Abstract
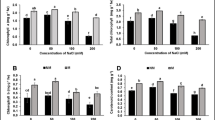
Plant salt damage caused by soil salinization is a common problem in the world. Regulating plant salt tolerance is regarded as one of the effective ways to solve soil salt damage. Choline chloride and rhamnolipid, two new materials, play a positive role in improving plant stress resistance, but the effects of combined application of choline chloride and rhamnolipid on plant salt tolerance are not clear. In this study, Provence tomato was used as material to study the effects of combined application of choline chloride and rhamnolipid on the growth, development, and physiological characteristics of tomato in moderately salinized soil. The results showed that the addition of choline chloride and rhamnolipid complexed with organic manures to soil decreased superoxide anion (O2−), malondialdehyde (MAD), and the ratio of Na+/K+ and increased peroxidase (POD) activity and osmolytes biosynthesis of proline. These indexes were related to the ratio of choline chloride and rhamnolipid, and the change range was the largest at an appropriate amount. Additionally, choline chloride and rhamnolipid application not only increased chlorophyll content, net photosynthetic rate, transpiration rate, and yield but also fruit quality, including soluble sugar and VC. Our findings highlight that choline chloride and rhamnolipid may be proposed as effective methods to improve salinity tolerance and increase yield and quality of plants in agriculture.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adetunji C, Oloke J, Kumar A, Swaranjit S, Akpor B (2017) Synergetic effect of rhamnolipid from Pseudomonas aeruginosa C1501 and phytotoxic metabolite from Lasiodiplodia pseudotheobromae C1136 on Amaranthus hybridus L. And Echinochloa crus-galli weeds. Environ Sci Pollut R 24(15):13700–13709. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-017-8983-8
Alasvandyari F, Mahdavi B, Madah H (2017) Glycine betaine affects the antioxidant system and ion accumulation and reduces salinity-induced damage in safflower seedlings. Arch Biol Sci 69(1):139–147. https://doi.org/10.2298/ABS160216089A
Alberte RS, Thornber JP (1977) Water stress effects on the content and organization of chlorophyll in mesophyll and bundle sheath chloroplasts of maize. Plant Physiol 59(3):351–353. https://doi.org/10.1104/PP.59.3.351
Altaf MA, Shahid R, Ren M, Altaf MM, Khan LU, Shahid S, Jahan MS (2021) Melatonin alleviates salt damage in tomato seedling: a root architecture system, photosynthetic capacity, ion homeostasis, and antioxidant enzymes analysis. Sci Hortic-Amsterdam. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scienta.2021.110145
Ashraf M, Shahzad SM, Imtiaz M, Rizwan MS (2018) Salinity effects on nitrogen metabolism in plants - focusing on the activities of nitrogen metabolizing enzymes: a review. J Plant Nutr 41(8):1065–1081. https://doi.org/10.1080/01904167.2018.1431670
Balusamy SR, Rahimi S, Sukweenadhi J, Sunderraj S, Shanmugam R, Thangavelu L, Mijakovic I, Perumalsamy H (2022) Chitosan, chitosan nanoparticles and modified chitosan biomaterials, a potential tool to combat salinity stress in plants. Carbohyd Polym 284:119189. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2022.119189
Bao SD (2000) Soil agro-chemistrical analysis. China Agriculture Press, Beijing
Câmara JM, Sousa MA, Barros Neto EL (2019) Optimization and characterization of biosurfactant rhamnolipid production by pseudomonas aeruginosa isolated from an artificially contaminated soil. J Surfactants Deterg 22(4):711–719. https://doi.org/10.1002/jsde.12287
Cao X, Islam MN, Zhong S, Pan X, Song M, Shang F, Nie H, Xu W, Duan Z (2020) Drying kinetics, antioxidants, and physicochemical properties of litchi fruits by ultrasound-assisted hot air-drying. J Food Biochem 44(1):e13073. https://doi.org/10.1111/jfbc.13073
Cui F, Sui N, Duan GY, Liu YY, Han Y, Liu SS, Wan SB, Li GW (2018) Identification of metabolites and transcripts involved in salt stress and recovery in peanut. Front Plant Sci 9:217. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpls.2018.00217
Cui DJ, Yin Y, Wang JQ, Wang ZW, Ding HB, Ma RN, Jiao Z (2019) Research on the physio-biochemical mechanism of non-thermal plasma-regulated seed germination and early seedling development in arabidopsis. Front Plant Sci 10:1322. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpls.2019.01322
Delauney AJ, Verma DPS (1993) Proline biosynthesis and osmoregulation in plants. Plant J 4:215–223
Delfani K, Asadi M, Golein B, Babakhani B, Razeghi Jadid R (2022) Foliar application of glycine betaine affects morpho-physiological, biochemical and fruit quality traits of thomson navel orange under deficit irrigation. J Plant Growth Regul. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00344-022-10753-8
Ding TT, Li PF, Cao L, Long XY, Liu B, Ma YQ (2021) Effects of dry matter translocation on yield formation of wheat with different genotypes under drought stress. Agric Res Arid Areas 39(06):62–72
Ding F, Qiang X, Jia Z, Li L, Hu J, Yin M, Xia S, Chen B, Qi J, Li Q, Gao Y, Zhang S, Sun S, Ma C, Yang L, Li Y (2022) Knockout of a novel salt responsive gene SlABIG1 enhance salinity tolerance in tomato. Environ Exp Bot 200:104903. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envexpbot.2022.104903
Dong X, Sun L, Guo J, Liu L, Han G, Wang B (2021) Exogenous boron alleviates growth inhibition by NaCl stress by reducing Cl− uptake in sugar beet (Beta vulgaris). Plant Soil 464(1–2):423–439. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11104-021-04946-5
Elayaraja D, Sathiyamurthi S (2020) Influence of organic manures and micronutrients fertilization on the soil properties and yield of sesame (Sesamum indicum L.) in coastal saline soil. Indian J Agric Res 54(1):89–94. https://doi.org/10.18805/IJARe.A-5422
Fao, 2021. Global soil partnership. https://www.fao.org/global-soil-partnership/resources/highlights/detail/en/c/1445579/(accessed).
Galli V, Da Silva MR, Perin EC, Borowski JM, Bamberg AL, Rombaldi CV (2016) Mild salt stress improves strawberry fruit quality. LWT 73:693–699. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.lwt.2016.07.001
Gao JF (2006) Plant physiology experiment instruction. Science Press, Beijing
Gao Q, Feng D, Liu J, Zhang JM, Han QS (2021) Main mechanisms and classification of exogenous substances alleviating plant salt stress. J Plant Nutr Fertil 27(11):2030–2044
Guo L, Yu H, Kharbach M, Wang J (2021) The response of nutrient uptake, photosynthesis and yield of tomato to biochar addition under reduced nitrogen application. Agronomy 11(8):1598. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy11081598
Ha J, Lee H, Jung J, Park C (2017) Thermo-Induced maintenance of photo-oxidoreductases underlies plant autotrophic development. Dev Cell 41(2):170–179. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.devcel.2017.03.005
Han SH, Kim DH, Kim GN, Byun JK (2011) Changes of leaf characteristics, pigment content and photosynthesis of forsythia saxatilis under two different light intensities. J Korean Forest Soc 100(4):609–615
Helle SS, Duff SJ, Cooper DG (1993) Effect of surfactants on cellulose hydrolysis. Biotechnol Bioeng 42(5):611–617. https://doi.org/10.1002/bit.260420509
Huang BC (2022) Effects of rhamnolipid and nano silicon fertilizer on salt tolerance of cotton. Tarim university.
Hussain I, Saleem MH, Mumtaz S, Rasheed R, Ashraf MA, Maqsood F, Rehman M, Yasmin H, Ahmed S, Ishtiaq M, Anwar S, Ali S (2021) Choline chloride mediates chromium tolerance in spinach (Spinacia oleracea L.) by restricting its uptake in relation to morpho-physio-biochemical attributes. J Plant Growth Regul 41(4):1594–1614. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00344-021-10401-7
Ivushkin K, Bartholomeus H, Bregt AK, Pulatov A, Kempen B, de Sousa L (2019) Global mapping of soil salinity change. Remote Sens Environ 231:111260. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rse.2019.111260
Kalaivani K, Nadarajah, (2020) ROS homeostasis in abiotic stress tolerance in plants. Int J Mol Sci 21(15):5208. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21155208
Li HS (2000) Plant physiological and biochemical experiment principles and techniques. Higher Education Press, Beijing
Lin S, Zeng S, A B, Yang X, Yang T, Zheng G, Mao G, Wang Y (2021) Integrative analysis of transcriptome and metabolome reveals salt stress orchestrating the accumulation of specialized metabolites in lycium barbarum L. Fruit. Int J Mol Sci. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22094414
Ma QQ, Wang W, Li YH, Li DQ, Zou Q (2006) Alleviation of photoinhibition in drought-stressed wheat (Triticum aestivum) by foliar-applied glycinebetaine. J Plant Physiol 163(2):165–175. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jplph.2005.04.023
Mahmood T, Ashraf M, Shahbaz M (2009) Does exogenous application of glycinebetaine as a pre-sowing seed treatment improve growth and regulate some key physiological attributes in wheat plants grown under water deficit conditions? Pak J Bot 41(3):1291–1302
Malekzadeh P (2015) Influence of exogenous application of glycinebetaine on antioxidative system and growth of salt-stressed soybean seedlings (Glycine max L.). Physiol Mol Biol Plants 21(2):225–232. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12298-015-0292-4
Mauromicale G, Ierna A, Marchese M (2006) Chlorophyll fluorescence and chlorophyll content in field-grown potato as affected by nitrogen supply, genotype, and plant age. Photosynthetica. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11099-005-0161-4
Munoz-Cupa C, Bassi A, Liu L (2022) Investigation of micellar-enhanced ultrafiltration (MEUF) using rhamnolipid for heavy metal removal from desalter effluent. Can J Chem Eng 100(9):2322–2330. https://doi.org/10.1002/cjce.24422
Nachshon U (2018) Cropland soil salinization and associated hydrology: trends, processes and examples. Water-Sui 10(8):1030. https://doi.org/10.3390/w10081030
Pourfadakari S, Ghafari S, Takdastan A, Jorfi S (2021) A salt resistant biosurfactant produced by moderately halotolerant Pseudomonas aeruginosa (AHV-KH10) and its application for bioremediation of diesel-contaminated sediment in saline environment. Biodegradation 32(3):327–341. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10532-021-09941-2
Qin C, Ahanger MA, Zhou J, Ahmed N, Wei C, Yuan S, Ashraf M, Zhang L (2020) Beneficial role of acetylcholine in chlorophyll metabolism and photosynthetic gas exchange in Nicotiana benthamiana seedlings under salinity stress. Plant Biol (stuttg) 22(3):357–365. https://doi.org/10.1111/plb.13079
Ram G, Melvin JM, Devraj S, Benson A (2019) Rhamnolipid production using Shewanella seohaensis BS18 and evaluation of its efficiency along with phytoremediation and bioaugmentation for bioremediation of hydrocarbon contaminated soils. Int J Phytoremediation 21(13):1375–1383. https://doi.org/10.1080/15226514.2019.1633254
Rehman MZU, Rizwan M, Ali S, Fatima N, Yousaf B, Naeem A, Sabir M, Ahmad HR, Ok YS (2016) Contrasting effects of biochar, compost and farm manure on alleviation of nickel toxicity in maize (Zea mays L.) in relation to plant growth, photosynthesis and metal uptake. Ecotox Environ Safe 133:218–225. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2016.07.023
Riaz S, Hussain I, Ibrahim M, Rasheed R, Ashraf MA (2021) Choline chloride mediates salinity tolerance in cluster bean (Cyamopsis tetragonoloba L.) by improving growth, oxidative defense, and secondary metabolism. Dose-Response : a Publication of International Hormesis Society. 19(4):1485804978. https://doi.org/10.1177/15593258211055026
Rossi M, Borromeo I, Capo C, Glick BR, Gallo MD, Pietrini F, Forni C (2021) PGPB Improve Photosynthetic Activity and Tolerance to Oxidative Stress in Brassica napus Grown on Salinized Soils. Appl Sci 11(23):11442. https://doi.org/10.3390/app112311442
Salama KHA, Mansour MMF (2015) Choline priming-induced plasma membrane lipid alterations contributed to improved wheat salt tolerance. Acta Physiol Plant. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11738-015-1934-4
Sancheti A, Ju LK (2020) Rhamnolipid effects on water imbibition, germination, and initial root and shoot growth of soybeans. J Surfactants Deterg 23(2):371–381. https://doi.org/10.1002/jsde.12383
Sarabi B, Ghashghaie J (2022) Evaluating the physiological and biochemical responses of melon plants to NaCl salinity stress using supervised and unsupervised statistical analysis. Plant Stress. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.stress.2022.100067
Seminario A, Song L, Zulet A, Nguyen HT, Gonzalez EM, Larrainzar E (2017) Drought stress causes a reduction in the biosynthesis of ascorbic acid in soybean plants. Front Plant Sci 8:1042. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpls.2017.01042
Shalata A, Neumann PM (2001) Exogenous ascorbic acid (vitamin C) increases resistance to salt stress and reduces lipid peroxidation. J Exp Bot 52(364):2207–2211. https://doi.org/10.1093/jexbot/52.364.2207
Shan T, Jin P, Zhang Y, Huang Y, Wang X, Zheng Y (2016) Exogenous glycine betaine treatment enhances chilling tolerance of peach fruit during cold storage. Postharvest Biol Tec 114:104–110. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.postharvbio.2015.12.005
Singh R, Glick BR, Rathore D (2018) Biosurfactants as a biological tool to increase micronutrient availability in soil: A review. Pedosphere 28(2):170–189. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1002-0160(18)60018-9
Sofy MR, Elhawat N, Alshaal T (2020) Glycine betaine counters salinity stress by maintaining high K+/Na+ ratio and antioxidant defense via limiting Na+ uptake in common bean (Phaseolus vulgaris L.). Ecotox Environ Safe 200:110732. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2020.110732
Strand A, Zrenner R, Trevanion S, Stitt M, Gustafsson P, Gardestrom P (2000) Decreased expression of two key enzymes in the sucrose biosynthesis pathway, cytosolic fructose-1,6-bisphosphatase and sucrose phosphate synthase, has remarkably different consequences for photosynthetic carbon metabolism in transgenic Arabidopsis thaliana. Plant J 23(6):759–770. https://doi.org/10.1046/j.1365-313x.2000.00847.x
Syeed S, Sehar Z, Masood A, Anjum NA, Khan NA (2021) Control of elevated ion accumulation, oxidative stress, and lipid peroxidation with salicylic Acid-Induced accumulation of glycine betaine in Salinity-Exposed vigna radiata l. Appl Biochem Biotech 193(10):1–20. https://doi.org/10.1007/S12010-021-03595-9
Taghadosi MM, Hasanlou M (2017) Trend analysis of soil salinity in different land cover types using landsat time series data (case study bakhtegan salt lake). Int Arch Photogrammetry Remote Sens Spatial Inf Sci. https://doi.org/10.5194/isprs-archives-XLII-4-W4-251-2017
Tandra SZ, Hassan L, Hannan A, Jahan J, Sagor GHM (2022) Screening and biochemical responses of tomato (Lycopersicum esculentum L.) genotypes for salt tolerance. Acta Physiol Plant. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11738-022-03376-9
Unwin N (2022) Structure of a cholinergic cell membrane. Proc Nat Acad Sci. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.2207641119
Upadhyay SK, Chauhan PK (2022) Optimization of eco-friendly amendments as sustainable asset for salt-tolerant plant growth-promoting bacteria mediated maize (Zea Mays L.) plant growth, Na uptake reduction and saline soil restoration. Environ Res 211:113081. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envres.2022.113081
van Zelm E, Zhang Y, Testerink C (2020) Salt tolerance mechanisms of plants. Annu Rev Plant Biol 71(1):403–433. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev-arplant-050718-100005
Wang W, Vinocur B, Altman A (2003) Plant responses to drought, salinity and extreme temperatures: towards genetic engineering for stress tolerance. Planta 218(1):1–14. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00425-003-1105-5
Wang MY, Li JP, Li JJ (2021) Research on china’s facility cultivation efficiency from the perspective of cost benefit—taking cucumber and tomato cultivation as an example. Chinese J Agric Res Reg Plan 42(12):170–183
Wei YT, Liu DY, Zhang W, Yu SB, Wu YK (2020) Characteristics and spatial variability of saline soil in desert-wet ecosystem area, Gansu Province. China Hydrogeol Eng Geol 47(02):183–190. https://doi.org/10.16030/j.cnki.issn.1000-3665.201906021
Wei L, Zhao H, Wang B, Wu X, Lan R, Huang X, Chen B, Chen G, Jiang C, Wang J, Liu Y, Zheng Q (2021) Exogenous melatonin improves the growth of rice seedlings by regulating redox balance and ion homeostasis under salt stress. J Plant Growth Regul 41(6):2108–2121. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00344-021-10417-z
Xiao Y, Zhao GX, Li T, Zhou X, Li JM (2019) Soil salinization of cultivated land in Shandong Province, China—Dynamics during the past 40 years. Land Degrad Dev 30(4):426–436. https://doi.org/10.1002/ldr.3236
Yang Y, Guo Y (2018) Unraveling salt stress signaling in plants. J Integr Plant Biol 60(09):796–804. https://doi.org/10.1111/jipb.12689
Yang H, Du T, Mao X, Ding R, Shukla MK (2019) A comprehensive method of evaluating the impact of drought and salt stress on tomato growth and fruit quality based on EPIC growth model. Agr Water Manage 213:116–127. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.agwat.2018.10.010
Yang XH, Luo YQ, Yang HC, Zhang FH, Lei JJ (2021) Soil salinity retrieval and spatial distribution of oasis farmland in Manasi river basin. J Arid Land Res Environ 35(02):156–161. https://doi.org/10.13448/j.cnki.jalre.2021.054
Yang YP (2021) Effects of rhamnolipids on the physical and chemical properties of salted cotton field soil and cotton growth.Tarim university.
Yao W, Xu T, Farooq SU, Jin P, Zheng Y (2018) Glycine betaine treatment alleviates chilling injury in zucchini fruit (Cucurbita pepo L.) by modulating antioxidant enzymes and membrane fatty acid metabolism. Postharvest Biol Tec 144:20–28. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.postharvbio.2018.05.007
Yin XW, Feng Q, Li Y, Deo RC, Liu W, Zhu M, Zheng XJ, Liu R (2022) An interplay of soil salinization and groundwater degradation threatening coexistence of oasis-desert ecosystems. Sci Total Environ 806(P2):150599. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.SCITOTENV.2021.150599
Yuan YX (2019) The production rate and malondialdehyde content of different tissue superoxide anions in wetland phrgmintes Australis. Sci Technol Eng 19(11):40–43
Zhang YP (2011) Effects of choline chloride on osmotic adjustment substances and reactive oxygen species metabolism of cucumber seedlings under salt stress. Acta Botan Boreali-Occiden Sin 31(01):137–143
Zhang Y, Jin P, Huang Y, Shan T, Wang L, Li Y, Zheng Y (2016) Effect of hot water combined with glycine betaine alleviates chilling injury in cold-stored loquat fruit. Postharvest Biol Tec 118:141–147. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.postharvbio.2016.04.010
Zhang YJ, Liao ZY, Zhao BS (2020) Glycine betaine: biosynthesis and biological function in halophilic microorganisms. Acta Microbiol Sinica 60(06):1074–1089. https://doi.org/10.13343/j.cnki.wsxb.20190536
Zhang K, Lyu W, Gao Y, Zhang X, Sun Y, Huang B (2021b) Choline-Mediated lipid reprogramming as a dominant salt tolerance mechanism in grass species lacking glycine betaine. Plant Cell Physiol 61(12):2018–2030. https://doi.org/10.1093/pcp/pcaa116
Zhang XH, Ma C, Zhang L, Su M, Wang J, Zheng S, Zhang TG (2022) GR24-mediated enhancement of salt tolerance and roles of H2O2 and Ca2+ in regulating this enhancement in cucumber. J Plant Physiol 270:153640. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.JPLPH.2022.153640
Zhang CF, Wang XP, Yang ZJ, Zheng G, Yang YP, Zhou HH, Zhang DD (2021a) Application of rhamnolipid in controlling soil and increasing cotton yield in saline-alkali soil.
Zhao S, Zhang Q, Liu M, Zhou H, Ma C, Wang P (2021) Regulation of plant responses to salt stress. Int J Mol Sci 22(9):4609. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22094609
Zhu H, Yang JS, Yao RJ, Gao S, Cao YF, Sun YP (2019) Effects of partial substitution of organic nitrogen for inorganic nitrogen in fertilization on salinity and nitrogen utilization in salinized coastal soil. Chinese J Eco-Agric 27(03):441–450. https://doi.org/10.13930/j.cnki.cjea.180689
Zhu L, Jia X, Li M, Wang Y, Zhang J, Hou J, Wang X (2021) Associative effectiveness of bio-organic fertilizer and soil conditioners derived from the fermentation of food waste applied to greenhouse saline soil in Shan Dong Province. China Appl Soil Ecol 167:104006. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsoil.2021.104006
Acknowledgements
The authors appreciate the Shaanxi Provincial Key Research and Development Project (2022ZDLNY02-05) and the major project for science and technology cooperation in Erdos City, Inner Mongolia Autonomous Region (k4050122019) for financial support of this research.
Funding
Shaanxi Provincial Key Research and Development Project, 2022ZDLNY02-05, Xudong Wang. Government of Inner Mongolia Autonomous Region, k4050122019, Xudong Wang.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
HK contributed to experimental work, data analysis, and writing and preparation of the original draft. SX contributed to experimental work and data analysis. YG and YH contributed to experimental work. XW contributed to funding acquisition and conceptualization.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Handling Editor: Branka Salopek Sondi.
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Hu, K., Xu, S., Gao, Y. et al. Choline Chloride and Rhamnolipid Combined with Organic Manures Improve Salinity Tolerance, Yield, and Quality of Tomato. J Plant Growth Regul 42, 4118–4130 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00344-022-10875-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00344-022-10875-z