Abstract
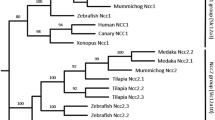
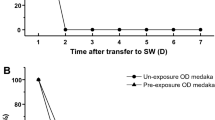
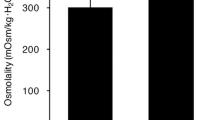
The ion regulation mechanisms of fishes have been recently studied in zebrafish (Danio rerio), a stenohaline species. However, recent advances using this organism are not necessarily applicable to euryhaline fishes. The euryhaline species medaka (Oryzias latipes), which, like zebrafish, is genetically well categorized and amenable to molecular manipulation, was proposed as an alternative model for studying osmoregulation during acclimation to different salinities. To establish its suitability as an alternative, the present study was conducted to (1) identify different types of ionocytes in the embryonic skin and (2) analyze gene expressions of the transporters during seawater acclimation. Double/triple in situ hybridization and/or immunocytochemistry revealed that freshwater (FW) medaka contain three types of ionocyte: (1) Na+/H+ exchanger 3 (NHE3) cells with apical NHE3 and basolateral Na+-K+-2Cl− cotransporter (NKCC), Na+-K+-ATPase (NKA) and anion exchanger (AE); (2) Na+-Cl− cotransporter (NCC) cells with apical NCC and basolateral H+-ATPase; and (3) epithelial Ca2+ channel (ECaC) cells [presumed accessory (AC) cells] with apical ECaC. On the other hand, seawater (SW) medaka has a single predominant ionocyte type, which possesses apical cystic fibrosis transmembrane conductance regulator (CFTR) and NHE3 and basolateral NKCC and NKA and is accompanied by smaller AC cells that express lower levels of basolateral NKA. Reciprocal gene expressions of decreased NHE3, AE, NCC and ECaC and increased CFTR and NKCC in medaka gills during SW were revealed by quantative PCR analysis.











Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ali S, Champagne DL, Spaink HP, Richardson MK (2011) Zebrafish embryos and larvae: a new generation of disease models and drug screens. Birth Defects Res C 93:115–133
Chang WJ, Hwang PP (2011) Development of zebrafish epidermis. Birth Defects Res C 93:205–214
Chang WJ, Wang YF, Hu HJ, Wang JH, Lee TH, Hwang PP (2013) Compensatory regulation of Na+ absorption by Na+/H+ exchanger and Na+-Cl− cotransporter in zebrafish (Danio rerio). Front Zool 10:46
Choi JH, Lee KM, Inokuchi M, Kaneko T (2011) Morphofunctional modifications in gill mitochondria-rich cells of Mozambique tilapia transferred from freshwater to 70 % seawater, detected by dual observations of whole-mount immunocytochemistry and scanning electron microscopy. Comp Biochem Physiol 158A:132–142
Claiborne JB, Edwards SL, Morrison-Shetlar AI (2002) Acid–base regulation in fishes: cellular and molecular mechanisms. J Exp Zool 293:302–319
Claiborne JB, Choe KP, Morrison-Shetlar AI, Weakley JC, Havird J, Freiji A, Evans DH, Edwards SL (2008) Molecular detection and immunological localization of gill Na+/H+ exchanger in the dogfish (Squalus acanthias). Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol 294:R1092–R1102
Dymowska A, Hwang PP, Goss GG (2012) Structure and function of ionocytes in the freshwater fish gill. Respir Physiol Neurobiol 184:282–292
Edwards SL, Weakley JC, Diamanduros AW, Claiborne JB (2010) Molecular identification of Na+-H+ exchanger isoforms (NHE2) in the gills of the euryhaline teleost Fundulus heteroclitus. J Fish Biol 76:415–426
Esaki M, Hoshijima K, Kobayashi S, Fukuda H, Kawakami K, Hirose S (2007) Visualization in zebrafish larvae of Na+ uptake in mitochondria-rich cells whose differentiation is dependent on foxi3a. Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol 292:R470–R480
Evans DH (2008) Teleost fish osmoregulation: what have we learned since August Krogh, Homer Smith, and Ancel Keys. Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol 295:R704–R713
Evans DH (2011) Freshwater fish gill ion transport: August Krogh to morpholinos and microprobes. Acta Physiol (Oxf) 202:349–359
Evans DH, Piermarini PM, Choe KP (2005) The multifunctional fish gill: dominant site of gas exchange, osmoregulation, acid–base regulation, and excretion of nitrogenous waste. Physiol Rev 85:97–177
Flik G, Verbost PM (1993) Calcium transport in fish gills and intestine. J Exp Biol 184:17–29
Furukawa F, Watanabe S, Inokuchi M, Kaneko T (2011) Responses of gill mitochondria-rich cells in mozambique tilapia exposed to acidic environments (pH 4.0) in combination with different salinities. Comp Biochem Physiol 158A:468–476
Furukawa F, Watanabe S, Kimura S, Kaneko T (2012) Potassium excretion through ROMK potassium channel expressed in gill mitochondrion-rich cells of Mozambique tilapia. Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol 302:R568–R576
Galvez F, Reid SD, Hawkings G, Goss GG (2002) Isolation and characterization of mitochondria-rich cell types from the gill of freshwater rainbow trout. Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol 282:R658–R668
Hiroi J, McCormick SD (2012) New insights into gill ionocyte and ion transporter function in euryhaline and diadromous fish. Respir Physiol Neurobiol 184:257–268
Hiroi J, Kaneko T, Uchida K, Hasegawa S, Tanaka M (1998) Immunolocalization of Vacuolar-Type H+-ATPase in the Yolk-Sac Membrane of Tilapia (Oreochromis mossambicus) Larvae. Zool Sci 15:447–453
Hiroi J, Kaneko T, Tanaka M (1999) In vivo sequential changes in chloride cell morphology in the yolk-sac membrane of Mozambique tilapia (Oreochromis mossambicus) embryos and larvae during seawater adaptation. J Exp Biol 202:3485–3495
Hiroi J, McCormick SD, Ohtani-Kaneko R, Kaneko T (2005) Functional classification of mitochondrion-rich cells in euryhaline Mozambique tilapia (Oreochromis mossambicus) embryos, by means of triple immunofluorescence staining for Na+/K+-ATPase, Na+/K+/2Cl− cotransporter and CFTR anion channel. J Exp Biol 208:2023–2036
Hiroi J, Yasumasu S, McCormick SD, Hwang PP, Kaneko T (2008) Evidences for an apical Na+-Cl− cotransporter involved in ion uptake in a teleost fish. J Exp Biol 211:2584–2599
Hirose S, Kaneko T, Naito N, Takei Y (2003) Molecular biology of major components of chloride cells. Comp Biochem Physiol 136B:593–620
Hootman SR, Philpott CW (1980) Accessory cells in teleost branchial epithelium. Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol 238:R199–R206
Horng JL, Lin LY, Huang CJ, Katoh F, Kaneko T, Hwang PP (2007) Knockdown of V-ATPase subunit A (atp6v1a) impairs acid secretion and ion balance in zebrafish (Danio rerio). Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol 292:R2068–R2076
Hwang PP (2009) Ion uptake and acid secretion in zebrafish (Danio rerio). J Exp Biol 212:1745–1752
Hwang PP, Chou MY (2013) Zebrafish as an animal model to study ion homeostasis. Pflugers Arch 465:1233–1247
Hwang PP, Hirano R (1985) Effects of environmental salinity on intercellular organization and junctional structure of chlorid cells in early stages of teleost development. J Exp Zool 236:115–126
Hwang PP, Lee TH (2007) New insights into fish ion regulation and mitochondrion-rich cells. Comp Biochem Physiol A 148:479–497
Hwang PP, Lin LY (2013) Gill ionic transport, acid–base regulation, and nitrogen excretion. In: Evans DH, Claiborne JB, Currie S (ed) The Physiology of Fishes, 4th eEon. CRC Press, Boca Raton
Hwang PP, Perry S (2010) Ionic and acid–base regulation. In: Perry S, Ekker, M, Farrell, AP , Brauner, CJ (ed) Fish Physiology, vol. 29. Academic, New York, pp 311–314
Hwang PP, Lee TH, Lin LY (2011) Ion regulation in fish gills: recent progress in the cellular and molecular mechanisms. Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol 301:R28–R47
Inokuchi M, Hiroi J, Watanabe S, Lee KM, Kaneko T (2008) Gene expression and morphological localization of NHE3, NCC and NKCC1a in branchial mitochondria-rich cells of Mozambique tilapia (Oreochromis mossambicus) acclimated to a wide range of salinities. Comp Biochem Physiol A 151:151–158
Inokuchi M, Hiroi J, Watanabe S, Hwang PP, Kaneko T (2009) Morphological and functional classification of ion-absorbing mitochondria-rich cells in the gills of Mozambique tilapia. J Exp Biol 212:1003–1010
Kang CK, Tsai SC, Lee TH, Hwang PP (2008) Differential expression of branchial Na+/K+-ATPase of two medaka species, Oryzias latipes and Oryzias dancena, with different salinity tolerances acclimated to fresh water, brackish water and seawater. Comp Biochem Physiol A 151:566–575
Kang CK, Tsai HJ, Liu CC, Lee TH, Hwang PP (2010) Salinity-dependent expression of a Na+, K+, 2Cl− cotransporter in gills of the brackish medaka Oryzias dancena: a molecular correlate for hyposmoregulatory endurance. Comp Biochem Physiol A 157:7–18
Katoh F, Hyodo S, Kaneko T (2003) Vacuolar-type proton pump in the basolateral plasma membrane energizes ion uptake in branchial mitochondria-rich cells of killifish Fundulus heteroclitus, adapted to a low ion environment. J Exp Biol 206:793–803
Katoh F, Cozzi RRF, Marshall WS, Goss GG (2008) Distinct Na+/K+/2Cl− cotransporter localization in kidneys and gills of two euryhaline species, rainbow trout and killifish. Cell Tissue Res 334:265–281
Lee YC, Yan JJ, Cruz SA, Horng JL, Hwang PP (2011) Anion exchanger 1b, but not sodium-bicarbonate cotransporter 1b, plays a role in transport functions of zebrafish H+-ATPase-rich cells. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol 300:C295–C307
Liao BK, Deng AN, Chen SC, Chou MY, Hwang PP (2007) Expression and water calcium dependence of calcium transporter isoforms in zebrafish gill mitochondrion-rich cells. BMC Genomics 8:354
Lin LY, Horng JL, Kunkel JG, Hwang PP (2006) Proton pump-rich cell secretes acid in skin of zebrafish larvae. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol 290:C371–C378
Lin CC, Lin LY, Hsu HH, Thermes V, Prunet P, Horng JL, Hwang PP (2012) Acid secretion by mitochondrion-rich cells of medaka (Oryzias latipes) acclimated to acidic freshwater. Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol 302:R283–R291
Liu ST, Tsung L, Horng JL, Lin LY (2013) Proton-facilitated ammonia excretion by ionocytes of medaka (Oryzias latipes) acclimated to seawater. Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol 305:R242–R251
Marshall WS, Bryson SE (1998) Transport mechanisms of seawater teleost chloride cells: an inclusive model of a multifunctional cell. Comp Biochem Physiol A 119:97–106
Pan TC, Liao BK, Huang CJ, Lin LY, Hwang PP (2005) Epithelial Ca2+ channel expression and Ca2+ uptake in developing zebrafish. Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol 289:R1202–R1211
Sardet C, Pisam M, Maetz J (1979) The surface epithelium of teleostean fish gills. Cellular and junctional adaptations of the chloride cell in relation to salt adaptation. J Cell Biol 80:96–117
Shahsavarani A, McNeill B, Galvez F, Wood CM, Goss GG, Hwang PP, Perry SF (2006) Characterization of a branchial epithelial calcium channel (ECaC) in freshwater rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss). J Exp Biol 209:1928–1943
Shen WP, Horng JL, Lin LY (2011) Functional plasticity of mitochondrion-rich cells in the skin of euryhaline medaka larvae (Oryzias latipes) subjected to salinity changes. Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol 300:R858–R868
Shih TH, Horng JL, Liu ST, Hwang PP, Lin LY (2012) Rhcg1 and NHE3b are involved in ammonium-dependent sodium uptake by zebrafish larvae acclimated to low-sodium water. Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol 302:R84–R93
Suzuki Y, Itakura M, Kashiwagi M, Nakamura N, Matuki T, Sauta H, Naito N, Takano K, Fujita T, Hirose S (1999) Identification by differential display of a hypertonicity-inducible inward rectifier potassium channel highly expressed in chloride cells. J Biol Chem 274:11376–11382
Takeda H, Shimada A (2010) The art of medaka genetics and genomics: what makes them so unique? Annu Rev Genet 44:217–241
Tang CH, Hwang LY, Shen ID, Chiu YH, Lee TH (2011) Immunolocalization of chloride transporters to gill epithelia of euryhaline teleosts with opposite salinity-induced Na+/K+-ATPase responses. Fish Physiol Biochem 37:709–724
Tse WKF, Au DWT, Wong CKC (2006) Characterization of ion channel and transporter mRNA expression in isolated gill chloride and pavement cells of seawater acclimating eels. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 346:1181–1190
van der Heijden AJ, Verbost PM, Bijvelds MJ, Atsma W, Wendelaar Bonga SE, Flik G (1999) Effects of sea water and stanniectomy on branchial Ca2+ handling and drinking rate in eel (Anguilla anguilla L.). J Exp Biol 202:2505–2511
Wagner CA, Mohebbi N, Uhlig U, Giebisch GH, Breton S, Brown D, Geibel JP (2011) The anion exchanger pendrin (SLC26A4) and renal acid–base homeostasis. Cell Physiol Biochem 28:497–504
Wang YF, Tseng YC, Yan JJ, Hiroi J, Hwang PP (2009) Role of SLC12A10.2, a Na+-Cl− cotransporter-like protein, in a Cl uptake mechanism in zebrafish (Danio rerio). Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol 296:R1650–R1660
Wilson JM, Laurent P, Tufts B, Benos DJ, Donowitz M, Vogl AW, Randall DJ (2000) NaCl uptake by the branchial epithelium in freshwater teleost fish: an immunological approach to ion-transport protein localization. J Exp Biol 203:2279–2296
Wittbrodt J, Shima A, Schartl M (2002) Medaka–a model organism from the far East. Nat Rev Genet 3:53–64
Wu SC, Horng JL, Hwang PP, Wen ZH, Lin CS, Lin LY (2010) Ammonium-dependent sodium uptake in mitochondrion-rich cells of medaka (Oryzias latipes) larvae. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol 298:C237–C250
Yan JJ, Chou MY, Kaneko T, Hwang PP (2007) Gene expression of Na+/H+ exchanger in zebrafish H+-ATPase-rich cells during acclimation to low-Na+ and acidic environments. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol 293:C1814–C1823
Acknowledgements
This study was financially supported by grants to P.P.H. from Academia Sinica and the National Science Council, Taiwan, R.O.C. We extend our thanks to Ms. Y.C. Tung for her assistance during the experiments.
Disclosures
The authors declare no conflicts of interest, financial or otherwise.
Author Contributions
Author contributions: H.-H.H., L.-Y.L., Y.-C.T. and J.-L.H. performed experiments; H.-H.H., L.-Y.L., Y.-C.T. and J.-L.H. analyzed data; H.-H.H., L.-Y.L., Y.-C.T., J.-L.H. and P.-P.H. interpreted experimental results; H.-H.H., Y.-C.T., J.-L.H. and P.-P.H. prepared figures; H.-H.H and J.-L.H. drafted the manuscript; L.-Y.L., J.-L.H. and P.-P.H. edited and revised the manuscript; J.-L.H. and P.-P.H. conceived and designed the study; P.-P.H. approved the final version of the manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Pung-Pung Hwang and Jiun-Lin Horng contributed equally to this study.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
ESM 1
(PDF 170 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hsu, HH., Lin, LY., Tseng, YC. et al. A new model for fish ion regulation: identification of ionocytes in freshwater- and seawater-acclimated medaka (Oryzias latipes). Cell Tissue Res 357, 225–243 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00441-014-1883-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00441-014-1883-z