Abstract
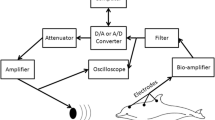
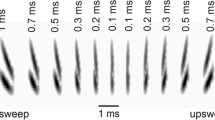
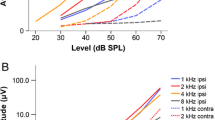
Studies of auditory temporal resolution in birds have traditionally examined processing capabilities by assessing behavioral discrimination of sounds varying in temporal structure. Here, temporal resolution of the brown-headed cowbird (Molothrus ater) was measured using two auditory evoked potential (AEP)-based methods: auditory brainstem responses (ABRs) to paired clicks and envelope following responses (EFRs) to amplitude-modulated tones. The basic patterns observed in cowbirds were similar to those found in other songbird species, suggesting similar temporal processing capabilities. The amplitude of the ABR to the second click was less than that of the first click at inter-click intervals less than 10 ms, and decreased to 30% at an interval of 1 ms. EFR amplitude was generally greatest at modulation frequencies from 335 to 635 Hz and decreased at higher and lower modulation frequencies. Compared to data from terrestrial mammals these results support recent behavioral findings of enhanced temporal resolution in birds. General agreement between these AEP results and behaviorally based studies suggests that AEPs can provide a useful assessment of temporal resolution in wild bird species.





Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- ABR:
-
Auditory brainstem response
- AEP:
-
Auditory evoked potential
- EFR:
-
Envelope following response
- MRTF:
-
Modulation rate transfer function
- SAM:
-
Sinusoidal amplitude modulated
References
Boersma P, Weenink D (2009) Praat: doing phonetics by computer, Version 5107 Computer program retrieved May 7, 2009, from http://wwwpraatorg/
Brittan-Powell EF, Dooling RJ, Gleich O (2002) Auditory brainstem responses (ABR) in adult budgerigars (Melopsittacus undulates). J Acoust Soc Am 112:999–1008
Caras ML, Brenowitz E, Rubel EW (2010) Peripheral auditory processing changes seasonally in Gambel’s white-crowned sparrow. J Comp Physiol A 196:581–599
Cook MLH, Varela RA, Goldstein JD, McCulloch SD, Bossart GD, Finneran JJ, Houser D, Mann DA (2006) Beaked whale auditory evoked potential hearing measurements. J Comp Physiol A 192:489–495
de Boer E (1996) Mechanics of the cochlea: modeling efforts. In: Dallos P, Popper AN, Fay RR (eds) The cochlea. Springer, New York, pp 258–317
Dolphin WF, Mountain DC (1992) The envelope following response: scalp potentials elicited in the Mongolian gerbil using sinusoidally AM acoustic signals. Hear Res 58:70–78
Dooling RJ, Lohr B, Dent ML (2000) Hearing in birds and reptiles. In: Dooling RJ, Popper AN, Fay RR (eds) Comparative hearing: birds and reptiles. Springer-Verlag, New York, pp 308–359
Dooling RJ, Leek MR, Gleich O, Dent ML (2002) Auditory temporal resolution in birds: discrimination of harmonic complexes. J Acoust Soc Am 112:748–759
Eggermont JJ, Spoor A (1973) Masking of action potentials in the guinea pig cochlea, its relation to adaptation. Audiol 12:221–241
Finneran JJ, Houser DS, Mase-Guthrie B, Ewing RY, Lingenfelser RG (2009) Auditory evoked potentials in a stranded Gervais’ beaked whale (Mesolplodon europaeus). J Acoust Soc Am 126:484–490
Frisina RD, Smith RL, Chamberlain SC (1990) Encoding of amplitude-modulation in the gerbil cochlear nucleus 1 A hierarchy of enhancement. Hear Res 44:99–122
Gall MD, Lucas JR (2010) Sex differences in auditory filters of brown-headed cowbirds (Molothrus ater). J Comp Physiol A 196:559–567
Gall MD, Brierley LE, Lucas JR (2011) Species and sex effects on auditory processing in brown-headed cowbirds and red-winged blackbirds Anim Behav 81:973–982
Gleich O, Klump GM (1995) Temporal-modulation transfer-functions in the European starling (Sturnus vulgaris): II responses of auditory-nerve fibres. Hear Res 82:81–92
Henry KS, Lucas JR (2008) Coevolution of auditory sensitivity and temporal resolution with acoustic signal space in three songbirds. Anim Behav 76:1659–1671
Henry KS, Lucas JR (2009) Vocally correlated seasonal auditory variation in the house sparrow (Passer domesticus). J Exp Biol 212:3817–3822
Henry KS, Lucas JR (2010) Auditory sensitivity and the frequency selectivity of auditory filters in the Carolina chickadee (Poecile carolinensis). Anim Behav 80:497–507
Henry KS, Gall MD, Lucas JR (2011) Songbirds trade off auditory frequency resolution and temporal resolution. J Comp Physiol A 197:351–359
Joris PX, Schreiner CE, Rees A (2004) Neural processing of amplitude-modulated sounds. Physiol Rev 84:541–577
Klump GM, Gleich O (1991) Gap detection in the European starling (Sturnus rulgaris): III processing in the peripheral auditory system. J Comp Physiol A 16:469–476
Konishi M (1969) Time resolution by single auditory neurones in birds. Nature 222:566–567
Köppl C (1997) Phase locking to high frequencies in the auditory nerve and cochlear nucleus magnocellularis of the barn owl, Tyto alba. J Neurosci 17:3312–3321
Kuwada S, Batra R, Maher VL (1986) Scalp potentials of normal and hearing-impaired subjects in response to sinusoidally amplitude-modulated tone. Hear Res 21:179–192
Langner G (1992) Periodicity coding in the auditory system. Hear Res 60:115–142
Lohr B, Dooling RJ, Bartone S (2006) The discrimination of temporal fine structure in call-like harmonic sounds by birds. J Comp Psychol 120:239–251
Lucas JR, Freeberg TM, Krishnan A, Long GR (2002) A comparative study of avian auditory brainstem responses: correlations with phylogeny and vocal complexity, and seasonal effects. J Comp Physiol A188:981–992
Lucas JR, Freeberg TM, Long GR, Krishnan A (2007) Seasonal variation in avian auditory evoked responses to tones: a comparative analysis of Carolina chickadees, tufted titmice, and white-breasted nuthatches. J Comp Physiol A 192:201–215
Mann DA, Colbert DE, Gaspard JC, Casper BM, Cook MLH, Reep RL, Bauer GB (2005) Temporal resolution of the Florida manatee (Trichechus manatus latirostris) auditory system. J Comp Physiol A 191:903–908
Moore BCJ (1993) Frequency analysis and pitch perception. In: Yost WA, Popper AN, Fay RR (eds) Human psychophysics. Springer, New York, pp 58–89
Noirot IC, Adler HJ, Cornil CA, Harada N, Dooling RJ, Balthazart J, Ball GF (2009) Presence of aromatase and estrogen receptor alpha in the inner ear of zebra finches. Hear Res 252:49–55
Ohashi T, Ochi K, Nishino H, Kenmochi M, Yoshida K (2005) Recovery of human compound action potential using a paired-click to stimulus paradigm. Hear Res 203:192–200
Okanoya K, Dooling RJ (1990) Minimum detectable gap in noise as a function of intensity and frequency for two avian species, budgerigars (Melopsittacus undulates) and zebra finches (Poephila guttata). Hear Res 50:185–192
Parham K, Zhao HB, Kim DO (1996) Responses of auditory nerve fibers of the unanesthetized decerebrate cat to click pairs as simulated echoes. J Neurophysiol 76:17–29
Ruggero MA (1994) Cochlear delays and traveling waves: comments on ‘Experimental look at cochlear mechanics’. Audiol 33:131–142
Supin AY, Popov VV (1995) Temporal resolution in the dolphin’s auditory system revealed by double-click evoked potential study. J Acoust Soc Am 97:2586–2593
Viemeister NF, Plack CJ (1993) Time analysis. In: Yost WA, Popper AN, Fay RR (eds) Human psychophysics. Springer, New York, pp 116–154
Wilkinson R, Howse PE (1975) Time resolution of acoustics signals by birds. Nature 258:320–321
Acknowledgments
We would like to thank E. Fernández-Juricic and P. Baumhardt for assistance in acquiring birds, and N. Robinson, L. Brierley, K. Ronald, J. Losier, J. Randolet, and B. Moore for their feedback on this manuscript. All methods were approved by the Purdue Animal Care and Use Committee under protocol number 08–132.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gall, M.D., Henry, K.S. & Lucas, J.R. Two measures of temporal resolution in brown-headed cowbirds (Molothrus ater). J Comp Physiol A 198, 61–68 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00359-011-0687-9
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00359-011-0687-9