Abstract
Purpose
The chronic consumption of a high-fat diet (HFD) induces obese–insulin resistance and impairs jawbone health via gut dysbiosis-stimulated inflammatory process. Our previous studies demonstrated that the probiotic Lactobacillus paracasei HII01, prebiotic xylooligosaccharide (XOS), and synbiotics improved several vital organ functions by reducing gut dysbiosis in HFD-induced obese rats. However, the impacts on the cellular level of jawbone microarchitecture have not been examined. Here, we hypothesized that the supplementation of L. paracasei HII01, XOS, and synbiotics ameliorated the bone microarchitectural pathology in HFD-fed rats by reducing systemic inflammation and other metabolic parameters.
Methods
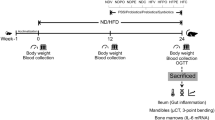
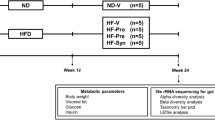
The dietary regimes (normal or high-fat diet) were provided to 48 male Wistar rats throughout 24-week experiment. After week 12, rats were given either a vehicle, pro-, pre-, or synbiotic for an additional 12 weeks before being killed. Then, blood analyses and bone histomorphometry of the jawbones were performed.
Results
The HFD-fed rats developed obese–insulin resistance with significantly elevated systemic inflammation. Bone histomorphometry of these rats showed a decrease in trabecular thickness with increased osteoclasts and active erosion surfaces. Mineral apposition and bone-formation rates were also remarkably diminished. The treatment with pro-, pre-, and synbiotics equally improved metabolic disturbance, reduced systemic inflammation, increased trabecular thickness, decreased osteoclasts and active erosion surfaces and restored mineral apposition and bone-formation rates.
Conclusion
The probiotic L. paracasei HII01, prebiotic XOS, and the synbiotics had similarly beneficial effects to improve jawbone microarchitecture in HFD-fed rats by possibly ameliorating osteoclast-related bone resorption and potentiating bone-formation activities.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Williams EP, Mesidor M, Winters K, Dubbert PM, Wyatt SB (2015) Overweight and obesity: prevalence, consequences, and causes of a growing public health problem. Curr Obes Rep 4(3):363–370
Eckel RH, Kahn SE, Ferrannini E, Goldfine AB, Nathan DM, Schwartz MW, Smith RJ, Smith SR (2011) Obesity and type 2 diabetes: what can be unified and what needs to be individualized? J Clin Endocrin Metab 96(6):1654–1663
Cao JJ (2011) Effects of obesity on bone metabolism. J Orthop Surg Res 6(30):78. https://doi.org/10.1186/1749-799x-6-30
Eaimworawuthikul S, Tunapong W, Chunchai T, Yasom S, Wanchai K, Suntornsaratoon P, Charoenphandhu N, Thiennimitr P, Chattipakorn N, Chattipakorn SC (2018) Effects of probiotics, prebiotics or synbiotics on jawbone in obese-insulin resistant rats. Eur J Nutr. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00394-018-1829-4
Pramojanee SN, Phimphilai M, Kumphune S, Chattipakorn N, Chattipakorn SC (2013) Decreased jaw bone density and osteoblastic insulin signaling in a model of obesity. J Dent Res 92(6):560–565
Cani PD, Amar J, Iglesias MA, Poggi M, Knauf C, Bastelica D, Neyrinck AM, Fava F, Tuohy KM, Chabo C, Waget A, Delmee E, Cousin B, Sulpice T, Chamontin B, Ferrieres J, Tanti JF, Gibson GR, Casteilla L, Delzenne NM, Alessi MC, Burcelin R (2007) Metabolic endotoxemia initiates obesity and insulin resistance. Diabetes 56(7):1761–1772
da Silva SV, Renovato-Martins M, Ribeiro-Pereira C, Citelli M, Barja-Fidalgo C (2016) Obesity modifies bone marrow microenvironment and directs bone marrow mesenchymal cells to adipogenesis. Obesity (Silver Spring, Md) 24(12):2522–2532
Luo Y, Chen GL, Hannemann N, Ipseiz N, Kronke G, Bauerle T, Munos L, Wirtz S, Schett G, Bozec A (2015) Microbiota from obese mice regulate hematopoietic stem cell differentiation by altering the bone niche. Cell Metab 22(5):886–894
He M, Shi B (2017) Gut microbiota as a potential target of metabolic syndrome: the role of probiotics and prebiotics. Cell Biosci 7:54
Hsu E, Pacifici R (2017) From osteoimmunology to osteomicrobiology: how the microbiota and the immune system regulate bone. Calcif Tissue Int. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00223-017-0321-0
de La Serre CB, Ellis CL, Lee J, Hartman AL, Rutledge JC, Raybould HE (2010) Propensity to high-fat diet-induced obesity in rats is associated with changes in the gut microbiota and gut inflammation. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol 299(2):G440–G448
Kim KA, Gu W, Lee IA, Joh EH, Kim DH (2012) High fat diet-induced gut microbiota exacerbates inflammation and obesity in mice via the TLR4 signaling pathway. PLoS One 7(10):e47713
Ejtahed HS, Soroush AR, Angoorani P, Larijani B, Hasani-Ranjbar S (2016) Gut microbiota as a target in the pathogenesis of metabolic disorders: a new approach to novel therapeutic agents. Horm Metab Res 48(06):349–358
Eaimworawuthikul S, Thiennimitr P, Chattipakorn N, Chattipakorn SC (2017) Diet-induced obesity, gut microbiota and bone, including alveolar bone loss. Arch Oral Biol 78:65–81
Collins FL, Kim SM, McCabe LR, Weaver CM (2017) Intestinal microbiota and bone health: the role of prebiotics, probiotics, and diet. In: Smith SY, Varela A, Samadfam R (eds) Bone toxicology. Springer International Publishing, Cham, pp 417–443
Schepper JD, Irwin R, Kang J, Dagenais K, Lemon T, Shinouskis A, Parameswaran N, McCabe LR (2017) Probiotics in gut–bone signaling. Adv Exp Med Biol 1033:225–247
McCabe L, Britton RA, Parameswaran N (2015) Prebiotic and probiotic regulation of bone health: role of the intestine and its microbiome. Curr Osteoporos Rep 13(6):363–371
Whisner CM, Castillo LF (2018) Prebiotics, bone and mineral metabolism. Calcif Tissue Int 102(4):443–479
Thiennimitr P, Yasom S, Tunapong W, Chunchai T, Wanchai K, Pongchaidecha A, Lungkaphin A, Sirilun S, Chaiyasut C, Chattipakorn N, Chattipakorn SC (2018) Lactobacillus paracasei HII01, xylooligosaccharides, and synbiotics reduce gut disturbance in obese rats. Nutrition 54:40–47
Tunapong W, Apaijai N, Yasom S, Tanajak P, Wanchai K, Chunchai T, Kerdphoo S, Eaimworawuthikul S, Thiennimitr P, Pongchaidecha A, Lungkaphin A, Pratchayasakul W, Chattipakorn SC, Chattipakorn N (2017) Chronic treatment with prebiotics, probiotics and synbiotics attenuated cardiac dysfunction by improving cardiac mitochondrial dysfunction in male obese insulin-resistant rats. Eur J Nutr. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00394-017-1482-3
Chunchai T, Thunapong W, Yasom S, Wanchai K, Eaimworawuthikul S, Metzler G, Lungkaphin A, Pongchaidecha A, Sirilun S, Chaiyasut C, Pratchayasakul W, Thiennimitr P, Chattipakorn N, Chattipakorn SC (2018) Decreased microglial activation through gut–brain axis by prebiotics, probiotics, or synbiotics effectively restored cognitive function in obese–insulin resistant rats. J Neuroinflamm 15(1):11
Wanchai K, Yasom S, Tunapong W, Chunchai T, Eaimworawuthikul S, Thiennimitr P, Chaiyasut C, Pongchaidecha A, Chatsudthipong V, Chattipakorn S, Chattipakorn N, Lungkaphin A (2018) Probiotic Lactobacillus paracasei HII01 protects rats against obese–insulin resistance-induced kidney injury and impaired renal organic anion transporter 3 function. Clin Sci (Lond) 132(14):1545–1563
Wanchai K, Yasom S, Tunapong W, Chunchai T, Thiennimitr P, Chaiyasut C, Pongchaidecha A, Chatsudthipong V, Chattipakorn S, Chattipakorn N, Lungkaphin A (2018) Prebiotic prevents impaired kidney and renal Oat3 functions in obese rats. J Endocrinol 237(1):29–42
Kilkenny C, Browne WJ, Cuthill IC, Emerson M, Altman DG (2010) Improving bioscience research reporting: the ARRIVE guidelines for reporting animal research. PLoS Biol 8(6):e1000412
Peerajan S, Chaiyasut C, Sirilun S, Chaiyasut K, Kesika P, Sivamaruthi BS (2016) Enrichment of nutritional value of Phyllanthus emblica fruit juice using the probiotic bacterium, Lactobacillus paracasei HII01 mediated fermentation. Food Sci Technol 36:116–123
Haffner SM, Miettinen H, Stern MP (1997) The homeostasis model in the San Antonio Heart Study. Diabetes Care 20(7):1087–1092
Charoenphandhu N, Suntornsaratoon P, Sa-Nguanmoo P, Tanajak P, Teerapornpuntakit J, Aeimlapa R, Chattipakorn N, Chattipakorn S (2018) Dipeptidyl peptidase-4 inhibitor, vildagliptin, improves trabecular bone mineral density and microstructure in obese, insulin-resistant, pre-diabetic rats. Can J Diabetes 42:545–552
Abbassy MA, Watari I, Soma K (2010) The effect of diabetes mellitus on rat mandibular bone formation and microarchitecture. Eur J Oral Sci 118(4):364–369
Dempster DW, Compston JE, Drezner MK, Glorieux FH, Kanis JA, Malluche H, Meunier PJ, Ott SM, Recker RR, Parfitt AM (2013) Standardized nomenclature, symbols, and units for bone histomorphometry: a 2012 update of the report of the ASBMR Histomorphometry Nomenclature Committee. J Bone Miner Res 28(1):2–17
Charoenphandhu N, Suntornsaratoon P, Jongwattanapisan P, Wongdee K, Krishnamra N (2012) Enhanced trabecular bone resorption and microstructural bone changes in rats after removal of the cecum. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab 303(8):E1069–E1075
Damanaki A, Memmert S, Nokhbehsaim M, Sanyal A, Gnad T, Pfeifer A, Deschner J (2018) Impact of obesity and aging on crestal alveolar bone height in mice. Ann Anat 218:227–235
Montalvany-Antonucci CC, Zicker MC, Ferreira AVM, Macari S, Ramos-Junior ES, Gomez RS, Pereira TSF, Madeira MFM, Fukada SY, Andrade I Jr, Silva TA (2018) High-fat diet disrupts bone remodeling by inducing local and systemic alterations. J Nutr Biochem 59:93–103
de Silva V, Lobato RV, Andrade EF, Orlando DR, Borges BDB, Zangeronimo MG, de Sousa RV, Pereira LJ (2017) Effects of beta-glucans ingestion on alveolar bone loss, intestinal morphology, systemic inflammatory profile, and pancreatic beta-cell function in rats with periodontitis and diabetes. Nutrients 9(9):1016
Gatej SM, Marino V, Bright R, Fitzsimmons TR, Gully N, Zilm P, Gibson RJ, Edwards S, Bartold PM (2018) Probiotic Lactobacillus rhamnosus GG prevents alveolar bone loss in a mouse model of experimental periodontitis. J Clin Periodontol 45(2):204–212
Jia X, Jia L, Mo L, Yuan S, Zheng X, He J, Chen V, Guo Q, Zheng L, Yuan Q, Xu X, Zhou X (2018) Berberine ameliorates periodontal bone loss by regulating gut microbiota. J Dent Res. https://doi.org/10.1177/0022034518797275
Ricoldi MST, Furlaneto FAC, Oliveira LFF, Teixeira GC, Pischiotini JP, Moreira ALG, Ervolino E, de Oliveira MN, Bogsan CSB, Salvador SL, Messora MR (2017) Effects of the probiotic Bifidobacterium animalis subsp. lactis on the non-surgical treatment of periodontitis. A histomorphometric, microtomographic and immunohistochemical study in rats. PLoS One 12(6):e0179946
Nagpal R, Kaur A (2011) Synbiotic effect of various prebiotics on in vitro activities of probiotic lactobacilli. Ecol Food Nutr 50(1):63–68
Li Z, Summanen PH, Komoriya T, Finegold SM (2015) In vitro study of the prebiotic xylooligosaccharide (XOS) on the growth of Bifidobacterium spp. and Lactobacillus spp. Int J Food Sci Nutr 66(8):919–922
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by Thailand Research Fund (TRF) Grants: TRF-Senior Research Scholar RTA6080003 (to SCC), RTA6080007 (to N. Charoenphandhu), IRN60W0001 (to N. Charoenphandhu) and MRG6180187 (to PT); Mahidol University (to N. Charoenphandhu); a CMU 50th Anniversary Grant by Chiang Mai University (PHD/014/2557 SE&SCC); a NSTDA Research Chair Grant from the National Science and Technology Development Agency Thailand (N. Chattipakorn) and a Chiang Mai University Center of Excellence Award (N. Chattipakorn).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
The authors’ responsibilities were as follows—SE, PT, and NC and SCC: designed the research; SE, WT, and TC: conducted the research; PS, NC, and PT: provided essential materials; SE, NC, and SCC: analyzed the data; SE, NC, NC, and SCC: wrote the manuscript; SCC: had primary responsibility for the final content; and all authors: read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that there are no conflicts of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Eaimworawuthikul, S., Tunapong, W., Chunchai, T. et al. Altered gut microbiota ameliorates bone pathology in the mandible of obese–insulin-resistant rats. Eur J Nutr 59, 1453–1462 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00394-019-02002-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00394-019-02002-8