Abstract
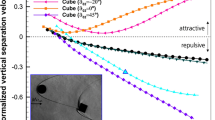
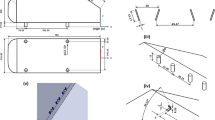
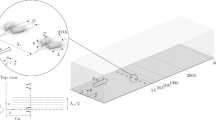
The wake/boundary–layer interactions over a cylinder/airfoil configuration are investigated using hydrogen bubble visualization and time-resolved particle image velocimetry. The chord Reynolds number of the NACA0012 airfoil is fixed at Rec = 6500. Both the wake-triggered double-secondary vortices topology reported over a multi-element airfoil configuration and the wake-triggered single-secondary vortex topology reported over a cylinder/flat-plate configuration are observed with the current configuration, as the vertical interval (yc/c) between the cylinder and the leading edge of the airfoil increases. The wake disturbances are found to penetrate the boundary layer above the airfoil with different patterns, leading to the change of wake-triggered topology. The wake-triggered secondary vortices effectively suppress the flow separation above the airfoil via a “momentum injection” mechanism, contributing to the enhancement of aerodynamic performance.
Graphical abstract


















Similar content being viewed by others
Availability of data and materials
Available from the authors upon reasonable request.
References
Basley J, Pastur L, Lusseyran F, Faure TM, Delprat N (2011) Experimental investigation of global structures in an incompressible cavity flow using time-resolved PIV. Exp Fluids 50(4):905–918
Boutilier MSH, Yarusevych S (2012) Effects of end plates and blockage on low-Reynolds-number flows over airfoils. AIAA J 50(7):1547–1559
Burgmann S, Dannemann J, Schröder W (2008) Time-resolved and volumetric PIV measurements of a transitional separation bubble on an SD7003 airfoil. Exp Fluids 44(4):609–622
Champagnat F, Plyer A, Le Besnerais G, Leclaire B, Davoust S, Le Sant Y (2011) Fast and accurate PIV computation using highly parallel iterative correlation maximization. Exp Fluids 50(4):1169–1182
Coull JD, Hodson HP (2011) Unsteady boundary-layer transition in low-pressure turbines. J Fluid Mech 681:370–410
Dellacasagrande M, Barsi D, Lengani D, Simoni D, Verdoya J (2020) Response of a flat plate laminar separation bubble to Reynolds number, free-stream turbulence and adverse pressure gradient variation. Exp Fluids 61:128
Doligalski T, Walker J (1984) The boundary layer induced by a convected two-dimensional vortex. J Fluid Mech 139:1–28
Durbin P, Wu X (2007) Transition beneath vortical disturbances. Annu Rev Fluid Mech 39(1):107–128
Forrest JS, Owen I, Padfield GD, Hodge SJ (2012) Ship-helicopter operating limits prediction using piloted flight simulation and time-accurate airwakes. J Aircr 49(4):1020–1031
Ganapathisubramani B, Longmire EK, Marusic I (2003) Characteristics of vortex packets in turbulent boundary layers. J Fluid Mech 478:35–46
Giret J-C, Sengissen A, Moreau S, Sanjosé M, Jouhaud J-C (2015) Noise source analysis of a rod–airfoil configuration using unstructured large-eddy simulation. AIAA J 53(4):1062–1077
Hain R, Kähler C, Radespiel R (2009) Dynamics of laminar separation bubbles at low-Reynolds-number aerofoils. J Fluid Mech 630:129–153
He G-S, Wang J-J, Pan C (2013) Initial growth of a disturbance in a boundary layer influenced by a circular cylinder wake. J Fluid Mech 718:116–130
He G-S, Pan C, Feng L-H, Gao Q, Wang J-J (2016) Evolution of lagrangian coherent structures in a cylinder-wake disturbed flat plate boundary layer. J Fluid Mech 792:274–306
He G-S, Wang J-J, Pan C, Feng L-H, Gao Q, Rinoshika A (2017) Vortex dynamics for flow over a circular cylinder in proximity to a wall. J Fluid Mech 812:698–720
Henning A, Koop L, Ehrenfried K (2010) Simultaneous particle image velocimetry and microphone array measurements on a rod-airfoil configuration. AIAA J 48(10):2263–2273
Hodson HP, Howell RJ (2005) Bladerow interactions, transition, and high-lift aerofoils in low-pressure turbines. Annu Rev Fluid Mech 37(1):71–98
Hosseinverdi S, Fasel HF (2019) Numerical investigation of laminar–turbulent transition in laminar separation bubbles: The effect of free-stream turbulence. J Fluid Mech 858:714–759
Huang RF, Wu JS (2007) Effects of cylinder wake on seperated boundary layer of a wing. AIAA J 45(1):247–256
Jacob MC, Boudet J, Casalino D, Michard M (2005) A rod-airfoil experiment as a benchmark for broadband noise modeling. Theor Comput Fluid Dyn 19(3):171–196
Jiang Y, Mao M-L, Deng X-G, Liu H-Y (2015) Numerical investigation on body-wake flow interaction over rod-airfoil configuration. J Fluid Mech 779:1–35
Jones L, Sandberg R, Sandham N (2010) Stability and receptivity characteristics of a laminar separation bubble on an aerofoil. J Fluid Mech 648:257–296
Kurelek JW, Lambert AR, Yarusevych S (2016) Coherent structures in the transition process of a laminar separation bubble. AIAA J 54(8):2295–2309
Kyriakides NK, Kastrinakis EG, Nychas SG, Goulas A (1999) Aspects of flow structure during a cylinder wake-induced laminar/turbulent transition. AIAA J 37(10):1197–1205
Lefebvre JN, Jones AR (2019) Experimental investigation of airfoil performance in the wake of a circular cylinder. AIAA J 57(7):2808–2818
Linehan T, Mohseni K (2020) On the maintenance of an attached leading-edge vortex via model bird alula. J Fluid Mech 897:A17
Lorenzoni V, Tuinstra M, Scarano F (2012) On the use of time-resolved particle image velocimetry for the investigation of rod–airfoil aeroacoustics. J Sound Vib 331(23):5012–5027
Lua KB, Lim T, Yeo K (2011) Effect of wing–wake interaction on aerodynamic force generation on a 2D flapping wing. Exp Fluids 51(1):177–195
Ma L-Q, Feng L-H, Pan C, Gao Q, Wang J-J (2015) Fourier mode decomposition of PIV data. Sci China Technol Sci 58(11):1935–1948
Mandal AC, Dey J (2011) An experimental study of boundary layer transition induced by a cylinder wake. J Fluid Mech 684:60–84
Meyer R (1958) The effect of wakes on the transient pressure and velocity distributions in turbomachines. Trans ASME 80(7):1544–1552
Munekata M, Kawahara K, Udo T, Yoshikawa H, Ohba H (2006) An experimental study on aerodynamic sound generated from wake interference of circular cylinder and airfoil vane in tandem. J Therm Sci 15(4):342–348
Obabko A, Cassel K (2002) Navier–stokes solutions of unsteady separation induced by a vortex. J Fluid Mech 465:99–130
Pan C, Wang H-P, Wang J-J (2013) Phase identification of quasi-periodic flow measured by particle image velocimetry with a low sampling rate. Meas Sci Technol 24(5):055305
Pan C, Wang J-J, Zhang P-F, Feng L-H (2008) Coherent structures in bypass transition induced by a cylinder wake. J Fluid Mech 603:367–389
Pan C, Xue D, Xu Y, Wang J-J, Wei R-J (2015) Evaluating the accuracy performance of Lucas-Kanade algorithm in the circumstance of PIV application. Sci China Phys Mech 58(10):1–16
Peridier VJ, Smith F, Walker J (1991) Vortex-induced boundary-layer separation. Part 1. The unsteady limit problem Re→∞. J Fluid Mech 232:99–131
Rao VN, Tucker P, Jefferson-Loveday R, Coull J (2013) Large eddy simulations in low-pressure turbines: Effect of wakes at elevated free-stream turbulence. Int J Heat Fluid Flow 43:85–95
Sarkar S (2009) Influence of wake structure on unsteady flow in a low pressure turbine blade passage. J Turbomach 131(4):041016
Scillitoe AD, Tucker PG, Adami P (2019) Large eddy simulation of boundary layer transition mechanisms in a gas-turbine compressor cascade. J Turbomach 141(6):061008
Simoni D, Ubaldi M, Zunino P, Lengani D, Bertini F (2012) An experimental investigation of the separated-flow transition under high-lift turbine blade pressure gradients. Flow Turbul Combust 88(1):45–62.
Squire L (1989) Interactions between wakes and boundary-layers. Prog Aerosp Sci 26(3):261–288
Stieger R, Hodson H (2003) The transition mechanism of highly-loaded LP turbine blades. In: The 2003 international joint power generation conference, pp 779–788
Thomas FO, Nelson R, Liu X (2000) Experimental investigation of the confluent boundary layer of a high-lift system. AIAA J 38(6):978–988
Walker J. (1978) The boundary layer due to rectilinear vortex. Proc Roy Soc Lond Math Phys Sci Data 359(1697):167–188.
Wang J-S, Wang J-J (2021a) Wake-induced transition in the low-Reynolds-number flow over a multi-element airfoil. J Fluid Mech 915:A28
Wang J-S, Wang J-J (2021b) Vortex dynamics for flow around the slat cove at low Reynolds numbers. J Fluid Mech 919:A27
Wang JS, Wang JJ, Kim KC (2019) Wake/shear layer interaction for low-Reynolds-number flow over multi-element airfoil. Exp Fluids 60:16
Welch P (1967) The use of fast fourier transform for the estimation of power spectra: a method based on time averaging over short, modified periodograms. IEEE Trans Audio Electroacoust 15(2):70–73
Wissink JG, Rodi W, Hodson HP (2006) The influence of disturbances carried by periodically incoming wakes on the separating flow around a turbine blade. Int J Heat Fluid Flow 27(4):721–729
Wissink JG, Zaki TA, Rodi W, Durbin PA (2014) The effect of wake turbulence intensity on transition in a compressor cascade. Flow Turbul Combust 93(4):555–576.
Wu X, Durbin PA (2001) Evidence of longitudinal vortices evolved from distorted wakes in a turbine passage. J Fluid Mech 446:199–228
Wu X, Jacobs RG, Hunt JC, Durbin PA (1999) Simulation of boundary layer transition induced by periodically passing wakes. J Fluid Mech 398:109–153
Zaki T, Wissink J, Durbin P, Rodi W (2009) Direct computations of boundary layers distorted by migrating wakes in a linear compressor cascade. Flow Turbul Combust 83(3):307–322.
Zaki TA, Wissink JG, Rodi W, Durbin PA (2010) Direct numerical simulations of transition in a compressor cascade: The influence of free-stream turbulence. J Fluid Mech 665:57–98
Zhang Z, Wang Z, Gursul I (2020) Lift enhancement of a stationary wing in a wake. AIAA J 58(11):4613–4619
Zhao Y, Sandberg RD (2020) Bypass transition in boundary layers subject to strong pressure gradient and curvature effects. J Fluid Mech 888:A4
Zhou J, Adrian RJ, Balachandar S, Kendall T (1999) Mechanisms for generating coherent packets of hairpin vortices in channel flow. J Fluid Mech 387:353–396
Acknowledgements
The authors really appreciate the financial support of the National Natural Science Foundation of China and the China Postdoctoral Science Foundation. The authors also thank the anonymous reviewers whose comments and suggestions greatly improved the quality and clarity of the manuscript.
Funding
National Natural Science Foundation of China (11721202) and the China Postdoctoral Science Foundation (2021M700010 and 2022T150036).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
All authors contributed to the study conception and reviewed the manuscript. J-S W contributed to the data analysis, methodology, original draft writing and editing; J W conducted the experiments and advised on the data analysis; J-J W contributed to the supervision, methodology and editing.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Ethical approval
No applicable.
Additional information
Publisher's note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, JS., Wu, J. & Wang, JJ. Wake-triggered secondary vortices over a cylinder/airfoil configuration. Exp Fluids 64, 6 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00348-022-03546-y
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00348-022-03546-y