratory investigations can help differentiating between CN and infection [14]. However, C-reactive protein, white blood cell count and erythrocyte sedimentation rate may also be elevated in active CN compared to non-active CN [16].
The aim of treatment is to save the affected limb and to maintain or restore mobility [2, 8]. While there is a trend for more aggressive surgical treatment to achieve a plantigrade foot, the preferred treatment for active CN is activity reduction and off-loading in a total contact cast [8, 14, 17, 18]. Off-loading is upheld until swelling and erythema have vanished and the difference in temperature is less than 2° Celsius compared to the contralateral foot [14, 18]. Protected weightbearing leads to a lower number of complications compared to unprotected weightbearing [19]. After transition to Eichenholtz stage 3, further treatment consists of individual orthopaedic shoes and prevention of complications. If conservative treatment fails or if it is impossible due to a non-plantigrade foot or instability, surgical treatment is indicated [8, 14, 20]. Most often, indications are recurrent ulcers, malalignement and soft tissue infection or even osteomyelitis. Procedures that are performed are simple ulcer debridements, open reductions, exostosectomies, arthrodesis with internal or external fixation, or finally amputations [8, 14, 20,21,22,23]. Amputations can be divided into minor and major amputations with the latter being procedures above the ankle joint [24]. In his benchmark analysis, Pinzur reported that 48.5% of CN patients can be treated conservatively [2].
But what is the clinical course of patients being treated conservatively? Complications such as ulcers, ulcer recurrence, amputation, CN reactivation, and contralateral CN involvement were investigated several times and showed a large variety of results. Ulcers occur in 37–67% [4, 25,26,27,28,29,30,31] and ulcer recurrence in 40–49% of cases [29, 30]. Amputation rates range from 8.9 to 25.7% and the annual amputation rate is 2.7% [23, 27, 30]. Reactivation of CN has been seen in 7.1–33% [4, 32, 33]. The contralateral foot is affected in 9.6% to 30% by CN [32, 33]. While there is a multitude of literature on short-term specific questions concerning CN, there is only little evidence with rather small cohorts on mid- to long-term clinical follow-up for patients being treated for CN initially conservatively [4, 25, 27,28,29,30,31, 34, 35]. None of these studies contains information on all of the above-mentioned complications of CN.
Therefore, the aim of this study was to describe the long-term outcome of patients being treated for CN initially conservatively. Primary outcome measure was the amount of major amputation-free survival. Secondary outcome measures were CN complications (ulcers, ulcer recurrence, CN reactivation, contralateral CN development) and surgical interventions. Further, we sought to determine risk factors for the occurrence of the above-mentioned CN complications as well as reactivation and contralateral CN development. Finally, we aimed to compare our results to literature on surgical treatment of CN. In the author`s opinion, it is appropriate to categorize these results as “long-term” as the study contains data of up to 20 years follow-up.
Patients and methods
Balgrist University Hospital is a tertiary orthopaedic surgery referral center with a specialized unit for “Technical Orthopaedics” (treatment of CN, diabetic feet, chronic wounds, PAD complications, and amputations as well as prosthetics and orthotics).
Patient’s data were retrospectively collected from medical records of patients during the period from January 1st 1995 to March 31st 2018 from the hospital's own information system. All patients were treated by or under direct supervision of one senior orthopaedic surgeon (T.B.). This study was approved by the local Research Ethics Committee (BASEC-Number 2018-00166).
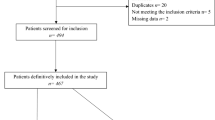
Inclusion criteria were first time diagnosis of CN at the time of admission (by the Eichenholtz criteria [11] and confirmation by conventional X-rays) and conservative treatment initially, age > 18 years, length of clinical follow-up of at least 2 years and informed patient consent obtained in accordance to the rules of the local Research Ethics Committee. Exclusion criteria were primarily surgically treated patients with CN due to a non-plantigrade foot, patients with insufficient documentation in the medical history, and clinical follow-up of less than 2 years. 253 patients were identified. 38 patients refused study participation and were excluded, 56 patients had inadequate patient documentation. In consequence, 159 patients with 184 affected feet were included in the study.
Primary outcome measure was the major amputation-free survival. Secondary outcome measures were CN reactivation, contralateral CN development, rates of ulcers and ulcer recurrence, rates of minor amputations and other surgical procedures related to the diagnosis of CN.
On admission, diagnosis of CN was made using the Eichenholtz criteria [11] and confirmed by conventional X-rays. Decision on conservative vs. surgical treatment was made under the supervision of T.B. Patients who needed immediate surgical correction were not analysed in this study. Patients with a non-collapsed plantigrade CN foot were conducted to conservative therapy. In 119 (64.7%) feet, a total contact cast treatment was initiated which lasted on average 191 days (range 7–640 days) due to CN activity (Eichenholtz stage one or two) or ulcer presence in need of offloading. Total contact casting was performed by one of three nurses who have been trained in casting diabetic and Charcot feet throughout the whole observation period. In the remaining 65 (35.3%) feet, orthopedic custom-made shoes or orthopedic serial-made shoes could be fitted immediately after diagnosis due to Eichenholtz stage three at initial presentation or patient`s refusal of total contact casting.
After total contact casting ended, 112 (60.9%) feet were provided with orthopedic custom-made shoes, 5 (2.7%) feet with orthopedic custom made shoes including an orthotic element for the purpose of hindfoot stabilization, 45 (24.5%) feet with orthopedic serial-made shoes, 2 (1.1%) feet with normal shoes (refusal of any kind of orthopaedic shoes), 5 (2.7%) feet with an ankle foot orthosis (AFO), 1 (0.5%) foot with a therapeutic shoe (patient`s own choice due to the ease of use), and 1 (0.5%) foot with a total contact cast (patient`s own choice instead of a recommended AFO). 13 (7.1%) feet needed a lower leg prosthesis due to major amputation. Besides the two patients (both had one CN foot) who refused any kind of orthopaedic footwear and 13 (7.1%) feet undergoing major amputation, all remaining 169 feet were fitted with a custom molded depth-insole by a certified orthopaedic shoemaker (Swiss master craftsman education). CN reactivation was defined as bony reaffection diagnosed by the clinical criteria of Eichenholtz [11] and confirmed by conventional X-rays and MRI.
Statistical analysis was performed using STATA/IC (version 13; Stata Corp., College Station, TX, USA). The Chi-squared and Wilcoxon rank sum tests were used for comparison of groups. Kaplan–Meier survival estimates were calculated for CN reactivation and for contralateral CN development. Further, Kaplan–Meier survival estimates were calculated for amputation-free survival using SPSS (IBM Corp., Version 26, Armonk, NY, USA). A two-tailed T-Test was used to compare our primary and secondary outcome measures to the results of surgical literature. Values with p < 0.05 were considered statistically significant.
Results
Patient`s demographics are summarized in Table 1. 49 (30.8%) patients were female, 77 (41.8%) feet were left feet. 21 (13.2%) patients died during follow-up after a median follow-up of 5.2 (IQR (interquartile range) 4.25, range 2.2–11.25) years after initiation of treatment. Median age at the time of first diagnosis of CN was 60.0 (IQR 15.5) years.
Clinical stage and sanders type
According to the modified Eichenholtz classification [11, 12], 12 (6.5%) feet were in the prodromal stage, 89 (48.4%) feet in stage 1, 18 (9.8%) feet in stage 2 and 53 (28.8%) feet in stage 3. 12 (6.5%) feet were at the stage of infection. Table 2 summarizes clinical and anatomical distribution at initial diagnosis and at reactivation.
Reactivation
In 25 (13.6%) feet, reactivation was detected clinically and confirmed by MRI. Median time to reactivation was 1.9 (IQR 2.2) years. Clinical and anatomical distributions are given in Table 2 while the Kaplan–Meier survival estimate for reactivation-free survival is given in Fig. 1.
Contralateral Charcot development
133 (83.6%) patients had unilateral CN at the time of initial diagnosis, 26 (16.4%) patients were affected bilaterally. 25/133 (18.8%) patients developed CN on the contralateral side during follow-up. Median latency to contralateral CN development was 1.1 (IQR 2.8) years. In summary, 51/159 (32.1%) patients had bilateral CN at the end of follow-up. Of note, three patients presented initially with contralateral major amputation without having contralateral CN prior to amputation. Kaplan–Meier survival estimate for contralateral CN development-free survival is given in Fig. 2.
Mobility
119 (74.8%) patients were still able to walk six blocks (483 m) without any aids at the end of the follow-up. 37 (23.3%) patients were able to walk six blocks with aids only (walking sticks, walker). Two (1.3%) patients were wheelchair-bound while one (0.6%) was bed-ridden.
Ulcers and ulcer recurrence
At least one ulcer occurred in 133 (72.3%) feet during follow-up: in 55 (29.9%) feet at first diagnosis and in 78 (42.4%) feet during follow-up. Median time to first time ulceration was 1.4 (IQR 2.4) years when patients presented without any ulcer initially. Ulcer distribution is shown in Table 3. A total of 89 (48.4%) patients had ulcer recurrence. The median latency between initial treatment and ulcer recurrence was 1.7 (IQR 3.3) years.
Surgical interventions
78 (42.4%) feet needed one or multiple CN-related surgical procedures during follow-up. The median latency between first consultation and surgery was 1.5 (IQR 4.1) years. One patient, who presented with an ulcer but without signs of infection initially, developed unexpected fulminant infection just 4 days after initial diagnosis and therefore, transtibial amputation had to be performed.
Surgical treatment was removal of exostoses in 10 (5.6%) feet, ulcer debridement in 30 (16.4%) feet, internal realignement arthrodesis in 8 (4.3%) feet, and one-staged external realignment arthrodesis using the Ilizarov ring fixator in 18 (9.8%) feet. In 35 (19.1%) feet, amputations had to be performed. 22 (12%) were minor amputations, 13 (7.1%) were major amputations (Fig. 3, 4, 5 and 6). Median time to major amputation was 2.1 (IQR 4.5) years. Amputation details are shown in Table 4.
Statistical analysis
CN reactivation
Presence of Diabetes mellitus was significantly associated with CN reactivation (p = 0.022). Reactivation could be seen more frequently in type 1 diabetics (6/18; 33%) than in type 2 diabetics (15/113; 13%) or in patients suffering from CN without diabetes (5/53; 8%). All other tested variables were not statistically associated with CN reactivation (Table 5).
Development of contralateral CN during follow-up
Female gender (p = 0.014) was significantly associated with development of contral CN during follow-up (13/57 (22.8%) female feet vs 12/127 (9.4%) male feet). All other tested variables were not statistically associated with Development of contralateral CN during follow-up (Table 6).
Ulcer development
PAD (p = 0.049) and smoking (p = 0.002) were significantly associated with ulcer development. All other tested variables were not statistically associated with ulcer development (Table 7).
Ulcer recurrence
Patients developing ulcer recurrence were significantly younger (median age 57 years) than those without ulcer recurrence (median age 61 years) (p = 0.038). Further, smokers were more likely to develop ulcer recurrence than non-smokers (p = 0.021) as were patients with PAD (p = 0.003), and patients suffering from diabetes (p = 0.023). Sanders type was significantly associated with ulcer recurrence (p = 0.003): 56.9% feet with ulcer recurrence had Sanders type 2 deformity initially. All other tested variables were not statistically associated with ulcer recurrence (Table 7).
Any amputation
Diabetes (p < 0.001), PAD (p < 0.004), and smoking (p < 0.001) were significantly associated with the need for amputation. All other tested variables were not statistically associated with any amputation (Table 8).
Major amputation
Presence of diabetes (p < 0.001) and smoking (p = 0.008) were significantly associated with the need for major amputation. All other tested variables were not statistically associated with major amputation (Table 8).
Power analysis
A post hoc sample size calculation for one of the secondary outcomes, the association of major amputation and smoking yielded a power of 92.7% with an actual alpha of 2.7% (amputations in smokers = 19 (35.2%) (n = 54) versus amputations in non-smokers = 16 (11.5%) (n = 139).
Discussion
Clinical relevance of the present study is that initial conservative treatment of Charcot Arthropathy leads to limb salvage in 92.9% of the affected feet after a median of 5.2 years follow-up.
The present study contains 159 CN patients with 184 affected feet and is not limited to CN in patients with diabetes. The patient number is the second largest in the literature to Jansen et al., who retrospectively analysed 173 patients and 176 CN feet with diabetic CN over a substantial shorter period with a mean follow-up of 2.6 years [31]. Other long-term outcome reports on CN had either fewer patients or shorter follow-up (Bariteau et al. [25], Christensen et al. [35], Fabrin et al. [4], Saltzmann et al. [30]), longer follow-up periods but substantially fewer patients than the present work (Nilsen et al. [27], Pakarinen et al. [29]) or fewer patients and inconclusive or missing information on duration of follow-up (Bergis et al. [34], O'Loughlin et al. [28]). All of the above-mentioned studies lacked one or more outcome information given in this study (Table 9). Hence, in the authors opinion, the present study contains the most comprehensive results in the literature concerning conservative treatment of CN and therefore contributes substantially to the understanding of CN`s clinical course when treated conservatively. Further, it does not preclude patients with CN developing from other reasons than diabetes. Limitations of this study are the retrospective study design with possible occurrence of a collection and/or information bias. Further, we lack a surgical control group. Also, application of total contact casts by three different nurses might have led to a treatment. Though they were trained identically, individual handling of cast techniques might have occurred. Analysis of comparable literature did not reveal information on application of total contact casts. We assume that different institutions face the same staff variability in total contact casting and therefore consider this treatment bias comparable to those of prior literature. Finally, with performance of a post hoc sample size calculation for one of the secondary outcomes, data need to be interpreted with care because this post hoc sample size calculation is not valid for all tests.
Reactivation of CN occurs in 12.5—29.6% [4, 31, 32, 35]. We detected reactivation clinically and radiologically (MRI) in 13.6%. The comparable study of Jansen reported of CN reactivation in 23.3% over a shorter follow-up period [31]. The difference can be explained by the fact that reactivation in Jansen´s study was defined by clinical symptoms (swelling, redness, temperature differences) alone. In our study, a positive MRI showing activity in the bones was a prerequisite for diagnosis of CN reactivation besides clinical signs. When relying on clinical symptoms alone, one may overestimate reactivation due to clinical signs of autonomic neuropathy. Most patients were detected in Eichenholtz stage 1 (n = 20, 80%) and most reactivations occurred at the same localization as initially, which is in accordance to previous reports [4, 32]. Median time to reactivation was 1.9 (IQR 2.2) years. Presence of Diabetes was significantly associated with CN reactivation and could be seen more frequently in type 1 diabetics (33%) than in type 2 diabetics (13%) or in patients suffering from CN without Diabetes (8%). To the best knowledge of the authors, this is new evidence and hints at different clinical courses depending on the etiology of CN. Unfortunately, Bariteau`s analysis of idiopathic CN did not contain information on reactivation which would have been interesting for comparison [25].
Reports of contralateral CN development range from 0 to 75% [4, 27, 29,30,31,32, 35,36,37]. The study of Clohisy with bilateral involvement of 75% reports 18 patients and thus most likely overestimates contralateral involvement [37]. In our study, 26 patients (16.4%) were affected bilaterally at the time of first CN diagnosis. During follow-up, another 25 patients (18.8%) developed contralateral CN. The median latency from diagnosis to contralateral CN was 1.1 years. At the end of follow-up, 51 patients (32.1%) were affected by bilateral CN. The slight increase compared to previous reports might be explained by longer follow-up. Further, the larger study population might have led to a more realistic result: the two studies outmatching our length of follow-up included far less patients than the present work.
Plantar pressure ulcers occur in 38–70.2% in CN [9, 27,28,29,30]. We detected ulcers in 72.3% of the affected feet at any stage of the clinical course. Most ulcers occurred at the toe or metatarsophalangeal joint level (63.2%) while the midfoot level was affected in 30%. Additionally, 6.8% had plantar heel ulcers. Presence of PAD and smoking were significantly associated with ulcer development while the Sanders type was surprisingly not. Pakarinen et al. [29] reported ulcer recurrence in 40%, while in Saltzmann et al. [30] series, 49% had ulcer recurrence and 29% even chronically recurrent ulcers. Ulcer recurrence occurred in 89 (48.4%) feet in our series. 67.4% were located at the toe level and 28.1% at the midfoot level. Younger age (perhaps reflecting more physical activity), smoking, PAD, Diabetes, and Sanders type 2 were associated with ulcer recurrence. The ulcer rate of our collective is slightly higher than in the two studies with longer follow-up (Nilsen and Pakarinen) [27, 29], which include substantially less patients and therefore might have underestimated the number of ulcers. Further, some studies reported only ulcers that derived from plantar CN-related exostoses or elevated pressure [27, 31]. Our report includes ulcers at the toe level (both plantar ulcers and dorsal mostly PIP located ulcers) as well. Substracting those, only 26.3% CN feet had at least one ulcer. Our rate of ulcer recurrence (48.4%) is within the range of previous studies. Substracting toe ulcers, the recurrence rate would be 15.8%. We attribute the low number of (recurrent) midfoot ulcers to consistent fitting of custom molded depth-insoles in 169/171 non-amputated feet.
A significant number of CN feet need any surgical procedure (30–56.1%) [25, 28,29,30]. In our study, 42.4% feet had at least one surgical procedure related to CN during follow-up. The median latency between first consultation and surgery was 1.5 (IQR 4.1) years. Removal of exostoses was necessary in 5.6%, and realignment arthrodesis in 14.1% (internal realignment arthrodesis: 4.3%, one-staged external realignment arthrodesis using the Ilizarov ring fixator: 9.8%). Pakarinen et al. reported of exostoses removal in 33.3% and realignment arthrodesis in 10% [29]. In Saltzman`s cohort, 54% affected feet had any surgical procedure [30]. 11 of those were exostoses removals and 14 realignment arthrodesis procedures. There was no information on possible multiple procedures on the same foot thus making percentage calculation impossible. Bariteau reported the need of surgical treatment in 56.1% of the affected feet and the absolute number of 15 realignment fusion procedures at different levels, but also failed to report if multiple realignment procedures were necessary on the same foot [25]. The slighty higher amount of realignment arthrodesis procedures might have been influenced by higher surgical experience and therefore faster indication. It could also reflect demerits in indicating conservative therapy. Both smoking and presence of a midfoot ulcer were significantly associated with the need of realignment arthrodesis. Interestingly, neither the Sanders type nor Diabetes were significantly associated with the need of realignment arthrodesis.
Overall amputation rates for patients of 20–25.7% are listed in the literature [27, 28]. In the present work, 19.1% feet needed an amputation procedure: 7.1% were major amputations and 12% minor amputations. The necessity of major amputations varies from 1.4 to 22.5% in the literature [4, 25, 27,28,29,30,31, 36, 38]. Fabrin’s 1.4% major amputation is not comparable to our data as it can be explained by the shorter follow-up period, and by inclusion of patients with follow-up periods of less than 2 years, who might have been amputated elsewhere [4]. Bariteau’s 2.4% might stem from the shorter follow-up and—more interestingly—from inclusion of idiopathic CN only [25]. Subanalysis of our patients with major amputation revealed that none of the 27 patients with idiopathic CN, but 9.3% of diabetic CN needed major amputation. Statistically presence of Diabetes was significantly associated with the need of major amputation besides active smoking. Neither the Sanders type nor presence of a midfoot ulcer were associated with major amputation. Thus, major amputation must be expected in any anatomical location. Elmarsafi et al. investigated risk factors for major amputation after CN reconstructive surgery [39]. They found a major amputation rate of 17.2% and identified PAD, renal disease, postoperative delayed healing (defined as nonhealing > 30 days), postoperative osteomyelitis, postreconstruction nonunions, the development of new CN sites, and increased HbA1c as risk factors for major amputation.
In comparison to surgical literature, we could find similar rates in limb salvage (92.9%) compared to studies with similar length of follow-up: 93.7% limbs could be saved according to Fragomen’s series of 16 reconstructed feet[40]. Another recent study by Spraul et al. reported a limb salvage rate of 89% while using the Hoffmann-external Fixator[41]. In a recent study with a mean of 35 months follow-up that analyzed the outcome of a one-staged reconstruction procedure using the Ilizarov principles, Wirth et al. reported successful limb salvage in 93% [42]. Ettinger et al. (31.3 months follow-up) reported a limb salvage rate of 94.8% in their series of surgically reconstructed CN ankles[43]. The same group published a case series (18 months follow-up) of tibiocalcaneal arthrodesis in CN-related talar breakdown, with 91.7% of the affected limbs being saved [44]. Pinzur et al. had a success rate of 97.3% limb salvage but had substantially less follow-up with 12 months [45]. Reinke et al. reported successful limb salvage using the Ilizarov principles in all five cases of CN with talar body necrosis after a follow-up of 27 months[46]. There were no differences in major amputations between the studies by Hegewald et al. [47], Ford et al. [48] and our study (p = 0.730 and p = 0.125, respectively; test on equality of proportions), but our study showed lower proportions of major amputations compared to Eschler et al. [49] and Elmarsafi et al. [39] (7.1% versus 28.6%, p = 0.030 and 7.1% versus 17.2%, p = 0.002, respectively). Compared to the studies by Hegewald et al. [47], Eschler et al. [49], and Elmarsafi et al. [39], our mean time to amputation was significantly different (p = 0.020, p = 0.026, and p = 0.006, respectively; t tests) with amputations occurring after a longer time frame in our study. In comparison to the study by Ford et al., our mean time to amputation showed a trend for differences (p = 0.056), indicating a longer major amputation-free survival as well. However, due to potential patient differences, these comparisons need to be interpreted with care.
Conclusion
With conservative therapy of CN, limb loss can be prevented in almost 93% after 5.2 years. Patients and physicians must be prepared for a high probability of facing complications. In patients with diabetic CN, reactivation of CN is more common than in non-diabetic CN. Diabetics were at an enhanced risk of major amputation and of developing ulcer recurrence. Smoking was significantly associated with the development of ulcers and necessity of amputation procedures. Therefore, when dealing with CN, physicians must take special care if the etiology of CN is of diabetic nature and must make every effort to convince patients to stop smoking.
References
Charcot J (1868) Sur quelques arthropathies qui paraissent dépendre d’une lésion du cerveau ou de la moelle épinière. Arch Physiol Norm et Pathol 1:161–178
Pinzur MS (1999) Benchmark analysis of diabetic patients with neuropathic (Charcot) foot deformity. Foot Ankle Int 20(9):564–567. https://doi.org/10.1177/107110079902000905
Rajbhandari SM, Jenkins RC, Davies C, Tesfaye S (2002) Charcot neuroarthropathy in diabetes mellitus. Diabetologia 45(8):1085–1096. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00125-002-0885-7
Fabrin J, Larsen K, Holstein PE (2000) Long-term follow-up in diabetic Charcot feet with spontaneous onset. Diabetes Care 23(6):796–800. https://doi.org/10.2337/diacare.23.6.796
Stuck RM, Sohn MW, Budiman-Mak E, Lee TA, Weiss KB (2008) Charcot arthropathy risk elevation in the obese diabetic population. Am J Med 121(11):1008–1014. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.amjmed.2008.06.038
Koeck FX, Bobrik V, Fassold A, Grifka J, Kessler S, Straub RH (2009) Marked loss of sympathetic nerve fibers in chronic Charcot foot of diabetic origin compared to ankle joint osteoarthritis. J Orthop Res 27(6):736–741. https://doi.org/10.1002/jor.20807
Frykberg RG, Kozak GP (1978) Neuropathic arthropathy in the diabetic foot. Am Fam Physician 17(5):105–113
Blume PA, Sumpio B, Schmidt B, Donegan R (2014) Charcot neuroarthropathy of the foot and ankle: diagnosis and management strategies. Clin Podiatr Med Surg 31(1):151–172. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cpm.2013.09.007
Armstrong DG, Todd WF, Lavery LA, Harkless LB, Bushman TR (1997) The natural history of acute Charcot’s arthropathy in a diabetic foot specialty clinic. J Am Podiatr Med Assoc 87(6):272–278. https://doi.org/10.7547/87507315-87-6-272
Petrova NL, Edmonds ME (2008) Charcot neuro-osteoarthropathy-current standards. Diabetes Metab Res Rev 24(Suppl 1):S58-61. https://doi.org/10.1002/dmrr.846
Eichenholtz SN (1966) Charcot joints. C. C, Thomas, Springfield, Ill
Shibata T, Tada K, Hashizume C (1990) The results of arthrodesis of the ankle for leprotic neuroarthropathy. J Bone Joint Surg Am 72(5):749–756
Sanders L (1991) Diabetic neuropathic osteoarthropathy: the Charcot foot. The high risk foot in diabetes mellitus. Diabetes Care 34(9):2123–2129
Dodd A, Daniels TR (2018) Charcot neuroarthropathy of the foot and ankle. J Bone Joint Surg Am 100(8):696–711. https://doi.org/10.2106/jbjs.17.00785
Khan A, Petropoulos IN, Ponirakis G, Menzies RA, Chidiac O, Pasquier J, Abi Khalil C, Talal TK, Malik RA (2018) Corneal confocal microscopy detects severe small fiber neuropathy in diabetic patients with Charcot neuroarthropathy. J Diabetes Investig 9(5):1167–1172. https://doi.org/10.1111/jdi.12806
Hingsammer AM, Bauer D, Renner N, Borbas P, Boeni T, Berli M (2016) Correlation of systemic inflammatory markers with radiographic stages of charcot osteoarthropathy. Foot Ankle Int 37(9):924–928. https://doi.org/10.1177/1071100716649173
Botek G, Figas S, Narra S (2019) Charcot neuroarthropathy advances: understanding pathogenesis and medical and surgical management. Clin Podiatr Med Surg 36(4):663–684. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cpm.2019.07.002
Ramanujam CL, Facaros Z (2011) An overview of conservative treatment options for diabetic Charcot foot neuroarthropathy. Diabet Foot Ankle. https://doi.org/10.3402/dfa.v2i0.6418
Renner N, Wirth SH, Osterhoff G, Böni T, Berli M (2016) Outcome after protected full weightbearing treatment in an orthopedic device in diabetic neuropathic arthropathy (Charcot arthropathy): a comparison of unilaterally and bilaterally affected patients. BMC Musculoskelet Disord 17(1):504. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12891-016-1357-4
Güven MF, Karabiber A, Kaynak G, Oğüt T (2013) Conservative and surgical treatment of the chronic Charcot foot and ankle. Diabet Foot Ankle. https://doi.org/10.3402/dfa.v4i0.21177
Pinzur MS (2016) Surgical treatment of the Charcot foot. Diabetes Metab Res Rev 32(Suppl 1):287–291. https://doi.org/10.1002/dmrr.2750
Pinzur MS, Schiff AP (2018) Deformity and clinical outcomes following operative correction of Charcot foot: a new classification with implications for treatment. Foot Ankle Int 39(3):265–270. https://doi.org/10.1177/1071100717742371
Schneekloth BJ, Lowery NJ, Wukich DK (2016) Charcot neuroarthropathy in patients with diabetes: an updated systematic review of surgical management. J Foot Ankle Surg 55(3):586–590. https://doi.org/10.1053/j.jfas.2015.12.001
Larsson J, Apelqvist J, Agardh CD, Stenström A (1995) Decreasing incidence of major amputation in diabetic patients: a consequence of a multidisciplinary foot care team approach? Diabet Med 12(9):770–776. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1464-5491.1995.tb02078.x
Bariteau JT, Tenenbaum S, Rabinovich A, Brodsky JW (2014) Charcot arthropathy of the foot and ankle in patients with idiopathic neuropathy. Foot Ankle Int 35(10):996–1001. https://doi.org/10.1177/1071100714543649
Larsen K, Fabrin J, Holstein PE (2001) Incidence and management of ulcers in diabetic Charcot feet. J Wound Care 10(8):323–328. https://doi.org/10.12968/jowc.2001.10.8.26113
Nilsen FA, Molund M, Hvaal KH (2018) High incidence of recurrent ulceration and major amputations associated with Charcot foot. J Foot Ankle Surg 57(2):301–304. https://doi.org/10.1053/j.jfas.2017.10.008
O’Loughlin A, Kellegher E, McCusker C, Canavan R (2017) Diabetic charcot neuroarthropathy: prevalence, demographics and outcome in a regional referral centre. Ir J Med Sci 186(1):151–156. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11845-016-1508-5
Pakarinen TK, Laine HJ, Mäenpää H, Mattila P, Lahtela J (2009) Long-term outcome and quality of life in patients with Charcot foot. Foot Ankle Surg 15(4):187–191. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fas.2009.02.005
Saltzman CL, Hagy ML, Zimmerman B, Estin M, Cooper R (2005) How effective is intensive nonoperative initial treatment of patients with diabetes and Charcot arthropathy of the feet? Clin Orthop Relat Res 435:185–190. https://doi.org/10.1097/00003086-200506000-00026
Jansen RB, Jørgensen B, Holstein PE, Møller KK, Svendsen OL (2018) Mortality and complications after treatment of acute diabetic Charcot foot. J Diabetes Complications 32(12):1141–1147. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jdiacomp.2018.09.013
Osterhoff G, Böni T, Berli M (2013) Recurrence of acute Charcot neuropathic osteoarthropathy after conservative treatment. Foot Ankle Int 34(3):359–364. https://doi.org/10.1177/1071100712464957
Rudrappa S, Game F, Jeffcoate W (2012) Recurrence of the acute Charcot foot in diabetes. Diabet Med 29(6):819–821. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1464-5491.2011.03539.x
Bergis D, Bergis PM, Hermanns N, Zink K, Haak T (2014) Coronary artery disease as an independent predictor of survival in patients with type 2 diabetes and Charcot neuro-osteoarthropathy. Acta Diabetol 51(6):1041–1048. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00592-014-0669-9
Christensen TM, Gade-Rasmussen B, Pedersen LW, Hommel E, Holstein PE, Svendsen OL (2012) Duration of off-loading and recurrence rate in Charcot osteo-arthropathy treated with less restrictive regimen with removable walker. J Diabetes Complications 26(5):430–434. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jdiacomp.2012.05.006
Berli M, Vlachopoulos L, Leupi S, Böni T, Baltin C (2017) Treatment of Charcot Neuroarthropathy and osteomyelitis of the same foot: a retrospective cohort study. BMC Musculoskelet Disord 18(1):460. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12891-017-1818-4
Clohisy DR, Thompson RC Jr (1988) Fractures associated with neuropathic arthropathy in adults who have juvenile-onset diabetes. J Bone Joint Surg Am 70(8):1192–1200
Doria M, Viadé J, Palomera E, Pérez R, Lladó M, Costa E, Huguet T, Reverter JL, Serra-Prat M, Franch-Nadal J, Mauricio D (2018) Short-term foot complications in Charcot neuroarthropathy: a retrospective study in tertiary care centres in Spain. Endocrinol Diabetes Nutr 65(9):479–485. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.endinu.2018.06.004
Elmarsafi T, Anghel EL, Sinkin J, Cooper PS, Steinberg JS, Evans KK, Kim PJ, Attinger CE (2019) Risk factors associated with major lower extremity amputation after osseous diabetic Charcot reconstruction. J Foot Ankle Surg 58(2):295–300. https://doi.org/10.1053/j.jfas.2018.08.059
Fragomen AT, Borst E, Schachter L, Lyman S, Rozbruch SR (2012) Complex ankle arthrodesis using the Ilizarov method yields high rate of fusion. Clinical Orthopaedics and Related Research 470(10):2864–2873. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11999-012-2470-9
Spraul AMS, Schönbach AM, Müller N, Müller UA, Koller A, Spraul M (2020) Long-term outcome of persons with diabetic and non-diabetic neuro-osteoarthropathy after foot correction using external fixation. Diabet Med 15:e14404. https://doi.org/10.1111/dme.14404
Wirth SH, Viehofer AF, Tondelli T, Hartmann R, Berli MC, Boni T, Waibel FWA (2020) Mid-term walking ability after Charcot foot reconstruction using the Ilizarov ring fixator. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg 140(12):1909–1917. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00402-020-03407-5
Ettinger S, Plaass C, Claassen L, Stukenborg-Colsman C, Yao D, Daniilidis K (2016) Surgical management of charcot deformity for the foot and ankle-radiologic outcome after internal/external fixation. J Foot Ankle Surg 55(3):522–528. https://doi.org/10.1053/j.jfas.2015.12.008
Ettinger S, Stukenborg-Colsman C, Plaass C, Yao D, Claassen L, Berger S, Waizy H, Becher CM, Daniilidis K (2016) Tibiocalcaneal arthrodesis as a limb salvage procedure for complex hindfoot deformities. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg 136(4):457–462. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00402-016-2420-1
Pinzur MS, Gil J, Belmares J (2012) Treatment of osteomyelitis in Charcot foot with single-stage resection of infection, correction of deformity, and maintenance with ring fixation. Foot Ankle Int 33(12):1069–1074. https://doi.org/10.3113/fai.2012.1069
Reinke C, Lotzien S, Yilmaz E, Hanusrichter Y, Ull C, Baecker H, Schildhauer TA, Gessmann J (2021) Tibiocalcaneal arthrodesis using the Ilizarov fixator in compromised hosts: an analysis of 19 patients. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00402-021-03751-0
Hegewald KW, Wilder ML, Chappell TM, Hutchinson BL (2016) Combined internal and external fixation for diabetic Charcot reconstruction: a retrospective case series. J Foot Ankle Surg 55(3):619–627. https://doi.org/10.1053/j.jfas.2015.04.016
Ford SE, Cohen BE, Davis WH, Jones CP (2019) Clinical outcomes and complications of midfoot Charcot reconstruction with intramedullary beaming. Foot Ankle Int 40(1):18–23. https://doi.org/10.1177/1071100718799966
Eschler A, Wussow A, Ulmar B, Mittlmeier T, Gradl G (2014) Intramedullary medial column support with the Midfoot Fusion Bolt (MFB) is not sufficient for osseous healing of arthrodesis in neuroosteoarthropathic feet. Injury 45:S38–S43. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.injury.2013.10.037
Acknowledgements
We are indebted to the study nurses and secretaries of the Unit for Clinical and Applied Research (UCAR) of Balgrist University Hospital, for their invaluable help in the follow-up of our study patients and the redaction of protocols.
Funding
Open Access funding provided by Universität Zürich.. The authors received no financial support for the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethical review committee statement
Attached below.
Location of work statement
The study was conducted at Balgrist University Hospital, Zurich Switzerland. It served as the doctoral thesis of Ms. Gratwohl.
Conflict of interest
Each author certifies that he or she has no commercial associations (eg, consultancies, stock ownership, equity interest, patent/licensing arrangements, etc.) that might pose a conflict of interest in connection with the submitted article.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article's Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article's Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/.
About this article
Cite this article
Gratwohl, V., Jentzsch, T., Schöni, M. et al. Long-term follow-up of conservative treatment of Charcot feet. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg 142, 2553–2566 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00402-021-03881-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00402-021-03881-5