Abstract
Hippocampal sclerosis (HS) is characterized by selective neuronal loss and gliosis in CA1 and the subiculum and has been associated with several disorders, including Alzheimer’s disease, frontotemporal lobar degeneration with ubiquitin immunoreactive inclusions (FTLD-U), vascular dementia and some tauopathies. In some cases, HS is not associated with other degenerative pathologies. Such cases are sometimes referred to as HS dementia (HSD). Differences between HSD and HS in the setting of FTLD-U have not been systematically investigated. To this end, eight cases of HSD and ten cases of HS associated with FTLD-U were studied with Nissl and periodic acid-Schiff stains to assess neuronal loss and corpora amylacea, respectively. Sections were immunostained with antibodies to glial fibrillary acidic protein, HLA-DR and synaptophysin and immunoreactivity was measured with image analysis in CA1 and the subiculum of each case. Additionally, sections were immunostained with antibodies to 4-R tau to determine the presence of argyrophilic grains. HSD was different from HS associated with FTLD-U. Specifically, it was more common in the elderly, and it was associated with more marked neuronal and synaptic loss and with greater reactive gliosis. Corpora amylacea tended to be more frequent in HSD than in FTLD-U, but there was no difference in frequency of argyrophilic grains.
Similar content being viewed by others
Avoid common mistakes on your manuscript.
Introduction
Hippocampal sclerosis (HS) is defined as selective neuronal loss and gliosis of CA1 and the subiculum of the hippocampus. Its prevalence in demented patients ranges from 2.8 to 13% [4–6, 15, 25, 26]. It is associated with several other disorders, including Alzheimer’s disease (AD), frontotemporal lobar degeneration with ubiquitin immunoreactive inclusions (FTLD-U), vascular dementia, dementia with Lewy bodies and some tauopathies. Occasionally, HS has been reported as an independent pathologic explanation for dementia, the so-called HS dementia (HSD). The reported prevalence of HSD ranges from 0.4 to 2% [2, 4, 15, 27].
The etiology of HS is uncertain in most cases, but it is hypothesized to be due to either hypoxic-ischemic injury or to neurodegeneration of selectively vulnerable neuronal populations in CA1 and the subiculum [4, 36]. An hypoxic-ischemic origin is supported by the known deficient hippocampal vascular supply [8] and the fact that CA1 hippocampal neurons have a higher susceptibility to hypoxia due to their concentration of glutamate receptors, which may be involved in excitotoxic cell death [30]. Further arguments in favor of this theory are the association of hypoxic-ischemic episodes in patients with HS [12, 34, 37] and the increased prevalence of cardiac [3, 10, 29] and cerebrovascular disease [11, 12, 26, 35] in cases of HS of presumed hypoxic-ischemic origin.
Since many cases of HS do not have histories of hypoxia or ischemia [2, 10, 12, 15, 27], cardiac disease [2, 11, 12, 27] or cerebrovascular accidents [10, 27], a degenerative cause is also proposed. This hypothesis is supported by the frequent association of HS with degenerative dementias like AD [3, 4, 12, 15, 16, 27, 29] and FTLD-U [3, 4, 13, 15, 19, 22, 24, 29] and the less frequently with tauopathies, mainly argyrophilic grain disease (AGD) and FTDP-17 [5, 12, 17].
The aim of this study was to compare the pathological characteristics of HSD versus HS in the setting of FTD-U.
Materials and methods
The Mayo Clinic Jacksonville brain bank database between 1998 and 2005 of individuals with dementia or degenerative neuropathology (N = 1,487) was screened for specimens with HS that had complete neuropathologic evaluations. This evaluation included description of gross and microscopic findings, as well as quantitative information about Alzheimer type pathology. Specifically, the reports include counts of senile plaques and neurofibrillary tangles in six cortical sections, four sectors of the hippocampus, two regions of the amygdala, as well as subcortical regions with thioflavin-S fluorescent microscopy. It also involves immunohistochemistry for tau, α-synuclein and ubiquitin, as appropriate, as previously described [4]. A Braak neurofibrillary tangle stage was assigned to all cases based upon the distribution of neurofibrillary tangles with thioflavin-S fluorescent microscopy, as previously described [4, 14, 21, 31, 33].
HS was detected in 103 cases; in 95 cases (92%) it was associated with a primary degenerative disease process, mostly AD (36; 18 men and 18 women; 85 ± 5 years of age) and FTLD-U (44; 23 men and 21 women; 75 ± 12 years of age; P < 0.01 compared to AD). HS was detected in about 5% of AD cases (36 of 637) and 75% of FTLD-U cases (44 of 59). The remainder of cases included HS in the setting of a wide range of pathologies, including Lewy body disease, progressive supranuclear palsy, corticobasal degeneration and multiple system atrophy. In eight cases, HS was not associated with degenerative pathology.
For this study, 18 cases were selected for further study and placed in one of two groups. The first group of eight cases was operationally termed HSD; most HSD cases (75%) were associated with evidence of cerebrovascular disease. When compared to a control group of 30 cases from the same brain bank matched for age, sex and Braak stage, cerebrovascular disease was detected in 80% of the controls, a frequency similar to that in HSD. Therefore, we could not necessarily assume that the HS was due to hypoxic-ischemic causes. In all HSD cases, FTLD-U was ruled out with ubiquitin immunohistochemistry. The second group (“FTLD-U HS”) included 10 cases of HS associated to FTLD-U. None of the FTLD-U HS cases had pathologic evidence of cerebrovascular disease or other pathologic processes, and HS was assumed to be related to FTLD.
In all 18 cases other pathologic processes, such as progressive supranuclear palsy, corticobasal degeneration or Lewy body disease were absent. Alzheimer type pathology was minimal. None of the cases in either the HSD or FTLD-U HS group had a Braak neurofibrillary tangle stage greater than IV. In none of the cases could neuronal loss in the hippocampus be attributed to neurofibrillary tangles, since none had many extracellular (“ghost”) neurofibrillary tangles. Medial temporal tauopathy due to AGD was not a basis for exclusion, and all cases were screened for this age-related pathology with immunohistochemistry using isotype-specific tau antibodies, as previously reported [17].
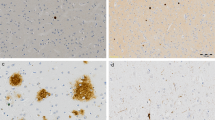
Coronal sections of the posterior hippocampus at the level of the lateral geniculate nucleus were cut at a thickness of 5 μm. Sections were stained with Nissl and periodic acid-Schiff (PAS) stains. Sections were immunostained on a DAKO Autostainer with antibodies to HLA-DR, glial fibrillary acidic protein (GFAP), 4R tau and synaptophysin using procedures similar to those reported previously [23]. The following primary antibodies were used: anti-GFAP (GA-5, monoclonal, 1:1,000, Biogenex, San Ramon, CA), anti-HLA-DR (LN3, monoclonal, 1:100, eBioscience, San Diego, CA), anti-4R tau (ET3, monoclonal, 1:25, Dr. Peter Davies, Albert Einstein College of Medicine, Bronx, NY) and anti-synaptophysin (EP10, monoclonal, 1: 10, Dr. Peter Davies, Albert Einstein College of Medicine, Bronx, NY). For antigen retrieval, slides were steamed in distilled water for 30 min. For ET3 immunostaining, which has been shown to be a sensitive and specific method for detecting AGD [17, 32], slides were also pretreated in 99% formic acid for 30 min.
The degree of neuronal loss in the subiculum, CA1, CA2/3, CA4 (end plate) and dentate gyrus was evaluated on Nissl stained sections using a three-point rating scale: 0, absent; 1, mild-to-moderate; and 2, marked. PAS staining was used to assess the density of corpora amylacea. Corpora amylacea were defined as round, PAS-positive structures in the neuropil, perivascular, subpial and subependymal areas [7]. Presence of corpora amylacea throughout the hippocampus was graded on a four-point scale: 0, absent; 1, sparse; 2, moderate; and 3, many.
To assess astrocytic, microglial and synaptic immunoreactivity, sections immunostained for GFAP, HLA-DR and synaptophysin were used. Standardized, non-overlapping, digital images of the pyramidal layer of CA1 and subiculum were taken under a 40× objective on a light microscope. Immunoreactivity was quantified as a percentage area using MetaMorph software, version 6.3r0 (Molecular Devices, Sunnyvale, CA).
Four-R (4R) tau immunostained slides were used to determine the presence of AGD. Cases were considered to have AGD if they had small dot- or comma-like argyrophilic lesions in neuronal processes of the pyramidal layer and the entorhinal cortex, as well as coiled bodies in temporal white matter, which are the same criteria used in other studies [31].
Clinical and neuropathologic records were reviewed to collect data on age, sex, Braak neurofibrillary tangle stage, brain weight and macroscopic and microscopic neuropathology findings at autopsy. The recorded gross findings at autopsy were lobar, hippocampal and mammillary body atrophy. The remarkable microscopic findings were vascular pathology, ischemic brain injury and white matter disease.
Differences between the two groups in age, Braak stage, brain weight, corpora amylacea, neuronal loss and glial and synaptic immunoreactivity pathology were analyzed with unpaired t test and Mann–Whitney U tests depending upon the variable. Fisher’s exact test was used to compare sex, presence of AGD and remarkable pathologic findings. The statistical analyses were performed using Sigma Stat for Windows, version 3.11 (Systat Software, Richmond, CA) and the significance levels were set at P < 0.05.
Results
A summary of the demographic and neuropathologic findings of the 18 cases included in this study is presented in Table 1. A comparison of the two groups is presented in Table 2. The cases with HSD had an older age of death than those with FTLD-U HS (84 vs. 65, P = 0.001). In the HSD group, six of eight cases were men, while four of six cases in the FTLD-U HS group were men, but this difference was not significant.
Neuropathologic findings
The Braak neurofibrillary tangle stage was significantly greater in HSD than in FTLD-U HS. The brain weight was also greater in HSD than in FTLD-U HS. Cortical atrophy was more frequent in FTLD-U HS than HSD in frontal (100% vs. 25%), medial temporal (78% vs. 13%), lateral temporal (67% vs. 33%) and parietal lobes (67% vs. 17%). The difference reached statistical significance in frontal and medial temporal regions. Both groups showed marked gross atrophy of the hippocampal formation and mammillary body.
In this comparative study, cerebrovascular pathology was virtually limited to the HSD group. Atherosclerosis of large vessels at the base of the brain was present in seven of eight HSD cases. Three had minimal, 1 had mild (occluding less than 50% of the lumen) and 3 had moderate atherosclerosis (occluding between 50% and 75% of the lumen). Arteriosclerosis defined by presence of hyalinosis of the media and adventitial fibrosis of small (<100 μm diameter) vessels was present in 5 (63%) cases and cerebral amyloid angiopathy (CAA) was present in 4 (50%) of 8 HSD. Three (30%) cases of FTLD-U HS had minimal atherosclerosis. None of the cases of this group had significant arteriolosclerosis or evidence of CAA.
Ischemic brain injury was present in six of eight HSD cases, but in none of the FTLD-U HS cases. The eight HSD cases included 3 (38%) with lacunar infarcts, 4 (50%) with microscopic infarcts and 5 (63%) with microscopic foci of ischemic gliosis.
Most cases, independent of their group, showed white matter pathology defined by rarefaction and attenuation of white matter, associated with dilated perivascular spaces, loss of myelinated fibers and gliosis. These findings were present in the periventricular white matter in seven of eight HSD cases. In three of these cases more diffuse white matter pathology was also present, involving the centrum semiovale. All of the cases with FTLD-U HS showed white matter pathology that followed the distribution of the cortical atrophy.
Two of the HSD cases (P4 and P7) had only minimal atherosclerosis and CAA, which was probably insufficient to cause hippocampal hypoperfusion, but both cases had a history of coronary artery disease and congestive heart failure, which might account for hypoxic-ischemic injury to the hippocampus, although this remains purely speculative, since these risk factors are common in individuals of this age without HS [12].
Another case of HSD (P6) with minimal atherosclerosis, arteriosclerosis and CAA had a history of epilepsy, as well as laminar ischemic gliosis in the watershed cortices and cortical cystic infarcts and thalamic ischemic gliosis. Epilepsy in this patient was probably secondary to a porencephalic cyst that was present in the temporal pole. Given the absence of degenerative pathology, this case was included in the HSD group, but presence of extensive cerebrovascular disease raises the possibility that HS in this case was related to hypoxic-ischemic injury.
Quantitative and semi-quantitative analyses
Both HSD and FTLD-U HS had severe neuronal loss in the pyramidal layer of CA1 and the subiculum. No significant differences were found in the severity of neuronal loss between the two regions; nevertheless, differences in the distribution of neuronal loss were noted. Most cases had neuronal loss in both CA1 and the subiculum, except for two cases of HSD that had isolated CA1 involvement and two cases of FTLD-U HS that had isolated subicular involvement.
The CA2/3 region and the endplate were not affected in most cases. Only cases of HSD occasionally had neuronal loss in these regions, with involvement of CA2/3 in P4 and involvement of CA2/3 and endplate in P6. The dentate was involved in half of the cases of both groups.
Synaptic loss assessed by image analysis of density of synaptophysin immunoreactivity was significantly less in CA1 region in HSD compared to FTLD-U HS (Fig. 1). A similar trend was noted in the subiculum. Gliosis as assessed by image analysis with GFAP and HLA-DR immunostains tended to be greater in HSD compared with FTLD-U HS (Fig. 1), although it did not reach statistical significance probably because of small sample size. Both GFAP and HLA-DR immunoreactivity were greater in HSD than in FTLD-U HS in both CA1 and the subiculum.
There tended to be more corpora amylacea in HSD than in FTLD-U HS, but this did not reach statistical significance. A concomitant diagnosis of AGD was made in two cases of FTLD HS and in one case of pure HS (P6).
Discussion
The present study confirmed the characteristic findings of neuronal loss and gliosis in CA1 and the subiculum in HS regardless of etiology; however, there were some significant differences between HSD and HS that occurs in FTLD-U. In addition, there were subjective differences that did not meet statistical significance probably related to the small sample size in this study. The results support the hypothesis that there are differences in underlying disease mechanisms in HSD compared to HS in FTLD-U.
From a demographic perspective, demented patients with HS have been shown to be older than demented patients without HS [11, 12, 27, 29], although there are exceptions [2, 10]. Data concerning the age distribution among patients with HS has to our knowledge not been reported. In the present study, we show HSD to mainly affect the elderly (>80 years of age) as opposed to HS in FTLD-U. The younger age of the FTLD-U may account for the lower frequency of concurrent cerebrovascular disease, since an age-, sex- and Braak neurofibrillary tangle stage-matched cohort had comparable frequency of cerebrovascular disease.
Microscopically, there were three important differences in the pathology in HSD compared with HS in FTLD-U. First, HSD had lower synaptophysin immunoreactivity, suggesting a more destructive process resulting in more severe synaptic loss, while in FTLD-U there is selective neuronal loss, but relative preservation of the neuropil, presumably from preserved afferent and efferent projections to sectors that show neuronal loss. Second, the difference in the distribution of neuronal loss suggested subicular involvement to be characteristic of HS in FTLD-U. Even though the differences in distribution of neuronal loss did not reach statistical significance, other observations support this idea [20]. Third, HSD was associated with greater astrocytic and microglial reaction compared to HS in FTLD-U. Glial activation has been proposed to be caused by neuronal damage, which is present in both, ischemic and degenerative pathology, but may be exacerbated in HSD due to more extensive tissue damage affecting not only neurons, but also the neuropil.
Macroscopically, FTLD-U HS had more severe cortical atrophy, a not surprising finding, since it correlates with FTLD [25]. HSD on the other hand showed a pattern of atrophy often localized to the hippocampal formation, arguing against this pathology being associated with more widespread cortical degeneration. This fits with results from previous studies of HSD that showed that loss of synaptophysin immunoreactivity in the hippocampus was not accompanied with similar loss in the cortex or basal ganglia [12].
Corpora amylacea have been proposed as a possible marker for hypoxic-ischemic HS, since they may be numerous in brains of patients exposed to repetitive hypoxic episodes [1, 6]. They have also been proposed as a useful marker for evaluating HS in surgical specimens removed for treatment of temporal lobe epilepsy [9]. Although there was a trend for more corpora amylacea in HSD than in FTLD-U HS, it did not reach statistical significance, which may be further evidence against the argument that HSD is due to hypoxic-ischemic injury.
Even though we did not find a difference in the frequency of AGD in HSD and HS associated with FTLD-U, the presence of AGD in 3 of the 18 cases, may suggest an association of HS with AGD as reported in previous studies [5, 17].
This study included two cases of HSD (P4 and P7) in which there was not only no evidence of degenerative pathology, but also no evidence of cerebrovascular pathology. Cases in which HS is the only pathologic explanation for dementia are rare. Hattanpa found some cases of HS to be false negative cases for FTLD-U after further studying them with ubiquitin immunohistochemistry [13]. Since we analyzed our cases with ubiquitin, false negatives were excluded, giving a probable explanation for the lower prevalence compared to the 0.48, 0.53 and 2% previously reported by others [2, 15, 27].
The two cases of HSD with neither degenerative nor cerebrovascular pathology had cardiovascular risk factors that could link HS to an ischemic condition of systemic origin. They are similar to the ones that have been reported by others [34, 37]. On the other hand, in a systematic survey of cardiovascular risk factors, including electrocardiograph abnormalities, congestive heart failure and cardiomegaly by imaging and autopsy studies, there was no increased frequency of these findings in HSD compared to age-matched controls without HS [12].
The present study confirms the finding that HS in the setting of dementia in most cases should be regarded as a feature linked to a concurrent degenerative disease process, particularly FTLD-U [13, 18, 19, 28]. In other cases, HS may be linked to a systemic condition (e.g., cardiorespiratory failure) or cerebrovascular disease [8, 36]. In rare cases, the etiology is unknown. The present study suggests that HSD is a disorder of the elderly that is associated with more marked neuronal and synaptic loss and greater reactive gliosis than that seen in HS associated with FTLD-U. This argues for a different pathogenesis
References
Abe H, Yagishita S (1995) Massive appearance of corpora amylacea in postnatal anoxic encephalopathy. Clin Neuropathol 14:207–210
Ala TA, Beh GO, Frey WH 2nd (2000) Pure hippocampal sclerosis: a rare cause of dementia mimicking Alzheimer’s disease. Neurology 54:843–848
Attems J, Jellinger KA (2006) Hippocampal sclerosis in Alzheimer disease and other dementias. Neurology 66:775
Barker WW, Luis CA, Kashuba A, Luis M, Harwood DG, Loewenstein D, Waters C, Jimison P, Shepherd E, Sevush S et al (2002) Relative frequencies of Alzheimer disease, Lewy body, vascular and frontotemporal dementia, and hippocampal sclerosis in the State of Florida Brain Bank. Alzheimer Dis Assoc Disord 16:203–212
Beach TG, Sue L, Scott S, Layne K, Newell A, Walker D, Baker M, Sahara N, Yen SH, Hutton M et al (2003) Hippocampal sclerosis dementia with tauopathy. Brain Pathol 13:263–278
Botez G, Rami A (2001) Immunoreactivity for Bcl-2 and C-Jun/AP1 in hippocampal corpora amylacea after ischaemia in humans. Neuropathol Appl Neurobiol 27:474–480
Cavanagh JB (1999) Corpora-amylacea and the family of polyglucosan diseases. Brain Res Brain Res Rev 29:265–295
Chui H (2005) Neuropathology lessons in vascular dementia. Alzheimer Dis Assoc Disord 19:45–52
Chung MH, Horoupian DS (1996) Corpora amylacea: a marker for mesial temporal sclerosis. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol 55:403–408
Corey-Bloom J, Sabbagh MN, Bondi MW, Hansen L, Alford MF, Masliah E, Thal LJ (1997) Hippocampal sclerosis contributes to dementia in the elderly. Neurology 48:154–160
Crystal HA, Dickson D, Davies P, Masur D, Grober E, Lipton RB (2000) The relative frequency of “dementia of unknown etiology” increases with age and is nearly 50% in nonagenarians. Arch Neurol 57:713–719
Dickson DW, Davies P, Bevona C, Van Hoeven KH, Factor SM, Grober E, Aronson MK, Crystal HA (1994) Hippocampal sclerosis: a common pathological feature of dementia in very old (≥80 years of age) humans. Acta Neuropathol (Berl) 88:212–221
Hatanpaa KJ, Blass DM, Pletnikova O, Crain BJ, Bigio EH, Hedreen JC, White CL 3rd, Troncoso JC (2004) Most cases of dementia with hippocampal sclerosis may represent frontotemporal dementia. Neurology 63:538–542
Ishizawa T, Ko LW, Cookson N, Davias P, Espinoza M, Dickson DW (2002) Selective neurofibrillary degeneration of the hippocampal CA2 sector is associated with four-repeat tauopathies. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol 61:1040–1047
Jellinger K (2000) Pure hippocampal sclerosis: a rare cause of dementia mimicking Alzheimer’s disease. Neurology 55:739–740
Jellinger KA (1994) Hippocampal sclerosis: a common pathological feature of dementia in very old humans. Acta Neuropathol (Berl) 88:599
Jicha GA, Petersen RC, Knopman DS, Boeve BF, Smith GE, Geda YE, Johnson KA, Cha R, Delucia MW, Braak H et al (2006) Argyrophilic grain disease in demented subjects presenting initially with amnestic mild cognitive impairment. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol 65:602–609
Josephs KA, Dickson DW (2006) Hippocampal sclerosis in tau-negative frontotemporal lobar degeneration. Neurobiol Aging
Josephs KA, Jones AG, Dickson DW (2004) Hippocampal sclerosis and ubiquitin-positive inclusions in dementia lacking distinctive histopathology. Dement Geriatr Cogn Disord 17:342–345
Josephs KA, Parisi JE, Knopman DS, Boeve BF, Petersen RC, Dickson DW (2006) Clinically undetected motor neuron disease in pathologically proven frontotemporal lobar degeneration with motor neuron disease. Arch Neurol 63:506–512
Josephs KA, Tsuboi Y, Cookson N, Watt H, Dickson DW (2004) Apolipoprotein E epsilon 4 is a determinant for Alzheimer-type pathologic features in tauopathies, synucleinopathies, and frontotemporal degeneration. Arch Neurol 61:1579–1584
Josephs KA, Whitwell JL, Jack CR, Parisi JE, Dickson DW (2006) Frontotemporal lobar degeneration without lobar atrophy. Arch Neurol 63:1632–1638
Katsuse O, Dickson DW (2005) Ubiquitin immunohistochemistry of frontotemporal lobar degeneration differentiates cases with and without motor neuron disease. Alzheimer Dis Assoc Disord 19(Suppl 1):S37–S43
Knopman DS, Mastri AR, Frey WH 2nd, Sung JH, Rustan T (1990) Dementia lacking distinctive histologic features: a common non-Alzheimer degenerative dementia. Neurology 40:251–256
Kril JJ, Halliday GM (2004) Clinicopathological staging of frontotemporal dementia severity: correlation with regional atrophy. Dement Geriatr Cogn Disord 17:311–315
Kril JJ, Patel S, Harding AJ, Halliday GM (2002) Patients with vascular dementia due to microvascular pathology have significant hippocampal neuronal loss. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 72:747–751
Leverenz JB, Agustin CM, Tsuang D, Peskind ER, Edland SD, Nochlin D, DiGiacomo L, Bowen JD, McCormick WC, Teri L et al (2002) Clinical and neuropathological characteristics of hippocampal sclerosis: a community-based study. Arch Neurol 59:1099–1106
Lippa CF, Dickson DW (2004) Hippocampal sclerosis dementia: expanding the phenotypes of frontotemporal dementias? Neurology 63:414–415
Marshall GA, Mendez MF, Fairbanks L, Cummings JL, Vinters HV (2005) Presence of hippocampal sclerosis in the elderly and co-occurrence with different dementias. Ann Neurol 58:S16
Olney JW, Collins RC, Sloviter RS (1986) Excitotoxic mechanisms of epileptic brain damage. Adv Neurol 44:857–877
Togo T, Cookson N, Dickson DW (2002) Argyrophilic grain disease: neuropathology, frequency in a dementia brain bank and lack of relationship with apolipoprotein E. Brain Pathol 12:45–52
Togo T, Sahara N, Yen SH, Cookson N, Ishizawa T, Hutton M, de Silva R, Lees A, Dickson DW (2002) Argyrophilic grain disease is a sporadic 4-repeat tauopathy. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol 61:547–556
Uchikado H, Lin WL, DeLucia MW, Dickson DW (2006) Alzheimer disease with amygdala Lewy bodies: a distinct form of alpha-synucleinopathy. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol 65:685–697
Volpe BT, Petito CK (1985) Dementia with bilateral medial temporal lobe ischemia. Neurology 35:1793–1797
Wegiel J, Kuchna I, Wisniewski T, de Leon MJ, Reisberg B, Pirttila T, Kivimaki T, Lehtimaki T (2002) Vascular fibrosis and calcification in the hippocampus in aging, Alzheimer disease, and Down syndrome. Acta Neuropathol (Berl) 103:333–343
Zarow C, Vinters HV, Ellis WG, Weiner MW, Mungas D, White L, Chui HC (2005) Correlates of hippocampal neuron number in Alzheimer’s disease and ischemic vascular dementia. Ann Neurol 57:896–903
Zweig RM, Schegg KM, Peacock JH, Melarkey D (1989) A case of Alzheimer’s disease and hippocampal sclerosis with normal cholinergic activity in basal forebrain, neocortex, and hippocampus. Neurology 39:288–290
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Supported by NIH P50-AG16574, P50-AG25711, P50-NS40256, P01-AG03949.
Rights and permissions
Open Access This is an open access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution Noncommercial License ( https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/2.0 ), which permits any noncommercial use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author(s) and source are credited.
About this article
Cite this article
Amador-Ortiz, C., Ahmed, Z., Zehr, C. et al. Hippocampal sclerosis dementia differs from hippocampal sclerosis in frontal lobe degeneration. Acta Neuropathol 113, 245–252 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00401-006-0183-4
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00401-006-0183-4