Abstract
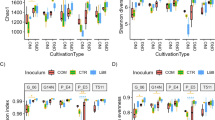
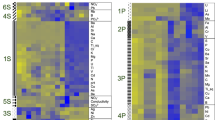
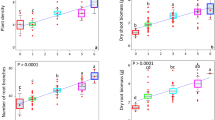
The rhizobial inoculation effects on the peanut rhizosphere bacterial community and metabolites were studied under different N availability following the five N application rates without rhizobial inoculation (N1–N5; 0, 40, 80, 110, 170 kg N ha−1) or with rhizobial inoculation (RN1–RN5) in a 3-year field trial. The effects of rhizobia on peanut growth, the rhizobacterial community, and root metabolites differed depending on the N availability. Plant height and nodule number were significantly increased by rhizobial inoculation, especially in RN3. Rhizobacterial abundance and richness were increased by rhizobial inoculation, except in RN1 (no N added). The number of 16S rRNA gene copies was higher in RN1–RN3 than in N1–N3 in both years. The largest number of differential bacterial genera between an inoculated treatment and its corresponding uninoculated treatment was in RN1 vs. N1. The beneficial bacteria Saccharimonadales and c_JG30-KF-CM66 (Chloroflexi) were most abundant in RN3. The concentrations of organic acids (3-methylglutaric acid, adipic acid, 3-hydroxyoctanoic acid, and octenedioic acid) were significantly increased in RN3 and were positively correlated with c_JG30-KF-CM66 (Chloroflexi), soil available N, and biomass. No metabolic pathways were significantly enriched by rhizobial inoculation at the highest N application rate (RN5). These results demonstrate that rhizobia positively affect peanut growth and yield under the best N availability via their ability to reshape the soil microbiome and metabolites.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adeleke R, Nwangburuka C, Oboirien B (2017) Origins, roles and fate of organic acids in soils: a review. S Afr J Bot 108:393–406
Akram NA, Shafiq F, Ashraf M (2018) Peanut (Arachis hypogaea L.): a prospective legume crop to offer multiple health benefits under changing climate. Compr Rev Food Sci F 17:1325–1338
Ali EA, Hassan AE (2001) Effect of foliar application of zinc, nitrogen fertilization and Bradyrhizobium inoculation on anatomical characters, yield and yield components of peanut (Arachis hipogaea L.). Annals of Agricultural Science, Moshtohor 39:1435–1453
Ashrafuzzaman M, Hossen FA, Ismail MR, Hoque MA, Islam MZ, Shahidullah SM, Meon S (2009) Efficiency of plant growth-promoting rhizobacteria (PGPR) for the enhancement of rice growth. Afr J Biotechnol 8:1247–1252
Beals EW (1984) Bray-Curtis ordination: an effective strategy for analysis of multivariate ecological data. In: Ford E (ed) Macfadyen A. Advances in Ecological Research. Academic Press, London, pp 1–55
Cameron KC, Di HJ, Moir JL (2013) Nitrogen losses from the soil/plant system: a review. Ann Appl Biol 162:145–173
Carvalhais LC, Dennis PG, Fan B, Fedoseyenko D, Kierul K, Becker A, von Wiren N, Borriss R (2013) Linking plant nutritional status to plant-microbe interactions. Plos One 8:e68555
Cathey SE, Sinclair TR, Mackowiak CL (2013) Nitrogen limitation of rhizoma peanut growth. J Plant Nutr 36:311–328
Chen L, Hao Z, Li K, Sha Y, Wang E, Sui X, Mi G, Tian C, Chen W (2021a) Effects of growth-promoting rhizobacteria on maize growth and rhizosphere microbial community under conservation tillage in northeast China. Microb Biotechnol 14:535–550
Chen L, Li K, Shang J, Wu Y, Chen T, Wanyan Y, Wang E, Tian C, Chen W, Chen W, Mi G, Sui X (2021b) Plant growth–promoting bacteria improve maize growth through reshaping the rhizobacterial community in low-nitrogen and low-phosphorus soil. Biol Fert Soils 57:1075–1088
Chen Q, Ding J, Zhu Y, He J, Hu H (2020) Soil bacterial taxonomic diversity is critical to maintaining the plant productivity. Environ Int 140:105766
Chen S, Waghmode TR, Sun R, Kuramae EE, Hu C, Liu B (2019) Root-associated microbiomes of wheat under the combined effect of plant development and nitrogen fertilization. Microbiome 7:136
Chu GX, Shen QR, Cao JL (2004) Nitrogen fixation and N transfer from peanut to rice cultivated in aerobic soil in an intercropping system and its effect on soil N fertility. Plant Soil 263:17–27
Dashti NEH, Al-Sarraf NYA, Cherian VM, Montasser MS (2021) Isolation and characterization of novel plant growth-promoting rhizobacteria (PGPR) isolates from tomato (Solanum lycopersicum L.) rhizospherical soil: a novel IAA producing bacteria. Kuwait J Sci. https://doi.org/10.48129/kjs.v48i2.8427
El-Sherbeny TMS, Mousa AM, Zhran MA (2022) Response of peanut (Arachis hypogaea L.) plant to bio-fertilizer and plant residues in sandy soil. Environ Geochem Hlth 45:253–265
Estaki M, Jiang L, Bokulich NA, Mcdonald D, Gonzalez A, Kosciolek T, Martino C, Zhu Q, Birmingham A, Vazquez-Baeza Y, Dillon MR, Bolyen E, Caporaso JG, Knight R (2020) QIIME 2 enables comprehensive end-to-end analysis of diverse microbiome data and comparative studies with publicly available data. Curr Protoc Bioinformatics 70:e100
Fabra A, Castro S, Taurian T, Angelini J, Ibanez F, Dardanelli M, Tonelli M, Bianucci E, Valetti L (2010) Interaction among Arachis hypogaea L. (Peanut) and beneficial soil microorganisms: how much is it known? Crit Rev Microbiol 36:179–194
Ferguson BJ, Mens C, Hastwell AH, Zhang M, Su H, Jones CH, Chu X, Gresshoff PM (2019) Legume nodulation: the host controls the party. Plant Cell Environ 42:41–51
Flieder M, Buongiorno J, Herbold CW, Hausmann B, Rattei T, Lloyd KG, Loy A, Wasmund K (2021) Novel taxa of Acidobacteriota implicated in seafloor sulfur cycling. ISME J 15:3159–3180
Galili G, Tang GL, Zhu XH, Karchi H, Miron D, Gakiere B, Stepansky A (2001) Molecular genetic dissection and potential manipulation of lysine metabolism in seeds. J Plant Physiol 158:515–520
Guo J, Jing X, Peng W, Nie Q, Zhai Y, Shao Z, Zheng L, Cai M, Li G, Zuo H, Zhang Z, Wang R, Huang D, Cheng W, Yu Z, Chen L, Zhang J (2016) Comparative genomic and functional analyses: unearthing the diversity and specificity of nematicidal factors in Pseudomonas putida strain 1A00316. Sci Rep 6:29211
Guvercin E, Gok M (2022) Effect of bacteria inoculation and iron application rates on nodulation and yield of different peanut varieties. Ziraat Fakultesi Dergisi 17:34–39
Haldar S, Sengupta S (2015) Impact of plant development on the rhizobacterial population of Arachis hypogaea: A multifactorial analysis. J Basic Microb 55:922–928
Han Q, Ma Q, Chen Y, Tian B, Xu L, Bai Y, Chen W, Li X (2020) Variation in rhizosphere microbial communities and its association with the symbiotic efficiency of rhizobia in soybean. ISME J 14:1915–1928
Hayat R, Ali S, Amara U, Khalid R, Ahmed I (2010) Soil beneficial bacteria and their role in plant growth promotion: a review. Ann Microbiol 60:579–598
Heydari L, Bayat H, Gregory AS (2021) Investigating the effect of inoculation of chickpea with rhizobium and mycorrhizal fungi (Funneliformis mosseae) on soil mechanical and physical behavior. Geoderma 385:114860
Ji ZJ, Yan H, Cui QG, Wang ET, Chen WF, Chen WX (2017) Competition between rhizobia under different environmental conditions affects the nodulation of a legume. Syst Appl Microbiol 40:114–119
Jones DE, Perez L, Ryan RO (2020) 3-Methylglutaric acid in energy metabolism. Clin Chim Acta 502:233–239
Khan A, Jiang HT, Bu JY, Adnan M, Gillani SW, Hussain MA, Zhang MQ (2022) Untangling the rhizosphere bacterial community composition and response of soil physiochemical properties to different nitrogen applications in sugarcane field. Front Microbiol 13:856078
Kong Z, Liu H (2022) Modification of rhizosphere microbial communities: a possible mechanism of plant growth promoting rhizobacteria enhancing plant growth and fitness. Front Plant Sci 13:920813
Lassaletta L, Billen G, Grizzetti B, Anglade J, Garnier J (2014) 50 year trends in nitrogen use efficiency of world cropping systems: the relationship between yield and nitrogen input to cropland. Environ Res Lett 9:105011
LBM S, DTF R, Petrovski S, Seviour RJ (2019) The phylogeny, biodiversity, and ecology of the chloroflexi in activated sludge. Front Microbiol 10:2015
Levy-Booth DJ, Winder RS (2010) Quantification of nitrogen reductase and nitrite reductase genes in soil of thinned and clear-cut douglas-fir stands by using real-time PCR. Appl Environ Microb 76:7116–7125
Li MS, Guo R, Yu F, Chen X, Zhao HY, Li HX, Wu J (2018) Indole-3-acetic acid biosynthesis pathways in the plant-beneficial bacterium Arthrobacter pascens ZZ21. Int J Mol Sci 19:443
Li YB, Wang MY, Chen SF (2021) Application of N2-fixing Paenibacillus triticisoli BJ-18 changes the compositions and functions of the bacterial, diazotrophic, and fungal microbiomes in the rhizosphere and root/shoot endosphere of wheat under field conditions. Biol Fert Soils 57:347–362
Liu KH, Ding XW, Wang JJ (2020) Soil metabolome correlates with bacterial diversity and co-occurrence patterns in root-associated soils on the Tibetan Plateau. Sci Total Environ 735:139572
Ma N, Li Y, Fan J (2018) Research progress on pharmacological action of acacetin. Chin J Mod Appl Pharm 35:1591–1595
Mahmud K, Makaju S, Ibrahim R, Missaoui A (2020) Current progress in nitrogen fixing plants and microbiome research. Plants (Basel) 9:97
Mohd-Radzman NA, Djordjevic MA, Imin N (2013) Nitrogen modulation of legume root architecture signaling pathways involves phytohornnones and small regulatory molecules. Front Plant Sci 4:385
Mondal M, Skalicky M, Garai S, Hossain A, Sarkar S, Banerjee H, Kundu R, Brestic M, Barutcular C, Erman M, El Sabagh A, Laing AM (2020) Supplementing nitrogen in combination with rhizobium inoculation and soil mulch in peanut (Arachis hypogaea L.) production system: part II. Effect on phenology, growth, yield attributes, pod quality, profitability and nitrogen use efficiency. Agronomy (Basel) 10:1582
Morel MA, Cagide C, Minteguiaga MA, Dardanelli MS, Castro-Sowinski S (2015) The pattern of secreted molecules during the co-inoculation of alfalfa plants with Sinorhizobium meliloti and Delftia sp. strain JD2: an interaction that improves plant yield. Mol Plant Microbe Interact 28:134–142
Myers L, Sirois MJ (2006) Spearman correlation coefficients, differences between. Encycl Stat Sci. https://doi.org/10.1002/0471667196.ess5050.pub2
Nannipieri P, Penton CR, Purahong W, Schloter M, van Elsas JD (2019) Recommendations for soil microbiome analyses. Biol Fert Soils 55:765–766
Otieno PE, Muthomi JW, Chemining’Wa GN, Nderitu JH (2009) Effect of rhizobia inoculation, farm yard manure and nitrogen fertilizer on nodulation and yield of food grain legumes. J Biol Sci 9:326-332
Ozbolat O, Sanchez-Navarro V, Zornoza R, Egea-Cortines M, Cuartero J, Ros M, Pascual JA, Boix-Fayos C, Almagro M, de Vente J, Diaz-Pereira E, Martinez-Mena M (2023) Long-term adoption of reduced tillage and green manure improves soil physicochemical properties and increases the abundance of beneficial bacteria in a Mediterranean rainfed almond orchard. Geoderma 429:116218
Pieterse CMJ, Zamioudis C, Berendsen RL, Weller DM, Van Wees SCM, Bakker PAHM (2014) Induced systemic resistance by beneficial microbes. Annu Rev Phytopathol 52:347–375
Razafintsalama H, Trap J, Rabary B, Razakatiana A, Ramanankierana H, Rabeharisoa L, Becquer T (2022) Effect of rhizobium inoculation on growth of common bean in low-fertility tropical soil amended with phosphorus and lime. Sustainability 14:4907
Regus JU, Wendlandt CE, Bantay RM, Gano-Cohen KA, Gleason NJ, Hollowell AC, O’Neill MR, Shahin KK, Sachs JL (2017) Nitrogen deposition decreases the benefits of symbiosis in a native legume. Plant Soil 414:159–170
Sanchez RCL, Eichler-Loebermann B, Padilla EG, Schnug E (2007) Response of Leucaena leucocephala cv. Peru to Rhizobium inoculation under salt stress. Landbauforschung (Braunschw) 57:307–311
Sasse J, Martinoia E, Northen T (2018) Feed your friends: do plant exudates shape the root microbiome? Trends Plant Sci 23:25–41
Schloss PD, Westcott SL, Ryabin T, Hall JR, Hartmann M, Hollister EB, Lesniewski RA, Oakley BB, Parks DH, Robinson CJ, Sahl JW, Stres B, Thallinger GG, Van Horn DJ, Weber CF (2009) Introducing mothur: open-source, platform-independent, community-supported software for describing and comparing microbial communities. Appl Environ Microb 75:7537–7541
Schmidt R, Köberl M, Mostafa A, Ramadan EM, Monschein M, Jensen KB, Bauer R, Berg G (2014) Effects of bacterial inoculants on the indigenous microbiome and secondary metabolites of chamomile plants. Front Microbiol 5:64
Shang JY, Wu Y, Huo B, Chen L, Wang ET, Sui Y, Chen WF, Tian CF, Chen WX, Sui XH (2021) Potential of Bradyrhizobia inoculation to promote peanut growth and beneficial rhizobacteria abundance. J Appl Microbiol 131:2500–2515
Shi L, Zhang P, He Y, Zeng F, Xu J, He L (2021) Enantioselective effects of cyflumetofen on microbial community and related nitrogen cycle gene function in acid-soil. Sci Total Environ 771:144831
Singh G, Virk HK, Aggarwal N, Gupta RK (2021) Growth, symbiotic traits, productivity and nutrient uptake as influenced by dose and time of nitrogen application and rhizobium inoculation in mungbean [Vigna radiata (L.) Wilczek]. J Plant Nutr 44:1982–1992
Sonali B, Abhijit S (2009) Effect of irrigation and rhizobium inoculation on growth, yield and consumptive use of summer groundnut (Arachis hypogaea Linn.). J Interacademicia 13:156–158
Stassen MJJ, Hsu S, Pieterse CMJ, Stringlis IA (2021) Coumarin communication along the Microbiome-Root-Shoot axis. Trends Plant Sci 26:169–183
Suarez-Moreno ZR, Caballero-Mellado J, Coutinho BG, Mendonca-Previato L, James EK, Venturi V (2012) Common features of environmental and potentially beneficial plant-associated burkholderia. Microb Ecol 63:249–266
Sun H, Wang Y, Wang M, Zhao C (2010) Effects of nitrogen fertilizer rate on senescence characteristics and yield of different peanut (Arachis Hypogaea L. ) Cultivars. Acta Ecologica Sinica 30:2671–2677
Sun L, Wang Y, Ma D, Wang L, Zhang X, Ding Y, Fan K, Xu Z, Yuan C, Jia H, Ren Y, Ding Z (2022) Differential responses of the rhizosphere microbiome structure and soil metabolites in tea (Camellia sinensis) upon application of cow manure. BMC Microbiol 22:55
Suominen S, van Vliet DM, Sanchez-Andrea I, van der Meer MTJ, Damste JSS, Villanueva L (2021) Organic matter type defines the composition of active microbial communities originating from anoxic baltic sea sediments. Front Microbiol 12:628301
Swift ML (1997) GraphPad prism, data analysis, and scientific graphing. J Chem Inf Comput Sci 37:411–412
Thevenot EA (2017) Ropls: PCA, PLS(-DA) and OPLS(-DA) for multivariate analysis and feature selection of omics data. R package version 1:1–25
Tonelli ML, Figueredo MS, Rodríguez J, Fabra A, Ibañez F (2020) Induced systemic resistance -like responses elicited by rhizobia. Plant Soil 448:1–14
Upadhyay RG, Singh A (2016) Effect of nitrogen and zinc on nodulation, growth and yield of cowpea (Vigna unguiculata). Legume Res 39:149–151
Van Loon LC (2007) Plant responses to plant growth-promoting rhizobacteria. Eur J Plant Pathol 119:243–254
Venturi V, Keel C (2016) Signaling in the rhizosphere. Trends Plant Sci 21:187–198
Vives-Peris V, de Ollas C, Gomez-Cadenas A, Perez-Clemente RM (2020) Root exudates: from plant to rhizosphere and beyond. Plant Cell Rep 39:3–17
Wan W, Liu S, Li X, Xing Y, Chen W, Huang Q (2021) Bridging rare and abundant bacteria with ecosystem multifunctionality in salinized agricultural soils: from community diversity to environmental adaptation. mSystems 6:e01221–e01220
Wang R, Chang YL, Zheng WT, Zhang D, Zhang XX, Sui XH, Wang ET, Hu JQ, Zhang LY, Chen WX (2013) Bradyrhizobium arachidis sp nov., isolated from effective nodules Arachis hypogaea grown in China. Syst Appl Microbiol 36:101–105
Wang R, Zhang H, Sun L, Qi G, Chen S, Zhao X (2017) Microbial community composition is related to soil biological and chemical properties and bacterial wilt outbreak. Sci Rep 7:343
Wang JJ, Li QQ, Xu S, Zhao W, Lei Y, Song CH, Huang ZY (2018) Traits-based integration of multi-species inoculants facilitates shifts of indigenous soil bacterial community. Front Microbiol 9:1692
Wang H, Gu C, Liu X, Yang C, Li W, Wang S (2020) Impact of soybean nodulation phenotypes and nitrogen fertilizer levels on the rhizosphere bacterial community. Front Microbiol 11:750
Wang G, Jin Z, Wang X, George TS, Feng G, Zhang L (2022a) Simulated root exudates stimulate the abundance of Saccharimonadales to improve the alkaline phosphatase activity in maize rhizosphere. Appl Soil Ecol 170:104274
Wang Y, Lyu J, Chen D (2022b) Performance assessment of peanut production in China. Acta Agric Scand B Soil Plant Sci 72:176–188
Wise ML, Doehlert DC, Mcmullen MS (2008) Association of avenanthramide concentration in oat (Avena sativa L.) grain with crown rust incidence and genetic resistance. Cereal Chem 85:639–641
Xie K, Sun M, Shi A, Di Q, Chen R, Jin D, Li Y, Yu X, Chen S, He C (2022) The application of tomato plant residue compost and plant growth-promoting rhizobacteria improves soil quality and enhances the ginger field soil bacterial community. Agronomy 12:1741
Xu H, Yang Y, Tian Y, Xu R, Zhong Y, Liao H (2020) Rhizobium inoculation drives the shifting of rhizosphere fungal community in a host genotype dependent manner. Front Microbiol 10:3135
Yin S, Suo F, Zheng Y, You X, Li H, Wang J, Zhang C, Li Y, Cheng Y (2022) Biochar-compost amendment enhanced sorghum growth and yield by improving soil physicochemical properties and shifting soil bacterial community in a coastal soil. Front Environ Sci 10:1036837
Youseif SH, Abd El-Megeed FH, Saleh SA (2017) Improvement of faba bean yield using Rhizobium/Agrobacterium inoculant in low-fertility sandy soil. Agronomy (Basel) 7:2
Zeng R, Chen T, Zhang H, Cao J, Li X, Wang X, Wang Y, Yao S, Gao Y, Chen Y, Zhang L (2022) Effect of waterlogging stress on grain nutritional quality and pod yield of peanut (Arachis hypogaea L.). J Agron Crop Sci 209:286–299
Zeng W, Huang KE, Luo Y, Li DX, Chen W, Yu XQ, Ke XH (2020) Nontargeted urine metabolomics analysis of the protective and therapeutic effects of Citri Reticulatae Chachiensis Pericarpium on high-fat feed-induced hyperlipidemia in rats. Biomed Chromatogr 34:e4795
Zhao S, Lü J, Xu X, Lin X, Luiz MR, Qiu S, Ciampitti I, He P (2021) Peanut yield, nutrient uptake and nutrient requirements in different regions of China. J Integr Agr 20:2502–2511
Zheng Y, Wang C, Liu Q, Wu Z, Wang C, Sun X, Zheng Y (2017) Effect of nitrogen fertilizer regulation on root growth and nodulating ability of peanut. He Nong Xue Bao 31:2418–2425
Zhong Y, Yang Y, Liu P, Xu R, Rensing C, Fu X, Liao H (2019) Genotype and rhizobium inoculation modulate the assembly of soybean rhizobacterial communities. Plant Cell Environ 42:2028–2044
Zhou XF, Lyu J, Sun L, Dong JW, Xu HW (2021) Metabolic programming of Rhododendron chrysanthum leaves following exposure to UVB irradiation. Funct Plant Biol 48:1175–1185
Zontov YV, Rodionova OY, Kucheryavskiy SV, Pomerantsev AL (2020) PLS-DA–a MATLAB GUI tool for hard and soft approaches to partial least squares discriminant analysis. Chemometr Intell Lab 203:104064
Acknowledgements
Special thanks to Yuwen Jia for her assistance with field management.
Funding
This work was financially supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (project U19A2035) and by National Key Research & Development Program of China (2022YFD1500705-03).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Xinhua Sui designed the study. Rui Wang and Bin Huo performed the experiments. La Chen and Keke Li gave suggestions to analyze the data. Rui Wang analyzed the data and prepared the figures and tables. Rui Wang, Entao Wang, and Xinhua Sui wrote the manuscript. Ganfeng Yi and Guohua Mi provided resources. All authors read and approved the paper.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary information
ESM 1
(DOCX 1553 kb)
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, R., Huo, B., Chen, L. et al. Rhizobia modulate the peanut rhizobacterial community and soil metabolites depending on nitrogen availability. Biol Fertil Soils 59, 887–900 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00374-023-01757-x
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00374-023-01757-x