Abstract
Background
Percutaneous vertebroplasty is an efficient procedure to treat painful osteoporotic vertebral compression fractures. However, refracture of cemented vertebrae occurs rarely after percutaneous vertebroplasty. This study was undertaken to investigate the incidence, characteristics, predisposing factors, and mistakes in technique associated with refracture of the same vertebra after percutaneous vertebroplasty.
Methods
From 2001 to 2008, PVP with bone cement (polymethylmethacrylate, PMMA) was carried out in 2,291 patients with 2,581 PVP procedures. The etiologies including pathologic fracture (including metastasis, osteolytic tumor, hemangioma) in 299 patients, infectious spondylitis in 4 patients and osteoporotic compression fractures in 1,988 patients. A total of 1,988 patients with 2,110 VCFs underwent PVP with PMMA cement after failing conservative treatment for at least 3 months. New recollapsed vertebral fractures were diagnosed as recurrent intractable back pain, postoperatively correlated with serial plain radiography and MR image. Clinical parameters such as age, gender, body mass index, and fracture-free interval (from the date of the initial intervention with percutaneous vertebroplasty to the diagnosis of subsequent fractures) were recorded. Parameters related to imaging and technical characteristics, including the amount of bone cement injected per procedure, level, the presence of osteonecrosis in the vertebral body, and the surgical approach (uni- or bipedicles), the restoration of kyphosis angle and height of the anterior border of the collapsed vertebral body, and any leakage of cement into the disk space were also recorded.
Results
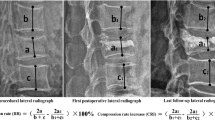
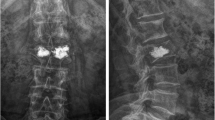
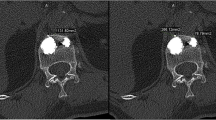
In a 2-year follow-up, 1,800 patients with 1,820 VCFs were retrospectively reviewed and 10 patients with 10 VCFs developed refracture of the same vertebra after PVP with an incidence rate of 0.56% (10 in 1,800). The mean age of the ten patients (nine females and one male) was 79.6 years, and the mean BMI is 22.3. Levels of refracture after PVP were all located in the thoracolumbar junction (T12-L2): three in T12; four in L1; and three in L2. Osteonecrosis was present in all patients and intradiscal cement leakage was noted in five patients. The mean of the restoration of kyphosis angle was 7.7° and height of the anterior border was 26%. Osteonecrosis, greater anterior vertebral height restoration, lesser kyphosis angle correction and cystic filling pattern were statistically significant.
Conclusions
Our study suggests that larger height restoration and solid lump filling cement are risk factors of refracture of cemented vertebral bodies. Symmetric cement distribution and fluid aspiration would be the potential ways to avoid refracture of cemented vertebral bodies.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Diamond TH, Champion B, Clark WA (2003) Management of acute osteoporotic vertebral fractures: a nonrandomized trial comparing percutaneous vertebroplasty with conservative therapy. Am J Med 114:257–265
Jensen ME, Evans AJ, Mathis JM, Kallmes DF, Cloft HJ, Dion JE (1997) Percutaneous polymethylmethacrylate vertebroplasty in the treatment of osteoporotic vertebral body compression fractures: technical aspects. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 18:1897–1904
Weill A, Chiras J, Simon JM, Rose M, Sola-Martinez T, Enkaoua E (1996) Spinal metastases: indications for and results of percutaneous injection of acrylic surgical cement. Radiology 199:241–247
Cotten A, Dewatre F, Cortet B, Assaker R, Leblond D, Duquesnoy B, Chastanet P, Clarisse J (1996) Percutaneous vertebroplasty for osteolytic metastases and myeloma: effects of the percentage of lesion filling and the leakage of methyl methacrylate at clinical follow-up. Radiology 200:525–530
Uppin AA, Hirsch JA, Centenera LV, Pfiefer BA, Pazianos AG, Choi IS (2003) Occurrence of new vertebral body fracture after percutaneous vertebroplasty in patients with osteoporosis. Radiology 226:119–124
Trout AT, Kallmes DF, Kaufmann TJ (2006) New fractures after vertebroplasty: adjacent fractures occur significantly sooner. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 27:217–223
Komemushi A, Tanigawa N, Kariya S, Kojima H, Shomura Y, Komemushi S, Sawada S (2006) Percutaneous vertebroplasty for osteoporotic compression fracture: multivariate study of predictors of new vertebral body fracture. Cardiovasc Interv Radiol 29:580–585
Kim SH, Kang HS, Choi JA, Ahn JM (2004) Risk factors of new compression fractures in adjacent vertebrae after percutaneous vertebroplasty. Acta Radiol 45:440–445
Lin EP, Ekholm S, Hiwatashi A, Westesson PL (2004) Vertebroplasty: cement leakage into the disc increases the risk of new fracture of adjacent vertebral body. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 25:175–180
Berlemann U, Ferguson SJ, Nolte LP, Heini PF (2002) Adjacent vertebral failure after vertebroplasty: a biomechanical investigation. J Bone Joint Surg Br 84:748–752
Lee ST, Chen JF (2004) A syringe compressor for vertebroplasty: technical note. Surg Neurol 61:580–584
Voormolen MH, Lohle PN, Juttmann JR, van der Graaf Y, Fransen H, Lampmann LE (2006) The risk of new osteoporotic vertebral compression fractures in the year after percutaneous vertebroplasty. J Vasc Interv Radiol 17:71–76
Cohen JE, Lylyk P, Ceratto R, Kaplan L, Umanskyt F, Gomori JM (2004) Percutaneous vertebroplasty: technique and results in 192 procedures. Neurol Res 26:41–49
Fourney DR, Schomer DF, Nader R, Chlan-Fourney J, Suki D, Ahrar K, Rhines LD, Gokaslan ZL (2003) Percutaneous vertebroplasty and kyphoplasty for painful vertebral body fractures in cancer patients. J Neurosurg 98:21–30
Kremer MA, Fruin A, Larson TC III, Roll J, Weil RJ (2003) Vertebroplasty in focal Paget disease of the spine. Case report. J Neurosurg 99:110–113
Baerlocher MO, Munk PL, Liu DM, Tomlinson G, Badii M, Kee ST, Loh CT, Hardy BW, Murphy KJ (2010) Clinical utility of vertebroplasty: need for better evidence. Radiology 255(3):669–674
Buchbinder R, Kallmes DF (2010) Vertebroplasty: when randomized placebo-controlled trial results clash with common belief. Spine J 10(3):241–243
Buchbinder R, Osborne R, Ebeling P, Wark JD, Mitchell P, Wriedt C, Graves S, Staples MP, Murphy B (2009) A randomized trial of vertebroplasty for painful osteoporotic vertebral fractures. N Engl J Med 361:557–568
Kallmes D, Comstock B, Heagerty P, Tuner JA, Wilson DJ, Diamond TH, Edwars R, Gray LA, Stout L, Owen S, Hollingworth W, Ghdoke B, Annesley-Willams DJ, Ralston SH, Jarvik JG (2009) A randomized trial of vertebroplasty for osteoporotic spinal fractures. N Engl J Med 361:569–579
Voormolen MH, Mali WP, Lohle PN, Fransen H, Lampmann LE, van der Graaf Y, Juttmann JR, Jansssens X, Verhaar HJ (2007) Percutaneous vertebroplasty compared with optimal pain medication short-term clinical outcome of patients with subacute or chronic painful osteoporotic vertebral compression fractures. The VERTOS study. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 28:555–560
Diel P, Merky D, Roder C, Popp A, Perler M, Heini PF (2009) Safety and efficacy of vertebroplasty: early results of a prospective one-year case series of osteoporosis patient in an academic high-volume center. Indian J Orthop 43:228–233
Yamada K, Matsumoto Y, Kita M, Yamamoto K, Kobayashi T, Takanaka T (2004) Long-term pain relief effects in four patients undergoing percutaneous vertebroplasty for metastatic vertebral tumor. J Anesth 18:292–295
Syed MI, Patel NA, Jan S, Harron MS, Morar K, Shaikh A (2005) New symptomatic vertebral compression fractures within a year following vertebroplasty in osteoporotic women. ANJR Am J Neuroradiol 26:1601–1604
Tanigawa N, Komemushi A, Kariya S, Kojima H, Shomura Y, Sawada S (2006) Radiological follow-up of new compression fractures following percutaneous vertebroplasty. Cardiovasc Interv Radiol 29:92–96
Lee WS, Sung KH, Jeong HT, Sung YS, Hyun YI, Choi JY, Kee KS, Ok CS, Choi YW (2006) Risk factors of developing new symptomatic vertebral compression fractures after percutaneous vertebroplasty in osteoporotic patients. Eur Spine J 15:1777–1783
Serra L, Kermani FM, Panagiotopoulos K, De Rosa V, Vizioli L (2007) Vertebroplasty in the treatment of osteoporotic vertebral fractures: results and functional outcome in a series of 175 consecutive patients. Minim Invasive Neurosurg 50:12–17
Hiwatashi A, Westesson PL (2007) Patients with osteoporosis on steroid medication tend to sustain subsequent fractures. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 28:1055–1057
Chang CY, Teng MH, Wei CJ, Luo CB, Chang FC (2006) Percutaneous vertebroplasty for patients with osteoporosis: a one-year follow-up. Acta Radiol 47:568–573
Lin CC, Chen IH, Yu TC, Chen A, Yen PS (2007) New symptomatic compression fracture after percutaneous vertebroplasty at the thoracolumbar junction. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 28:1042–1045
Chou LH, Knight RQ (1997) Idiopathic avascular necrosis of a vertebral body. Case report and literature review. Spine 22:1928–1932
Leslie-Mazwi T, Deen HG (2006) Repeated fracture of a vertebral body after treatment with balloon kyphoplasty: case illustration. J Neurosurg Spine 4:270
Wagner AL, Baskurt E (2006) Refracture with cement extrusion following percutaneous vertebroplasty of a large interbody cleft. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 27:230–231
Gaughen JR Jr, Jensen ME, Schweickert PA, Marx WF, Kallmes DF (2002) The therapeutic benefit of repeat percutaneous vertebroplasty at previously treated vertebral levels. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 23:1657–1661
Yu CW, Hsu CY, Shih TT, Chen BB, Fu CJ (2007) Vertebral osteonecrosis: MR imaging findings and related changes on adjacent levels. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 28:42–47
Young WF, Brown D, Kendler A, Clements D (2002) Delayed post-traumatic osteonecrosis of a vertebral body (Kummell’s disease). Acta Orthop Belg 68:13–19
Teng MM, Wei CJ, Wei LC, Luo CB, Lirng JF, Chang FC, Liu CL, Chang CY (2003) Kyphosis correction and height restoration effects of percutaneous vertebroplasty. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 24:1893–1900
Hiwatashi A, Moritani T, Numaguchi Y, Westesson PL (2003) Increase in vertebral body height after vertebroplasty. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 24:185–189
McKiernan F, Faciszewski T, Jensen R (2003) Reporting height restoration in vertebral compression fractures. Spine 28:2517–2521
McKiernan F, Faciszewski T, Jensen R (2005) Does vertebral height restoration achieved at vertebroplasty matter? J Vasc Interv Radiol 16:973–979
Liebschner MAK, Rosenberg WS, Keaveny TM (2001) Effects of bone cement volume and distribution on vertebral stiffness after vertebroplasty. Spine 26:1547–1554
Belkoff SM, Mathis JM, Jasper LE, Deramond H (2001) The biomechanics of vertebroplasty: the effect of cement volume on mechanical behavior. Spine 26:1537–1541
Lane JI, Maus TP, Wald JT, Thielen KR, Bobra S, Luetmer PH (2002) Intravertebral clefts opacified during vertebroplasty: pathogenesis, technical implications, and prognostic significance. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 23:1642–1646
Peh WC, Gelbart MS, Gilula LA, Peck DD (2003) Percutaneous vertebroplasty: treatment of painful vertebral compression fractures with intraosseous vacuum phenomena. AJR Am J Roentgenol 180:1411–1417
McKiernan F, Jensen R, Faciszewski T (2003) The dynamic mobility of vertebral compression fractures. J Bone Miner Res 18:24–29
Acknowledgments
We thank the Department of Orthopaedic Surgery for their contribution to the study.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
M.-K. Hsieh, J.-C. Liao, P.-L. Lai, C.-C. Niu, T.-S. Fu, T.-T. Tsai, and W.-J. Chen contributed equally to this work.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chen, LH., Hsieh, MK., Liao, JC. et al. Repeated percutaneous vertebroplasty for refracture of cemented vertebrae. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg 131, 927–933 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00402-010-1236-7
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00402-010-1236-7