Summary
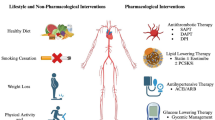
Nowadays, about 6–8% of the German population suffers from diabetes mellitus mostly type 2 but in patients with angiopathies about 30% have known diabetes and a further 30% have newly diagnosed diabetes or impaired glucose tolerance. Therefore diagnosis and therapy of glucose impairment play a central role for management of these patients. The antidiabetic therapy for secondary prevention of cardiovascular disease has to be embedded in a multifactorial concept with management of hypertension, hyperlipidemia and hypercoagulability. The management of diabetes following guidelines is a stepwise therapy with lifestyle interventions (diet, exercise) and oral drugs or insulin. Metformin has shown favorable outcome in overweight patients if aware of side effects; insulin is a safe drug in multimorbid patients and with planned interventions or operations. We are awaiting the results of multiple endpoint studies with newer antidiabetic drugs which may change our current concept of management of diabetes mellitus in these patients in the near future.
Zusammenfassung
Zirka 6–8% der Bevölkerung in Deutschland sind heute an einem Diabetes mellitus, meist vom Typ 2, erkrankt. Bei Patienten mit manifester Angiopathie haben etwa 30% einen bekannten Diabetes und weitere 30% leiden an einem bisher nicht diagnostiziertem Diabetes bzw. einer gestörten Glukosetoleranz. Daher ist Diagnostik und Therapie der Glukosestoffwechselstörung zentraler Bestandteil der Betreuung dieser Patienten. Zur Sekundärprävention kardiovaskulärer Ereignisse muss die antidiabetische Therapie in ein multimodales Konzept mit Behandlung von Hypertonie, Fettstoffwechselstörung und Hyperkoagulabilität eingeordnet werden. Die leitliniengerechte Therapie des Diabetes folgt einem Stufenmodell mit Änderung des Lebensstils (Ernährung, Bewegung) und medikamentöser Therapie mit Tabletten und Insulin. Besondere Vorteile hat Metformin bei übergewichtigen Patienten unter Beachtung der Anwendungsbeschränkungen. Insulin ist bei schweren Begleiterkrankungen sowie geplanten interventionellen und operativen Eingriffen eine sichere Therapie. In den nächsten Jahren werden die Ergebnisse mehrerer Endpunktstudien mit neueren oralen Antidiabetika erwartet, die unsere Therapieempfehlungen erweitern könnten.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Chiasson JL, Josse RG, Gomis R, Hanefeld M, Karasik A, Laakso M, STOP-NIDDM Trial Research Group (2003) Acarbose treatment and the risk of cardiovascular disease and hypertension in patients with impaired glucose tolerance: the STOP-NIDDM trial. JAMA 290:486–494
Gaede P, Vedel P, Larsen N, Jensen GV, Parving HH, Pedersen O (2003) Multifactorial intervention and cardiovascular disease in patients with type 2 diabetes. N Engl J Med 348:383–393
Haffner SM, Lehto S, Ronnemaa T, Pyorala K, Laakso M (1998) Mortality from coronary heart disease in subjects with type 2 diabetes and in nondiabetic subjects with and without prior myocardial infarction. N Engl J Med 339:229–234
Inzucchi SE, Masoudi FA, Wang Y, Kosiborod M, Foody JM, Setaro JF, Havranek EP, Krumholz HM (2005) Insulin-sensitizing antihyperglycemic drugs and mortality after acute myocardial infarction: insights from the National Heart Care Project. Diab Care 28:1680–1689
Knowler WC, Barrett-Connor E, Fowler SE, Hamman RF, Lachin JM, Walker EA, Nathan DM, Diabetes Prevention Program Research Group (2002) Reduction in the incidence of type 2 diabetes with lifestyle intervention or metformin. N Engl J Med 346:393–403
Olsson J, Lindberg G, Gottsater M, Lindwall K, Sjostrand A, Tisell A, Melander A (2000) Increased mortality in type 2 diabetic patients using sulphonyurea and metformin in combination: a population-based observational study. Diabetologia 43:558–560
Pfützner A, Marx N, Lubben G, Langenfeld M, Walcher D, Konrad T, Forst T (2005) Improvement of cardiovascular risk markers by pioglitazone is independent from glycemic control: results from the pioneer study. J Am Coll Cardiol 45:1925–1931
Schatz H (Hrsg) (2001) Diabetologie kompakt. Blackwell, Berlin Wien
Tuomilehto J, Lindstrom J, Eriksson JG, Valle TT, Hamalainen H, Hanne-Parikka P, Keinanen-Kiukaanniemi S, Laakso M, Louheranta A, Rastas M, Salminen V, Uusitupa M, Finnish Diabetes Prevention Study Group (2001) Prevention of type 2 diabetes mellitus by changes in lifestyle among subjects with impaired glucose tolerance. N Engl J Med 344:1343–1350
UKPDS Group (1998) Intensive blood glucose control with sulphonylureas or insulin compared with conventional treatment and risk of complications in patients with type 2 diabetes (UKPDS 33). Lancet 352:837–853
UKPDS Group (1998) Effect of intensive blood-glucose control with metformin on complications in overweight patients with type 2 diabetes (UKPDS 34). Lancet 352:854–865
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lohmann, T. Führung des Diabetes mellitus bei Angiopathien. ZS Kardiologie 94 (Suppl 4), iv28–iv30 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00392-005-1408-6
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00392-005-1408-6