Abstract
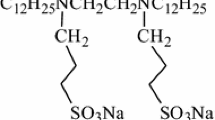
The rheological characterization of dilute and semi-dilute equimolar cetyltrimethylammonium bromide and sodium salicylate solutions is reported, including their linear and nonlinear responses. Start-up experiments and direct birefringence measurements suggest that even at a concentration of as low as 1.0 mM, temporal shear oscillations occur at low shear rates. At concentrations above 10 mM, those low-stress structures vanish and give way to shear-thickening and shear-banding behaviors as seen for other semi-dilute surfactant solutions. Also, the degradation of these solutions after exposure to rubber pump tubing is covered.















Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aradian A, Cates ME (2006) Minimal model for chaotic shear banding in shear thickening fluids. Phys Rev E 73:041508
Azzouzzi H, Decruppe JP, Lerouge S, Greffier O (2005) Temporal oscillations of the shear stress and scattered light in a shear-banding-shear-thickening micellar solution. Eur Phys J E 17:507
Britton MM, Callaghan PT (1997) Two-phase shear band structures at uniform stress. Phys Rev Lett 78(26):4930
Britton MM, Callaghan PT (1999) Shear banding instability in wormlike micellar solutions. Eur Phys J B 7:237
Cates ME (1987) Reptation of living polymers: dynamics of entangled polymers in the presence of reversible chain-scission reactions. Macromeolecules 20:2289
Cates ME, Candau SJ (1990) Statics and dynamics of worm-like surfactant micelles. J Phys, Condens Matter 2:6869
Cates ME, Candau SJ (2001) Ring-driven shear thickening in wormlike micelles? Europhys Lett 55(6):887
Cates ME, McLeich TCB, Marrucci G (1993) The rheology of entangled polymers at very high shear rates. Europhys Lett 21(4):451
Dhont JKG, Briels WJ (2008) Gradient and vorticity banding. Rheol Acta 47:257
Ewoldt RH, McKinley GH (2007) Creep ringing in rheometry or how to deal with oft-discarded data in step stress tests. Rheol Bull 76(1):4–6
Ezrahi S, Tuval E, Aserin A (2006) Properties, main applications and perspectives of worm micelles. Adv Colloid Interface Sci 128–130:77
Fischer P (2000) Time dependent flow in equimolar micellar solutions: transient behavior of the shear stress and first normal stress difference in shear induced structures coupled with flow instabilities. Rheol Acta 39:234
Fischer P, Rehage H (1997) Non-linear flow properties of viscoelastic surfactant solutions. Rheol Acta 36:13
Fischer P, Wheeler EK, Fuller GG (2002) Shear-banding structure orientated in the vorticity direction observed for equimolar micellar solution. Rheol Acta 41:35
Fischer P, Ouriev B, Windhab EJ (2009) Macroscopic pipe flow of micellar solutions investigated by Ultrasound Doppler velocimetry. Tenside Surfactants Deterg 46:140
Frank M, Anderson D, Weeks ER, Morris JF (2003) Particle migration in pressure-driven flow of a Brownian suspension. J Fluid Mech 493:363
Gamboa C, Sepulveda L (1986) High viscosities of cationic and anionic micellar solutions in the presence of added salt. J Colloid Interface Sci 113(2):566
Goymann CCM (2004) Physicochemical characterization of colloidal drug delivery systems such as reverse micelles, vesicles, liquid crystals and nanoparticles for topical administration. Eur J Pharm Biopharm 58:343
Hadri F, Guillou S (2010) Drag reduction by surfactant in closed turbulent flow. Int J Eng Sci Technol 2(12):6876
Hartmann V, Cressely R (1997a) Influence of sodium salicylate on the rheological behavior of an aqueous CTAB solution. Colloids Surf, A Physicochem Eng Asp 121:151
Hartmann V, Cressely R (1997b) Simple salts effects on the characteristics of the shear thickening exhibited by an aqueous micellar solution of CTAB/NaSal. Europhys Lett 40(6):691
Helgeson ME, Vazquez PA, Kaler EW, Wagner NJ (2009a) Rheology and spatially resolved structure of cetyltrimethylammonium bromide wormlike micelles through the shear banding transition. J Rheol 53(3):727
Helgeson ME, Reichert MD, Hu YT, Wagner NJ (2009b) Relating shear banding, structure, and phase behavior in wormlike micellar solutions. Soft Matter 5:3858
Herle V, Fischer P, Windhab EJ (2005) Stress driven shear bands and the effect of confinement on their structures: a rheological, flow visualization, and rheo-SALS study. Langmuir 21:9051
Herle V, Kohlbrecher J, Pfister B, Fischer P, Windhab EJ (2007) Alternating vorticity bands in a solution of wormlike micelle. Phys Rev Lett 99:158302
Herle V, Manneville S, Fischer P (2008) Ultrasound velocimetry in a shear-thickening wormlike micellar solution: evidence for the coexistence of radial and vorticity shear bands. Eur Phys J E 26:3
Hoffmann H, Ulbricht W (1989) Transition of rodlike to globular micelles by the solubilization of additives. J Colloid Interface Sci 129(2):388
Hofmann S, Rauscher A, Hoffmann H (1991) Shear induced micellar structures. J Phys Chem 95:153
Hu Y, Wang SQ, Jamieson AM (1993a) Kinetics studies of shear thickening micellar studies. J Colloid Interface Sci 156:31
Hu Y, Wang SQ, Jamieson AM (1993b) Rheological and flow birefringence studies of a shear-thickening complex fluid: a surfactant model system. J Rheol 37(3):531
Hu Y, Rajaram CV, Wang SQ, Jamieson AM (1994) Shear thickening behavior of a rheopectic micellar solution: salt effects. Langmuir 10:80
Hu Y, Matthys EF (1995) Characterization of micellar structure dynamics for a drag-reducing surfactant solution under shear: normal stress studies and flow geometry effects. Rheol Acta 34:450
Hu YT, Boltenhagen P, Pine DJ (1998a) Shear thickening in low-concentration solutions of wormlike micelles. I. Direct visualization of transient behavior and phase transitions. J Rheol 42(5):1185
Hu YT, Boltenhagen P, Matthys E, Pine DJ (1998b) Shear thickening in low-concentration solutions of wormlike micelles. II. Slip, fracture, and stability of the shear-induced phase. J Rheol 42(5):1209
ISO 1817 (2005) Rubber, vulcanized—determination of the effect of liquids, 4th edn
Israelachvili JN (1985) Intermolecular and surface forces. Academic, London
KaIus J, Hoffmann H, Chen SH, Lindner P (1989) Small-angle neutron scattering experiments of micellar solutions under shear. J Phys Chem 93:4261
Kallus S, Willenbacher N, Kirsch S, Distler D, Neidhfer T, Wilhelm M, Spiess HW (2001) Characterization of polymer dispersions by Fourier transform rheology. Rheol Acta 40:552
Kim WJ, Yang SM (2000) Effects of sodium salicylate on the microstructure of an aqueous micellar solution and its rheological responses. J Colloid Interface Sci 232:225
Koch S, Schneider T, Kuter W (1998) The velocity field of dilute cationic surfactant solutions in a Couette-viscometer. J Non-Newton Fluid Mech 78:47
Lin B, Mohanty S, McCormick AV, Davis HT (2003) Study of the effect of added salt on micellization of cetyltrimethylammonium bromide surfactant. In: Mesoscale phenomena in fluid systems, ACS symposium series, vol 861, pp 313–326
Liu CH, Pine DJ (1996) Shear-induced gelation and fracture in micellar solutions. Phys Rev Lett 77(10):2121
Mair RW, Callaghan PT (1996) Observation of shear banding in worm-like micelles by NMR velocity imaging. Europhys Lett 36: 719
Marin-Santibanez BM, Perez-Gonzalez J, Vargas L, Rodrıguez-Gonzalez F, Huelsz G (2006) Rheometry-PIV of shear-thickening wormlike micelles. Langmuir 22:4015
Miller E, Rothstein JP (2007) Transient evolution of shear-banding wormlike micellar solutions. J Non-Newton Fluid Mech 143: 22
Mohanty S, Davis HT, McCormick AV (2001) Complementary use of simulations and free energy models for CTAB/NaSal systems. Langmuir 17:7160
Normand V, Ravey JC (1997) Dynamic study of gelatin gels by creep measurements. Rheol Acta 36:610
Olmsted PD (2008) Perspectives on shear banding in complex fluids. Rheol Acta 47:283
Olmsted PD, Lu CYD (1997) Coexistence and phase separation in sheared complex fluids. Phys Rev E 56:55
Prötzl B, Springer J (1997) Light scattering experiments on shear induced structures of micellar solutions. J Colloid Interface Sci 190:327
Rehage H, Hoffmann H (1982) Shear induced phase transitions in highly dilute aqueous detergent solutions. Rheol Acta 21:561
Rehage H, Hoffmann H (1991) Viscoelastic surfactant solutions: model systems for rheological research. Mol Phys 74:933
Rehage H, Wunderlich I, Hoffmann H (1986) Shear induced phase transitions in dilute aqueous surfactant solutions. Colloid Polym Sci 72:51
Rothstein JP (2008) Strong flows of viscoelastic wormlike micelle solutions. Rheol Rev 2009:1–46
Russel WB, Saville DA, Schowalter WR (1989) Colloidal dispersions. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge
Saito S, Mizuta Y (1967) Solubilization of polymers in aqueous cationic surfactant solution. J Colloid Interface Sci 23:604
Schweitzer PA (2006) Corrosion of polymer and elastomers. Taylor & Francis, New York.
Shikata T, Sakaiguchi Y, Uragami H, Tamura A, Hirata H (1987) Enormously elongated cationic surfactant micelle formed in CTAB-aromatic additive systems. J Colloid Interface Sci 119:291
Shikata T, Hirata H, Kotaka T (1988) Micelle formation of detergent molecules in aqueous media. 2. Role of free salicylate ions on viscoelastic properties of aqueous cetyltrimethylammonium bromide-sodium salicylate solutions. Langmuir 4(2):355
Shikata T, Hirata H, Kotaka T (1989) Micelle formation of detergent molecules in aqueous media. 3. Viscoelastic properties of aqueous cetyltrimethylammonium bromide-salicylic acid solutions. Langmuir 5:398
Teixeira RE, Hazem PB, Shaqfeh ESG, Chu S (2005) Shear thinning and tumbling dynamics of single polymers in the flow-gradient plane. Macromolecules 38:581
Tripathi D (2002) Practical guide to polypropylene. Rapra Technology Limited, Shrewbury
Vasudevan M, Shen A, Khomami B, Sureshkumar R (2008) Self-similar shear thickening behavior in CTAB/NaSal surfactant solutions. J Rheol 52(2):527
Wilhelm M, Maring D, Spiess HW (1998) Fourier-transform rheology. Rheol Acta 37:399
Wilhelm M, Reinheimer P, Ortseifer M (1999) High sensitivity Fourier-transform rheology. Rheol Acta 38:349
Wheeler EK, Fischer P, Fuller GG (1998) Time-periodic flow induced structures and instabilities in a viscoelastic surfactant solution. J Non-Newton Fluid Mech 75:193
Wunderlich AM, Brunn PO (1989) The complex rheological behavior of an aqueous cationic surfactant solution investigated in a Couette-type viscometer. Colloid Polym Sci 267:627
Acknowledgements
VLB acknowledges financial support by ETH Zurich and PSI as well as SANS measurements time. This work is also a collaboration with the Erasmus Mundus MaMaSELF program (Master in Materials Science Exploiting Large Scale Facilities—mamaself.eu) with the grant number 2010-0138.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lutz-Bueno, V., Kohlbrecher, J. & Fischer, P. Shear thickening, temporal shear oscillations, and degradation of dilute equimolar CTAB/NaSal wormlike solutions. Rheol Acta 52, 297–312 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00397-012-0672-4
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00397-012-0672-4