Abstract
Purpose
Our previous studies demonstrated the beneficial effects of the probiotic Lactobacillus paracasei HII01, prebiotic xylooligosaccharide (XOS), and synbiotics on several parameters in high-fat diet (HFD)-induced obese rats. However, the gut microbiota composition in these rats has not been investigated. Therefore, this study aimed to investigate the impact of biotic therapies on gut microbiota in HFD-induced obese-insulin-resistant rats.
Methods
Male Wistar rats were fed with a normal diet (ND, n = 5) and a HFD (n = 20) for 24 weeks. At week 13, HFD-fed rats were given either a probiotic (L. paracasei, HF-Pro, n = 5), prebiotic (XOS, HF-Pre, n = 5), synbiotic (XOS + L. paracasei, HF-Syn, n = 5), or vehicle (HF-V, n = 5) for 12 weeks. ND-fed rats received vehicle (ND-V, n = 5). At week 24, all rats were decapitated, and metabolic parameters and gut microbiota were analyzed.
Results
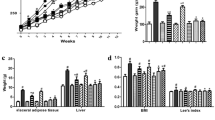
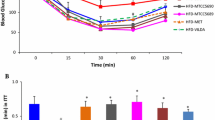
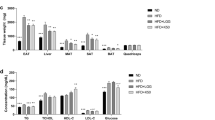
HF-V rats developed an obese-insulin-resistant condition as indicated by impaired metabolic parameters. The prebiotic and synbiotic restored those metabolic parameters to the same level of ND-V rats. The gut microbiota composition of ND-V and HF-V rats differed as indicated by beta diversity. Verrucomicrobia in ND-V rats and Firmicutes and Proteobacteria in HF-V rats were dominant. Interestingly, Verrucomicrobia was also prominent in the HF-Syn rats. HF-Pre rats showed a distinct gut microbiota the predominant family being Ruminococcaceae.
Conclusion
The changes in gut microbiota after HFD consumption included increased Firmicutes and Proteobacteria. The treatment with the prebiotic and synbiotic showed an association with the increase in Ruminococcaceae and Verrucomicrobia, respectively. These changes in gut microbiota due to biotics may mediate the beneficial effects on metabolic parameters.






Similar content being viewed by others
Availability of data and material
The data described in the manuscript will be made available upon request.
Code availability
Not applicable.
References
Festi D, Schiumerini R, Eusebi LH, Marasco G, Taddia M, Colecchia A (2014) Gut microbiota and metabolic syndrome. World J Gastroenterol 20(43):16079–16094. https://doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v20.i43.16079
Everard A, Cani PD (2013) Diabetes, obesity and gut microbiota. Best Pract Res Clin Gastroenterol 27(1):73–83. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bpg.2013.03.007
Kim KA, Gu W, Lee IA, Joh EH, Kim DH (2012) High fat diet-induced gut microbiota exacerbates inflammation and obesity in mice via the TLR4 signaling pathway. PLoS ONE 7(10):e47713. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0047713
de La Serre CB, Ellis CL, Lee J, Hartman AL, Rutledge JC, Raybould HE (2010) Propensity to high-fat diet-induced obesity in rats is associated with changes in the gut microbiota and gut inflammation. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol 299(2):G440-448. https://doi.org/10.1152/ajpgi.00098.2010
Cani PD, Bibiloni R, Knauf C, Waget A, Neyrinck AM, Delzenne NM, Burcelin R (2008) Changes in gut microbiota control metabolic endotoxemia-induced inflammation in high-fat diet-induced obesity and diabetes in mice. Diabetes 57(6):1470–1481. https://doi.org/10.2337/db07-1403
Backhed F, Ding H, Wang T, Hooper LV, Koh GY, Nagy A, Semenkovich CF, Gordon JI (2004) The gut microbiota as an environmental factor that regulates fat storage. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 101(44):15718–15723. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.0407076101
Tremaroli V, Backhed F (2012) Functional interactions between the gut microbiota and host metabolism. Nature 489(7415):242–249. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature11552
Schulz MD, Atay C, Heringer J, Romrig FK, Schwitalla S, Aydin B, Ziegler PK, Varga J, Reindl W, Pommerenke C, Salinas-Riester G, Bock A, Alpert C, Blaut M, Polson SC, Brandl L, Kirchner T, Greten FR, Polson SW, Arkan MC (2014) High-fat-diet-mediated dysbiosis promotes intestinal carcinogenesis independently of obesity. Nature 514(7523):508–512. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature13398
Park HJ, Lee SE, Kim HB, Isaacson RE, Seo KW, Song KH (2014) Association of obesity with serum leptin, adiponectin, and serotonin and gut microflora in beagle dogs. J Vet Internal Med. https://doi.org/10.1111/jvim.12455
Cani PD, Amar J, Iglesias MA, Poggi M, Knauf C, Bastelica D, Neyrinck AM, Fava F, Tuohy KM, Chabo C, Waget A, Delmee E, Cousin B, Sulpice T, Chamontin B, Ferrieres J, Tanti JF, Gibson GR, Casteilla L, Delzenne NM, Alessi MC, Burcelin R (2007) Metabolic endotoxemia initiates obesity and insulin resistance. Diabetes 56(7):1761–1772. https://doi.org/10.2337/db06-1491
Delzenne NM, Neyrinck AM, Backhed F, Cani PD (2011) Targeting gut microbiota in obesity: effects of prebiotics and probiotics. Nat Rev Endocrinol 7(11):639–646
Patel R, DuPont HL (2015) New approaches for bacteriotherapy: prebiotics, new-generation probiotics, and synbiotics. Clin Infect Dis 60(Suppl 2):S108-121. https://doi.org/10.1093/cid/civ177
Delzenne NM, Cani PD (2010) Nutritional modulation of gut microbiota in the context of obesity and insulin resistance: potential interest of prebiotics. Int Dairy J 20(4):277–280. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.idairyj.2009.11.006
Kaila M, Isolauri E, Soppi E, Virtanen E, Laine S, Arvilommi H (1992) Enhancement of the circulating antibody secreting cell response in human diarrhea by a human Lactobacillus strain. Pediatr Res 32(2):141–144. https://doi.org/10.1203/00006450-199208000-00002
Wang J, Tang H, Zhang C, Zhao Y, Derrien M, Rocher E, van-Hylckama Vlieg JE, Strissel K, Zhao L, Obin M, Shen J (2015) Modulation of gut microbiota during probiotic-mediated attenuation of metabolic syndrome in high fat diet-fed mice. The ISME J 9(1):1–15. https://doi.org/10.1038/ismej.2014.99
Kadooka Y, Sato M, Imaizumi K, Ogawa A, Ikuyama K, Akai Y, Okano M, Kagoshima M, Tsuchida T (2010) Regulation of abdominal adiposity by probiotics (Lactobacillus gasseri SBT2055) in adults with obese tendencies in a randomized controlled trial. Eur J Clin Nutr 64(6):636–643. https://doi.org/10.1038/ejcn.2010.19
Stsepetova J, Sepp E, Kolk H, Loivukene K, Songisepp E, Mikelsaar M (2011) Diversity and metabolic impact of intestinal Lactobacillus species in healthy adults and the elderly. Br J Nutr 105(8):1235–1244. https://doi.org/10.1017/s0007114510004770
Wang LX, Liu K, Gao DW, Hao JK (2013) Protective effects of two Lactobacillus plantarum strains in hyperlipidemic mice. World J Gastroenterol 19(20):3150–3156. https://doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v19.i20.3150
Aronsson L, Huang Y, Parini P, Korach-Andre M, Hakansson J, Gustafsson JA, Pettersson S, Arulampalam V, Rafter J (2010) Decreased fat storage by Lactobacillus paracasei is associated with increased levels of angiopoietin-like 4 protein (ANGPTL4). PLoS ONE. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0013087
Tanida M, Shen J, Maeda K, Horii Y, Yamano T, Fukushima Y, Nagai K (2008) High-fat diet-induced obesity is attenuated by probiotic strain Lactobacillus paracasei ST11 (NCC2461) in rats. Obesity Res Clin Pract. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.orcp.2008.04.003
Li Y, Liu M, Liu H, Wei X, Su X, Li M, Yuan J (2020) Oral supplements of combined Bacillus licheniformis Zhengchangsheng(R) and Xylooligosaccharides improve high-fat diet-induced obesity and modulate the gut microbiota in rats. Biomed Res Int 2020:9067821. https://doi.org/10.1155/2020/9067821
Thiennimitr P, Yasom S, Tunapong W, Chunchai T, Wanchai K, Pongchaidecha A, Lungkaphin A, Sirilun S, Chaiyasut C, Chattipakorn N, Chattipakorn SC (2018) Lactobacillus paracasei HII01, xylooligosaccharides, and synbiotics reduce gut disturbance in obese rats. Nutrition 54:40–47. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nut.2018.03.005
Tang T, Song J, Li J, Wang H, Zhang Y, Suo H (2020) A synbiotic consisting of Lactobacillus plantarum S58 and hull-less barley β-glucan ameliorates lipid accumulation in mice fed with a high-fat diet by activating AMPK signaling and modulating the gut microbiota. Carbohydr Polym 243:116398. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2020.116398
Ke X, Walker A, Haange SB, Lagkouvardos I, Liu Y, Schmitt-Kopplin P, von Bergen M, Jehmlich N, He X, Clavel T, Cheung PCK (2019) Synbiotic-driven improvement of metabolic disturbances is associated with changes in the gut microbiome in diet-induced obese mice. Mol Metab 22:96–109. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molmet.2019.01.012
Sergeev IN, Aljutaily T, Walton G, Huarte E (2020) Effects of synbiotic supplement on human gut microbiota, body composition and weight loss in obesity. Nutrients 12(1):222
Pratchayasakul W, Kerdphoo S, Petsophonsakul P, Pongchaidecha A, Chattipakorn N, Chattipakorn SC (2011) Effects of high-fat diet on insulin receptor function in rat hippocampus and the level of neuronal corticosterone. Life Sci 88(13–14):619–627. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.lfs.2011.02.003
Chunchai T, Thunapong W, Yasom S, Wanchai K, Eaimworawuthikul S, Metzler G, Lungkaphin A, Pongchaidecha A, Sirilun S, Chaiyasut C, Pratchayasakul W, Thiennimitr P, Chattipakorn N, Chattipakorn SC (2018) Decreased microglial activation through gut-brain axis by prebiotics, probiotics, or synbiotics effectively restored cognitive function in obese-insulin resistant rats. J Neuroinflammation 15(1):11. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12974-018-1055-2
Matthews DR, Hosker JP, Rudenski AS, Naylor BA, Treacher DF, Turner RC (1985) Homeostasis model assessment: insulin resistance and beta-cell function from fasting plasma glucose and insulin concentrations in man. Diabetologia 28(7):412–419. https://doi.org/10.1007/bf00280883
Wutthi-In M, Cheevadhanarak S, Yasom S, Kerdphoo S, Thiennimitr P, Phrommintikul A, Chattipakorn N, Kittichotirat W, Chattipakorn S (2020) Gut microbiota profiles of treated metabolic syndrome patients and their relationship with metabolic health. Sci Rep 10(1):10085. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-020-67078-3
Bolyen E, Rideout JR, Dillon MR, Bokulich NA, Abnet CC, Al-Ghalith GA, Alexander H, Alm EJ, Arumugam M, Asnicar F, Bai Y, Bisanz JE, Bittinger K, Brejnrod A, Brislawn CJ, Brown CT, Callahan BJ, Caraballo-Rodriguez AM, Chase J, Cope EK, Da Silva R, Diener C, Dorrestein PC, Douglas GM, Durall DM, Duvallet C, Edwardson CF, Ernst M, Estaki M, Fouquier J, Gauglitz JM, Gibbons SM, Gibson DL, Gonzalez A, Gorlick K, Guo J, Hillmann B, Holmes S, Holste H, Huttenhower C, Huttley GA, Janssen S, Jarmusch AK, Jiang L, Kaehler BD, Kang KB, Keefe CR, Keim P, Kelley ST, Knights D, Koester I, Kosciolek T, Kreps J, Langille MGI, Lee J, Ley R, Liu YX, Loftfield E, Lozupone C, Maher M, Marotz C, Martin BD, McDonald D, McIver LJ, Melnik AV, Metcalf JL, Morgan SC, Morton JT, Naimey AT, Navas-Molina JA, Nothias LF, Orchanian SB, Pearson T, Peoples SL, Petras D, Preuss ML, Pruesse E, Rasmussen LB, Rivers A, Robeson MS 2nd, Rosenthal P, Segata N, Shaffer M, Shiffer A, Sinha R, Song SJ, Spear JR, Swafford AD, Thompson LR, Torres PJ, Trinh P, Tripathi A, Turnbaugh PJ, Ul-Hasan S, van der Hooft JJJ, Vargas F, Vazquez-Baeza Y, Vogtmann E, von Hippel M, Walters W, Wan Y, Wang M, Warren J, Weber KC, Williamson CHD, Willis AD, Xu ZZ, Zaneveld JR, Zhang Y, Zhu Q, Knight R, Caporaso JG (2019) Reproducible, interactive, scalable and extensible microbiome data science using QIIME 2. Nat Biotechnol 37(8):852–857. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41587-019-0209-9
Callahan BJ, McMurdie PJ, Rosen MJ, Han AW, Johnson AJ, Holmes SP (2016) DADA2: High-resolution sample inference from Illumina amplicon data. Nat Methods 13(7):581–583. https://doi.org/10.1038/nmeth.3869
Weiss S, Xu ZZ, Peddada S, Amir A, Bittinger K, Gonzalez A, Lozupone C, Zaneveld JR, Vazquez-Baeza Y, Birmingham A, Hyde ER, Knight R (2017) Normalization and microbial differential abundance strategies depend upon data characteristics. Microbiome 5(1):27. https://doi.org/10.1186/s40168-017-0237-y
Pedregosa F, Varoquaux G, Gramfort A, Michel V, Thirion B, Grisel O, Blondel M, Prettenhofer P, Weiss R, Dubourg V, Vanderplas J, Passos A, Cournapeau D, Brucher M, Perrot M, Duchesnay É (2011) Scikit-learn: machine learning in Python. J Mach Learn Res 12(85):2825–2830
Pruesse E, Quast C, Knittel K, Fuchs BM, Ludwig W, Peplies J, Glöckner FO (2007) SILVA: a comprehensive online resource for quality checked and aligned ribosomal RNA sequence data compatible with ARB. Nucleic Acids Res 35(21):7188–7196. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkm864
Segata N, Izard J, Waldron L, Gevers D, Miropolsky L, Garrett WS, Huttenhower C (2011) Metagenomic biomarker discovery and explanation. Genome Biol 12(6):R60. https://doi.org/10.1186/gb-2011-12-6-r60
Mosca A, Leclerc M, Hugot JP (2016) Gut microbiota diversity and human diseases: should we reintroduce key predators in our ecosystem? Front Microbiol 7:455. https://doi.org/10.3389/fmicb.2016.00455
Saiyasit N, Chunchai T, Prus D, Suparan K, Pittayapong P, Apaijai N, Pratchayasakul W, Sripetchwandee J, Chattipakorn MDPDN, Chattipakorn SC (2020) Gut dysbiosis develops before metabolic disturbance and cognitive decline in high-fat diet-induced obese condition. Nutrition 69:110576. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nut.2019.110576
Crovesy L, Masterson D, Rosado EL (2020) Profile of the gut microbiota of adults with obesity: a systematic review. Eur J Clin Nutr 74(9):1251–1262. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41430-020-0607-6
Kaakoush NO (2015) Insights into the role of erysipelotrichaceae in the human host. Front Cell Infect Microbiol 5:84. https://doi.org/10.3389/fcimb.2015.00084
Rosadini CV, Kagan JC (2017) Early innate immune responses to bacterial LPS. Curr Opin Immunol 44:14–19. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.coi.2016.10.005
Salguero MV, Al-Obaide MAI, Singh R, Siepmann T, Vasylyeva TL (2019) Dysbiosis of Gram-negative gut microbiota and the associated serum lipopolysaccharide exacerbates inflammation in type 2 diabetic patients with chronic kidney disease. Exp Ther Med 18(5):3461–3469. https://doi.org/10.3892/etm.2019.7943
Cani PD, Osto M, Geurts L, Everard A (2012) Involvement of gut microbiota in the development of low-grade inflammation and type 2 diabetes associated with obesity. Gut Microbes 3(4):279–288. https://doi.org/10.4161/gmic.19625
Depommier C, Everard A, Druart C, Plovier H, Van Hul M, Vieira-Silva S, Falony G, Raes J, Maiter D, Delzenne NM, de Barsy M, Loumaye A, Hermans MP, Thissen JP, de Vos WM, Cani PD (2019) Supplementation with Akkermansia muciniphila in overweight and obese human volunteers: a proof-of-concept exploratory study. Nat Med 25(7):1096–1103. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41591-019-0495-2
Lensu S, Pariyani R, Makinen E, Yang B, Saleem W, Munukka E, Lehti M, Driuchina A, Linden J, Tiirola M, Lahti L, Pekkala S (2020) Prebiotic xylo-oligosaccharides ameliorate high-fat-diet-induced hepatic steatosis in rats. Nutrients. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu12113225
Tunapong W, Apaijai N, Yasom S, Tanajak P, Wanchai K, Chunchai T, Kerdphoo S, Eaimworawuthikul S, Thiennimitr P, Pongchaidecha A, Lungkaphin A, Pratchayasakul W, Chattipakorn SC, Chattipakorn N (2018) Chronic treatment with prebiotics, probiotics and synbiotics attenuated cardiac dysfunction by improving cardiac mitochondrial dysfunction in male obese insulin-resistant rats. Eur J Nutr 57(6):2091–2104. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00394-017-1482-3
Eaimworawuthikul S, Tunapong W, Chunchai T, Suntornsaratoon P, Charoenphandhu N, Thiennimitr P, Chattipakorn N, Chattipakorn SC (2020) Altered gut microbiota ameliorates bone pathology in the mandible of obese-insulin-resistant rats. Eur J Nutr 59(4):1453–1462. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00394-019-02002-8
Li Z, Summanen PH, Komoriya T, Finegold SM (2015) In vitro study of the prebiotic xylooligosaccharide (XOS) on the growth of Bifidobacterium spp and Lactobacillus spp. Int J Food Sci Nutr 66(8):919–922. https://doi.org/10.3109/09637486.2015.1064869
Lim SM, Kim E, Shin JH, Seok PR, Jung S, Yoo SH, Kim Y (2018) Xylobiose prevents high-fat diet induced mice obesity by suppressing mesenteric fat deposition and metabolic dysregulation. Molecules. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules23030705
Fei Y, Wang Y, Pang Y, Wang W, Zhu D, Xie M, Lan S, Wang Z (2019) Xylooligosaccharide modulates gut microbiota and alleviates colonic inflammation caused by high fat diet induced obesity. Front Physiol 10:1601. https://doi.org/10.3389/fphys.2019.01601
Funding
This work was supported by Senior Research Scholar Grant from the National Research Council of Thailand (SCC.), the NSTDA Research Chair Grant from the National Science and Technology Development Agency Thailand (NC), and the Chiang Mai University Center of Excellence Award (NC).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Conceptualization: SS, WK, NC, and SCC; methodology: WK; formal analysis and investigation: SS, WK, TC; writing—original draft preparation: SS; writing—review and editing: WK and SCC; funding acquisition: NC and SCC; resources: WK, NC, and SCC; supervision: NC and SCC.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors have no conflicts of interest to declare that are relevant to the content of this article.
Ethical approval
All animal studies were approved by the Institutional Animal Care and Use Committee (IACUC) of the Faculty of Medicine, Chiang Mai University (Permit number: 13/2558).
Consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sriwichaiin, S., Kittichotirat, W., Chunchai, T. et al. Profiles of gut microbiota in obese-insulin-resistant rats treated with biotics. Eur J Nutr 61, 2493–2505 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00394-022-02839-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00394-022-02839-6