Abstract
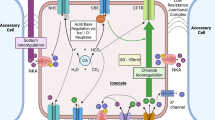
The endocrine system is an essential regulator of the osmoregulatory organs that enable euryhaline fishes to maintain hydromineral balance in a broad range of environmental salinities. Because branchial ionocytes are the primary site for the active exchange of Na+, Cl−, and Ca2+ with the external environment, their functional regulation is inextricably linked with adaptive responses to changes in salinity. Here, we review the molecular-level processes that connect osmoregulatory hormones with branchial ion transport. We focus on how factors such as prolactin, growth hormone, cortisol, and insulin-like growth-factors operate through their cognate receptors to direct the expression of specific ion transporters/channels, Na+/K+-ATPases, tight-junction proteins, and aquaporins in ion-absorptive (freshwater-type) and ion-secretory (seawater-type) ionocytes. While these connections have historically been deduced in teleost models, more recently, increased attention has been given to understanding the nature of these connections in basal lineages. We conclude our review by proposing areas for future investigation that aim to fill gaps in the collective understanding of how hormonal signaling underlies ionocyte-based processes.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Agustsson T, Sundell K, Sakamoto T et al (2001) Growth hormone endocrinology of Atlantic salmon (Salmo salar): pituitary gene expression, hormone storage, secretion and plasma levels during parr-smolt transformation. J Endocrinol 170:227–234. https://doi.org/10.1677/joe.0.1700227
Amemiya CT, Alföldi J, Lee AP et al (2013) The African coelacanth genome provides insights into tetrapod evolution. Nature 496(7445):311–316. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature12027
Anderson WG (2012) The endocrinology of 1α-hydroxycorticosterone in elasmobranch fish: a review. Comp Biochem Physiol A 162:73–80. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cbpa.2011.08.015
Aruna A, Nagarajan G, Chang CF (2012a) Involvement of corticotrophin-releasing hormone and corticosteroid receptors in the brain–pituitary–gill of tilapia during the course of seawater acclimation. J Neuroendocrinol 24:818–830. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2826.2012.02282.x
Aruna A, Nagarajan G, Chang CF (2012b) Differential expression patterns and localization of glucocorticoid and mineralocorticoid receptor transcripts in the osmoregulatory organs of tilapia during salinity stress. Gen Comp Endocrinol 179:465–476. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ygcen.2012.08.028
Baker ME (2003) Evolution of glucocorticoid and mineralocorticoid responses: go fish. Endocrinology 144:4223–4225. https://doi.org/10.1210/en.2003-0843
Barany A, Shaughnessy CA, Fuentes J, Mancera JM, McCormick SD (2020) Osmoregulatory role of the intestine in the sea lamprey (Petromyzon marinus). Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol 318(2):R410–R417. https://doi.org/10.1152/ajpregu.00033.2019
Barany A, Shaughnessy CA, McCormick SD (2021a) Corticosteroid control of Na+/K+-ATPase in the intestine of the sea lamprey (Petromyzon marinus). Gen Comp Endocrinol 307:113756. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ygcen.2021.113756
Barany A, Shaughnessy CA, Pelis RM et al (2021b) Tissue and salinity specific Na+/Cl- cotransporter (NCC) orthologues involved in the adaptive osmoregulation of sea lamprey (Petromyzon marinus). Sci Rep 11:22698. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-021-02125-1
Bartels H, Potter IC (2004) Cellular composition and ultrastructure of the gill epithelium of larval and adult lampreys: implications for osmoregulation in fresh and seawater. J Exp Biol 207:3447–3462. https://doi.org/10.1242/jeb.01157
Berishvili G, D’Cotta H, Baroiller JF, Segner H, Reinecke M (2006) Differential expression of IGF-I mRNA and peptide in the male and female gonad during early development of a bony fish, the tilapia Oreochromis niloticus. Gen Comp Endocrinol 146(3):204–210. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ygcen.2005.11.008
Bernard B, Leguen I, Mandiki SNM et al (2020) Impact of temperature shift on gill physiology during smoltification of Atlantic salmon smolts (Salmo salar L.). Comp Biochem Physiol A Mol Integr Physiol 244:110685. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cbpa.2020.110685
Bisbal GA, Specker JL (1991) Cortisol stimulates hypo-osmoregulatory ability in Atlantic salmon, Salmo salar L. J Fish Biol 39:421–432. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1095-8649.1991.tb04373.x
Björnsson BT (1997) The biology of salmon growth hormone: from daylight to dominance. Fish Physiol Biochem 17:9–24. https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1007712413908
Boeuf G, Le Bail PY, Prunet P (1989) Growth hormone and thyroid hormones during Atlantic salmon, Salmo salar L., smolting, and after transfer to seawater. Aquaculture 82:257–268. https://doi.org/10.1016/0044-8486(89)90413-4
Bollinger RJ, Ellis LV, Bossus MC, Tipsmark CK (2018) Prolactin controls Na+, Cl– cotransporter via Stat5 pathway in the teleost gill. Mol Cell Endocrinol 477:163–171. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mce.2018.06.014
Bossus MC, Madsen SS, Tipsmark CK (2015) Functional dynamics of claudin expression in Japanese medaka (Oryzias latipes): response to environmental salinity. Comp Biochem Physiol A Mol Integr Physiol 187:74–85. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cbpa.2015.04.017
Bossus MC, Bollinger RJ, Reed PJ, Tipsmark CK (2017) Prolactin and cortisol regulate branchial claudin expression in Japanese medaka. Gen Comp Endocrinol 240:77–83. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ygcen.2016.09.010
Boyle D, Clifford AM, Orr E, Chamot D, Goss GG (2014) Mechanisms of Cl- uptake in rainbow trout: cloning and expression of slc26a6, a prospective Cl-/HCO3- exchanger. Comp Biochem Physiol A Mol Integr Physiol 180:43–50. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cbpa.2014.11.001
Braasch I, Gehrke AR, Smith JJ et al (2016) The spotted gar genome illuminates vertebrate evolution and facilitates human-teleost comparisons. Nat Genet 48(4):427–437. https://doi.org/10.1038/ng.3526
Breves JP (2019) Prolactin controls branchial clcn2c but not atp1a1a.2 in zebrafish Danio rerio. J Fish Biol 94(1):168–172. https://doi.org/10.1111/jfb.13854
Breves JP, Fox BK, Pierce AL et al (2010a) Gene expression of growth hormone family and glucocorticoid receptors, osmosensors, and ion transporters in the gill during seawater acclimation of Mozambique tilapia, Oreochromis mossambicus. J Exp Zool 313A:432–441. https://doi.org/10.1002/jez.613
Breves JP, Hasegawa S, Yoshioka M et al (2010b) Acute salinity challenges in Mozambique and Nile tilapia: differential responses of plasma prolactin, growth hormone and branchial expression of ion transporters. Gen Comp Endocrinol 167:135–142. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ygcen.2010.01.022
Breves JP, Watanabe S, Kaneko T et al (2010c) Prolactin restores branchial mitochondrion-rich cells expressing Na+/Cl− cotransporter in hypophysectomized Mozambique tilapia. Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol 299(2):R702–R710. https://doi.org/10.1152/ajpregu.00213.2010
Breves JP, Seale AP, Helms RE et al (2011) Dynamic gene expression of GH/PRL-family hormone receptors in gill and kidney during freshwater-acclimation of Mozambique tilapia. Comp Biochem Physiol A 158(2):194–200. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cbpa.2010.10.030
Breves JP, Serizier SB, Goffin V et al (2013) Prolactin regulates transcription of the ion uptake Na+/Cl- cotransporter (ncc) gene in zebrafish gill. Mol Cell Endocrinol 369(1–2):98–106. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mce.2013.01.021
Breves JP, McCormick SD, Karlstrom RO (2014a) Prolactin and teleost ionocytes: new insights into cellular and molecular targets of prolactin in vertebrate epithelia. Gen Comp Endocrinol 203:21–28. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ygcen.2013.12.014
Breves JP, Seale AP, Moorman BP et al (2014b) Pituitary control of branchial NCC, NKCC and Na+, K+-ATPase α-subunit gene expression in Nile tilapia, Oreochromis niloticus. J Comp Physiol B 184:513–523. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00360-014-0817-0
Breves JP, Inokuchi M, Yamaguchi Y et al (2016) Hormonal regulation of aquaporin 3: opposing actions of prolactin and cortisol in tilapia gill. J Endocrinol 230(3):325–337. https://doi.org/10.1530/JOE-16-0162
Breves JP, Fujimoto CK, Phipps-Costin SK et al (2017a) Variation in branchial expression among insulin-like growth-factor binding proteins (igfbps) during Atlantic salmon smoltification and seawater exposure. BMC Physiol 17:1–11. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12899-017-0028-5
Breves JP, Keith PLK, Hunt BL et al (2017b) clc-2c is regulated by salinity, prolactin and extracellular osmolality in tilapia gill. J Mol Endocrinol 59(4):391–402. https://doi.org/10.1530/JME-17-0144
Breves JP, Springer-Miller RH, Chenoweth DA et al (2020) Cortisol regulates insulin-like growth-factor binding protein (igfbp) gene expression in Atlantic salmon parr. Mol Cell Endocrinol 518:110989. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mce.2020.110989
Breves JP, Nelson NN, Koltenyuk V et al (2021) Enhanced expression of ncc1 and clc2c in the kidney and urinary bladder accompanies freshwater acclimation in Mozambique tilapia. Comp Biochem Physiol A 260:111021. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cbpa.2021.111021
Breves JP, Puterbaugh KM, Bradley SE et al (2022) Molecular targets of prolactin in mummichogs (Fundulus heteroclitus): Ion transporters/channels, aquaporins, and claudins. Gen Comp Endocrinol 325:114051. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ygcen.2022.114051
Breves JP, Runiewicz ER, Richardson SG et al (2024) Transcriptional regulation of esophageal, intestinal, and branchial solute transporters by salinity, growth hormone, and cortisol in Atlantic salmon. J Exp Zool Part Ecol Integr Physiol 341:107–117. https://doi.org/10.1002/jez.2766
Bridgham JT, Carroll SM, Thornton JW (2006) Evolution of hormone-receptor complexity by molecular exploitation. Science 312:97–101. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.1123348
Brunelli E, Mauceri A, Salvatore F et al (2010) Localization of aquaporin 1 and 3 in the gills of the rainbow wrasse Coris julis. Acta Histochem 112(3):251–258. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.acthis.2008.11.030
Bui P, Kelly SP (2014) Claudin-6, -10d and -10e contribute to seawater acclimation in the euryhaline puffer fish Tetraodon nigroviridis. J Exp Biol 217(Pt 10):1758–1767. https://doi.org/10.1242/jeb.099200
Bui P, Bagherie-Lachidan M, Kelly SP (2010) Cortisol differentially alters claudin isoforms in cultured puffer fish gill epithelia. Mol Cell Endocrinol 317:120–126. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mce.2009.12.002
Burden CE (1956) The failure of hypophysectomized Fundulus heteroclitus to survive in fresh water. Biol Bull 110:8–28
Bury NR, Sturm A, Le Rouzic P et al (2003) Evidence for two distinct functional glucocorticoid receptors in teleost fish. J Mol Endocrinol 31:141–156. https://doi.org/10.1677/jme.0.0310141
Bystriansky JS, Richards JG, Schulte PM, Ballantyne JS (2006) Reciprocal expression of gill Na+/K+-ATPase alpha-subunit isoforms alpha1a and alpha1b during seawater acclimation of three salmonid fishes that vary in their salinity tolerance. J Exp Biol 209(Pt 10):1848–1858. https://doi.org/10.1242/jeb.02188
Cerdà J, Finn RN (2010) Piscine aquaporins: an overview of recent advances. J Exp Zool A 313(10):623–650. https://doi.org/10.1002/jez.634
Chakraborti P, Mukherjee D (1995) Effects of prolactin and fish pituitary extract on plasma calcium levels in common carp, Cyprinus carpio. Gen Comp Endocrinol 97(3):320–326. https://doi.org/10.1006/gcen.1995.1032
Chasiotis H, Kelly SP (2011) Effect of cortisol on permeability and tight junction protein transcript abundance in primary cultured gill epithelia from stenohaline goldfish and euryhaline trout. Gen Comp Endocrinol 172:494–504. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ygcen.2011.04.023
Chasiotis H, Kelly SP (2012) Effects of elevated circulating cortisol levels on hydromineral status and gill tight junction protein abundance in the stenohaline goldfish. Gen Comp Endocrinol 175:277–283. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ygcen.2011.11.024
Chasiotis H, Effendi JC, Kelly SP (2009) Occludin expression in goldfish held in ion-poor water. J Comp Physiol B 179(2):145–154. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00360-008-0297-1
Chasiotis H, Kolosov D, Bui P, Kelly SP (2012) Tight junctions, tight junction proteins and paracellular permeability across the gill epithelium of fishes: a review. Respir Physiol Neurobiol 184:269–281. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.resp.2012.05.020
Chen M, Huang X, Yuen DS, Cheng CH (2011) A study on the functional interaction between the GH/PRL family of polypeptides with their receptors in zebrafish: evidence against GHR1 being the receptor for somatolactin. Mol Cell Endocrinol 337(1–2):114–121. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mce.2011.02.006
Chen YC, Liao BK, Lu YF et al (2019) Zebrafish Klf4 maintains the ionocyte progenitor population by regulating epidermal stem cell proliferation and lateral inhibition. PLoS Genet 15(4):e1008058. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pgen.1008058
Cheng P, Huang Y, Du H et al (2019) Draft genome and complete Hox-cluster characterization of the sterlet (Acipenser ruthenus). Front Genet 10:776. https://doi.org/10.3389/fgene.2019.00776
Choi YJ, Shin HS, Kim NN et al (2013) Expression of aquaporin-3 and -8 mRNAs in the parr and smolt stages of sockeye salmon, Oncorhynchus nerka: effects of cortisol treatment and seawater acclimation. Comp Biochem Physiol A 165(2):228–236. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cbpa.2013.03.013
Clifford AM, Tresguerres M, Goss GG, Wood CM (2022) A novel K+-dependent Na+ uptake mechanism during low pH exposure in adult zebrafish (Danio rerio): new tricks for old dogma. Acta Physiol (oxf) 234(3):e13777. https://doi.org/10.1111/apha.13777
Close DA, Yun S-S, McCormick SD et al (2010) 11-Deoxycortisol is a corticosteroid hormone in the lamprey. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 107:13942–13947. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.0914026107
Colombe L, Fostier A, Bury N et al (2000) A mineralocorticoid-like receptor in the rainbow trout, Oncorhynchus mykiss: cloning and characterization of its steroid binding domain. Steroids 65:319–328. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0039-128X(00)00090-8
Cruz SA, Chao PL, Hwang PP (2013a) Cortisol promotes differentiation of epidermal ionocytes through Foxi3 transcription factors in zebrafish (Danio rerio). Comp Biochem Physiol A 164(1):249–257. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cbpa.2012.09.011
Cruz SA, Lin CH, Chao PL, Hwang PP (2013b) Glucocorticoid receptor, but not mineralocorticoid receptor, mediates cortisol regulation of epidermal ionocyte development and ion transport in zebrafish (Danio rerio). PLoS One 8:e77997. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0077997
Cui G, Hong J, Chung-Davidson YW et al (2019) An ancient CFTR ortholog informs molecular evolution in ABC transporters. Dev Cell 51(4):421-430.e3. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.devcel.2019.09.017
Cutler CP, Cramb G (2002) Branchial expression of an aquaporin 3 (AQP-3) homologue is downregulated in the European eel Anguilla anguilla following seawater acclimation. J Exp Biol 205(Pt 17):2643–2651. https://doi.org/10.1242/jeb.205.17.2643
Cutler CP, Phillips C, Hazon N, Cramb G (2007) Cortisol regulates eel (Anguilla anguilla) aquaporin 3 (AQP3) mRNA expression levels in gill. Gen Comp Endocrinol 152:310–313. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ygcen.2007.01.031
Dalziel AC, Bittman J, Mandic M et al (2014) Origins and functional diversification of salinity-responsive Na+, K+ ATPase α1 paralogs in salmonids. Mol Ecol 23(14):3483–3503. https://doi.org/10.1111/mec.12828
Dauder S, Young G, Hass L, Bern HA (1990) Prolactin receptors in liver, kidney, and gill of the tilapia (Oreochromis mossambicus): characterization and effect of salinity on specific binding of iodinated ovine prolactin. Gen Comp Endocrinol 77(3):368–377. https://doi.org/10.1016/0016-6480(90)90226-c
Deane EE, Woo NYS (2009) Modulation of fish growth hormone levels by salinity, temperature, pollutants and aquaculture related stress: a review. Rev Fish Biol Fish 19:97–120. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11160-008-9091-0
Du K, Stöck M, Kneitz S et al (2020) The sterlet sturgeon genome sequence and the mechanisms of segmental rediploidization. Nat Ecol Evol 4(6):841–852. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41559-020-1166-x
Dymowska AK, Hwang PP, Goss GG (2012) Structure and function of ionocytes in the freshwater fish gill. Respir Physiol Neurobiol 184(3):282–292. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.resp.2012.08.025
Dymowska AK, Schultz AG, Blair SD et al (2014) Acid-sensing ion channels are involved in epithelial Na+ uptake in the rainbow trout Oncorhynchus mykiss. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol 307(3):C255–C265. https://doi.org/10.1152/ajpcell.00398.2013
Eckert SM, Yada T, Shepherd BS et al (2001) Hormonal control of osmoregulation in the channel catfish Ictalurus punctatus. Gen Comp Endocrinol 122(3):270–286. https://doi.org/10.1006/gcen.2001.7633
Einarsdóttir IE, Gong N, Jönsson E et al (2014) Plasma growth hormone-binding protein levels in Atlantic salmon Salmo salar during smoltification and seawater transfer. J Fish Biol 85:1279–1296. https://doi.org/10.1111/jfb.12473
Ellis LV, Bollinger RJ, Weber HM et al (2019) Differential expression and localization of branchial AQP1 and AQP3 in Japanese medaka (Oryzias latipes). Cells 8(5):422. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells8050422
Evans DH, Piermarini PM, Choe KP (2005) The multifunctional fish gill: dominant site of gas exchange, osmoregulation, acid-base regulation, and excretion of nitrogenous waste. Physiol Rev 85(1):97–177. https://doi.org/10.1152/physrev.00050.2003
Fargher RC, McKeown BA (1989) The effect of prolactin on calcium homeostasis in coho salmon (Oncorhynchus kisutch). Gen Comp Endocrinol 73(3):398–403. https://doi.org/10.1016/0016-6480(89)90197-4
Faught E, Vijayan MM (2018) The mineralocorticoid receptor is essential for stress axis regulation in zebrafish larvae. Sci Rep 8:18081. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-018-36681-w
Ferreira-Martins D, Coimbra J, Antunes C, Wilson JM (2016) Effects of salinity on upstream-migrating, spawning sea lamprey, Petromyzon marinus. Conserv Physiol 4:1–16. https://doi.org/10.1093/conphys/cov064
Ferreira-Martins D, Wilson JM, Kelly SP et al (2021) A review of osmoregulation in lamprey. J Gt Lakes Res 47:S59–S71. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jglr.2021.05.003
Ferreira-Martins D, Walton E, Karlstrom RO et al (2023) The GH/IGF axis in the sea lamprey during metamorphosis and seawater acclimation. Mol Cell Endocrinol. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mce.2023.111937
Fiol DF, Kültz D (2007) Osmotic stress sensing and signaling in fishes. FEBS J 274(22):5790–5798. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1742-4658.2007.06099.x
Fiol DF, Sanmarti E, Sacchi R, Kültz D (2009) A novel tilapia prolactin receptor is functionally distinct from its paralog. J Exp Biol 212(Pt 13):2007–2015. https://doi.org/10.1242/jeb.025601
Flik G, Fenwick JC, Wendelaar Bonga SE (1989) Calcitropic actions of prolactin in freshwater North American eel (Anguilla rostrata LeSueur). Am J Physiol 257(1 Pt 2):R74-79. https://doi.org/10.1152/ajpregu.1989.257.1.R74
Flik G, Atsma W, Fenwick JC et al (1993) Homologous recombinant growth hormone and calcium metabolism in the tilapia, Oreochromis mossambicus, adapted to fresh water. J Exp Biol 185:107–119. https://doi.org/10.1242/jeb.185.1.107
Flik G, Rentier-Delrue F, Wendelaar Bonga SE (1994) Calcitropic effects of recombinant prolactins in Oreochromis mossambicus. Am J Physiol 266(4 Pt 2):R1302-1308. https://doi.org/10.1152/ajpregu.1994.266.4.R1302
Flik G, Klaren PHM, Schoenmakers TJM et al (1996) Cellular calcium transport in fish: unique and universal mechanisms. Physiol Biochem Zool 69:403–417. https://doi.org/10.1086/physzool.69.2.30164192
Flores AM, Shrimpton MJ (2012) Differential physiological and endocrine responses of rainbow trout, Oncorhynchus mykiss, transferred from fresh water to ion-poor or salt water. Gen Comp Endocrinol 175:244–250. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ygcen.2011.11.002
Fontaine M, Hatey J (1954) Sur la teneur en 17-hydroxycorticosteroides du plasma de saumon (Salmo salar L.). CR Acad Sci Ser D 239:319–321
Fuentes J, Brinca L, Guerreiro PM, Power DM (2010) PRL and GH synthesis and release from the sea bream (Sparus auratus L.) pituitary gland in vitro in response to osmotic challenge. Gen Comp Endocrinol 168(1):95–102. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ygcen.2010.04.005
Fuller PJ, Yao YZ, Jin R et al (2019) Molecular evolution of the switch for progesterone and spironolactone from mineralocorticoid receptor agonist to antagonist. Proc Natl Acad Sci. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1903172116
Furukawa F, Watanabe S, Inokuchi M, Kaneko T (2011) Responses of gill mitochondria-rich cells in Mozambique tilapia exposed to acidic environments (pH 4.0) in combination with different salinities. Comp Biochem Physiol A 158(4):468–476. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cbpa.2010.12.003
Geering K (2008) Functional roles of Na, K-ATPase subunits. Curr Opin Nephrol Hypertens 17(5):526–532. https://doi.org/10.1097/MNH.0b013e3283036cbf
Gilmour KM, Collier CL, Dey CJ, Perry SF (2011) Roles of cortisol and carbonic anhydrase in acid-base compensation in rainbow trout, Oncorhynchus mykiss. J Comp Physiol B 181(4):501–515. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00360-010-0540-4
Gong N, Ferreira-Martins D, McCormick SD, Sheridan MA (2020) Divergent genes encoding the putative receptors for growth hormone and prolactin in sea lamprey display distinct patterns of expression. Sci Rep 10:1674. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-020-58344-5
Gong N, Ferreira-Martins D, Norstog JL et al (2022) Discovery of prolactin-like in lamprey: role in osmoregulation and new insight into the evolution of the growth hormone/prolactin family. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 119:e2212196119. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.2212196119
Gray ES, Young G, Bern HA (1990) Radioreceptor assay for growth hormone in coho salmon (Oncorhynchus kisutch) and its application to the study of stunting. J Exp Zool 256:290–296. https://doi.org/10.1002/jez.1402560308
Guh YJ, Lin CH, Hwang PP (2015) Osmoregulation in zebrafish: ion transport mechanisms and functional regulation. EXCLI J 14:627–659. https://doi.org/10.17179/excli2015-246
Herndon TM, McCormick SD, Bern HA (1991) Effects of prolactin on chloride cells in opercular membrane of seawater-adapted tilapia. Gen Comp Endocrinol 83(2):283–289. https://doi.org/10.1016/0016-6480(91)90032-2
Hirano T (1986) The spectrum of prolactin action in teleosts. Prog Clin Biol Res 205:53–74
Hirata T, Kaneko T, Ono T et al (2003) Mechanism of acid adaptation of a fish living in a pH 3.5 lake. Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol 284(5):R1199–R1212. https://doi.org/10.1152/ajpregu.00267.2002
Hiroi J, McCormick SD (2012) New insights into gill ionocyte and ion transporter function in euryhaline and diadromous fish. Respir Physiol Neurobiol 184(3):257–268. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.resp.2012.07.019
Hiroi J, Yasumasu S, McCormick SD et al (2008) Evidence for an apical Na-Cl cotransporter involved in ion uptake in a teleost fish. J Exp Biol 211(Pt 16):2584–2599. https://doi.org/10.1242/jeb.018663
Hoar WS (1988) The physiology of smolting salmonids. In: Hoar WS, Randall DJ (eds) Fish physiology. Academic Press, New York, pp 275–343
Hoshijima K, Hirose S (2007) Expression of endocrine genes in zebrafish larvae in response to environmental salinity. J Endocrinol 193(3):481–491. https://doi.org/10.1677/JOE-07-0003
Hsiao CD, You MS, Guh YJ et al (2007) A positive regulatory loop between foxi3a and foxi3b is essential for specification and differentiation of zebrafish epidermal ionocytes. PLoS One 2(3):e302. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0000302
Hsu HH, Lin LY, Tseng YC et al (2014) A new model for fish ion regulation: identification of ionocytes in freshwater- and seawater-acclimated medaka (Oryzias latipes). Cell Tissue Res 357(1):225–243. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00441-014-1883-z
Huang X, Jiao B, Fung CK et al (2007) The presence of two distinct prolactin receptors in seabream with different tissue distribution patterns, signal transduction pathways and regulation of gene expression by steroid hormones. J Endocrinol 194(2):373–392. https://doi.org/10.1677/JOE-07-0076
Hwang PP, Lin LY (2014) Gill ionic transport, acid-base regulation, and nitrogen excretion. In: Evans DH, Claiborne JB, Currie S (eds) The physiology of fishes, 4th edn. CRC Press, Boca Raton, p 453
Inokuchi M, Hiroi J, Watanabe S et al (2008) Gene expression and morphological localization of NHE3, NCC and NKCC1a in branchial mitochondria-rich cells of Mozambique tilapia (Oreochromis mossambicus) acclimated to a wide range of salinities. Comp Biochem Physiol A 151(2):151–158. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cbpa.2008.06.012
Inokuchi M, Hiroi J, Watanabe S et al (2009) Morphological and functional classification of ion-absorbing mitochondria-rich cells in the gills of Mozambique tilapia. J Exp Biol 2212(Pt 7):1003–1010. https://doi.org/10.1242/jeb.025957
Inokuchi M, Breves JP, Moriyama S et al (2015) Prolactin 177, prolactin 188, and extracellular osmolality independently regulate the gene expression of ion transport effectors in gill of Mozambique tilapia. Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol 309(10):R1251-1263. https://doi.org/10.1152/ajpregu.00168.2015
Inokuchi M, Nakamura M, Miyanishi H et al (2017) Functional classification of gill ionocytes and spatiotemporal changes in their distribution after transfer from seawater to freshwater in Japanese seabass. J Exp Biol 220(Pt 24):4720–4732. https://doi.org/10.1242/jeb.167320
Inokuchi M, Hiroi J, Kaneko T (2022) Why can Mozambique tilapia acclimate to both freshwater and seawater? Insights from the plasticity of ionocyte functions in the euryhaline teleost. Front Physiol 13:914277. https://doi.org/10.3389/fphys.2022.914277
Ivanis G, Esbaugh AJ, Perry SF (2008) Branchial expression and localization of SLC9A2 and SLC9A3 sodium/hydrogen exchangers and their possible role in acid-base regulation in freshwater rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss). J Exp Biol 211(Pt 15):2467–2477. https://doi.org/10.1242/jeb.017491
Jung D, MacIver B, Jackson BP et al (2012) A novel aquaporin 3 in killifish (Fundulus heteroclitus) is not an arsenic channel. Toxicol Sci 127(1):101–109. https://doi.org/10.1093/toxsci/kfs078
Kakizawa S, Kaneko T, Hasegawa S, Hirano T (1993) Activation of somatolactin cells in the pituitary of the rainbow trout Oncorhynchus mykiss by low environmental calcium. Gen Comp Endocrinol 91(3):298–306. https://doi.org/10.1006/gcen.1993.1130
Kaneko T, Hirano T (1983) Role of prolactin and somatolactin in calcium regulation in fish. J Exp Biol 184(1):31–45. https://doi.org/10.1242/jeb.184.1.31
Kaneko T, Watanabe S, Lee KM (2008) Functional morphology of mitochondrion-rich cells in euryhaline and stenohaline teleosts. Aqua BioSci Monogr 1:1–62. https://doi.org/10.5047/absm.2008.00101.0001
Katsu Y, Oka K, Baker ME (2018) Evolution of human, chicken, alligator, frog, and zebrafish mineralocorticoid receptors: allosteric influence on steroid specificity. Sci Signal 11:35–37. https://doi.org/10.1126/scisignal.aao1520
Kawauchi H, Suzuki K, Yamazaki T et al (2002) Identification of growth hormone in the sea lamprey, an extant representative of a group of the most ancient vertebrates. Endocrinology 143(12):4916–4921. https://doi.org/10.1210/en.2002-220810
Kelly SP, Chasiotis H (2011) Glucocorticoid and mineralocorticoid receptors regulate paracellular permeability in a primary cultured gill epithelium. J Exp Biol 214:2308–2318. https://doi.org/10.1242/jeb.055962
Kelly SP, Wood CM (2002) Cultured gill epithelia from freshwater tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus): effect of cortisol and homologous serum supplements from stressed and unstressed fish. J Membr Biol 190(1):29–42. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00232-002-1020-x
Kelly SP, Chow IN, Woo NY (1999) Effects of prolactin and growth hormone on strategies of hypoosmotic adaptation in a marine teleost, Sparus sarba. Gen Comp Endocrinol 113(1):9–22. https://doi.org/10.1006/gcen
Khodabandeh S, Mosafer S, Khoshnood Z (1999) Effects of cortisol and salinity acclimation on Na+/K+/2Cl- cotransporter gene expression and Na+, K+-ATPase activity in the gill of Persian sturgeon, Acipenser persicus, fry. Sci Mar 73S1:111–116. https://doi.org/10.3989/scimar.2009.73s1111
Kiilerich P, Kristiansen K, Madsen SS (2007a) Hormone receptors in gills of smolting Atlantic salmon, Salmo salar: expression of growth hormone, prolactin, mineralocorticoid and glucocorticoid receptors and 11β-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase type 2. Gen Comp Endocrinol 152:295–303. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ygcen.2006.12.018
Kiilerich P, Kristiansen K, Madsen SS (2007b) Cortisol regulation of ion transporter mRNA in Atlantic salmon gill and the effect of salinity on the signaling pathway. J Endocrinol 194:417–427. https://doi.org/10.1677/JOE-07-0185
Kiilerich P, Milla S, Sturm A et al (2011a) Implication of the mineralocorticoid axis in rainbow trout osmoregulation during salinity acclimation. J Endocrinol 209:221–235. https://doi.org/10.1530/JOE-10-0371
Kiilerich P, Pedersen SH, Kristiansen K, Madsen SS (2011b) Corticosteroid regulation of Na+, K+-ATPase α1-isoform expression in Atlantic salmon gill during smolt development. Gen Comp Endocrinol 170:283–289. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ygcen.2010.02.014
Kiilerich P, Tipsmark CK, Borski RJ, Madsen SS (2011c) Differential effects of cortisol and 11-deoxycorticosterone on ion transport protein mRNA levels in gills of two euryhaline teleosts, Mozambique tilapia (Oreochromis mossambicus) and striped bass (Morone saxatilis). J Endocrinol 209:115–126. https://doi.org/10.1530/JOE-10-0326
Klaren PH, Guzmán JM, Reutelingsperger SJ et al (2007) Low salinity acclimation and thyroid hormone metabolizing enzymes in gilthead seabream (Sparus auratus). Gen Comp Endocrinol 152(2–3):215–222. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ygcen.2007.02.010
Knoeppel SJ, Atkins DL, Packer RK (1982) The role of the thyroid in osmotic and ionic regulation in Fundulus heteroclitus acclimated to freshwater and seawater. Comp Biochem Physiol A 73:25–29. https://doi.org/10.1016/0300-9629(82)90087-1
Kolosov D, Kelly SP (2017) Claudin-8d is a cortisol-responsive barrier protein in the gill epithelium of trout. J Mol Endocrinol 59(3):299–310. https://doi.org/10.1530/JME-17-0108
Kolosov D, Kelly SP (2019) The mineralocorticoid receptor contributes to barrier function of a model fish gill epithelium. J Exp Biol 222(Pt 11):jeb192096. https://doi.org/10.1242/jeb.192096
Kolosov D, Bui P, Donini A et al (2017a) A role for tight junction-associated MARVEL proteins in larval sea lamprey (Petromyzon marinus) osmoregulation. J Exp Biol 220:3657–3670. https://doi.org/10.1242/jeb.161562
Kolosov D, Donini A, Kelly SP (2017b) Claudin-31 contributes to corticosteroid-induced alterations in the barrier properties of the gill epithelium. Mol Cell Endocrinol 439:457–466. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mce.2016.10.034
Kolosov D, Bui P, Wilkie MP, Kelly SP (2020) Claudins of sea lamprey (Petromyzon marinus)—organ-specific expression and transcriptional responses to water of varying ion content. J Fish Biol. https://doi.org/10.1111/jfb.14274
Kültz D (2015) Physiological mechanisms used by fish to cope with salinity stress. J Exp Biol 218(Pt 12):1907–1914. https://doi.org/10.1242/jeb.118695
Kumai Y, Bahubeshi A, Steele S, Perry SF (2011) Strategies for maintaining Na+ balance in zebrafish (Danio rerio) during prolonged exposure to acidic water. Comp Biochem Physiol A 160(1):52–62. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cbpa.2011.05.001
Kumai Y, Nesan D, Vijayan MM, Perry SF (2012) Cortisol regulates Na+ uptake in zebrafish, Danio rerio, larvae via the glucocorticoid receptor. Mol Cell Endocrinol 364(1–2):113–125. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mce.2012.08.017
Lai KP, Li JW, Gu J et al (2015) Transcriptomic analysis reveals specific osmoregulatory adaptive responses in gill mitochondria-rich cells and pavement cells of the Japanese eel. BMC Genom 16:1072. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12864-015-2271-0
Langhorn P, Simpson TH (1986) The interrelationship of cortisol, gill Na+/K+ ATPase, and homeostasis during the parr-smolt transformation of Atlantic salmon (Salmo salar L.). Gen Comp Endocrinol 61:203–213. https://doi.org/10.1016/0016-6480(86)90198-X
Lee KM, Kaneko T, Aida K (2006) Prolactin and prolactin receptor expressions in a marine teleost, pufferfish Takifugu rubripes. Gen Comp Endocrinol 146(3):318–328. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ygcen.2005.12.003
Leguen I, Le Cam A, Montfort J et al (2015) Transcriptomic analysis of trout gill ionocytes in fresh water and sea water using laser capture microdissection combined with microarray analysis. PLoS One 10(10):e0139938. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0139938
Lema SC, Carvalho PG, Egelston JN et al (2018) Dynamics of gene expression responses for ion transport proteins and aquaporins in the gill of a euryhaline pupfish during freshwater and high-salinity acclimation. Physiol Biochem Zool 91(6):1148–1171. https://doi.org/10.1086/700432
Liao BK, Deng AN, Chen SC et al (2007) Expression and water calcium dependence of calcium transporter isoforms in zebrafish gill mitochondrion-rich cells. BMC Genom 8:354. https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-2164-8-354
Liao BK, Chen RD, Hwang PP (2009) Expression regulation of Na+-K+-ATPase alpha1-subunit subtypes in zebrafish gill ionocytes. Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol 296(6):R1897–R1906. https://doi.org/10.1152/ajpregu.00029.2009
Lignot JH, Cutler CP, Hazon N, Cramb G (2002) Immunolocalisation of aquaporin 3 in the gill and the gastrointestinal tract of the European eel Anguilla anguilla (L.). J Exp Biol 205(Pt 17):2653–2663. https://doi.org/10.1242/jeb.205.17.2653
Lin CH, Hwang PP (2016) The control of calcium metabolism in zebrafish (Danio rerio). Int J Mol Sci 17(11):1783. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms17111783
Link K, Berishvili G, Shved N et al (2010) Seawater and freshwater challenges affect the insulin-like growth factors IGF-I and IGF-II in liver and osmoregulatory organs of the tilapia. Mol Cell Endocrinol 327(1–2):40–46. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mce.2010.05.011
Link K, Shved N, Serrano N et al (2022) Effects of seawater and freshwater challenges on the Gh/Igf system in the saline-tolerant blackchin tilapia (Sarotherodon melanotheron). Front Endocrinol 13:976488. https://doi.org/10.3389/fendo.2022.976488
López-Bojórquez L, Villalobos P, García-G C et al (2007) Functional identification of an osmotic response element (ORE) in the promoter region of the killifish deiodinase 2 gene (FhDio2). J Exp Biol 210(Pt 17):3126–3132. https://doi.org/10.1242/jeb.004150
Loretz CA, Bern HA (1982) Prolactin and osmoregulation in vertebrates: an update. Neuroendocrinology 35(4):292–304. https://doi.org/10.1159/000123397
Mackie P, Wright PA, Glebe BD, Ballantyne JS (2005) Osmoregulation and gene expression of Na+/K+ ATPase in families of Atlantic salmon (Salmo salar) smolts. Can J Fish Aquat Sci 62(11):2661–2672. https://doi.org/10.1139/f05-168
Madsen SS (1990a) Enhanced hypoosmoregulatory response to growth hormone after cortisol treatment in immature rainbow trout, Salmo gairdneri. Fish Physiol Biochem 8:271–279. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00003422
Madsen SS (1990b) The role of cortisol and growth hormone in seawater adaptation and development of hypoosmoregulatory mechanisms in sea trout parr (Salmo trutta trutta). Gen Comp Endocrinol 79:1–11. https://doi.org/10.1016/0016-6480(90)90082-W
Madsen SS, Bern HA (1993) In-vitro effects of insulin-like growth factor-I on gill Na+, K+-ATPase in coho salmon, Oncorhynchus kisutch. J Endocrinol 138(1):23–30. https://doi.org/10.1677/joe.0.1380023
Madsen SS, Korsgaard B (1991) Opposite effects of 17β-estradiol and combined growth hormone-cortisol treatment on hypo-osmoregulatory performance in sea trout presmolts, Salmo trutta. Gen Comp Endocrinol 83:276–282. https://doi.org/10.1016/0016-6480(91)90031-Z
Madsen SS, Kiilerich P, Tipsmark CK (2009) Multiplicity of expression of Na+, K+-ATPase alpha-subunit isoforms in the gill of Atlantic salmon (Salmo salar): cellular localisation and absolute quantification in response to salinity change. J Exp Biol 212(Pt 1):78–88. https://doi.org/10.1242/jeb.024612
Mancera JM, McCormick SD (1998) Evidence for growth hormone/insulin-like growth factor I axis regulation of seawater acclimation in the euryhaline teleost Fundulus heteroclitus. Gen Comp Endocrinol 111:103–112. https://doi.org/10.1006/gcen.1998.7086
Mancera JM, Carrión RL, del Río MPM (2002) Osmoregulatory action of PRL, GH, and cortisol in the gilthead seabream (Sparus aurata L.). Gen Comp Endocrinol 129(2):95–103. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0016-6480(02)00522-1
Manzon LA (2002) The role of prolactin in fish osmoregulation: a review. Gen Comp Endocrinol 125(2):291–310. https://doi.org/10.1006/gcen.2001.7746
Marlétaz F, de la Calle-Mustienes E, Acemel RD et al (2023) The little skate genome and the evolutionary emergence of wing-like fins. Nature 616(7957):495–503. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41586-023-05868-1
Marshall WS, Grosell M (2006) Ion transport, osmoregulation, and acid-base balance. In: Evans DH, Claiborne JB (eds) The physiology of fishes, 3rd edn. CRC Press, Boca Raton, pp 177–230
Marshall WS, Breves JP, Doohan EM et al (2018) claudin-10 isoform expression and cation selectivity change with salinity in salt-secreting epithelia of Fundulus heteroclitus. J Exp Biol 221(Pt 1):jeb168906. https://doi.org/10.1242/jeb.168906
Marsigliante S, Barker S, Jimenez E, Storelli C (2000) Glucocorticoid receptors in the euryhaline teleost Anguilla anguilla. Mol Cell Endocrinol 162:193–201. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0303-7207(99)00262-2
Maule AG, Schreck CB (1990) Glucocorticoid receptors in leukocytes and gill of juvenile coho salmon (Oncorhynchus kisutch). Gen Comp Endocrinol 77:448–455. https://doi.org/10.1016/0016-6480(90)90236-f
Mazurais D, Ducouret B, Tujague M et al (1998) Regulation of the glucocorticoid receptor mRNA levels in the gills of Atlantic salmon (Salmo salar) during smoltification. Bull Fr Pêche Piscic 350–351:499–510. https://doi.org/10.1051/kmae:1998019
McCormick SD (1996) Effects of growth hormone and insulin-like growth factor I on salinity tolerance and gill Na+, K+-ATPase in Atlantic salmon (Salmo salar): interaction with cortisol. Gen Comp Endocrinol 101:3–11. https://doi.org/10.1006/gcen.1996.0002
McCormick SD (2001) Endocrine control of osmoregulation in teleost fish. Am Zool 41:781–794. https://doi.org/10.1093/icb/41.4.781
McCormick SD (2013) Smolt physiology and endocrinology. In: McCormick SD, Farrell AP, Brauner CJ (eds) Fish Physiology: Euryhaline Fishes. Academic Press Inc, Amsterdam, pp 191–251
McCormick SD, Bern HA (1989) In vitro stimulation of Na+-K+-ATPase activity and ouabain binding by cortisol in coho salmon gill. Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol 256:R707-715. https://doi.org/10.1152/ajpregu.1989.256.3.r707
McCormick SD, Saunders RL (1987) Preparatory physiological adaptations for marine life of salmonids: osmoregulation, growth, and metabolism. Am Fish Soc Symp 1:211–229. https://doi.org/10.1016/0022-4596(90)90074-8
McCormick SD, Dickhoff WW, Duston J et al (1991) Developmental differences in the responsiveness of gill Na+, K+-ATPase to cortisol in salmonids. Gen Comp Endocrinol 84:308–317. https://doi.org/10.1016/0016-6480(91)90054-A
McCormick SD, Shrimpton JM, Moriyama S, Björnsson BT (2007) Differential hormonal responses of Atlantic salmon parr and smolt to increased daylength: a possible developmental basis for smolting. Aquaculture 273:337–344. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aquaculture.2007.10.015
McCormick SD, Regish A, O’Dea MF, Shrimpton JM (2008) Are we missing a mineralocorticoid in teleost fish? Effects of cortisol, deoxycorticosterone and aldosterone on osmoregulation, gill Na+, K+-ATPase activity and isoform mRNA levels in Atlantic salmon. Gen Comp Endocrinol 157:35–40. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ygcen.2008.03.024
McCormick SD, Regish AM, Christensen AK (2009) Distinct freshwater and seawater isoforms of Na+/K+-ATPase in gill chloride cells of Atlantic salmon. J Exp Biol 212(Pt 24):3994–4001. https://doi.org/10.1242/jeb.037275
McCormick SD, Regish AM, Christensen AK, Björnsson BT (2013) Differential regulation of sodium–potassium pump isoforms during smolt development and seawater exposure of Atlantic salmon. J Exp Biol 216:1142–1151. https://doi.org/10.1242/jeb.080440
McCormick SD, Taylor ML, Regish AM (2020) Cortisol is an osmoregulatory and glucose-regulating hormone in Atlantic sturgeon, a basal ray-finned fish. J Exp Biol 223:jeb220251. https://doi.org/10.1242/jeb.220251
McGuire A, Aluru N, Takemura A et al (2010) Hyperosmotic shock adaptation by cortisol involves upregulation of branchial osmotic stress transcription factor 1 gene expression in Mozambique tilapia. Gen Comp Endocrinol 165(2):321–329. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ygcen.2009.07.016
Mizuno S, Ura K, Onodera Y et al (2001) Changes in transcript levels of gill cortisol receptor during smoltification in wild masu salmon, Oncorhynchus masou. Zool Sci 18:853–860. https://doi.org/10.2108/zsj.18.853
Motoshima T, Nagashima A, Ota C et al (2023) Na+/Cl- cotransporter 2 is not fish-specific and is widely found in amphibians, non-avian reptiles, and select mammals. Physiol Genom 55(3):113–131. https://doi.org/10.1152/physiolgenomics.00143.2022
Moyle PB, Cech JJ (2004) Fishes: an introduction to ichthyology, 4th edn. Prentice Hall, Upper Saddle River
Nilsen TO, Ebbesson LO, Madsen SS et al (2007) Differential expression of gill Na+, K+-ATPase alpha- and beta-subunits, Na+, K+, 2Cl− cotransporter and CFTR anion channel in juvenile anadromous and landlocked Atlantic salmon Salmo salar. J Exp Biol 210(Pt 16):2885–2896. https://doi.org/10.1242/jeb.002873
Nilsen TO, Ebbesson LOE, Kiilerich P et al (2008) Endocrine systems in juvenile anadromous and landlocked Atlantic salmon (Salmo salar): seasonal development and seawater acclimation. Gen Comp Endocrinol 155:762–772. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ygcen.2007.08.006
Notch EG, Chapline C, Flynn E et al (2012) Mitogen activated protein kinase 14-1 regulates serum glucocorticoid kinase 1 during seawater acclimation in Atlantic killifish, Fundulus heteroclitus. Comp Biochem Physiol A 162(4):443–448. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cbpa.2012.04.025
Nozaki M, Ominato K, Shimotani T et al (2008) Identity and distribution of immunoreactive adenohypophysial cells in the pituitary during the life cycle of sea lampreys, Petromyzon marinus. Gen Comp Endocrinol 155:403–412. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ygcen.2007.07.012
Pang PK, Schreibman MP, Balbontin F, Pang RK (1978) Prolactin and pituitary control of calcium regulation in the killifish, Fundulus heteroclitus. Gen Comp Endocrinol 36(2):306–316. https://doi.org/10.1016/0016-6480(78)90037-0
Parks SK, Tresguerres M, Goss GG (2007) Interactions between Na+ channels and Na+-HCO3- cotransporters in the freshwater fish gill MR cell: a model for transepithelial Na+ uptake. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol 292(2):C935–C944. https://doi.org/10.1152/ajpcell.00604.2005
Pavlovic D, Fuller W, Shattock MJ (2013) Novel regulation of cardiac Na pump via phospholemman. J Mol Cell Cardiol 61:83–93. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.yjmcc.2013.05.002
Pelis RM, McCormick SD (2001) Effects of growth hormone and cortisol on Na+–K+–2Cl− cotransporter localization and abundance in the gills of Atlantic salmon. Gen Comp Endocrinol 124:134–143. https://doi.org/10.1006/gcen.2001.7703
Pérez-Rius C, Gaitán-Peñas H, Estévez R, Barrallo-Gimeno A (2015) Identification and characterization of the zebrafish ClC-2 chloride channel orthologs. Pflugers Arch 467(8):1769–1781. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00424-014-1614-z
Perry SF, Goss GG, Fenwick JC (1992) Interrelationships between gill chloride cell morphology and calcium uptake in freshwater teleosts. Fish Physiol Biochem 10(4):327–337. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00004482
Peter MCS, Lock RA, Wendelaar Bonga SE (2000) Evidence for an osmoregulatory role of thyroid hormones in the freshwater Mozambique tilapia Oreochromis mossambicus. Gen Comp Endocrinol 120(2):157–167. https://doi.org/10.1006/gcen.2000.7542
Pickford GE (1953) A study of the hypophysectomized male Fundulus heteroclitus (Linn.) Bull Bingham. Oceanogr Collect 14(2):5–45
Pickford GE, Atz JW (1957) The physiology of the pituitary gland of fishes. New York Zoological Society, New York
Pickford GE, Phillips JG (1959) Prolactin, a factor in promoting survival of hypophysectomized killifish in fresh water. Science 130:454–455. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.130.3373.454
Pickford GE, Griffith RW, Torretti J et al (1970a) Branchial reduction and renal stimulation of (Na+, K+)-ATPase by prolactin in hypophysectomized killifish in fresh water. Nature 228(5269):378–379. https://doi.org/10.1038/228378a0
Pickford GE, Pang PKT, Weinstein E et al (1970b) The response of the hypophysectomized cyprinodont, Fundulus heteroclitus, to replacement therapy with cortisol: effects on blood serum and sodium-potassiurn activated adenosine triphosphatase in the gills, kidney, and intestinal mucosa. Gen Comp Endocrinol 14:524–534. https://doi.org/10.1016/0016-6480(70)90036-5
Pierce AL, Fox BK, Davis LK et al (2007) Prolactin receptor, growth hormone receptor, and putative somatolactin receptor in Mozambique tilapia: tissue specific expression and differential regulation by salinity and fasting. Gen Comp Endocrinol 154(1–3):31–40. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ygcen.2007.06.023
Pierce AL, Breves JP, Moriyama S et al (2011) Differential regulation of Igf1 and Igf2 mRNA levels in tilapia hepatocytes: effects of insulin and cortisol on GH sensitivity. J Endocrinol 211(2):201–210. https://doi.org/10.1530/JOE-10-0456
Pisam M, Auperin B, Prunet P et al (1993) Effects of prolactin on alpha and beta chloride cells in the gill epithelium of the saltwater adapted tilapia “Oreochromis niloticus”. Anat Rec 235(2):275–284. https://doi.org/10.1002/ar.1092350211
Poppinga J, Kittilson J, McCormick SD, Sheridan MA (2007) Effects of somatostatin on the growth hormone-insulin-like growth factor axis and seawater adaptation of rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss). Aquaculture 273:312–319. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aquaculture.2007.10.021
Potts WTW, Evans DH (1966) The effects of hypophysectomy and bovine prolactin on salt fluxes in fresh-water-adapted Fundulus heteroclitus. Biol Bull 131:362–368
Prunet P, Auperin B (1994) Prolactin receptors. In: Sherwood NM, Hew CL (eds) Fish physiology, vol 13. Molecular Endocrinology of Fish. Academic Press, New York, pp 367–391
Prunet P, Boeuf G, Bolton JP, Young G (1989) Smoltification and seawater adaptation in Atlantic salmon (Salmo salar): plasma prolactin, growth hormone, and thyroid hormones. Gen Comp Endocrinol 74:355–364. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0016-6480(89)80031-0
Prunet P, Pisam M, Claireaux JP et al (1994) Effects of growth hormone on gill chloride cells in juvenile Atlantic salmon (Salmo salar). Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol 266:R850–R857. https://doi.org/10.1152/ajpregu.1994.266.3.R850
Prunet P, Sturm A, Milla S (2006) Multiple corticosteroid receptors in fish: from old ideas to new concepts. Gen Comp Endocrinol 147:17–23. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ygcen.2006.01.015
Rai S, Szeitz A, Roberts BW et al (2015) A putative corticosteroid hormone in Pacific lamprey, Entosphenus tridentatus. Gen Comp Endocrinol 212:178–184. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ygcen.2014.06.019
Refstie T (1982) The effect of feeding thyroid hormones on saltwater tolerance and growth rate of Atlantic salmon. Can J Zool 60(11):2706–2712. https://doi.org/10.1139/z82-346
Reindl KM, Sheridan MA (2012) Peripheral regulation of the growth hormone-insulin-like growth factor system in fish and other vertebrates. Comp Biochem Physiol A 163(3–4):231–245. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cbpa.2012.08.003
Reinecke M, Schmid A, Ermatinger R, Loffing-Cueni D (1997) Insulin-like growth factor I in the teleost Oreochromis mossambicus, the tilapia: gene sequence, tissue expression, and cellular localization. Endocrinology 138(9):3613–3619. https://doi.org/10.1210/endo.138.9.5375
Reis-Santos P, McCormick SD, Wilson JM (2008) Ionoregulatory changes during metamorphosis and salinity exposure of juvenile sea lamprey (Petromyzon marinus L.). J Exp Biol 211:978–988. https://doi.org/10.1242/jeb.014423
Ren J, Chung-Davidson YW, Yeh CY et al (2015) Genome-wide analysis of the ATP-binding cassette (ABC) transporter gene family in sea lamprey and Japanese lamprey. BMC Genom 16(1):436. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12864-015-1677-z
Rhee JS, Kim RO, Seo JS et al (2010) Effects of salinity and endocrine-disrupting chemicals on expression of prolactin and prolactin receptor genes in the euryhaline hermaphroditic fish, Kryptolebias marmoratus. Comp Biochem Physiol C 152(4):413–423. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cbpc.2010.07.001
Richards JG, Semple JW, Bystriansky JS, Schulte PM (2003) Na+/K+-ATPase alpha-isoform switching in gills of rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss) during salinity transfer. J Exp Biol 206(Pt 24):4475–4486. https://doi.org/10.1242/jeb.00701
Rouzic PL, Sandra O, Grosclaude J et al (2002) Evidence of rainbow trout prolactin interaction with its receptor through unstable homodimerisation. Mol Cell Endocrinol 172(1–2):105–113. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0303-7207(00)00377-4
Ruhr IM, Wood CM, Schauer KL et al (2020) Is aquaporin-3 involved in water-permeability changes in the killifish during hypoxia and normoxic recovery, in freshwater or seawater? J Exp Zool A 333(7):511–525. https://doi.org/10.1002/jez.2393
Saito K, Nakamura N, Ito Y et al (2010) Identification of zebrafish Fxyd11a protein that is highly expressed in ion-transporting epithelium of the gill and skin and its possible role in ion homeostasis. Front Physiol 1:129. https://doi.org/10.3389/fphys.2010.00129
Sakamoto T, Hirano T (1991) Growth hormone receptors in the liver and osmoregulatory organs of rainbow trout: characterization and dynamics during adaptation to seawater. J Endocrinol 130:425–433. https://doi.org/10.1677/joe.0.1300425
Sakamoto T, McCormick SD (2006) Prolactin and growth hormone in fish osmoregulation. Gen Comp Endocrinol 147(1):24–30. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ygcen.2005.10.008
Sakamoto T, Shepherd BS, Madsen SS et al (1997) Osmoregulatory actions of growth hormone and prolactin in an advanced teleost. Gen Comp Endocrinol 106(1):95–101. https://doi.org/10.1006/gcen.1996.6854
Santos CR, Ingleton PM, Cavaco JE et al (2001) Cloning, characterization, and tissue distribution of prolactin receptor in the sea bream (Sparus aurata). Gen Comp Endocrinol 121(1):32–47. https://doi.org/10.1006/gcen.2000.7553
Saunders RL, McCormick SD, Henderson EB et al (1985) The effect of orally administered 3,5,3′-triiodo-L-thyronine on growth and salinity tolerance of Atlantic salmon (Salmo salar L.). Aquaculture 45:143–156. https://doi.org/10.1016/0044-8486(85)90265-0
Schreiber AM, Specker JL (1999) Metamorphosis in the summer flounder, Paralichthys dentatus: thyroidal status influences salinity tolerance. J Exp Zool 284(4):414–424. https://doi.org/10.1002/(sici)1097-010x(19990901)284:4%3c414::aid-jez8%3e3.0.co;2-e
Schreiber AM, Specker JL (2000) Metamorphosis in the summer flounder, Paralichthys dentatus: thyroidal status influences gill mitochondria-rich cells. Gen Comp Endocrinol 117(2):238–250. https://doi.org/10.1006/gcen.1999.7407
Schultz ET, McCormick SD (2013) Euryhalinity in an evolutionary context. In: McCormick SD, Farrell AP, Brauner CJ (eds) Euryhaline fishes. Elsevier, New York, pp 477–529
Scott GR, Keir KR, Schulte PM (2005) Effects of spironolactone and RU486 on gene expression and cell proliferation after freshwater transfer in the euryhaline killifish. J Comp Physiol B 175:499–510. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00360-005-0014-2
Seale AP, Riley LG, Leedom TA et al (2002) Effects of environmental osmolality on release of prolactin, growth hormone and ACTH from the tilapia pituitary. Gen Comp Endocrinol 128:91–101. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0016-6480(02)00027-8
Seale AP, Watanabe S, Grau EG (2012) Osmoreception: perspectives on signal transduction and environmental modulation. Gen Comp Endocrinol 176(3):354–360. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ygcen.2011.10.005
Seale AP, Pavlosky KK, Celino-Brady FT et al (2019) Systemic versus tissue-level prolactin signaling in a teleost during a tidal cycle. J Comp Physiol B 189(5):581–594. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00360-019-01233-9
Seale LA, Gilman CL, Zavacki AM et al (2021) Regulation of thyroid hormones and branchial iodothyronine deiodinases during freshwater acclimation in tilapia. Mol Cell Endocrinol 538:111450. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mce.2021.111450
Shaughnessy CA, Breves JP (2021) Molecular mechanisms of Cl- transport in fishes: new insights and their evolutionary context. J Exp Zool A 335(2):207–216. https://doi.org/10.1002/jez.2428
Shaughnessy CA, McCormick SD (2020) Functional characterization and osmoregulatory role of the Na+-K+-2Cl- cotransporter in the gill of sea lamprey (Petromyzon marinus), a basal vertebrate. Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol 318(1):R17–R29. https://doi.org/10.1152/ajpregu.00125.2019
Shaughnessy CA, Barany A, McCormick SD (2020) 11-Deoxycortisol controls hydromineral balance in the most basal osmoregulating vertebrate, sea lamprey (Petromyzon marinus). Sci Rep 10:12148. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-020-69061-4
Shimomura T, Nakajima T, Horikoshi M et al (2012) Relationships between gill Na+, K+-ATPase activity and endocrine and local insulin-like growth factor-I levels during smoltification of masu salmon (Oncorhynchus masou). Gen Comp Endocrinol 178:427–435. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ygcen.2012.06.011
Shir-Mohammadi K, Perry SF (2020) Expression of ion transport genes in ionocytes isolated from larval zebrafish (Danio rerio) exposed to acidic or Na+-deficient water. Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol 319(4):R412–R427. https://doi.org/10.1152/ajpregu.00095.2020
Shrimpton JM, McCormick SD (1998) Regulation of gill cytosolic corticosteroid receptors in juvenile Atlantic salmon: interaction effects of growth hormone with prolactin and triiodothyronine. Gen Comp Endocrinol 112(2):262–274. https://doi.org/10.1006/gcen.1998.7172
Shrimpton J, McCormick SD (1999) Responsiveness of gill Na+/K+-ATPase to cortisol is related to gill corticosteroid receptor concentration in juvenile rainbow trout. J Exp Biol 202:987–995. https://doi.org/10.1242/jeb.202.8.987
Shrimpton JM, Randall DJ (1994) Downregulation of corticosteroid receptors in gills of coho salmon due to stress and cortisol treatment. Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol 267:R432-438. https://doi.org/10.1152/ajpregu.1994.267.2.R432
Shrimpton JM, Bernier NJ, Randall DJ (1994) Changes in cortisol dynamics in wild and hatchery-reared juvenile coho salmon (Oncorhynchus kisutch) during smoltification. Can J Fish Aquat Sci 51:2179–2187. https://doi.org/10.1139/f94-219
Singer TD, Finstad B, McCormick SD et al (2003) Interactive effects of cortisol treatment and ambient seawater challenge on gill Na+, K+-ATPase and CFTR expression in two strains of Atlantic salmon smolts. Aquaculture 222:15–28. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0044-8486(03)00099-1
Sloman KA, Desforges PR, Gilmour KM (2001) Evidence for a mineralocorticoid-like receptor linked to branchial chloride cell proliferation in freshwater rainbow trout. J Exp Biol 204:3953–3961. https://doi.org/10.1242/jeb.204.22.3953
Smith JJ, Kuraku S, Holt C et al (2013) Sequencing of the sea lamprey (Petromyzon marinus) genome provides insights into vertebrate evolution. Nat Genet 45(4):415–421. https://doi.org/10.1038/ng.2568
Smith JJ, Timoshevskaya N, Ye C et al (2018) The sea lamprey germline genome provides insights into programmed genome rearrangement and vertebrate evolution. Nat Genet 50(2):270–277. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41588-017-0036-1
Specker JL, Kobuke L (1987) Seawater-acclimation and the thyroidal response to thyrotropin in juvenile coho salmon (Oncorhynchus kisutch). J Exp Zool 241:327–332. https://doi.org/10.1002/jez.1402410307
Specker JL, Schreck CB (1982) Changes in plasma corticosteroids during smoltification of coho salmon, Oncorhynchus kisutch. Gen Comp Endocrinol 46:53–58. https://doi.org/10.1016/0016-6480(82)90162-9
Sturm A, Bury N, Dengreville L et al (2005) 11-Deoxycorticosterone is a potent agonist of the rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss) mineralocorticoid receptor. Endocrinology 146:47–55. https://doi.org/10.1210/en.2004-0128
Sugimoto A, Oka K, Sato R et al (2016) Corticosteroid and progesterone transactivation of mineralocorticoid receptors from Amur sturgeon and tropical gar. Biochem J 473:3655–3665. https://doi.org/10.1042/BCJ20160579
Takabe S, Inokuchi M, Yamaguchi Y, Hyodo S (2016) Distribution and dynamics of branchial ionocytes in houndshark reared in full-strength and diluted seawater environments. Comp Biochem Physiol A 198:22–32. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cbpa.2016.03.019
Takahashi H, Sakamoto T (2013) The role of “mineralocorticoids” in teleost fish: relative importance of glucocorticoid signaling in the osmoregulation and “central” actions of mineralocorticoid receptor. Gen Comp Endocrinol 181:223–228. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ygcen.2012.11.016
Takei Y (2021) The digestive tract as an essential organ for water acquisition in marine teleosts: lessons from euryhaline eels. Zool Lett 7(1):10. https://doi.org/10.1186/s40851-021-00175-x
Takei Y, McCormick SD (2013) Hormonal control of fish euryhalinity. In: McCormick SD, Brauner CJ, Farrell AP (eds) Fish physiology, vol 32. Euryhaline Fishes. Academic Press, Amsterdam, pp 69–123
Takei Y, Hiroi J, Takahashi H, Sakamoto T (2014) Diverse mechanisms for body fluid regulation in teleost fishes. Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol 307(7):R778-792. https://doi.org/10.1152/ajpregu.00104.2014
Takvam M, Denker E, Gharbi N et al (2021) Sulfate homeostasis in Atlantic salmon is associated with differential regulation of salmonid-specific paralogs in gill and kidney. Physiol Rep 9(19):e15059. https://doi.org/10.14814/phy2.15059
Tang CH, Lee TH (2011) Ion-deficient environment induces the expression of basolateral chloride channel, ClC-3-like protein, in gill mitochondrion-rich cells for chloride uptake of the tilapia Oreochromis mossambicus. Physiol Biochem Zool 84(1):54–67. https://doi.org/10.1086/657161
Tingaud-Sequeira A, Calusinska M, Finn RN et al (2010) The zebrafish genome encodes the largest vertebrate repertoire of functional aquaporins with dual paralogy and substrate specificities similar to mammals. BMC Evol Biol 10:38. https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-2148-10-38
Tipsmark CK (2018) Identification of FXYD protein genes in a teleost: tissue-specific expression and response to salinity change. Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol 294(4):R1367-1378. https://doi.org/10.1152/ajpregu.00454.2007
Tipsmark CK, Madsen SS (2009) Distinct hormonal regulation of Na+, K+-atpase genes in the gill of Atlantic salmon (Salmo salar L.). J Endocrinol 203:301–310. https://doi.org/10.1677/JOE-09-0281
Tipsmark CK, Madsen SS, Seidelin M et al (2002) Dynamics of Na+, K+, 2Cl− cotransporter and Na+, K+-ATPase expression in the branchial epithelium of brown trout (Salmo trutta) and Atlantic salmon (Salmo salar). J Exp Zool 293:106–118. https://doi.org/10.1002/jez.10118
Tipsmark CK, Baltzegar DA, Ozden O et al (2008a) Salinity regulates claudin mRNA and protein expression in the teleost gill. Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol 294(3):R1004-1014. https://doi.org/10.1152/ajpregu.00112.2007
Tipsmark CK, Kiilerich P, Nilsen TO et al (2008b) Branchial expression patterns of claudin isoforms in Atlantic salmon during seawater acclimation and smoltification. Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol 294(5):R1563-1574. https://doi.org/10.1152/ajpregu.00915.2007
Tipsmark CK, Jørgensen C, Engelund M et al (2009) Effects of cortisol, growth hormone and prolactin on gill claudin expression in Atlantic salmon. Gen Comp Endocrinol 163:270–277. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ygcen.2009.04.020
Tipsmark CK, Sørensen KJ, Madsen SS (2010) Aquaporin expression dynamics in osmoregulatory tissues of Atlantic salmon during smoltification and seawater acclimation. J Exp Biol 213(3):368–379. https://doi.org/10.1242/jeb.034785
Tipsmark CK, Breves JP, Seale AP et al (2011) Switching of Na+, K+-ATPase isoforms by salinity and prolactin in the gill of a cichlid fish. J Endocrinol 209(2):237–244. https://doi.org/10.1530/JOE-10-0495
Tomy S, Chang YM, Chen YH et al (2009) Salinity effects on the expression of osmoregulatory genes in the euryhaline black porgy Acanthopagrus schlegeli. Gen Comp Endocrinol 161(1):123–132. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ygcen.2008.12.003
Trayer V, Hwang PP, Prunet P, Thermes V (2013) Assessment of the role of cortisol and corticosteroid receptors in epidermal ionocyte development in the medaka (Oryzias latipes) embryos. Gen Comp Endocrinol 194:152–161. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ygcen.2013.09.011
Tse WK, Au DW, Wong CK (2006) Characterization of ion channel and transporter mRNA expressions in isolated gill chloride and pavement cells of seawater acclimating eels. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 346(4):1181–1190. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbrc.2006.06.028
Tse WK, Au DW, Wong CK (2007) Effect of osmotic shrinkage and hormones on the expression of Na+/H+ exchanger-1, Na+/K+/2Cl- cotransporter and Na+/K+-ATPase in gill pavement cells of freshwater adapted Japanese eel, Anguilla japonica. J Exp Biol 210(Pt 12):2113–2120. https://doi.org/10.1242/jeb.004101
Tseng YC, Yan JJ, Furukawa F et al (2022) Teleostean fishes may have developed an efficient Na+ uptake for adaptation to the freshwater system. Front Physiol 13:947958. https://doi.org/10.3389/fphys.2022.947958
Vialle RA, de Souza JES, Lopes KP et al (2018) Whole genome sequencing of the pirarucu (Arapaima gigas) supports independent emergence of major teleost clades. Genome Biol Evol 10(9):2366–2379. https://doi.org/10.1093/gbe/evy130
Wang PJ, Lin CH, Hwang HH, Lee TH (2008) Branchial FXYD protein expression in response to salinity change and its interaction with Na+/K+-ATPase of the euryhaline teleost Tetraodon nigroviridis. J Exp Biol 211(Pt 23):3750–3758. https://doi.org/10.1242/jeb.018440
Wang YF, Tseng YC, Yan JJ et al (2009) Role of SLC12A10.2, a Na-Cl cotransporter-like protein, in a Cl uptake mechanism in zebrafish (Danio rerio). Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol 296(5):R1650–R1660. https://doi.org/10.1152/ajpregu.00119.2009
Wang YF, Yan JJ, Tseng YC et al (2015) Molecular physiology of an extra-renal Cl− uptake mechanism for body fluid Cl− homeostasis. Int J Biol Sci 11(10):1190–1203. https://doi.org/10.7150/ijbs.11737
Watanabe S, Kaneko T, Aida K (2005) Aquaporin-3 expressed in the basolateral membrane of gill chloride cells in Mozambique tilapia Oreochromis mossambicus adapted to freshwater and seawater. J Exp Biol 208(Pt 14):2673–2682. https://doi.org/10.1242/jeb.01684
Watanabe S, Itoh K, Kaneko T (2016) Prolactin and cortisol mediate the maintenance of hyperosmoregulatory ionocytes in gills of Mozambique tilapia: exploring with an improved gill incubation system. Gen Comp Endocrinol 232:151–159. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ygcen.2016.04.024
Weisbart M, Chakraborti PK, Gallivan G, Eales JG (1987) Dynamics of cortisol receptor activity in the gills of the brook trout, Salvelinus fontinalis, during seawater adaptation. Gen Comp Endocrinol 68:440–448
Weng CF, Lee TH, Hwang PP (1997) Immune localization of prolactin receptor in the mitochondria-rich cells of the euryhaline teleost (Oreochromis mossambicus) gill. FEBS Lett 405(1):91–94. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0014-5793(97)00162-2
Whitehead A, Roach JL, Zhang S, Galvez F (2011) Genomic mechanisms of evolved physiological plasticity in killifish distributed along an environmental salinity gradient. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 108(15):6193–6198. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1017542108
Wongdee K, Charoenphandhu N (2013) Regulation of epithelial calcium transport by prolactin: from fish to mammals. Gen Comp Endocrinol 181:235–240. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ygcen.2012.07.006
Wright PA, Wood CM (2015) Regulation of ions, acid–base, and nitrogenous wastes in elasmobranchs. In: Shadwick RE, Farrell AP, Brauner CJ (eds) Fish physiology. Academic Press, pp 279–345
Wu CY, Lee TH, Tseng DY (2023) Mineralocorticoid receptor mediates cortisol regulation of ionocyte development in tilapia (Oreochromis mossambicus). Fishes 8(6):283. https://doi.org/10.3390/fishes8060283
Xu B, Miao H, Zhang P, Li D (1997) Osmoregulatory actions of growth hormone in juvenile tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus). Fish Physiol Biochem 17:295–301. https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1007750022878
Yada T, Miyamoto K, Miura G, Munakata A (2014) Seasonal changes in gene expression of corticoid receptors in anadromous and non-anadromous strains of rainbow trout Oncorhynchus mykiss. J Fish Biol 85:1263–1278. https://doi.org/10.1111/jfb.12521
Yamaguchi K, Hara Y, Tatsumi K et al (2020) Inference of a genome-wide protein coding gene set of the inshore hagfish Eptatretus burgeri. bioRxiv. https://doi.org/10.1101/2020.07.24.218818
Yamaguchi Y, Ikeba K, Yoshida MA, Takagi W (2023) Molecular basis of the unique osmoregulatory strategy in the inshore hagfish, Eptatretus burgeri. Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol. https://doi.org/10.1152/ajpregu.00166.2023
Yan JJ, Hwang PP (2019) Novel discoveries in acid-base regulation and osmoregulation: a review of selected hormonal actions in zebrafish and medaka. Gen Comp Endocrinol 277:20–29. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ygcen.2019.03.007
Yao K, Niu PD, Gac FL, Bail PYL (1991) Presence of specific growth hormone binding sites in rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss) tissues: characterization of the hepatic receptor. Gen Comp Endocrinol 81:72–82. https://doi.org/10.1016/0016-6480(91)90126-Q
Young G, Björnsson BT, Prunet P et al (1989) Smoltification and seawater adaptation in coho salmon (Oncorhynchus kisutch): plasma prolactin, growth hormone, thryroid hormones, and cortisol. Gen Comp Endocrinol 74:335–345. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0016-6480(89)80029-2
Yu D, Ren Y, Uesaka M et al (2023) Hagfish genome illuminates vertebrate whole genome duplications and their evolutionary consequences. bioRxiv. https://doi.org/10.1101/2023.04.08.536076
Zhou B, Kelly SP, Ianowski JP, Wood CM (2003) Effects of cortisol and prolactin on Na+ and Cl- transport in cultured branchial epithelia from FW rainbow trout. Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol 285(6):R1305-1316. https://doi.org/10.1152/ajpregu.00704.2002
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors have no competing interests to declare that are relevant to the content of this article.
Data availability
Data sharing is not applicable to this article as no new data were created or analyzed.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Breves, J.P., Shaughnessy, C.A. Endocrine control of gill ionocyte function in euryhaline fishes. J Comp Physiol B (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00360-024-01555-3
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00360-024-01555-3