Abstract
Purpose
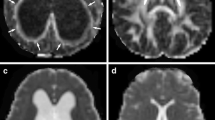
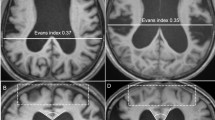
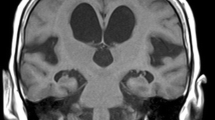
To compare a pediatric population diagnosed with benign external hydrocephalus (BEH) to normal age-matched controls using diffusion tensor imaging (DTI) techniques.
Methods
We retrospectivelyidentified 17 BEH patients by specific clinical and neuroimaging criteria. Fractional anisotropy (FA) and mean diffusivity (MD) values obtained from DTI scans were compared to a population of age-matched controls andgroup differences were examined by mixed model analysis. A longitudinal comparison was completed on a subset that underwent multiple scans (n = 8).
Results
In the genu of the corpus callosum (gCC), six of 15 BEH children had an FA value above the upper limit of 95% prediction interval, nine of 15 BEH children had MD values below the lower limit of 95% prediction interval. A similar trend applied to the other regions of interest (ROIs): splenium of the corpus callosum (sCC), ALIC, and PLIC. Statistical analysis demonstrated significant differences in FA within the gCC, sCC, and PLIC and in MD within the sCC between BEH patients and controls given (P = 0.05). No statistical differences were identified at any ROIs at the later scans.
Conclusions
We found a significant increase in FA and decrease in MD in children with BEH compared with normal children in specific white matter (WM) ROIs, notably in the gCC and sCC; furthermore, in longitudinal comparison, DTI parameters normalized over time. The current study further demonstrates the ability of DTI to distinguish between subtle diffusion changes in periventricular white matter andestablishes preliminary objective radiographic parameters for watchful observation of patients with BEH.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Papasian NC, Frim DM (2000) A theoretical model of benign external hydrocephalus that predicts a predisposition towards extra-axial hemorrhage after minor head trauma. Pediatr Neurosurg 33:188–193
Bradley WG Jr, Bahl G, Alksne JF (2006) Idiopathic normal pressure hydrocephalus may be a "two hit" disease: benign external hydrocephalus in infancy followed by deep white matter ischemia in late adulthood. J Magn Reson Imaging 24:747–755
Alvarez LA, Maytal J, Shinnar S (1986) Idiopathic external hydrocephalus: natural history and relationship to benign familial macrocephaly. Pediatrics 77:901–907
Medina LS, Frawley K, Zurakowski D, Buttros D, DeGrauw AJ, Crone KR (2001) Children with macrocrania: clinical and imaging predictors of disorders requiring surgery. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 22:564–570
Kumar R (2006) External hydrocephalus in small children. Childs Nerv Syst 22:1237–1241
Pettit RE, Kilroy AW, Allen JH (1980) Macrocephaly with head growth parallel to normal growth pattern: neurological, developmental, and computerized tomography findings in full-term infants. Arch Neurol 37:518–521
Suara RO, Trouth AJ, Collins M (2001) Benign subarachnoid space enlargement of infancy. J Natl Med Assoc 93:70–73
Air EL, Yuan W, Holland SK, Jones BV, Bierbrauer K, Altaye M, Mangano FT (2010) Longitudinal comparison of pre- and postoperative diffusion tensor imaging parameters in young children with hydrocephalus. J Neurosurg Pediatr 5:385–391
Girard NJ, Raybaud CA (2001) Ventriculomegaly and pericerebral CSF collection in the fetus: early stage of benign external hydrocephalus? Childs Nerv Syst 17:239–245
Nevo Y, Kramer U, Shinnar S, Leitner Y, Fattal-Valevski A, Villa Y, Harel S (2002) Macrocephaly in children with developmental disabilities. Pediatr Neurol 27:363–368
Olney AH (2007) Macrocephaly syndromes. Semin Pediatr Neurol 14:128–135
Smith R, Leonidas JC, Maytal J (1998) The value of head ultrasound in infants with macrocephaly. Pediatr Radiol 28:143–146
Tarnaris A, Kitchen ND, Watkins LD (2009) Noninvasive biomarkers in normal pressure hydrocephalus: evidence for the role of neuroimaging. J Neurosurg 110:837–851
Assaf Y, Ben-Sira L, Constantini S, Chang LC, Beni-Adani L (2006) Diffusion tensor imaging in hydrocephalus: initial experience. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 27:1717–1724
Gauvain KM, McKinstry RC, Mukherjee P, Perry A, Neil JJ, Kaufman BA, Hayashi RJ (2001) Evaluating pediatric brain tumor cellularity with diffusion-tensor imaging. AJR Am J Roentgenol 177:449–454
Hattingen E, Jurcoane A, Melber J, Blasel S, Zanella FE, Neumann-Haefelin T, Singer OC (2010) Diffusion tensor imaging in patients with adult chronic idiopathic hydrocephalus. Neurosurgery 66:917–924
Suskauer SJ, Huisman TA (2009) Neuroimaging in pediatric traumatic brain injury: current and future predictors of functional outcome. Dev Disabil Res Rev 15:117–123
Wozniak JR, Krach L, Ward E, Mueller BA, Muetzel R, Schnoebelen S, Kiragu A, Lim KO (2007) Neurocognitive and neuroimaging correlates of pediatric traumatic brain injury: a diffusion tensor imaging (DTI) study. Arch Clin Neuropsychol 22:555–568
Wilde EA, Bigler ED, Haider JM, Chu Z, Levin HS, Li X, Hunter JV (2006) Vulnerability of the anterior commissure in moderate to severe pediatric traumatic brain injury. J Child Neurol 21:769–776
Ashwal S, Holshouser BA, Tong KA (2006) Use of advanced neuroimaging techniques in the evaluation of pediatric traumatic brain injury. Dev Neurosci 28:309–326
Boujraf S, Luypaert R, Shabana W, De Meirleir L, Sourbron S, Osteaux M (2002) Study of pediatric brain development using magnetic resonance imaging of anisotropic diffusion. Magn Reson Imaging 20:327–336
Pena A, Green HA, Carpenter TA, Price SJ, Pickard JD, Gillard JH (2006) Enhanced visualization and quantification of magnetic resonance diffusion tensor imaging using the p:q tensor decomposition. Br J Radiol 79:101–109
Cascio CJ, Gerig G, Piven J (2007) Diffusion tensor imaging: application to the study of the developing brain. J Am Acad Child Adolesc Psychiatry 46:213–223
Saksena S, Husain N, Malik GK, Trivedi R, Sarma M, Rathore RS, Pandey CM, Gupta RK (2008) Comparative evaluation of the cerebral and cerebellar white matter development in pediatric age group using quantitative diffusion tensor imaging. Cerebellum 7:392–400
Gao W, Lin W, Chen Y, Gerig G, Smith JK, Jewells V, Gilmore JH (2009) Temporal and spatial development of axonal maturation and myelination of white matter in the developing brain. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 30:290–296
Schmithorst VJ, Yuan W (2010) White matter development during adolescence as shown by diffusion MRI. Brain Cogn 72:16–25
Yuan W, Mangano FT, Air EL, Holland SK, Jones BV, Altaye M, Bierbrauer K (2009) Anisotropic diffusion properties in infants with hydrocephalus: a diffusion tensor imaging study. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 30:1792–1798
Yuan W, Holland SK, Schmithorst VJ, Walz NC, Cecil KM, Jones BV, Karunanayaka P, Michaud L, Wade SL (2007) Diffusion tensor MR imaging reveals persistent white matter alteration after traumatic brain injury experienced during early childhood. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 28:1919–1925
O'Hayon BB, Drake JM, Ossip MG, Tuli S, Clarke M (1998) Frontal and occipital horn ratio: a linear estimate of ventricular size for multiple imaging modalities in pediatric hydrocephalus. Pediatr Neurosurg 29:245–249
Yuan W, Holland SK, Jones BV, Crone K, Mangano FT (2008) Characterization of abnormal diffusion properties of supratentorial brain tumors: a preliminary diffusion tensor imaging study. J Neurosurg Pediatr 1:263–269
Jiang H, van Zijl PC, Kim J, Pearlson GD, Mori S (2006) DtiStudio: resource program for diffusion tensor computation and fiber bundle tracking. Comput Methods Programs Biomed 81:106–116
Basser PJ, Pierpaoli C (1996) Microstructural and physiological features of tissues elucidated by quantitative-diffusion-tensor MRI. J Magn Reson B 111:209–219
Hermoye L, Saint-Martin C, Cosnard G, Lee SK, Kim J, Nassogne MC, Menten R, Clapuyt P, Donohue PK, Hua K, Wakana S, Jiang H, van Zijl PC, Mori S (2006) Pediatric diffusion tensor imaging: normal database and observation of the white matter maturation in early childhood. NeuroImage 29:493–504
Benjamini Y, Drai D, Elmer G, Kafkafi N, Golani I (2001) Controlling the false discovery rate in behavior genetics research. Behav Brain Res 125:279–284
Provenzale JM, Liang L, DeLong D, White LE (2007) Diffusion tensor imaging assessment of brain white matter maturation during the first postnatal year. AJR Am J Roentgenol 189:476–486
Leliefeld PH, Gooskens RH, Braun KP, Ramos LM, Uiterwaal CS, Regli LP, Tulleken CA, Kappelle LJ, Hanlo PW (2009) Longitudinal diffusion-weighted imaging in infants with hydrocephalus: decrease in tissue water diffusion after cerebrospinal fluid diversion. J Neurosurg Pediatr 4:56–63
Leliefeld PH, Gooskens RH, Tulleken CA, Regli L, Uiterwaal CS, Han KS, Kappelle LJ (2010) Noninvasive detection of the distinction between progressive and compensated hydrocephalus in infants: is it possible? J Neurosurg Pediatr 5:562–568
Le Bihan D, Mangin JF, Poupon C, Clark CA, Pappata S, Molko N, Chabriat H (2001) Diffusion tensor imaging: concepts and applications. J Magn Reson Imaging 13:534–546
Ewing-Cobbs L, Prasad MR, Swank P, Kramer L, Cox CS Jr, Fletcher JM, Barnes M, Zhang X, Hasan KM (2008) Arrested development and disrupted callosal microstructure following pediatric traumatic brain injury: relation to neurobehavioral outcomes. NeuroImage 42:1305–1315
Oni MB, Wilde EA, Bigler ED, McCauley SR, Wu TC, Yallampalli R, Chu Z, Li X, Hunter JV, Vasquez AC, Levin HS (2010) Diffusion tensor imaging analysis of frontal lobes in pediatric traumatic brain injury. J Child Neurol 25:976–984
Acknowledgements
This study was supported in part by the Robert L. McLaurin MD Faculty Development Scholarship at Cincinnati Children’s Hospital Medical Center.
Disclosure
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sun, M., Yuan, W., Hertzler, D.A. et al. Diffusion tensor imaging findings in young children with benign external hydrocephalus differ from the normal population. Childs Nerv Syst 28, 199–208 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00381-011-1651-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00381-011-1651-2