Abstract
Introduction
Individuals with Down syndrome (DS) have an increased risk of acute leukemia compared to a markedly decreased incidence of solid tumors. Medulloblastoma, the most common malignant brain tumor of childhood, is particularly rare in the DS population, with only one published case. As demonstrated in a mouse model, DS is associated with cerebellar hypoplasia and a decreased number of cerebellar granule neuron progenitor cells (CGNPs) in the external granule cell layer (EGL). Treatment of these mice with sonic hedgehog signaling pathway (Shh) agonists promote normalization of CGNPs and improved cognitive functioning.
Case report
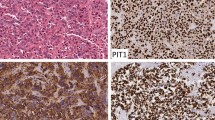
We describe a 21-month-old male with DS and concurrent desmoplastic/nodular medulloblastoma (DNMB)—a tumor derived from Shh dysregulation and over-activation of CGNPs. Molecular profiling further classified the tumor into the new consensus SHH molecular subgroup. Additional testing revealed a de novo heterozygous germ line mutation in the PTCH1 gene encoding a tumor suppressor protein in the Shh pathway.
Discussion
The developmental failure of CGNPs in DS patients offers a plausible explanation for the rarity of medulloblastoma in this population. Conversely, patients with PTCH1 germline mutations experience Shh overstimulation resulting in Gorlin (Nevoid Basal Cell Carcinoma) syndrome and an increased incidence of malignant transformation of CGNPs leading to medulloblastoma formation. This represents the first documented report of an individual with DS simultaneously carrying PTCH1 germline mutation.
Conclusion
We have observed a highly unusual circumstance in which the PTCH1 mutation appears to “trump” the effects of DS in causation of Shh-activated medulloblastoma.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Amlashi SFA, Riffaud L, Brassier G, Morandi X (2003) Nevoid basal cell carcinoma syndrome: relation with desmoplastic medulloblastoma in infancy. A population-based study and review of the literature. Cancer 98(3):618–624. doi:10.1002/cncr.11537
Aylward EH, Habbak R, Warren AC, Pulsifer MB, Barta PE, Jerram M, Pearlson GD (1997) Cerebellar volume in adults with Down syndrome. Arch Neurol 54(2):209–212
Baek KH, Zaslavsky A, Lynch RC, Britt C, Okada Y, Siarey RJ, Lensch MW, Park IH, Yoon SS, Minami T, Korenberg JR, Folkman J, Daley GQ, Aird WC, Galdzicki Z, Ryeom S (2009) Down syndrome suppression of tumour growth and the role of the calcineurin inhibitor DSCR1. Nature 459(7250):1126–1130. doi:10.1038/nature08062
Baxter LL, Moran TH, Richtsmeier JT, Troncoso J, Reeves RH (2000) Discovery and genetic localization of Down syndrome cerebellar phenotypes using the Ts65Dn mouse. Hum Mol Genet 9(2):195–202. doi:10.1093/hmg/9.2.195
Benesch M, Moser A, Sovinz P, Lackner H, Schwinger W, Eder H, Urban C (2009) Medulloblastoma in a child with Down syndrome: long-term remission with multimodality treatment. Pediatr Blood Cancer 53(6):1150–1151. doi:10.1002/pbc.22109
Berman DM, Karhadkar SS, Hallahan AR, Pritchard JI, Eberhart CG, Watkins DN, Chen JK, Cooper MK, Taipale J, Olson JM, Beachey PA (2002) Medulloblastoma growth inhibition by hedgehog pathway blockade. Science 297(5586):1559–1561. doi:10.1126/science.1073733
Costa AC (2011) On the promise of pharmacotherapies targeted at cognitive and neurodegenerative components of Down syndrome. Dev Neurosci 33(5):414–427. doi:10.1159/000330861
Das I, Park JM, Shin JH, Jeon SK, Lorenzi H, Linden DJ, Worley PF, Reeves RH (2013) Hedgehog agonist therapy corrects structural and cognitive deficits in a Down syndrome mouse model. Sci Transl Med 5(201):201ra120. doi:10.1126/scitranslmed.3005983
Dlugosz AA, Talpaz M (2009) Following the hedgehog to new cancer therapies. N Engl J Med 361(12):1202–1205. doi:10.1056/NEJMe0906092
Evans DG, Farndon PA, Burnell LD, Gattamaneni HR, Birch JM (1991) The incidence of Gorlin syndrome in 173 consecutive cases of medulloblastoma. Br J Cancer 64(5):959–961
Fabia J, Drolette M (1970) Malformations and leukemia in children with Down syndrome. Pediatrics 45(1):60–70
Fujii K, Miyashita T (2014) Gorlin syndrome (nevoid basal cell carcinoma syndrome): update and literature review. Pediatr Int 56(5):667–674. doi:10.1111/ped.12461
Fujii M, Noguchi K, Urade M, Muraki Y, Kishimoto H, Hashimoto-Tamaoki T, Nakano Y (2011) Novel PTCH1 mutations in Japanese nevoid basal cell carcinoma syndrome patients: two familial and three sporadic cases including the first Japanese patient with medulloblastoma. J Hum Genet 56(4):277–283. doi:10.1038/jhg.2011.2
Hasle H, Clemmensen IH, Mikkelsen M (2000) Risks of leukaemia and solid tumours in individuals with Down’s syndrome. Lancet 355(9199):165–169
Hasle H (2001) Pattern of malignant disorders in individuals with Down’s syndrome. Lancet Oncol 2(7):429–436
Heretsch P, Tzagkaroulaki L, Giannis A (2010) Modulators of the hedgehog signaling pathway. Bioorg Med Chem 18(18):6613–6624. doi:10.1016/j.bmc.2010.07.038
Hori A, Walter GF, Haas J, Becker H (1992) Down syndrome complicated by brain tumors: case report and review of the literature. Brain Dev 14(6):396–400
Kieran MW (2014) Targeted treatment for sonic hedgehog-dependent medulloblastoma. Neuro-Oncology 16(8):1037–1047. doi:10.1093/neuonc/nou109
Kool M, Jones DT, Jager N, Northcott PA, Pugh TJ, Hovestadt V, Piro RM, Esparza LA, Markant SL, Remke M, Milde T, Bourdeaut F, Ryzhova M, Sturm D, Pfaff E, Stark S, Hutter S, Seker-Cin H, Johann P, Bender S, Schmidt C, Rausch T, Shih D, Reimand J, Sieber L, Wittman A, Linke L, Witt H, Weber UD, Zapatka M, König R, Beroukhim R, Bergthold G, van Sluis P, Volckmann R, Koster J, Versteeg R, Schmidt S, Wolf S, Lawerencz C, Bartholomae CC, von Kalle C, Unterberg A, Herold-Mende C, Hofer S, Kulozik AE, von Deimling A, Scheurlen W, Felsberg J, Reifenberger G, Hasselblatt M, Crawford JR, Grant GA, Jabado N, Perry A, Cowdrey C, Croul S, Zadeh G, Korbel JO, Doz F, Delattre O, Bader GD, McCabe MG, Collins VP, Kieran MW, Cho YJ, Pomeroy SL, Witt O, Brors B, Taylor MD, Schüller U, Korshunov A, Eils R, Wechsler-Reya RJ, Lichter P, Pfister SM (2014) Genome sequencing of SHH medulloblastoma predicts genotype-related response to smoothened inhibition. Cancer Cell 25(3):393–405. doi:10.1016/j.ccr.2014.02.004
Liu H, Gu D, Xie J (2011) Clinical implications of hedgehog signaling pathway inhibitors. Chin J Cancer 30(1):13–26
Narod SA, Stiller C, Lenoir GM (1991) An estimate of the heritable fraction of childhood cancer. Br J Cancer 63(6):993–999
Northcott PA, Jones DT, Kool M, Robinson GW, Gilbertson RJ, Cho YJ, Pomeroy SL, Korshunov A, Pichter P, Taylor MD, Pfsiter SM (2012) Medulloblastomics: the end of the beginning. Nat Rev Cancer 12(12):818–834. doi:10.1038/nrc3410
Olson JM, Hamilton A, Breslow NE (1995) Non-11p constitutional chromosome abnormalities in Wilms’ tumor patients. Med Pediatr Oncol 24(5):305–309
Paulino AC (2002) Current multimodality management of medulloblastoma. Curr Probl Cancer 26(6):317–356
Polkinghorn WR, Tarbell NJ (2007) Medulloblastoma: tumorigenesis, current clinical paradigm, and efforts to improve risk stratification. Nat Clin Pract Oncol 4(5):295–304. doi:10.1038/ncponc0794
Rabin KR, Whitlock JA (2009) Malignancy in children with trisomy 21. Oncologist 14(2):164–173. doi:10.1634/theoncologist.2008-0217
Raz N, Torres IJ, Briggs SD, Spencer WD, Thornton AE, Loken WJ, Gunning FM, McQuain JD, Driesen NR, Acker JD (1995) Selective neuroanatomic abnormalities in Down’s syndrome and their cognitive correlates: evidence from MRI morphometry. Neurology 45(2):356–366
Reynolds LE, Watson AR, Baker M, Jones TA, D’Amico G, Robinson SD, Joffre C, Garrido-Urbani S, Rodriguez-Manzaneque JC, Martino-Echarri E, Aurrand-Lions M, Sheer D, Dagna-Bricarelli F, Nizetic D, McCabe CJ, Turnell AS, Kermorgant S, Imhof BA, Adams R, Fisher EM, Tybulewicz VL, Hart IR, Hodivala-Dilke KM (2010) Tumour angiogenesis is reduced in the Tc1 mouse model of Down’s syndrome. Nature 465(7299):813–817. doi:10.1038/nature09106
Rickert CH, Göcke H, Paulus W (2002) Fetal ependymoma associated with Down’s syndrome. Acta Neuropathol 103(1):78–81
Romer J, Curran T (2005) Targeting medulloblastoma: small-molecule inhibitors of the sonic hedgehog pathway as potential cancer therapeutics. Cancer Res 65(12):4975–4978. doi:10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-05-0481
Romer JT, Kimura H, Magdaleno S, Sasai K, Fuller C, Baines H, Connelly M, Stewart CF, Gould S, Rubin LL, Curran T (2004) Suppression of the Shh pathway using a small molecule inhibitor eliminates medulloblastoma in Ptc1(+/−)p53(−/−) mice. Cancer Cell 6(3):229–240. doi:10.1016/j.ccr.2004.08.019
Roper RJ, Baxter LL, Saran NG, Klinedinst DK, Beachy PA, Reeves RH (2006) Defective cerebellar response to mitogenic hedgehog signaling in Down [corrected] syndrome mice. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 103(5):1452–1456. doi:10.1073/pnas.0510750103
Rubin LL, de Sauvage FJ (2006) Targeting the hedgehog pathway in cancer. Nat Rev Drug Discov 5(12):1026–1033. doi:10.1038/nrd2086
Rutkowski S, Cohen B, Finlay J, Luksch R, Ridola V, Valteau-Couanet D, Hara J, Garre ML, Grill J (2010) Medulloblastoma in young children. Pediatr Blood Cancer 54(4):635–637. doi:10.1002/pbc.22372
Ryeom S, Folkman J (2009) Role of endogenous angiogenesis inhibitors in Down syndrome. J Craniomaxillofac Surg 20(Suppl 1):595–596
Sahm F, Schrimpf D, Jones DT, Meyer J, Kratz A, Reuss D, Capper D, Koelsche C, Korshunov A, Wiestler B, Buchhalter I, Milde T, Selt F, Sturm D, Kool M, Hummel M, Bewerunge-Hudler M, Mawrin C, Schüller U, Jungk C, Wick A, Witt O, Platten M, Herold-Mende C, Unterberg A, Pfister SM, Wick W, von Deimling A (2015) Next-generation sequencing in routine brain tumor diagnostics enables an integrated diagnosis and identifies actionable targets. Acta neuropathologica.
Satgé D (1996) A decreased incidence of neuroblastomas in Down’s syndrome and overproduction of S-100 b protein. Med Hypotheses 46(4):393–399. doi:10.1016/S0306-9877(96)90193-0
Satgé D, Monteil P, Sasco AJ, Vital A, Ohgaki H, Geneix A, Vekemans M, Réthoré MO (2001) Aspects of intracranial and spinal tumors in patients with Down syndrome and report of a rapidly progressing grade 2 astrocytoma. Cancer 91(8):1458–1466
Satgé D, Rickert CH (2009) A medical enigma: persons with Down syndrome do not develop medulloblastoma. Neuroepidemiology 32(2):164. doi:10.1159/000184749
Satgé D, Sasco AJ, Carlsen NL, Stiller CA, Rubie H, Hero B, de Bernardi B, de Kraker J, Coze C, Kogner P, Langmark F, Hakvoort-Cammel FG, Beck D, von der Weid N, Parkes S, Hartmann O, Lippens RJ, Kamps WA, Sommelet D (1998) A lack of neuroblastoma in Down syndrome: a study from 11 European countries. Cancer Res 58(3):448–452
Satgé D, Sommelet D, Geneix A, Nishi M, Malet P, Vekemans M (1998) A tumor profile in Down syndrome. Am J Med Genet 78(3):207–216
Satgé D, Stiller CA, Rutkowski S, von Bueren AO, Lacour B, Sommelet D, Nishi M, Massimino M, Garré ML, Moreno F, Hasle H, Jakab Z, Greenberg M, von der Weid N, Kuehni C, Zurriaga O, Vicente ML, Peris-Bonet R, Benesch M, Vekemans M, Sullivan SG, Rickert G (2013) A very rare cancer in Down syndrome: medulloblastoma. Epidemiological data from 13 countries. J Neuro-Oncol 112(1):107–114. doi:10.1007/s11060-012-1041-y
Slade I, Murray A, Hanks S, Kumar A, Walker L, Hargrave D, Douglas J, Stiller C, Izatt L, Rahman N (2011) Heterogeneity of familial medulloblastoma and contribution of germline PTCH1 and SUFU mutations to sporadic medulloblastoma. Familial Cancer 10(2):337–342. doi:10.1007/s10689-010-9411-0
Smith MJ, Beetz C, Williams SG, Bhaskar SS, O’Sullivan J, Anderson B, Daly SB, Urquhart JE, Bholah Z, Oudit D, Cheesman E, Kelsey A, McCabe MG, Newman WG, Evans DG (2014) Germline mutations in SUFU cause Gorlin syndrome-associated childhood medulloblastoma and redefine the risk associated with PTCH1 mutations. J Clin Oncol 32(36):4155–4161. doi:10.1200/JCO.2014.58.2569
Sussan TE, Yang A, Li F, Ostrowski MC, Reeves RH (2008) Trisomy represses Apc(Min)-mediated tumours in mouse models of Down's syndrome. Nature 451(7174):73–75. doi:10.1038/nature06446
Thomas WD, Chen J, Gao YR, Cheung B, Koach J, Sekyere E, Norris MD, Haber M, Ellis T, Wainwright B, Marshall GM (2009) Patched1 deletion increases N-Myc protein stability as a mechanism of medulloblastoma initiation and progression. Oncogene 28(13):1605–1615. doi:10.1038/onc.2009.3
Threadgill DW (2008) Down’s syndrome: paradox of a tumour repressor. Nature 451(7174):21–22. doi:10.1038/451021a
Trazzi S, Mitrugno VM, Valli E, Fuchs C, Rizzi S, Guidi S, Perini G, Bartesaghi R, Ciani E (2011) APP-dependent up-regulation of Ptch1 underlies proliferation impairment of neural precursors in Down syndrome. Hum Mol Genet 20(8):1560–1573. doi:10.1093/hmg/ddr033
Vaillant C, Monard D (2009) SHH pathway and cerebellar development. Cerebellum 8(3):291–301. doi:10.1007/s12311-009-0094-8
Yang L, Xie G, Fan Q, Xie J (2010) Activation of the hedgehog-signaling pathway in human cancer and the clinical implications. Oncogene 29(4):469–481. doi:10.1038/onc.2009.392
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mangum, R., Varga, E., Boué, D.R. et al. SHH desmoplastic/nodular medulloblastoma and Gorlin syndrome in the setting of Down syndrome: case report, molecular profiling, and review of the literature. Childs Nerv Syst 32, 2439–2446 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00381-016-3185-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00381-016-3185-0