Abstract
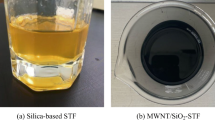
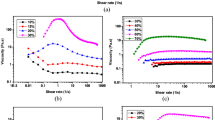
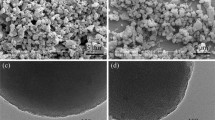
In this study, the rheological behavior of fumed silica nanoparticles suspended in polyethylene glycol (PEG) and those containing multi-walled carbon nanotubes (MWNTs) was measured at steady and oscillatory shear stress using a stress-controlled rheometer. The obtained results showed that the critical viscosity of the concentrated silica suspension, decreased with the addition of MWNTs. Moreover, the onset of shear thickening for the suspension containing MWNTs appeared at higher shear rate than those without MWNTs. Oscillatory shear measurement shows that the storage modulus and loss modulus of silica suspension were higher than the suspension containing MWNTs. The higher complex viscosity of silica suspensions than the suspension containing MWNTs was also evident over the entire range of the frequency studied. The proposed mechanism of nanotube incorporation in dispersion revealed that the observed shear-thickening behavior of a suspension containing MWNTs could be attributed to the increased interaction force between MWNTs and PEG, as a result of increase in the number of hydrogen bonds. This finding suggests that MWNTs could be used as an efficient tool for tuning of the onset of shear thickening and rheological behavior of concentrated silica suspensions.










Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bender J, Wagner NJ (1996) Reversible shear thickening in monodisperse and bidisperse colloidal dispersions. J Rheol 40:899–916. doi:10.1122/1.550767
Bender JW, Wagner NJ (1995) Optical measurement of the contributions of colloidal forces to the rheology of concentrated suspensions. J Colloid Interface Sci 172:171–184. doi:10.1006/jcis.1995.1240
Boersma WH, Laven J, Stein HN (1992) Viscoelastic properties of concentrated shear-thickening dispersions. J Colloid Interface Sci 149:10–22. doi:10.1016/0021-9797(92)90385-Y
Brady JF, Bossis G (1988) Stokesian dynamics. Annu Rev Fluid Mech 20:111–157. doi:10.1146/annurev.fl.20.010188.000551
Crawford NC, Popp LB, Johns KE, Caire LM, Peterson BN, Liberatore MW (2013a) Shear thickening of corn starch suspensions: does concentration matter? J Colloid Interface Sci 396:83–89. doi:10.1016/j.jcis.2013.01.024
Crawford NC, Williams SKR, Boldridge D, Liberatore MW (2013b) Shear thickening and defect formation of fumed silica CMP slurries. Colloid Surf A 436:87–96. doi:10.1016/j.jcis.2013.01.024
Egres RG, Wagner NJ (2005) The rheology and microstructure of acicular precipitated calcium carbonate colloidal suspensions through the shear thickening transition. J Rheol 49:719–746. doi:10.1122/1.1895800
Fahool M, Sabet AR (2015) UV-visible assessment of hydrocluster formation and rheological behavior in bimodal and mono-disperse shear thickening fluids. Rheol Acta 54:77–83. doi:10.1007/s00397-014-0821-z
Hasanzadeh M, Mottaghitalab V, Rezaei M (2015) Rheological and viscoelastic behavior of concentrated colloidal suspensions of silica nanoparticles: a response surface methodology approach. Adv Powder Technol 26:1570–1577. doi:10.1016/j.apt.2015.08.011
Hoffman RL (1972) Discontinuous and dilatant viscosity behavior in concentrated suspensions. I. Observation of a flow instability. Trans Soc Rheol 16:155–173. doi:10.1122/1.549250
Hoffman RL (1974) Discontinuous and dilatant viscosity behavior in concentrated suspensions. II. Theory and experimental tests. J Colloid Interface Sci 46:491–506. doi:10.1016/0021-9797(74)90059-9
Hoffman RL (1998) Explanations for the cause of shear thickening in concentrated colloidal suspensions. J Rheol 42:111–123. doi:10.1122/1.550884
Jiang W, Ye F, He Q, Gong X, Feng J, Lu L, Xuan S (2014) Study of the particles’ structure dependent rheological behavior for polymer nanospheres based shear thickening fluid. J Colloid Interface Sci 413:8–16. doi:10.1016/j.jcis.2013.09.020
Kang TJ, Kim CY, Hong KH (2012) Rheological behavior of concentrated silica suspension and its application to soft armor. J Appl Polym Sci 124:1534–1541. doi:10.1002/app.34843
Keller DE, Visser T, Soulimani F, Koningsberger DC, Weckhuysen BM (2007) Hydration effects on the molecular structure of silica-supported vanadium oxide catalysts: a combined IR, Raman, UV–Vis and EXAFS study. Vib Spectrosc 43:140–151. doi:10.1016/j.vibspec.2006.07.005
Laun HM, Bung R, Hess S, Loose W, Hess O, Hahn K, Hädicke E, Hingmann R, Schmidt F, Lindner P (1992) Rheological and small angle neutron scattering investigation of shear-induced particle structures of concentrated polymer dispersions submitted to plane Poiseuille and Couette flow. J Rheol 36:743–787. doi:10.1122/1.550314
Lee BW, Kim IJ, Kim CG (2009) The influence of the particle size of silica on the ballistic performance of fabrics impregnated with silica colloidal suspension. J Compos Mater 2009(43):2679. doi:10.1177/0021998309345292
Lim AS, Lopatnikov SL, Wagner NJ, Gillespie JW Jr (2010) Investigating the transient response of a shear thickening fluid using the split Hopkinson pressure bar technique. Rheol Acta 49:879–890. doi:10.1007/s00397-010-0463-8
Maranzano BJ, Wagner NJ (2001a) The effects of interparticle interactions and particle size on reversible shear thickening: hard-sphere colloidal dispersions. J Rheol 45:1205–1222. doi:10.1122/1.1392295
Maranzano BJ, Wagner NJ (2001b) The effects of particle size on reversible shear thickening of concentrated colloidal dispersions. J Chem Phys 114:10514–10527. doi:10.1063/1.1373687
Pavia DL, Lampman GM, Kriz GS, Vyvyan JR (2001) Introduction to spectroscopy, 4th ed.; Brooks/Cole; Cengage Learning: Independence, KY.
Saito Y, Hirose Y, Otsubo Y (2011) Effect of poly (ethylene oxide) on the rheological behavior of silica suspensions. Rheol Acta 50:291–301. doi:10.1007/s00397-010-0523-0
Sha X, Yu K, Cao H, Qian K (2013) Shear thickening behavior of nanoparticle suspensions with carbon nanofillers. J Nanopart Res 15:1–11. doi:10.1007/s11051-013-1816-x
Shan L, Tian Y, Jiang J, Zhang X, Meng Y (2015) Effects of pH on shear thinning and thickening behaviors of fumed silica suspensions. Colloid Surf A 464:1–7. doi:10.1016/j.colsurfa.2014.09.040
Srivastava A, Majumdar A, Butola BS (2012) Improving the impact resistance of textile structures by using shear thickening fluids: a review. Crit Rev Solid State Mater Sci 37:115–129. doi:10.1080/10408436.2011.613493
Warren J, Offenberger S, Toghiani H, Pittman CU Jr, Lacy TE, Kundu S (2015) Effect of temperature on the shear-thickening behavior of Fumed silica suspensions. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 7:18650–18661. doi:10.1021/acsami.5b05094
White EEB, Chellamuthu M, Rothstein JP (2010) Extensional rheology of a shear-thickening cornstarch and water suspension. Rheol Acta 49:119–129. doi:10.1007/s00397-009-0415-3
Acknowledgment
The authors gratefully acknowledge University of Guilan and Iran Nanotechnology Initiative Council for financial support of this research. We would also like to thank Dr. Ashkan Zolriasatien for his useful comments.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hasanzadeh, M., Mottaghitalab, V. Tuning of the rheological properties of concentrated silica suspensions using carbon nanotubes. Rheol Acta 55, 759–766 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00397-016-0950-7
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00397-016-0950-7