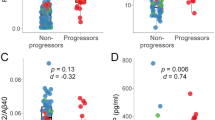
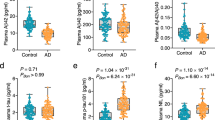
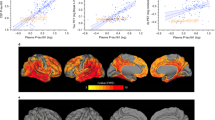
Abstract
While plasma biomarkers for Alzheimer’s disease (AD) are increasingly being evaluated for clinical diagnosis and prognosis, few population-based autopsy studies have evaluated their utility in the context of predicting neuropathological changes. Our goal was to investigate the utility of clinically available plasma markers in predicting Braak staging, neuritic plaque score, Thal phase, and overall AD neuropathological change (ADNC).We utilized a population-based prospective study of 350 participants with autopsy and antemortem plasma biomarker testing using clinically available antibody assay (Quanterix) consisting of Aβ42/40 ratio, p-tau181, GFAP, and NfL. We utilized a variable selection procedure in cross-validated (CV) logistic regression models to identify the best set of plasma predictors along with demographic variables, and a subset of neuropsychological tests comprising the Mayo Clinic Preclinical Alzheimer Cognitive Composite (Mayo-PACC). ADNC was best predicted with plasma GFAP, NfL, p-tau181 biomarkers along with APOE ε4 carrier status and Mayo-PACC cognitive score (CV AUC = 0.798). Braak staging was best predicted using plasma GFAP, p-tau181, and cognitive scores (CV AUC = 0.774). Neuritic plaque score was best predicted using plasma Aβ42/40 ratio, p-tau181, GFAP, and NfL biomarkers (CV AUC = 0.770). Thal phase was best predicted using GFAP, NfL, p-tau181, APOE ε4 carrier status and Mayo-PACC cognitive score (CV AUC = 0.754). We found that GFAP and p-tau provided non-overlapping information on both neuritic plaque and Braak stage scores whereas Aβ42/40 and NfL were mainly useful for prediction of neuritic plaque scores. Separating participants by cognitive status improved predictive performance, particularly when plasma biomarkers were included. Plasma biomarkers can differentially inform about overall ADNC pathology, Braak staging, and neuritic plaque score when combined with demographics and cognitive variables and have significant utility for earlier detection of AD.





Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
Deidentified data and analysis software can be made available upon request.
References
American Psychiatric Association D, Association AP (2013) Diagnostic and statistical manual of mental disorders: DSM-5. American Psychiatric Association, Washington
Ashton NJ, Janelidze S, Mattsson-Carlgren N, Binette AP, Strandberg O, Brum WS et al (2022) Differential roles of Aβ42/40, p-tau231 and p-tau217 for Alzheimer’s trial selection and disease monitoring. Nat Med. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41591-022-02074-w
Ashton NJ, Pascoal TA, Karikari TK, Benedet AL, Lantero-Rodriguez J, Brinkmalm G et al (2021) Plasma p-tau231: a new biomarker for incipient Alzheimer’s disease pathology. Acta Neuropathol 141:709–724
Braak H, Alafuzoff I, Arzberger T, Kretzschmar H, Del Tredici K (2006) Staging of Alzheimer disease-associated neurofibrillary pathology using paraffin sections and immunocytochemistry. Acta Neuropathol 112:389–404
Brickman AM, Manly JJ, Honig LS, Sanchez D, Reyes-Dumeyer D, Lantigua RA et al (2021) Plasma p-tau181, p-tau217, and other blood-based Alzheimer’s disease biomarkers in a multi-ethnic, community study. Alzheimers Dement 17:1353–1364
Cicognola C, Janelidze S, Hertze J, Zetterberg H, Blennow K, Mattsson-Carlgren N et al (2021) Plasma glial fibrillary acidic protein detects Alzheimer pathology and predicts future conversion to Alzheimer dementia in patients with mild cognitive impairment. Alzheimer’s Res Ther 13:1–9
Clark C, Lewczuk P, Kornhuber J, Richiardi J, Maréchal B, Karikari TK et al (2021) Plasma neurofilament light and phosphorylated tau 181 as biomarkers of Alzheimer’s disease pathology and clinical disease progression. Alzheimer’s Res Ther 13:1–11
Cullen NC, Leuzy A, Janelidze S, Palmqvist S, Svenningsson AL, Stomrud E et al (2021) Plasma biomarkers of Alzheimer’s disease improve prediction of cognitive decline in cognitively unimpaired elderly populations. Nat Commun 12:1–9
Graff-Radford J, Mielke MM, Hofrenning EI, Kouri N, Lesnick TG, Moloney CM et al (2022) Association of plasma biomarkers of amyloid and neurodegeneration with cerebrovascular disease and Alzheimer’s disease. Neurobiol Aging 119:1–7
Graff-Radford J, Mielke MM, Hofrenning EI, Kouri N, Lesnick T, Moloney CM et al (2022) Plasma biomarkers of amyloid and neurodegeneration predictive of neuropathologic scales of cerebrovascular disease. Alzheimers Dement 18:e067350
Grothe MJ, Moscoso A, Ashton NJ, Karikari TK, Lantero-Rodriguez J, Snellman A et al (2021) Associations of fully automated CSF and novel plasma biomarkers with Alzheimer disease neuropathology at autopsy. Neurology 97:e1229-1242. https://doi.org/10.1212/WNL.0000000000012513
Hansson O, Edelmayer RM, Boxer AL, Carrillo MC, Mielke MM, Rabinovici GD et al (2022) The Alzheimer’s Association appropriate use recommendations for blood biomarkers in Alzheimer’s disease. Alzheimers Dement. https://doi.org/10.1002/alz.070020
Hyman BT, Phelps CH, Beach TG, Bigio EH, Cairns NJ, Carrillo MC et al (2012) National Institute on Aging–Alzheimer’s Association guidelines for the neuropathologic assessment of Alzheimer’s disease. Alzheimers Dement 8:1–13
Jack CR, Bennett DA, Blennow K, Carrillo MC, Feldman HH, Frisoni GB et al (2016) A/T/N: an unbiased descriptive classification scheme for Alzheimer disease biomarkers. Neurology 87:539–547
Janelidze S, Bali D, Ashton NJ, Barthélemy NR, Vanbrabant J, Stoops E et al (2022) Head-to-head comparison of 10 plasma phospho-tau assays in prodromal Alzheimer’s disease. Brain. https://doi.org/10.1093/brain/awac333
Janelidze S, Mattsson N, Palmqvist S, Smith R, Beach TG, Serrano GE et al (2020) Plasma P-tau181 in Alzheimer’s disease: relationship to other biomarkers, differential diagnosis, neuropathology and longitudinal progression to Alzheimer’s dementia. Nat Med 26:379–386
Janelidze S, Teunissen CE, Zetterberg H, Allué JA, Sarasa L, Eichenlaub U et al (2021) Head-to-head comparison of 8 plasma amyloid-β 42/40 assays in Alzheimer disease. JAMA Neurol 78:1375–1382
Karikari TK, Pascoal TA, Ashton NJ, Janelidze S, Benedet AL, Rodriguez JL et al (2020) Blood phosphorylated tau 181 as a biomarker for Alzheimer’s disease: a diagnostic performance and prediction modelling study using data from four prospective cohorts. Lancet Neurol 19:422–433
Lantero Rodriguez J, Karikari TK, Suárez-Calvet M, Troakes C, King A, Emersic A et al (2020) Plasma p-tau181 accurately predicts Alzheimer’s disease pathology at least 8 years prior to post-mortem and improves the clinical characterisation of cognitive decline. Acta Neuropathol 140:267–278
McLeod A, Xu C (2010) bestglm: Best subset GLM. CRAN. http://cran.nexr.com/web/packages/bestglm/vignettes/bestglm.pdf
Mielke MM, Hagen CE, Wennberg AM, Airey DC, Savica R, Knopman DS et al (2017) Association of plasma total tau level with cognitive decline and risk of mild cognitive impairment or dementia in the mayo clinic study on aging. JAMA Neurol 74:1073–1080
Mielke MM, Hagen CE, Xu J, Chai X, Vemuri P, Lowe VJ et al (2018) Plasma phospho-tau181 increases with Alzheimer’s disease clinical severity and is associated with tau-and amyloid-positron emission tomography. Alzheimers Dement 14:989–997
Mielke MM, Syrjanen JA, Blennow K, Zetterberg H, Vemuri P, Skoog I et al (2019) Plasma and CSF neurofilament light: relation to longitudinal neuroimaging and cognitive measures. Neurology 93:e252–e260
Milà-Alomà M, Ashton NJ, Shekari M, Salvadó G, Ortiz-Romero P, Montoliu-Gaya L et al (2022) Plasma p-tau231 and p-tau217 as state markers of amyloid-β pathology in preclinical Alzheimer’s disease. Nat Med 29:1787–1801
Mirra SS, Heyman A, McKeel D, Sumi S, Crain BJ, Brownlee L et al (1991) The Consortium to Establish a Registry for Alzheimer’s Disease (CERAD): Part II. Standardization of the neuropathologic assessment of Alzheimer’s disease. Neurology 41:479–479
Moloney CM, Labuzan SA, Crook JE, Siddiqui H, Castanedes-Casey M, Lachner C et al (2022) Phosphorylated tau sites that are elevated in Alzheimer’s disease fluid biomarkers are visualized in early neurofibrillary tangle maturity levels in the post mortem brain. Alzheimers Dement 19:1029–1040
Montine TJ, Phelps CH, Beach TG, Bigio EH, Cairns NJ, Dickson DW et al (2012) National Institute on Aging–Alzheimer’s Association guidelines for the neuropathologic assessment of Alzheimer’s disease: a practical approach. Acta Neuropathol 123:1–11
Murray AM, Vemuri P (2022) Kidney Disease and Brain Health: Current Knowledge and Next Steps. Am J Kidney Dis. https://doi.org/10.1053/j.ajkd.2022.09.007
Murray ME, Moloney CM, Kouri N, Syrjanen JA, Matchett BJ, Rothberg DM et al (2022) Global neuropathologic severity of Alzheimer’s disease and locus coeruleus vulnerability influences plasma phosphorylated tau levels. Mol Neurodegener 17:1–14
Oberstein TJ, Schmidt MA, Florvaag A, Haas A-L, Siegmann E-M, Olm P et al (2022) Amyloid-β levels and cognitive trajectories in non-demented pTau181-positive subjects without amyloidopathy. Brain 145:4032–4041
Palmqvist S, Janelidze S, Quiroz YT, Zetterberg H, Lopera F, Stomrud E et al (2020) Discriminative accuracy of plasma phospho-tau217 for Alzheimer disease vs other neurodegenerative disorders. JAMA 324:772–781
Palmqvist S, Stomrud E, Cullen N, Janelidze S, Manuilova E, Jethwa A et al (2022) An accurate fully automated panel of plasma biomarkers for Alzheimer’s disease. Alzheimers Dement. https://doi.org/10.1002/alz.12751
Pereira JB, Janelidze S, Smith R, Mattsson-Carlgren N, Palmqvist S, Teunissen CE et al (2021) Plasma GFAP is an early marker of amyloid-β but not tau pathology in Alzheimer’s disease. Brain 144:3505–3516
Petersen RC (2004) Mild cognitive impairment as a diagnostic entity. J Intern Med 256:183–194
Shen XN, Li JQ, Wang HF, Li HQ, Huang YY, Yang YX et al (2020) Plasma amyloid, tau, and neurodegeneration biomarker profiles predict Alzheimer’s disease pathology and clinical progression in older adults without dementia. Alzheimer’s Dement 12:e12104
Simrén J, Leuzy A, Karikari TK, Hye A, Benedet AL, Lantero-Rodriguez J et al (2021) The diagnostic and prognostic capabilities of plasma biomarkers in Alzheimer’s disease. Alzheimers Dement 17:1145–1156
Smirnov DS, Ashton NJ, Blennow K, Zetterberg H, Simren J, Lantero-Rodriguez J et al (2022) Plasma biomarkers for Alzheimer’s disease in relation to neuropathology and cognitive change. Acta Neuropathol 143:487–503. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00401-022-02408-5
St Sauver JL, Chamberlain AM, Bobo WV, Boyd CM, Rutten LJF, Jacobson DJ et al (2021) Implementing the US Department of Health and Human Services definition of multimorbidity: a comparison between billing codes and medical record review in a population-based sample of persons 40–84 years old. BMJ Open 11:e042870
Stricker NH, Twohy EL, Albertson SM, Karstens AJ, Kremers WK, Machulda MM et al (2022) Mayo-PACC: A parsimonious preclinical Alzheimer’s disease cognitive composite comprised of public-domain measures to facilitate clinical translation. Alzheimers Dement. https://doi.org/10.1002/alz.12895
Syrjanen JA, Campbell MR, Algeciras-Schimnich A, Vemuri P, Graff-Radford J, Machulda MM et al (2022) Associations of amyloid and neurodegeneration plasma biomarkers with comorbidities. Alzheimers Dement 18:1128–1140
Thal DR, Rüb U, Orantes M, Braak H (2002) Phases of Aβ-deposition in the human brain and its relevance for the development of AD. Neurology 58:1791–1800
Thijssen EH, La Joie R, Strom A, Fonseca C, Iaccarino L, Wolf A et al (2021) Plasma phosphorylated tau 217 and phosphorylated tau 181 as biomarkers in Alzheimer’s disease and frontotemporal lobar degeneration: a retrospective diagnostic performance study. Lancet Neurol 20:739–752
Tosun D, Veitch D, Aisen P, Jack CR Jr, Jagust WJ, Petersen RC et al (2021) Detection of β-amyloid positivity in Alzheimer’s Disease Neuroimaging Initiative participants with demographics, cognition MRI and plasma biomarkers. Brain Commun 3:008
Winder Z, Sudduth TL, Anderson S, Patel E, Neltner J, Martin BJ et al (2022) Examining the association between blood-based biomarkers and human post mortem neuropathology in the University of Kentucky Alzheimer’s Disease Research Center autopsy cohort. Alzheimers Dement. https://doi.org/10.1002/alz.12639
Acknowledgements
We thank all the study participants and staff in the Mayo Clinic Study of Aging, Mayo Alzheimer’s Disease Research Center, and Aging Dementia Imaging Research laboratory at the Mayo Clinic for making this study possible. This work was supported by grants from National Institutes of Health (NIH) (U01 AG006786, R01 AG034676, RF1 AG069052). Its contents are solely the responsibility of the authors and do not necessarily represent the official views of the NIH.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
CB, JGR, JAS, WK, and PV contributed to the conception and design of the study; CB, JGR, JAS, NS, AAS, NK, WK, RCP, CRJ, DSK, DWD, ATN, RRR, MRM, MMM, PV contributed to the acquisition and analysis of data; CB, JGR, JAS, WK, PV contributed to drafting the text or preparing the figures.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors do not have any pertinent conflicts of interest relevant to this study.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Bermudez, C., Graff-Radford, J., Syrjanen, J.A. et al. Plasma biomarkers for prediction of Alzheimer’s disease neuropathologic change. Acta Neuropathol 146, 13–29 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00401-023-02594-w
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00401-023-02594-w