Abstract
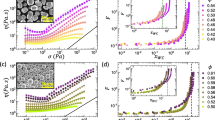
We have explored the effect of shear force on aggregate size, the secondary structure of proteins, and the viscosity of protein bovine serum albumin solution. The size of protein aggregates and secondary structures of the protein are dependent on the external variables such as temperature, the magnitude of shear, time of shearing, and process of applying shear. The process of application of shear, which can be continuous or intermittent periodic stoppage, can control the characteristics of aggregates of BSA. The viscosity of the protein solution is expected to depend on the size of the aggregates. We have proposed a mechanism of the association of BSA molecules leading to the formation of aggregates. Small aggregates at 40 °C are formed through the interaction of side chains, while bigger aggregates formed at 60 °C through β-sheet interaction. The indication of the opening of the BSA molecules at an intermediate temperature is confirmed by the appearance of more side chain and random coil. The shear leads to a highly anisotropic structure at a temperature beyond 60 °C and leads to the higher hydrodynamic radius. This makes the solution to undergo transition from dilute to semi-dilute regime and increase in viscosity by a factor fourfold. Subsequently, we have shown that the viscosity depends on the proportion of β-sheet within the aggregate.










Similar content being viewed by others
References
Atmeh RF, Arafa IM, Al-Khateeb M (2007) Albumin aggregates: hydrodynamic shape and physico-chemical properties. Jordan J Chem 2:169–182
Bagger HL, Ogendal LH, Westh P (2007) Solute effects on the irreversible aggregation of serum albumin. Biophys Chem 130:17–25
Bandekar J (1920) Amide modes and protein conformation. Biochim Biophys Acta Protein Struct Mol Enzymol 1120:123–143
Bekard IB, Asimakis P, Bertolini J, Dunstan DE (2011a) The effects of shear flow on protein structure and function. Biopolymers 95:733–745
Bekard IB, Asimakis P, Teoh CL, Ryan T, Howlett GJ, Bertolini J, Dunstan DE (2011b) Bovine serum albumin unfolds in couette flow. Soft Matter 8:385–389
Bhattacharya M, Jain N, Mukhopadhyay S (2011) Insights into the mechanism of aggregation and fibril formation from bovine serum albumin. J Phys Chem B 115:4195–4205
Borzova VA, Markossian KA, Chebotareva NA, Kleymenov SY, Poliansky NB, Muranov KO, Kurganov BI (2016) Kinetics of thermal denaturation and aggregation of bovine serum albumin. PLoS One 11:e0153495
Bramanti E, Ferrari C, Angeli V, Onor M, Synovec RE (2011) Characterization of BSA unfolding and aggregation using a single-capillary viscometer and dynamic surface tension detector. Talanta 85:2553–2561
Bull HB (1940) Viscosity of solutions of denatured and native egg albumin. J Biol Chem 133:39–49
Byler DM, Susi H (1983c) Protein structure by fourier transform infrared spectroscopy: second derivative spectra. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 115:391–397
Byler DM, Susi H (1986a) Examination of the secondary structure of proteins by deconvolved FTIR spectra. Biopolymers 25:469–487
Byler DM, Susi H (1986b) Resolution-enhanced Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy of enzymes. Methods Enzymol 130:290–311
Castellanos MM, Pathak JA, Colby RH (2014) Both protein adsorption and aggregation contribute to shear yielding and viscosity increase in protein solutions. Soft Matter 10:122–131
Chittur KK (1998) FTIR/ATR for protein adsorption to biomaterial surfaces. Biomaterials 19:357–369
Clark AH, Judge FJ, Richards JB, Stubbs JM, Suggett A (1981) Electron microscopy of network structures in thermally-induced globular protein gels. Int J Pept Protein Res 17:380–392
Curvale R, Cesco C (2009) Intrinsic viscosity determination by ‘single-point’ and ‘double-point’ equations. Appl Rheol 19:53347
Curvale R, Masuelli MA, Perez Padilla A (2008) Intrinsic viscosity of bovine serum albumin conformers. Int J Biol Macromol 42:133–137
Ding F, Borreguero JM, Buldyrey SV, Stanley HE, Dokholyan NV (2003) Mechanism for the α-helix to β-hairpin transition. Proteins Struct Funct Genet 53:220–228
Douglas JF, Curtis R, Sarangapani PS, Hudson SD, Jones RL, Pathak JA (2017) Hard spheres with purely repulsive interactions have positive diffusion interaction parameter, kD. Biophys J 113:753–754
Foster JF (1977) Some aspects of the structure and conformational properties of serum albumin, Albumin structure, function and uses. Pergamon, New York, pp 53–84
Green DW, Perry RH (2007) Gas-solid operations and equipment, Perry’s chemical engineers’ handbook, 8th edn. McGraw Hill Professional
Hedoux A, Willart JF, Paccou L, Guinet Y, Affouard F, Lerbret A, Descamps M (2009) Thermostabilization mechanism of bovine serum albumin by trehalose. J Phys Chem B 113:6119–6126
Hirayama K, Akashi S, Furuya M, Fukuhara K (1990) Rapid confirmation and revision of the primary structure of bovine serum albumin by ESIMS and FRIT-fab LC/MS. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 173:639–646
Ismail AA, Mantsch HH, Wong PT (1992) Aggregation of chymotrypsinogen: portrait by infrared spectroscopy. Biochim Biophys Acta 1121:183–188
Juairez J, Loipez SG, Camboin A, Taboada P, Mosquera V (2009) Influence of electrostatic interactions on the fibrillation process of human serum albumin. J Phys Chem B 113:10521–10529
Kong J, Yu S (2007) Fourier transform infrared spectroscopic analysis of protein secondary structures. Acta Biochim Biophys Sin 39:549–559
Kumar S, Pattanayek SK (2018) Semi-flexible polymer engendered aggregation/dispersion of fullerene (C60) nano-particles: an atomistic investigation. Chem Phys Lett 701:22–29
Lefevre T, Subirade M (2000) Molecular differences in the formation and structure of fine-stranded and particulate -lactoglobulin gels. Biopolymers 54:578–586
MacGillivray RT, Chung A, Davie EW (1979) Biosynthesis of bovine plasma proteins in a cell-free system: amino-terminal sequence of preproalbumin. Eur J Biochem 98:477–485
Masuelli MA (2013) Study of bovine serum albumin solubility in aqueous solutions by intrinsic viscosity measurements. Adv Phys Chem 2013:1–8
Masuelli MA, Gassmann J (2017) Intrinsic viscosity bovine serum albumin in aqueous solutions: temperature influence on Mark-Houwink parameters. In: Masuelli M, Renard D (eds) Advances in physicochemical properties of biopolymers (part 1). Bentham Science Publishers – Sharjah, UAE, pp 28–59
Masuelli MA, Sansone MG (2012) Hydrodynamic properties of gelatin-studies from intrinsic viscosity measurements. In: Verbeek C (ed) Products and applications of biopolymers. INTECHOpen Access Publisher, London, pp 85–116
Mewis J, Wagner NJ (2012) Colloidal suspension rheology. Cambridge University Press, New York
Militello V, Vetri V, Leone M (2003a) Conformational changes involved in thermal aggregation processes of bovine serum albumin. Biophys Chem 105:133–141
Militello V, Casarino C, Emanuele A, Giostra A, Pullara F, Leone M (2004b) Aggregation kinetics of bovine serum albumin studied by FTIR spectroscopy and light scattering. Biophys Chem 107:175–187
Monkos K (1996) Viscosity of bovine serum albumin aqueous solutions as a function of temperature and concentration. Int J Biol Macromol 18:61–68
Monkos K (2004) On the hydrodynamics and temperature dependence of the solution conformation of human serum albumin from viscometry approach. Biochim Biophys Acta 1700:27–34
Morris AM, Watzky MA, Finke RG (2009) Protein aggregation kinetics, mechanism, and curve-fitting: a review of the literature. Biochim Biophys Acta 1794:375–397
Murayama K, Tomida M (2004) Heat-induced secondary structure and conformation change of bovine serum albumin investigated by Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy. Biochemistry 43:11526–11153
Pandey NK, Ghosh S, Dasgupta S (2010) Fibrillation in human serum albumin is enhanced in the presence of copper(II). J Phys Chem B 114:10228–10233
Patterson JE, Geller DM (1977) Bovine microsomal albumin: amino terminal sequence of bovine proalbumin. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 74:1220–1226
Perticaroli S, Nickels JD, Ehlers G, Sokolov AP (2014) Rigidity, secondary structure, and the universality of the boson peak in proteins. Biophys J 106:2667–2674
Pindrus MA, Cole JL, Kaur J, Shire SJ, Yadav S, Kalonia DS (2017) Effect of aggregation on the hydrodynamic properties of bovine serum albumin. Pharm Res 34:2250–2259
Qin Z, Buehler MJ (2010) Molecular dynamics simulation of the α-helix to b-sheet transition in coiled protein filaments: evidence for a critical filament length scale. Phys Rev Lett 104:1–4
Reed RG, Putnam FW, Peters T (1980) Sequence of residues 400--403 of bovine serum albumin. Biochem J 191:867–868
Surewicz WK, Mantsch HH (1988) New insight into protein secondary structure from resolution-enhanced infrared spectra. Biochim Biophys Acta 952:115–130
Takeda K, Wada A, Yamamoto K, Moriyama Y, Aoki K (1989) Conformational change of bovine serum albumin by heat treatment. J Protein Chem 8:653–659
Urbanc B, Borreguero JM, Cruz L, Stanley HE (2006) Ab initio discrete molecular dynamics approach to protein folding and aggregation. Methods Enzymol 412:314–338
Wang W, Roberts CJ (2010) Aggregation of therapeutic proteins. Wiley
Wang XQ, Liu J, Sun LM, Yu L, Jiao JJ, Wang R (2012) Interaction of bovine serum albumin with ester-functionalized anionic surface-active ionic liquids in aqueous solution: a detailed physicochemical and conformational study. J Phys Chem B 116:12479–12488
Wright AK, Thompson MR (1975) Hydrodynamic structure of bovine serum albumin determined by transient electric birefringence. Biophys J 15:137–141
Yamasaki M, Yano H, Aoki K (1990) Differential scanning calorimetric studies on bovine serum albumin: i. effects of pH and ionic strength. Int J Biol Macromol 12:263–268
Yang JT (1960) The viscosity of macromolecules in relation to molecular conformation. Adv Protein Chem 16:323–400
Yohannes G, Wiedmer SK, Elomaa M, Jussila M, Aseyev V, Riekkola ML (2010) Thermal aggregation of bovine serum albumin studied by asymmetrical flow field-flow fractionation. Anal Chim Acta 675:191–198
Yu P (2005) Multicomponent peak modeling of protein secondary structures: comparison of Gaussian with Lorentzian analytical methods for plant feed and seed molecular biology and chemistry research. Appl Spectrosc 59:1372–1380
Funding
This work received a financial support from SERB, DST, Ministry of Science and Technology, India (sanction number SB/S3/CE/086/2013).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
ESM 1
(DOCX 3269 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sharma, I., Pattanayek, S.K. Effect of characteristics of shear force on secondary structures and viscosity of bovine serum albumin solution. Rheol Acta 57, 801–812 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00397-018-1116-6
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00397-018-1116-6