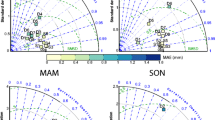
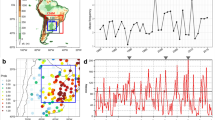
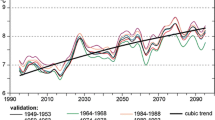
Abstract
Given the coarse spatial resolution of General Circulation Models, finer scale projections of variables affected by local-scale processes such as precipitation are often needed to drive impacts models, for example in hydrology or ecology among other fields. This need for high-resolution data leads to apply projection techniques called downscaling. Downscaling can be performed according to two approaches: dynamical and statistical models. The latter approach is constituted by various statistical families conceptually different. If several studies have made some intercomparisons of existing downscaling models, none of them included all those families and approaches in a manner that all the models are equally considered. To this end, the present study conducts an intercomparison exercise under the EURO- and MED-CORDEX initiative hindcast framework. Six Statistical Downscaling Models (SDMs) and five Regional Climate Models (RCMs) are compared in terms of precipitation outputs. The downscaled simulations are driven by the ERAinterim reanalyses over the 1989–2008 period over a common area at 0.44° of resolution. The 11 models are evaluated according to four aspects of the precipitation: occurrence, intensity, as well as spatial and temporal properties. For each aspect, one or several indicators are computed to discriminate the models. The results indicate that marginal properties of rain occurrence and intensity are better modelled by stochastic and resampling-based SDMs, while spatial and temporal variability are better modelled by RCMs and resampling-based SDM. These general conclusions have to be considered with caution because they rely on the chosen indicators and could change when considering other specific criteria. The indicators suit specific purpose and therefore the model evaluation results depend on the end-users point of view and how they intend to use with model outputs. Nevertheless, building on previous intercomparison exercises, this study provides a consistent intercomparison framework, including both SDMs and RCMs, which is designed to be flexible, i.e., other models and indicators can easily be added. More generally, this framework provides a tool to select the downscaling model to be used according to the statistical properties of the local-scale climate data to drive properly specific impact models.














Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ambrosino C, Chandler R, Todd M (2014) Rainfall-derived growing season characteristics for agricultural impact assessments in South Africa. Theor Appl Climatol 115(3–4):411–426. doi:10.1007/s00704-013-0896-y
Bardossy A, Plate EJ (1992) Space–time model for daily rainfall using atmospheric circulation patterns. Water Resour Res 28(5):1247–1259. doi:10.1029/91WR02589
Barnston AG, Livezey RE (1987) Classification, seasonality and persistence of low-frequency atmospheric circulation patterns. Mon Weather Rev 115(6):1083–1126. doi:10.1175/1520-0493(1987)115<1083:CSAPOL>2.0.CO;2
Bellone E, Hughes JP, Guttorp P (2000) A hidden Markov model for downscaling synoptic atmospheric patterns to precipitation amounts. J Hydrol 15(1):1–12. http://www.int-res.com/abstracts/cr/v15/n1/p1-12/
Bougeault P (1985) A simple parameterization of the large-scale effects of cumulus convection. Mon Weather Rev 113(12):2108–2121. doi:10.1175/1520-0493(1985)113<2108:ASPOTL>2.0.CO;2
Bouvier C, Cisneros L, Dominguez R, Laborde JP, Lebel T (2003) Generating rainfall fields using principal components (pc) decomposition of the covariance matrix: a case study in mexico city. J Hydrol 278(1–4):107–120. doi:10.1016/S0022-1694(03)00122-7. http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0022169403001227
Brier GW (1950) Verification of forecasts expressed in terms of probability. Mon Weather Rev 78(1):1–3. doi:10.1175/1520-0493(1950)078
Buishand TA, Shabalova MV, Brandsma T (2004) On the choice of the temporal aggregation level for statistical downscaling of precipitation. J Clim 17(9):1816–1827. doi:10.1175/1520-0442(2004)017<1816:OTCOTT>2.0.CO;2
Bürger G, Murdock TQ, Werner AT, Sobie SR, Cannon AJ (2012) Downscaling extremes—an intercomparison of multiple statistical methods for present climate. J Clim 25(12). doi:10.1175/JCLI-D-11-00408.1
Cavazos T, Hewitson C Bruce (2005) Performance of NCEP-NCAR reanalysis variables in statistical downscaling of daily precipitation. Clim Res 28(2):95–107. doi:10.3354/cr028095. http://www.int-res.com/abstracts/cr/v28/n2/p95-107/
Chaboureau JP, Bechtold P (2002) A simple cloud parameterization derived from cloud resolving model data: diagnostic and prognostic applications. J Atmos Sci 59(15):2362–2372. doi:10.1175/1520-0469(2002)059<2362:ASCPDF>2.0.CO;2
Chaboureau JP, Bechtold P (2005) Statistical representation of clouds in a regional model and the impact on the diurnal cycle of convection during tropical convection, cirrus and nitrogen oxides (troccinox). J Geophys Res Atmos 110(D17). doi:10.1029/2004JD005645
Chandler RE, Wheater HS (2002) Analysis of rainfall variability using generalized linear models: a case study from the west of Ireland. Water Resour Res 38(10):1192. doi:10.1029/2001WR000906
Chardon J, Hingray B, Favre A, Autin P, Gailhard J, Zin I, Obled C (2014) Spatial similarity and transferability of analog dates for precipitation downscaling over france. J Clim 27(13):5056–5074. doi:10.1175/JCLI-D-13-00464.1
Charles SP, Bates BC, Whetton PH, Hughes JP (1999) Validation of downscaling models for changed climate conditions: case study of southwestern Australia. Clim Res 12(1):1–14. doi:10.3354/cr012001. http://www.int-res.com/abstracts/cr/v12/n1/p1-14/
Chiriaco M, Bastin S, Yiou P, Haeffelin M, Dupont JC, Stéfanon M (2014) European heatwave in July 2006: observations and modeling showing how local processes amplify conducive large-scale conditions. Geophys Res Lett 41(15):5644–5652. doi:10.1002/2014GL060205
Christensen J, Carter T, Rummukainen M, Amanatidis G (2007) Evaluating the performance and utility of regional climate models: the PRUDENCE project. Clim Change 81(1):1–6. doi:10.1007/s10584-006-9211-6
Coiffier J (2011) Fundamentals of numerical weather prediction. Cambridge University Press. doi:10.1017/CBO9780511734458 (Cambridge books online)
Colin J, Déqué M, Radu R, Somot S (2010) Sensitivity study of heavy precipitation in limited area model climate simulations: influence of the size of the domain and the use of the spectral nudging technique. Tellus A 62(5):591–604. doi:10.1111/j.1600-0870.2010.00467.x
Crawford T, Betts NL, Favis-Mortlock D (2007) GCM grid-box choice and predictor selection associated with statistical downscaling of daily precipitation over Northern Ireland. Clim Res 34(2):145–160. doi:10.3354/cr034145. http://www.int-res.com/abstracts/cr/v34/n2/p145-160/
Cuxart J, Bougeault P, Redelsperger JL (2000) A turbulence scheme allowing for mesoscale and large-eddy simulations. Q J R Meteorol Soc 126(562):1–30. doi:10.1002/qj.49712656202
Dee DP, Uppala SM, Simmons AJ, Berrisford P, Poli P, Kobayashi S, Andrae U, Balmaseda MA, Balsamo G, Bauer P, Bechtold P, Beljaars ACM, van de Berg L, Bidlot J, Bormann N, Delsol C, Dragani R, Fuentes M, Geer AJ, Haimberger L, Healy SB, Hersbach H, Hólm EV, Isaksen L, Kållberg P, Köhler M, Matricardi M, McNally AP, Monge-Sanz BM, Morcrette JJ, Park BK, Peubey C, de Rosnay P, Tavolato C, Thépaut JN, Vitart F (2011) The ERA-interim reanalysis: configuration and performance of the data assimilation system. Q J R Meteorol Soc 137(656):553–597. doi:10.1002/qj.828
Denis B, Laprise R, Caya D (2003) Sensitivity of a regional climate model to the resolution of the lateral boundary conditions. Clim Dyn 20(2–3):107–126. doi:10.1007/s00382-002-0264-6
Dibike YB, Coulibaly P (2006) Temporal neural networks for downscaling climate variability and extremes. Neural Netw 19(2):135–144. doi:10.1016/j.neunet.2006.01.003. http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0893608006000062 (Earth Sciences and Environmental Applications of Computational Intelligence)
Domínguez M, Romera R, Sánchez E, Fita L, Fernández J, Jiménez-Guerrero P, Montávez J, Cabos W, Liguori G, Gaertner M (2013) Present-climate precipitation and temperature extremes over spain from a set of high resolution rcms). Clim Res 58(2):149–164. doi:10.3354/cr01186. http://www.int-res.com/abstracts/cr/v58/n2/p149-164/
Douville H, Planton S, Royer J, Stephenson D, Tyteca S, Kergoat L, Lafont S, Betts R (2000) The importance of vegetation feedbacks in doubled-CO2 time-slice experiments. Ann Geophys 11(12):1095–1115
Drobinski P, Ducrocq V, Alpert P, Anagnostou E, Béranger K, Borga M, Braud I, Chanzy A, Davolio S, Delrieu G, Estournel C, Boubrahmi NF, Font J, Grubišić V, Gualdi S, Homar V, Ivančan-Picek B, Kottmeier C, Kotroni V, Lagouvardos K, Lionello P, Llasat MC, Ludwig W, Lutoff C, Mariotti A, Richard E, Romero R, Rotunno R, Roussot O, Ruin I, Somot S, Taupier-Letage I, Tintore J, Uijlenhoet R, Wernli H (2014) Hymex: a 10-year multidisciplinary program on the mediterranean water cycle. Bull Am Meteorol Soc 95(7):1063–1082. doi:10.1175/BAMS-D-12-00242.1
Déqué M (2007) Frequency of precipitation and temperature extremes over France in an anthropogenic scenario: model results and statistical correction according to observed values. Glob Planet Change 57(1–2):16–26. doi:10.1016/j.gloplacha.2006.11.030. http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0921818106002748
Déqué M, Piedelievre J (1995) High resolution climate simulation over Europe. Clim Dyn 11(6):321–339. doi:10.1007/BF00215735
ECMWF (2004) IFS documentation CY28r1. ECMWF, reading, pp 7–32. http://www.oldecmwfint/research/ifsdocs/CY28r1/pdf_files/Physics.pdf
Ek MB, Mitchell KE, Lin Y, Rogers E, Grunmann P, Koren V, Gayno G, Tarpley JD (2003) Implementation of Noah land surface model advances in the national centers for environmental prediction operational mesoscale eta model. J Geophys Res Atmos 108(D22). doi:10.1029/2002JD003296
Fealy R, Sweeney J (2007) Statistical downscaling of precipitation for a selection of sites in Ireland employing a generalised linear modelling approach. Int J Climatol 27(15):2083–2094. doi:10.1002/joc.1506
Flaounas E, Bastin S, Janicot S (2011) Regional climate modelling of the 2006 West African monsoon: sensitivity to convection and planetary boundary layer parameterisation using wrf. Clim Dyn 36(5–6):1083–1105. doi:10.1007/s00382-010-0785-3
Flaounas E, Drobinski P, Vrac M, Bastin S, Lebeaupin-Brossier C, Stéfanon M, Borga M, Calvet JC (2013) Precipitation and temperature space–time variability and extremes in the mediterranean region: evaluation of dynamical and statistical downscaling methods. Clim Dyn 40(11–12):2687–2705. doi:10.1007/s00382-012-1558-y
Foufoula-Georgiou E, Tsonis A (1996) Preface [to the special section on space–time variability and dynamics of rainfall]. J Geophys Res Atmos 101(D21):26,161–26,163. doi:10.1029/96JD03121
Fu C, Wang S, Xiong Z, Gutowski WJ, Lee DK, McGregor JL, Sato Y, Kato H, Kim JW, Suh MS (2005) Regional climate model intercomparison project for Asia. Bull Am Meteorol Soc 86(2):257–266. doi:10.1175/BAMS-86-2-257
Gaitan C, Hsieh W, Cannon A (2014) Comparison of statistically downscaled precipitation in terms of future climate indices and daily variability for southern Ontario and Quebec, Canada. Clim Dyn 1–17. doi:10.1007/s00382-014-2098-4
Gallardo C, Gil V, Hagel E, Tejeda C, de Castro M (2013) Assessment of climate change in Europe from an ensemble of regional climate models by the use of Köppen–Trewartha classification. Int J Climatol 33(9):2157–2166. doi:10.1002/joc.3580
Gillett NP, Zwiers FW, Weaver AJ, Stott PA (2003) Detection of human influence on sea-level pressure. Nature 422(6929):292–294. doi:10.1038/nature01487
Giorgi F, Jones C, Asrar GR (2009) Addressing climate information needs at the regional level: the CORDEX framework. Bull World Meteorol Organ 58(3):175–183
Grell GA, Dévényi D (2002) A generalized approach to parameterizing convection combining ensemble and data assimilation techniques. Geophys Res Lett 29(14):38-€œ1–38-€œ4. doi:10.1029/2002GL015311
Grenier P, Parent AC, Huard D, Anctil F, Chaumont D (2013) An assessment of six dissimilarity metrics for climate analogs. J Appl Meteorol Climatol 52(4):733–752. doi:10.1175/JAMC-D-12-0170.1
Gudmundsson L, Bremnes JB, Haugen JE, Engen-Skaugen T (2012) Technical note: downscaling RCM precipitation to the station scale using statistical transformations—a comparison of methods. Hydrol Earth Syst Sci 16(9):3383–3390. doi:10.5194/hess-16-3383-2012. http://www.hydrol-earth-syst-sci.net/16/3383/2012/
Hagedorn R, Doblas-Reyes FJ, Palmer TN (2005) The rationale behind the success of multi-model ensembles in seasonal forecasting—i. Basic concept. Tellus A 57(3):219–233. doi:10.1111/j.1600-0870.2005.00103.x
Harpham C, Wilby RL (2005) Multi-site downscaling of heavy daily precipitation occurrence and amounts. J Hydrol 312(1–4):235–255. doi:10.1016/j.jhydrol.2005.02.020. http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0022169405000922
Hastie T, Tibshirani R (1990) Generalized additive models. Monographs on statistics and applied probability. Chapman and Hall. http://books.google.co.uk/books?id=qa29r1Ze1coC
Haylock MR, Cawley GC, Harpham C, Wilby RL, Goodess CM (2006) Downscaling heavy precipitation over the United Kingdom: a comparison of dynamical and statistical methods and their future scenarios. Int J Climatol 26(10):1397–1415. doi:10.1002/joc.1318
Haylock MR, Hofstra N, Klein Tank AMG, Klok EJ, Jones PD, New M (2008) A European daily high-resolution gridded data set of surface temperature and precipitation for 1950–2006. J Geophys Res Atmos 113(D20). doi:10.1029/2008JD010201
Herrmann M, Somot S, Calmanti S, Dubois C, Sevault F (2011) Representation of spatial and temporal variability of daily wind speed and of intense wind events over the mediterranean sea using dynamical downscaling: impact of the regional climate model configuration. Nat Hazards Earth Syst Sci 11(7):1983–2001. doi:10.5194/nhess-11-1983-2011. http://www.nat-hazards-earth-syst-sci.net/11/1983/2011/
Hewitson B, Crane R (1996) Climate downscaling: techniques and application. Clim Res 7(2):85–95. doi:10.3354/cr007085. http://www.int-res.com/abstracts/cr/v07/n2/p85-95/
Hewitt CD (2004) Ensembles-based predictions of climate changes and their impacts. Eos, Trans Am Geophys Union 85(52):566. doi:10.1029/2004EO520005
Hofstra N, Haylock M, New M, Jones PD (2009) Testing E-OBS European high-resolution gridded data set of daily precipitation and surface temperature. J Geophys Res Atmos 114(D21). doi:10.1029/2009JD011799
Hong SY, Lim JOJ (2006) The wrf single-moment 6-class microphysics scheme (wsm6). J Korean Meteorol Soc 42(2):129–151
Hong SY, Dudhia J, Chen SH (2004) A revised approach to ice microphysical processes for the bulk parameterization of clouds and precipitation. Mon Weather Rev 132(1):103–120. doi:10.1175/1520-0493(2004)132<0103:ARATIM>2.0.CO;2
Hong SY, Noh Y, Dudhia J (2006) A new vertical diffusion package with an explicit treatment of entrainment processes. Mon Weather Rev 134(9):2318–2341. doi:10.1175/MWR3199.1
Hourdin F, Musat I, Bony S, Braconnot P, Codron F, Dufresne JL, Fairhead L, Filiberti MA, Friedlingstein P, Grandpeix JY, Krinner G, LeVan P, Li ZX, Lott F (2006) The LMDZ4 general circulation model: climate performance and sensitivity to parametrized physics with emphasis on tropical convection. Clim Dyn 27(7–8):787–813. doi:10.1007/s00382-006-0158-0
Iacono MJ, Delamere JS, Mlawer EJ, Shephard MW, Clough SA, Collins WD (2008) Radiative forcing by long-lived greenhouse gases: calculations with the aer radiative transfer models. J Geophys Res Atmos 113(D13). doi:10.1029/2008JD009944
Jacob D, Bärring L, Christensen O, Christensen J, de Castro M, Déqué M, Giorgi F, Hagemann S, Hirschi M, Jones R, Kjellström E, Lenderink G, Rockel B, Sánchez E, Schär C, Seneviratne S, Somot S, van Ulden A, van den Hurk B (2007) An inter-comparison of regional climate models for europe: model performance in present-day climate. Clim Change 81(1):31–52. doi:10.1007/s10584-006-9213-4
Jacob D, Petersen J, Eggert B, Alias A, Christensen O, Bouwer L, Braun A, Colette A, Déqué M, Georgievski G, Georgopoulou E, Gobiet A, Menut L, Nikulin G, Haensler A, Hempelmann N, Jones C, Keuler K, Kovats S, Kröner N, Kotlarski S, Kriegsmann A, Martin E, van Meijgaard E, Moseley C, Pfeifer S, Preuschmann S, Radermacher C, Radtke K, Rechid D, Rounsevell M, Samuelsson P, Somot S, Soussana JF, Teichmann C, Valentini R, Vautard R, Weber B, Yiou P (2014) EURP-CORDEX: new high-resolution climate change projections for European impact research. Reg Environ Change 14(2):563–578. doi:10.1007/s10113-013-0499-2
Jeong D, St-Hilaire A, Ouarda T, Gachon P (2012) Multisite statistical downscaling model for daily precipitation combined by multivariate multiple linear regression and stochastic weather generator. Clim Change 114(3–4):567–591. doi:10.1007/s10584-012-0451-3
Jiménez-Guerrero P, Montávez J, Domínguez M, Romera R, Fita L, Fernández J, Cabos W, Liguori G, Gaertner M (2013) Mean fields and interannual variability in RCM simulations over Spain: the ESCENA project. Clim Res 57(3):201–220. doi:10.3354/cr01165. http://www.int-res.com/abstracts/cr/v57/n3/p201-220/
Kain J, Fritsch J (1993) Convective parameterization for mesoscale models: the Kain–Fritsch scheme. The representation of cumulus convection in numerical models. No. 46 in Meteorological Monographs, American Meteorological Society
Kain JS (2004) The Kain–Fritsch convective parameterization: an update. J Appl Meteorol 43(1):170–181. doi:10.1175/1520-0450(2004)043<0170:TKCPAU>2.0.CO;2
Khan MS, Coulibaly P, Dibike Y (2006) Uncertainty analysis of statistical downscaling methods. J Hydrol 319(1–4):357–382. doi:10.1016/j.jhydrol.2005.06.035. http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0022169405003719
Kilsby C, Jones P, Burton A, Ford A, Fowler H, Harpham C, James P, Smith A, Wilby R (2007) A daily weather generator for use in climate change studies. Environ Model Softw 22(12):1705–1719. doi:10.1016/j.envsoft.2007.02.005. http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S136481520700031X
Kleiber W, Katz RW, Rajagopalan B (2012) Daily spatiotemporal precipitation simulation using latent and transformed Gaussian processes. Water Resour Res 48(1). doi:10.1029/2011WR011105
Klein WH, Lewis BM, Enger I (1959) Objective prediction of five-day mean temperatures during winter. J Meteorol 16(9):972–682. doi:10.1175/1520-0469(1959)016<0672:OPOFDM>2.0.CO;2
Krinner G, Viovy N, de Noblet-Ducoudré N, Ogée J, Polcher J, Friedlingstein P, Ciais P, Sitch S, Prentice IC (2005) A dynamic global vegetation model for studies of the coupled atmosphere–biosphere system. Glob Biogeochem Cycles 19(1). doi:10.1029/2003GB002199
Lambert SJ, Boer GJ (2001) Cmip1 evaluation and intercomparison of coupled climate models. Clim Dyn 17(2–3):83–106. doi:10.1007/PL00013736
Laprise R, de Elía R, Caya D, Biner S, Lucas-Picher P, Diaconescu E, Leduc M, Alexandru A, Separovic L (2008) Challenging some tenets of regional climate modelling. Meteorol Atmos Phys 100(1–4):3–22. doi:10.1007/s00703-008-0292-9
Lavaysse C, Vrac M, Drobinski P, Lengaigne M, Vischel T (2012) Statistical downscaling of the French Mediterranean climate: assessment for present and projection in an anthropogenic scenario. Nat Hazards Earth Syst Sci 12(3):651–670. doi:10.5194/nhess-12-651-2012. http://www.nat-hazards-earth-syst-sci.net/12/651/2012/
Levavasseur G, Vrac M, Roche DM, Paillard D, Martin A, Vandenberghe J (2011) Present and LGM permafrost from climate simulations: contribution of statistical downscaling. Clim Past 7(4):1225–1246. doi:10.5194/cp-7-1225-2011. http://www.clim-past.net/7/1225/2011/
Lo JCF, Yang ZL, Pielke RA (2008) Assessment of three dynamical climate downscaling methods using the Weather Research and Forecasting (WRF) model. J Geophys Res Atmos 113(D9). doi:10.1029/2007JD009216
Machenhauer B, Windelband M, Botzet M, Hesselbjerg J, Déqué M, Jones G, Ruti P, Visconti G (1998) Validation and analysis of regional present-day climate and climate change simulations over europe. Max-Planck Institute of Meteorology Report No 275, pp 87
Maraun D, Widmann M, Gutiérrez JM, Kotlarski S, Chandler RE, Hertig E, Wibig J, Huth R, Wilcke RA (2015) Value: a framework to validate downscaling approaches for climate change studies. Earth’s Future 3(1):1–14. doi:10.1002/2014EF000259
Mearns L, Sain S, Leung L, Bukovsky M, McGinnis S, Biner S, Caya D, Arritt R, Gutowski W, Takle E, Snyder M, Jones R, Nunes A, Tucker S, Herzmann D, McDaniel L, Sloan L (2013) Climate change projections of the North American Regional Climate Change Assessment Program (NARCCAP). Clim Change 120(4):965–975. doi:10.1007/s10584-013-0831-3
Mezghani A, Hingray B (2009) A combined downscaling-disaggregation weather generator for stochastic generation of multisite hourly weather variables over complex terrain: development and multi-scale validation for the Upper Rhone River basin. J Hydrol 377(3–4):245–260. doi:10.1016/j.jhydrol.2009.08.033. http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0022169409005149
Michelangeli PA, Vrac M, Loukos H (2009) Probabilistic downscaling approaches: application to wind cumulative distribution functions. Geophys Res Lett 36(11). doi:10.1029/2009GL038401
Morcrette JJ (1990) Impact of changes to the radiation transfer parameterizations plus cloud optical. Properties in the ECMWF model. Mon Weather Rev 118(4):847–873. doi:10.1175/1520-0493(1990)118<0847:IOCTTR>2.0.CO;2
Nabat P, Somot S, Mallet M, Sevault F, Chiacchio M, Wild M (2014) Direct and semi-direct aerosol radiative effect on the Mediterranean climate variability using a coupled regional climate system model. Clim Dyn 1–29. doi:10.1007/s00382-014-2205-6
Noguer M, Jones R, Murphy J (1998) Sources of systematic errors in the climatology of a regional climate model over Europe. Clim Dyn 14(10):691–712. doi:10.1007/s003820050249
Oettli P, Sultan B, Baron C, Vrac M (2011) Are regional climate models relevant for crop yield prediction in West Africa? Environ Res Lett 6(1):014008. http://stacks.iop.org/1748-9326/6/i=1/a=014008
Omrani H, Drobinski P, Dubos T (2012a) Investigation of indiscriminate nudging and predictability in a nested quasi-geostrophic model. Q J R Meteorol Soc 138(662):158–169. doi:10.1002/qj.907
Omrani H, Drobinski P, Dubos T (2012b) Spectral nudging in regional climate modelling: how strongly should we nudge? Q J R Meteorol Soc 138(668):1808–1813. doi:10.1002/qj.1894
Onof C, Chandler RE, Kakou A, Northrop P, Wheater HS, Isham V (2000) Rainfall modelling using poisson-cluster processes: a review of developments. Stoch Environ Res Risk Assess 14(6):384–411. doi:10.1007/s004770000043
Palmer TN, Shukla J (2000) Editorial. Q J R Meteorol Soc 126(567):1989–1990. doi:10.1002/qj.49712656701
Pavan V, Doblas-Reyes FJ (2000) Multi-model seasonal hindcasts over the Euro-Atlantic: skill scores and dynamic features. Clim Dyn 16(8):611–625. doi:10.1007/s003820000063
Perrone TJ, Miller RG (1985) Generalized exponential markov and model output statistics: a comparative verification. Mon Weather Rev 113(9):1524–1541. doi:10.1175/1520-0493(1985)113<1524:GEMAMO>2.0.CO;2
Piani C, Weedon G, Best M, Gomes S, Viterbo P, Hagemann S, Haerter J (2010) Statistical bias correction of global simulated daily precipitation and temperature for the application of hydrological models. J Hydrol 395(3–4):199–215. doi:10.1016/j.jhydrol.2010.10.024. http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0022169410006475
Radanovics S, Vidal JP, Sauquet E, Ben Daoud A, Bontron G (2013) Optimising predictor domains for spatially coherent precipitation downscaling. Hydrol Earth Syst Sci 17(10):4189–4208. doi:10.5194/hess-17-4189-2013. http://www.hydrol-earth-syst-sci.net/17/4189/2013/
Raje D, Mujumdar P (2010) Reservoir performance under uncertainty in hydrologic impacts of climate change. Adv Water Resour 33(3):312–326. doi:10.1016/j.advwatres.2009.12.008. http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0309170810000047
Ricard J, Royer J (1993) A statistical cloud scheme for use in an AGCM. Ann Geophys 11(12):1095–1115
Ruti PM, Williams JE, Hourdin F, Guichard F, Boone A, Van Velthoven P, Favot F, Musat I, Rummukainen M, Domínguez M, Gaertner MA, Lafore JP, Losada T, Rodriguez de Fonseca MB, Polcher J, Giorgi F, Xue Y, Bouarar I, Law K, Josse B, Barret B, Yang X, Mari C, Traore AK (2011) The west african climate system: a review of the amma model inter-comparison initiatives. Atmos Sci Lett 12(1):116–122. doi:10.1002/asl.305
Sachindra DA, Huang F, Barton AF, Perera BJC (2014) Multi-model ensemble approach for statistically downscaling general circulation model outputs to precipitation. Q J R Meteorol Soc 140(681):1161–1178. doi:10.1002/qj.2205
Salameh T, Drobinski P, Vrac M, Naveau P (2009) Statistical downscaling of near-surface wind over complex terrain in southern France. Meteorol Atmos Phys 103(1–4):253–265. doi:10.1007/s00703-008-0330-7
Sanders F (1963) On subjective probability forecasting. J Appl Meteorol 2(2):191–201. doi:10.1175/1520-0450(1963)002<0191:OSPF>2.0.CO;2
Schmidli J, Goodess CM, Frei C, Haylock MR, Hundecha Y, Ribalaygua J, Schmith T (2007) Statistical and dynamical downscaling of precipitation: an evaluation and comparison of scenarios for the European Alps. J Geophys Res Atmos 112(D4). doi:10.1029/2005JD007026
Schnur R, Lettenmaier DP (1998) A case study of statistical downscaling in Australia using weather classification by recursive partitioning. J Hydrol 212–213(0):362–379. doi:10.1016/S0022-1694(98)00217-0. http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0022169498002170
Schoof J, Pryor S (2001) Downscaling temperature and precipitation: a comparison of regression-based methods and artificial neural networks. Int J Climatol 21(7):773–790. doi:10.1002/joc.655
Semenov MA, Stratonovitch P (2010) Use of multi-model ensembles from global climate models for assessment of climate change impacts. Clim Res 41(1):1–14. doi:10.3354/cr00836. http://www.int-res.com/abstracts/cr/v41/n1/p1-14/
Semenov MA, Brooks RJ, Barrow EM, Richardson CW (1998) Comparison of the WGEN and LARS-WG stochastic weather generators for diverse climates. Clim Res 10(2):95–107. doi:10.3354/cr010095. http://www.int-res.com/abstracts/cr/v10/n2/p95-107/
Seth A, Giorgi F (1998) The effects of domain choice on summer precipitation simulation and sensitivity in a regional climate model. J Clim 11(10):2698–2712. doi:10.1175/1520-0442(1998)011<2698:TEODCO>2.0.CO;2
Skamarock W, Klemp J, Dudhia J, Gill D, Barker D, Duda M, Huang X, Wang W, Powers J (2008) A description of the advanced research wrf version 3. Technical Report, NCAR
Smirnova TG, Brown JM, Benjamin SG (1997) Performance of different soil model configurations in simulating ground surface temperature and surface fluxes. Mon Weather Rev 125(8):1870–1884. doi:10.1175/1520-0493(1997)125<1870:PODSMC>2.0.CO;2
Solman S, Sanchez E, Samuelsson P, da Rocha R, Li L, Marengo J, Pessacg N, Remedio A, Chou S, Berbery H, Le Treut H, de Castro M, Jacob D (2013) Evaluation of an ensemble of regional climate model simulations over South America driven by the era-interim reanalysis: model performance and uncertainties. Clim Dyn 41(5–6):1139–1157. doi:10.1007/s00382-013-1667-2
Stephens GL, L’Ecuyer T, Forbes R, Gettlemen A, Golaz JC, Bodas-Salcedo A, Suzuki K, Gabriel P, Haynes J (2010) Dreary state of precipitation in global models. J Geophys Res Atmos 115(D24). doi:10.1029/2010JD014532
Stern RD, Coe R (1984) A model fitting analysis of daily rainfall data. J R Stat Soc Ser A (Stat Soc) 147(1):1–34
Sun Y, Solomon S, Dai A, Portmann RW (2006) How often does it rain? J Clim 19(6):916–934. doi:10.1175/JCLI3672.1
Takle ES, Gutowski WJ, Arritt RW, Pan Z, Anderson CJ, da Silva RR, Caya D, Chen SC, Giorgi F, Christensen JH, Hong SY, Juang HMH, Katzfey J, Lapenta WM, Laprise R, Liston GE, Lopez P, McGregor J, Pielke RA, Roads JO (1999) Project to intercompare regional climate simulations (PIRCS): description and initial results. J Geophys Res Atmos 104(D16):19443–19461. doi:10.1029/1999JD900352
Vautard R, Yiou P (2009) Control of recent European surface climate change by atmospheric flow. Geophys Res Lett 36(22). doi:10.1029/2009GL040480
Vautard R, Gobiet A, Jacob D, Belda M, Colette A, Déqué M, Fernández J, García-Díez M, Goergen K, Güttler I, Halenka T, Karacostas T, Katragkou E, Keuler K, Kotlarski S, Mayer S, Meijgaard E, Nikulin G, Patarčić M, Scinocca J, Sobolowski S, Suklitsch M, Teichmann C, Warrach-Sagi K, Wulfmeyer V, Yiou P (2013) The simulation of European heat waves from an ensemble of regional climate models within the EURO-CORDEX project. Clim Dyn 41(9–10):2555–2575. doi:10.1007/s00382-013-1714-z
Vigaud N, Vrac M, Caballero Y (2013) Probabilistic downscaling of GCM scenarios over southern India. Int J Climatol 33(5):1248–1263. doi:10.1002/joc.3509
Vischel T, Lebel T, Massuel S, Cappelaere B (2009) Conditional simulation schemes of rain fields and their application to rainfall-runoff modeling studies in the Sahel. J Hydrol 375(1–2):273–286. doi:10.1016/j.jhydrol.2009.02.028. http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0022169409000900 (Surface processes and water cycle in West Africa, studied from the AMMA-CATCH observing system)
Vrac M, Friederichs P (2014) Multivariate–intervariable, spatial, and temporal–bias correction. J Clim 28(1):218–237. doi:10.1175/JCLI-D-14-00059.1
Vrac M, Naveau P (2007) Stochastic downscaling of precipitation: from dry events to heavy rainfalls. Water Resour Res 43(7). doi:10.1029/2006WR005308
Vrac M, Marbaix P, Paillard D, Naveau P (2007a) Non-linear statistical downscaling of present and LGM precipitation and temperatures over Europe. Clim Past 3(4):669–682. doi:10.5194/cp-3-669-2007. http://www.clim-past.net/3/669/2007/
Vrac M, Stein ML, Hayhoe K (2007b) Statistical downscaling of precipitation through nonhomogeneous stochastic weather typing. Clim Res 34(3):169–184. doi:10.3354/cr00696. http://www.int-res.com/abstracts/cr/v34/n3/p169-184/
Vrac M, Stein ML, Hayhoe K, Liang XZ (2007c) A general method for validating statistical downscaling methods under future climate change. Geophys Res Lett 34(18). doi:10.1029/2007GL030295
Vrac M, Drobinski P, Merlo A, Herrmann M, Lavaysse C, Li L, Somot S (2012) Dynamical and statistical downscaling of the french mediterranean climate: uncertainty assessment. Nat Hazards Earth Syst Sci 12(9):2769–2784. doi:10.5194/nhess-12-2769-2012. http://www.nat-hazards-earth-syst-sci.net/12/2769/2012/
Vrac M, Vaittinada Ayar P, Yiou P (2014) Trends and variability of seasonal weather regimes. Int J Climatol 34(2):472–480. doi:10.1002/joc.3700
van Vuuren D, Edmonds J, Kainuma M, Riahi K, Thomson A, Hibbard K, Hurtt G, Kram T, Krey V, Lamarque JF, Masui T, Meinshausen M, Nakicenovic N, Smith S, Rose S (2011) The representative concentration pathways: an overview. Clim Change 109(1–2):5–31. doi:10.1007/s10584-011-0148-z
Wilby R, Wigley T (1997) Downscaling general circulation model output: a review of methods and limitations. Prog Phys Geogr 21(4):530–548. doi:10.1177/030913339702100403. http://ppg.sagepub.com/content/21/4/530.abstract. http://ppg.sagepub.com/content/21/4/530.full+html
Wilby RL, Dawson CW, Barrow EM (2002) SDSM—a decision support tool for the assessment of regional climate change impacts. Environ Model Softw 17(2):145–157
Wilks DS (2010) Use of stochastic weathergenerators for precipitation downscaling. Wiley Interdiscip Rev Clim Change 1(6):898–907. doi:10.1002/wcc.85
Wilks DS (2012) Stochastic weather generators for climate-change downscaling, part ii: multivariable and spatially coherent multisite downscaling. Wiley Interdiscip Rev Clim Change 3(3):267–278. doi:10.1002/wcc.167
Wingo MT, Cecil DJ (2009) Effects of vertical wind shear on tropical cyclone precipitation. Mon Weather Rev 138(3):645–662. doi:10.1175/2009MWR2921.1
Witten DM, Tibshirani R, Hastie T (2009) A penalized matrix decomposition, with applications to sparse principal components and canonical correlation analysis. Biostatistics 10(3):515–534.doi:10.1093/biostatistics/kxp008. http://biostatistics.oxfordjournals.org/content/10/3/515.abstract. http://biostatistics.oxfordjournals.org/content/10/3/515.full+html
Xiaoli L, Coulibaly P, Evora N (2008) Comparison of data-driven methods for downscaling ensemble weather forecasts. Hydrol Earth Syst Sci 12(2):615–624. doi:10.5194/hess-12-615-2008. http://www.hydrol-earth-syst-sci.net/12/615/2008/
Yang C, Chandler RE, Isham VS, Wheater HS (2005) Spatial–temporal rainfall simulation using generalized linear models. Water Resour Res 41(11):W11415. doi:10.1029/2004WR003739
Yang W, Bárdossy A, Caspary HJ (2010) Downscaling daily precipitation time series using a combined circulation- and regression-based approach. Theor Appl Climatol 102(3–4):439–454. doi:10.1007/s00704-010-0272-0
Yee TW (2010) The VGAM package for categorical data analysis. J Stat Softw 32(10):1–34. http://www.jstatsoft.org/v32/i10
Yiou P (2014) AnaWEGE: a weather generator based on analogues of atmospheric circulation. Geosci Model Dev 7(2):531–543. doi:10.5194/gmd-7-531-2014. http://www.geosci-model-dev.net/7/531/2014/
Yiou P, Nogaj M (2004) Extreme climatic events and weather regimes over the North Atlantic: when and where? Geophys Res Lett 31(7). doi:10.1029/2003GL019119
Yiou P, Vautard R, Naveau P, Cassou C (2007) Inconsistency between atmospheric dynamics and temperatures during the exceptional 2006/2007 fall/winter and recent warming in Europe. Geophys Res Lett 34(21). doi:10.1029/2007GL031981
Yiou P, Salameh T, Drobinski P, Menut L, Vautard R, Vrac M (2013) Ensemble reconstruction of the atmospheric column from surface pressure using analogues. Clim Dyn 41(5–6):1333–1344. doi:10.1007/s00382-012-1626-3
Zorita E, von Storch H (1999) The analog method as a simple statistical downscaling technique: comparison with more complicated methods. J Clim 12(8):2474–2489. doi:10.1175/1520-0442(1999)012
Acknowledgments
The authors are thankful to all the RCM data providers, especially to R. Vautard (IPSL) and A. Colette (INERIS) for the WRF-IPSL-INERIS44 EURO-CORDEX run and Météo-France/CNRM (A. Alias, S. Somot) for the CNRM-ALADIN52 MED-CORDEX run. The MED-CORDEX simulations used in this work are downloaded from the MED-CORDEX data portal (www.medcordex.eu/medcordex.php). This work has been partially funded by the Spanish Ministry of Education and Science and the European Regional Development Fund, through Grant CGL2007-66440-C04-02. We also thank F. Blondot (HSM) who, in collaboration with Julie Carreau, helped us for the predictors selection. All the estimations and simulations for the stochastic and the TF models have been done with the R-package “VGAM” (Yee 2010). Special thanks are due to Thomas Yee, the “VGAM” package author for his help. The MOS model has been computed thanks to the R-package CDFt (Michelangeli et al. 2009). This work has been supported by the ANR StaRMIP project, the ANR REMEMBER project and the REMedHE GICC project. It is a contribution to the HyMeX program (HYdrological cycle in The Mediterranean EXperiment) through INSU-MISTRALS support and the MED-CORDEX program. It was supported by the IPSL group for regional climate and environmental studies, with granted access to the HPC resources of IDRIS (under allocation i2011010227). It is a contribution to the CORDEX-ESD initiative (http://wcrp-cordex.ipsl.jussieu.fr/index.php/community/cordex-esd) and to the COST Action VALUE (http://www.value-cost.eu/, Maraun et al. 2015).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Appendix: Technical features
Appendix: Technical features
See Table 6.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Vaittinada Ayar, P., Vrac, M., Bastin, S. et al. Intercomparison of statistical and dynamical downscaling models under the EURO- and MED-CORDEX initiative framework: present climate evaluations. Clim Dyn 46, 1301–1329 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00382-015-2647-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00382-015-2647-5