Abstract
Sensitive detection of hydrogen sulfide (H2S) at different pressure levels using a cantilever-enhanced photoacoustic detector in combination with a telecom NIR L-band laser source is reported. Amplitude and wavelength modulation schemes for photoacoustic signal generation are compared. A detection limit (3σ) of 8 ppmv was achieved for amplitude modulation mode with a 50-s averaging time for the H2S absorption near 1.6 µm. As compared to simulated spectra, the cantilever-enhanced photoacoustic detection approach in combination with the sufficiently stable and narrow bandwidth NIR laser is able to reproduce the rotationally resolved H2S spectrum at low pressures of 300 mbar.
Similar content being viewed by others
Avoid common mistakes on your manuscript.
1 Introduction
Sensitive detection of hydrogen sulfide (H2S) is essential for production control and environmental monitoring purposes in the field of petrochemical, paper and pulp as well as biotechnological processes. The occupational exposure limit recommended by the European Agency for Safety and Health at Work (OSHA) is 7.1 mg m−3 (5 ppmv) [1]. The permissible exposure limit value for H2S, recommended by US National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health (NIOSH), is 10 ppmv, the Immediately Dangerous to Life and Health (IDLH) level is 300 ppmv and lethal concentrations are in the range of 2000 ppmv [2]. Although H2S concentrations as low as 500 pptv manifesting in the characteristic odor of rotten eggs can already be detected by the human olfactory sense, the total loss of olfactory sensation starts at 150–200 ppmv [3]. Because of the wide occurrence of H2S in industrial processes and its often negative impact on process stabilities and product quality, its concentration needs to be tightly monitored. Furthermore, safety considerations and legal concentration limits also necessitate the accurate determination of H2S levels. In practice, concentrations ranging from sub-ppm levels at low pressures to several per cents at atmospheric conditions need to be monitored. Due to such diverse requirements, H2S analyzers based on different measurement technologies have been developed and are in industrial use. Apart from spectroscopic techniques based on absorption measurements, a range of other analytical techniques such as pulsed UV fluorescence [4], sulfur chemiluminescence [5], colorimetry employing a lead acetate tape [6], flame photometry as detector in gas chromatography [7] as well as electrochemical detection techniques ranging from potentiometric, galvanic, coulometric and amperometric detection [8] is frequently employed. It is interesting to note that in the petrochemical industry the lead acetate tape method is still in frequent use. Also, gas chromatographic methods are popular as they can be used to detect several components almost simultaneously, but this technique requires preparation and extraction of the sample gas leading to a time-consuming measurement. A general drawback of nonspectroscopic techniques is the fact that they do not allow for direct measurements. This, however, also applies to H2S detection based on UV fluorescence as this technique requires sample combustion as well as detection by chemoluminescence, where addition of reagents is required.
Most of the spectroscopic techniques are based on the detection of the absorption spectrum of the molecules in the infrared (IR) spectral region. Sensors based on tuneable diode laser absorption spectroscopy (TDLAS) mostly utilize near-infrared diode lasers due to their distinguished properties, such as single-mode operation, good beam quality, high repetition rate, relatively narrow line width, large current tuning range, good operability, low power consumption and low investment costs [9–11]. When measuring H2S by IR spectroscopy, high sensitivities are difficult to achieve. This is due to the intrinsically weak linestrengths of the H2S ro-vibrational features within the spectral range covered by diode lasers. These are several magnitudes lower compared to other gases of industrial interest. For example, the absorbance of CH4 at 1.646 µm is 1.800 × 10−5 ppm−1 m−1 compared to the H2S absorbance of 5.573 × 10−7 ppm−1 m−1 at 1.601 µm (factor 32) [12]. A way to overcome this drawback is to increase the interaction path length by using multipass gas cells [13–16]. This generally adds to the bulkiness of the systems, and hence, a small size is hardly achieved with H2S TDLAS sensors. The path length can be reduced by using wavelength modulation or balanced detection approaches, which furthermore improve the sensitivity of TDLAS sensors [17–19]. Although the detection of H2S concentrations of several ppb has been demonstrated by employing integrated cavity output spectroscopy approach (ICOS) [20], such sensitivities are difficult to obtain in field measurements as the robustness of this kind of systems remains limited [21, 22]. Possible alternatives to bulky multipass absorption or delicate sensing schemes based on cavity spectroscopy are photoacoustic H2S measurement strategies [23–26]. A fully developed and industry-tailored H2S sensor to meet the specific selectivity requirements based on photoacoustic spectroscopy employing dual-channel longitudinal-type resonator cell with capacitive microphone readout and a LOD of 0.5 ppmv is described in [23]. An interesting rather new development in this regard is the technique of cantilever-enhanced photoacoustic spectroscopy (CEPAS) [27]. In this paper, we report on our results on sensitive H2S detection at different pressure levels using a cantilever-enhanced photoacoustic detector in combination with a telecom NIR L-band laser source.
2 Spectral characteristics of H2S in the NIR region
The 6500–6000-cm−1 near-infrared spectral region is of interest as it can be easily accessed with commercially available telecommunication laser technology. Furthermore, this spectral interval corresponds to an atmospheric window with very few cross-interactions stemming from other molecules. Vibrational overtone and combination bands of H2S can be located at 6450–6150 cm−1 (refer to Fig. 1).
Regarding the spectral H2S features in the 1.6-µm region (6270–6220 cm−1), extensive research and simulation was conducted by Edwards et al. [28] and extended by Lechuga-Fossat et al. [29]. In this region, accurate line positions can be addressed to the (210) (111) and (102) bands. Resonances between these three states can be addressed to Coriolis interactions between the rotational levels of the (111) vibrational state and the levels of the (210) and (012) states as well as to Darling-Dennison interactions between the (210) and (012) vibrational states [29].
In this work, the strongest absorption feature around 6245 cm−1 (1601 nm) corresponding to the 3 transition lines listed in Table 1 was chosen for selective H2S measurements. The rotational levels of H2S as a three-dimensional asymmetric top rotator with three different reciprocal moments of inertia are labeled by the three standard quantum numbers J, K a and K c [30].
The absorption spectrum in this region is shown in Fig. 1, indicating an absorbance of 5.57 × 10−7 ppm−1 m−1 [12]. A HITRAN simulated H2S absorption spectrum around 6245 cm−1 with a total pressure ranging from 1000 to 300 mbar is shown in Fig. 2a. Splitting of the H2S band into its strongest ro-vibrational transition components (111–000) can be observed at reduced pressures. Although the sensor investigation in this work was limited to certified H2S in N2 mixtures, the possibility of water (H2O) and carbon dioxide (CO2) interference is investigated via simulation. Absorbance spectra at a total pressure of 300 mbar of 100 ppmv H2S in a standard air matrix with 100 ppmv water and 500 ppmv CO2 content and 100 ppmv H2S in a possible process air matrix of 10,000 ppmv H2O and 5000 ppmv CO2 are shown in Fig. 2b. Negligible spectral interference can be expected from H2O lines in this wave number region, whereas possible CO2 interference has to be accounted for. Taking advantage of spectral line resolution starting at a reduced pressure of 300 mbar, a sufficient separation of ~0.3 cm−1 from the interfering CO2 transitions can be expected for the targeted H2S feature.
Simulated H2S absorption spectrum around 6245 cm−1, total pressure of 1000, 500 and 300 mbar (a). Absorbance spectra at a total pressure of 300 mbar of 100 ppmv H2S in a standard air matrix with 100 ppmv water and 500 ppmv CO2 content and 100 ppmv H2S in a possible process air matrix of 10,000 ppmv H2O and 5000 ppmv CO2 (b)
3 Cantilever-enhanced photoacoustic spectroscopy
Photoacoustic spectroscopy (PAS) is an established technique for sensitive gas analysis [31, 32]. The fundamental principle of PAS is based on the absorption of electromagnetic radiation by the target molecules, which are excited to higher electronic, vibrational, or rotational quantum states. The nonradiative relaxation processes by collisions with molecules produce local heating of the sample gas. Adiabatically generated pressure fluctuations by thermal expansion can be detected in the form of acoustic waves. The detection of the PA signal traditionally encompasses the use of sensitive microphones or other piezo-transducers.
The PA signal S measured by the transducer is given by the Eq. 1:
where C is the frequency-dependent cell constant (V cm W−1), P the optical power of the laser source and α the absorption coefficient which is related to the gas concentration (N, number density of molecules) and absorption cross section (σ) by \(\alpha = N\sigma\), with L and V the length and the volume of the cell, respectively, γ = (c p/c v) the specific heat constant, f the modulation frequency, G the geometrical factor and Q the quality factor of the generated acoustic resonance.
The cell constant C is influenced by the geometry of the sample cell, the beam profile, the transducer response and the nature of the acoustic mode [32]. The absorption of modulated light generates an acoustic signal in the cell, which can be amplified by tuning the modulation frequency to one of the acoustic resonances of the sample cell. In this resonant case, the cell works as an acoustic amplifier and the absorbed laser power is subsequently accumulated in the acoustic mode of the resonator for Q oscillation periods, where Q is the quality factor, typically in the range of 10–300 [31].
Due to the relatively high sensitivity typically around 5 × 10−9 cm−1 W Hz−1/2, PAS can potentially yield smaller sensors compared to traditional absorption methods [33]. However, PAS is a power scalable technique and therefore calls for excitation sources with high output powers [34]. Therefore, PAS applications usually utilize NIR distributed feedback (DFB) lasers, which typically provide output power between 10 and 40 mW. A further advantage of NIR laser sources in combination with PAS is the possibility of a fiber-coupled light output, which simplifies the optical complexity of the system. Telecommunication NIR diode lasers have been used by several groups in various photoacoustic applications with traditional capacitive microphones as the pressure sensing device [24].
A novel detection approach, developed by Wilcken and Kauppinen [35], utilizes a silicon cantilever as an optical microphone with interferometric measurement of the sensor displacement and is termed cantilever-enhanced photoacoustic spectroscopy (CEPAS) [27, 35, 36]. The frequency-dependent total system response combining the effects of the cantilever itself, gas heat transfer, relaxation pathways of the excited molecules and leakage through the gap and thermal diffusion to cell walls is discussed and derived in detail in [34, 35] and is depicted in Fig. 3.
Model of different frequency-dependent components influencing the total cantilever-enhanced photoacoustic system response (calculated from [34])
The isolated response of the cantilever can be treated as constant until the resonance frequency is reached. Heat transfer and leakage through the gap between the frame and the cantilever and thermal diffusion effects to the cell walls dominate the shape of the response function at low frequencies, revealing a maximum of the total system response at the frequency range between 0.5 and 10 Hz. The total system response decreases due to contributions of heat transfer and relaxation mechanisms until the resonant frequency of the cantilever, where a local maximum is seen. After passing the resonance frequency, the total system response decreases rapidly, mainly due to relaxation mechanisms and the isolated cantilever response function. This fact is limiting the practicable measurement range well below the resonance frequency.
The optimum sensitivity achieved for the cantilever pressure transducer is superior to other cell designs using capacitive microphones, and the nonresonant operation of CEPAS cells can avoid the matrix influences on the PA signal [34, 37]. A sensitive TDL-PAS setup based on cantilever-enhanced detection of oxygen (O2) was demonstrated by Cattaneo et al. [38] A LOD of 20 ppmv could be achieved with a 30-mW DFB laser. Laurila et al. employed carbon dioxide (CO2) CEPAS detection. A normalized sensitivity of 2.2 × 10−9 cm−1W Hz−1/2 for CO2 detection at 1572 nm was achieved [39]. Using a 4.7-W 532-nm Nd:YVO4 laser, Peltola et al. [40] reported a normalized sensitivity of 2.6 × 10−10 cm−1W Hz−1/2 for nitrogen dioxide (NO2) detection.
Such a high sensitivity suggests that reasonable detection limits for H2S could also be achieved using medium power light sources such NIR laser diodes around 1600 nm.
3.1 Modulation schemes in PAS
In the most basic form, the generation of the PA signal can be accomplished by modulating the laser injection current with a square waveform of 50 % duty cycle between laser threshold and the designated upper current level (amplitude modulation, AM).
In wavelength modulation (WM), the injection current itself is modulated or superimposed with an arbitrary periodic function. As a consequence, the emission wavelength is modulated at a certain depth (in wave numbers) and frequency f 0. Here the modulation depth and modulation frequency of the laser were driven with a triangular waveform in order to improve the harmonic signal components [41]. In general, a periodic modulation of the argument of a nonlinear transfer function produces an output signal that contains higher harmonics of the fundamental frequency [42]. Therefore, when performing wavelength modulation (WM), additional detection possibilities arise as higher harmonics of f 0 can be extracted from the frequency-domain spectrum. When scanning the absorption line while performing WM, the analytical signal also contains information on the shape of the absorption line in the scanned region. A detailed overview of the underlying mechanisms of different modulation schemes is discussed in [43, 44].
In both modulation schemes, the resulting time-domain cantilever signal from the analog circuit module is digitized and subsequently Fourier-transformed, providing a frequency power spectrum. When amplitude or wavelength-modulated laser light with a modulation frequency of f 0 is used as the excitation source, the fundamental and, respectively, higher harmonics can be extracted from the frequency-domain spectrum. Analysis of higher frequency components in AM is not considered as these frequencies do not contain additional information. Wavelength modulation (WM) schemes result in complex FFT spectra with contribution of all harmonics.
As an example, several positions along the H2S peak around 1600 nm (6344.8 cm−1) at normal temperature and pressure condition (293.15 K and 1013 mbar) with the according CEPAS raw signal waveforms and the postprocessed FFT signals are outlined for a WM detection scheme. Slowly scanning the modulated laser emission wavelength over the characteristic peak of the target analyte H2S alters the interferometer signal of the cantilever as outlined in Fig. 4.
The H2S absorption peak transduces the WM modulated laser emission into an AM modulated waveform with varying amplitudes of the harmonic components. Starting at point (1), the FFT signal only shows a major contribution of the first harmonic component, whereas the second harmonic contribution increases following points (2–5), according to the slope of the H2S peak. Pure second harmonic components in the raw cantilever signal can be extracted at point (6). Nearly equal contributions from the harmonic components can be observed at point (7), whereas points (8–10) mark a continuous decrease in the second harmonic contribution.
Similar to the well-established wavelength modulation spectroscopy techniques, slow scanning over the absorption feature of interest and recording of the extracted nth harmonic component of the raw cantilever signal result in nth derivative (nf) like spectra.
As opposed to recording the nf spectrum with TLAS and phase-locked loop (PLL) detection schemes, the phase information is not extracted by FFT. As a consequence derivative, WM-PA spectra only show absolute values. AM and WM PAS spectra up to the third harmonic of the H2S feature in the 6244.0–6245.5-cm−1 spectral region are illustrated in Fig. 5. Slight distortions and asymmetry of the 2f and 3f lineshape wings can be attributed to amplitude modulation effects and due to interference from neighboring transitions.
4 Experimental setup and sample preparation
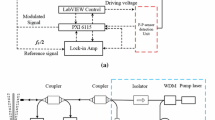
The experimental setup was located on a vibration-isolated laser table and is shown in Fig. 6 along with a detailed view on the measurement cell for performing cantilever-enhanced photoacoustic measurements.
4.1 Laser and laser operation
The NIR light source (NLK 1556 STB) used was a pigtailed InGaAs DFB telecomm laser from NTT Electronics (Tokyo, Japan) operating in the L-band around 1600 nm with output power of 20 mW. This laser had an integrated TEC element and a single-mode fiber output and was operated from 290 to 293 K with a maximum injection current of 130 mA. The side-mode suppression ratio was 35 dB. A temperature (TED200C) and current (LD205) controller both from Thorlabs (Newton, NJ, USA) were used to adjust and stabilize the operation temperature to 0.01 K and to control the injection current of the laser. Coarse control of the laser diode emission wavelength control was achieved by adjusting the laser temperature, whereas fine-tuning of the laser emission wavelength was accomplished by variation in the injection current. The output power of the laser source was monitored with the integrated photodiode and with a Gentec Solo 2 (Gentec-EO, Quebec, Canada) power meter. The tuning characteristics for different laser temperatures (NTC values) and injection currents are shown in Fig. 7. Additionally, the H2S spectrum in the tuning range of the laser is shown as well.
4.2 Cantilever-enhanced photoacoustic cell
The cell used in this work was a PA201 model manufactured by Gasera Ltd (Turku, Finland). The PA201 consists of the photoacoustic cell body with the interferometric cantilever microphone. The gas cell is located inside the body and the valves, and the connectors for the gas exchange are attached on the sample cell and balance cell sides of the cantilever. The gas exchange through the sample-in and sample-out ports is controlled with an external control unit. The lowest possible sample gas pressure was limited by the included pumping unit to 300 mbar. As shown in Fig. 6, the cantilever separates the gas volume inside the body into two parts: the photoacoustic (PA) cell and the balance cell. The PA cell (yellow) is a polished and gold-coated cylindrical stainless steel tube (inner diameter of 6 mm and length of 100 mm) closed with a ZnSe window on the front end and a beam dump in the rear end of the tube. The balance cell is used for compensating the acceleration noise and reducing the effective spring constant due to the reduced gas spring effect [34, 45]. The displacement of the silicon cantilever induced by the pressure wave from the dissipation of the absorbed infrared laser radiation is recorded by a compact Michelson interferometer. The carrier signals of the interferometer are calculated in an analog circuit module and produce a signal proportional to the cantilever displacement. The time-domain signal from the analog circuit module is digitized and subsequently Fourier-transformed, providing a frequency power spectrum. The magnitude of the peaks is directly proportional to the cantilever displacement, and hence, a linear dynamic range can be achieved for quantitative analysis [34].
4.3 Operation by amplitude and wavelength modulation
Photoacoustic measurements were taken in amplitude modulation (AM) as well as wavelength modulation (WM) schemes. For AM experiments, the laser was electronically chopped with frequencies ranging from 10 to 700 Hz. The signal was recorded at the fundamental frequency of the resulting frequency power spectrum. In WM, the modulation depth and modulation frequency of the laser was driven with a sinusoidal waveform. The signal was recorded at the second harmonic of the resulting frequency power spectrum.
4.4 Gas sample preparation
Different H2S concentration levels were prepared by N2 dilution from a 2000-ppmv H2S standardized gas bottle (matrix N2) with a mass flow and pressure-controlled gas handling system, developed in house.
4.5 Reference measurement and reference data
Reference spectra were recorded on a Bruker Vertex 80v FT-IR spectrometer (Bruker Optics, Germany) with 0.075 cm−1 spectral resolution. Additional spectral information and reference data in the 6300–6200-cm−1 region was gained via simulation with the Hitran 2012 database [46].
5 Results and discussion
5.1 Influence of operational parameters of amplitude and wavelength modulation in CEPAS on the obtained signal-to-noise ratio
Following Eq. 1 and the different contributions to the total cantilever-enhanced photoacoustic signal S as outlined in Fig. 3, it is interesting to note that S is direct proportional to the laser power, concentration of the analyte, a possible Q factor of the photoacoustic cell, which in general refers to acoustic resonances of the measurement cell. In addition to these parameters and contributions, dependencies of S on further parameters such as modulation (chopping) frequency and depth and gas pressure are expected as well.
For investigating the influence of the chopping frequency on the AM signal, a concentration of 1000 ppmv H2S at a total gas pressure of 1013 mbar was applied. When aiming for an optimal signal-to-noise ratio, the dependency of the photoacoustic signal S as well as the corresponding noise level from a given chopping frequency is of interest. Figure 8 illustrates the dependency of the FFT-transformed interferometer signal with the chopping frequency for a H2S concentration of 1000 ppmv and a recording time of 100 s and a FFT block size of 16,384 samples (corresponding to 778.9 ms at a sampling rate of 21,035 samples s−1). For evaluating the signal-to-noise ratio (SNR, μ/σ), the relative standard deviation σ of the measured signal of the empty (N2 filled) cell (\(\sigma_{{{\text{N}}_{2} }}\)) was calculated and plotted together with the calculated mean μ of the recorded photoacoustic signal with H2S present (\(\mu_{{{\text{H}}_{2} {\text{S}}}}\)).
With the 20-mW laser, the optimal chopping frequency was in the range from 10 to 200 Hz with relatively stable interferometer signal better than 2 % in terms of standard deviation σ. A trend of increasing noise signal with higher chopping frequencies could be found. In the region of the resonance frequency of the PA cell, the interferometer signal stability is improved but could not reach the value of comparable signal magnitudes at 20–100 Hz chopping frequency. Judging from the obtained SNR of the PA signal (\(\mu_{{{\text{H}}_{2} {\text{S}}}} /\sigma_{{{\text{N}}_{2} }}\)), optimal chopping frequencies in the 20- to 80-Hz range could be identified.
Concerning WM modulation, the influence of the modulation depth on the photoacoustic signal was investigated and is displayed in Fig. 9. The laser injection current of 100 mA was superimposed with a 20-Hz sinusoidal modulation current ranging from 0 to 8 mA.
The optimum modulation depth in terms of signal strength was found to be between 4 and 5 mA, although the 2f-PA signal mean to its standard deviation ratio μ/σ suggested a wide applicable range of modulation depths between 1 and 6 mA.
The PA signal dependency on the total gas pressure is shown in Fig. 10. The available pressure range from the system could be set from 300 to 1000 mbar. Unlike laser-based direct absorption spectroscopy, where the integrated absorbance is linearly scaling with increasing pressure, the photoacoustic signal pressure dependence is of nonlinear nature [47]. Several studies were conducted in order to address and deduce the sources of the pressure dependence of the photoacoustic sensitivity. For both resonant and nonresonant types of photoacoustic systems, slow vibrational relaxation in dilute mixtures due to the absence of suitable collision partners, the geometry of the cell and the pressure transducer and the strong pressure dependence of the Q factor could be identified as main contributors for the pressure dependence of the photoacoustic sensitivity [48–52].
In the case of complex matrices, it would be crucial to balance between improved peak resolution and decreased signal amplitude when applying low-pressure measurements.
5.2 Photoacoustic H2S spectrum in the range of 6245.5–6244 cm−1
A recorded photoacoustic H2S spectrum in the range of 6245.5–6244 cm−1 at pressure levels of 1000 and 300 mbar is shown in Fig. 11. According to the applied modulation schemes, normal absorption spectra are obtained with AM, and spectra with derivative information are recorded with WM mode. At 300 mbar splitting of the H2S band into its main ro-vibrational transition components of the (111–000) band could be observed (Figs. 12, 13).
5.3 Quantitative H2S measurements
Due to the fact of higher signal amplitudes and better SNR for AM photoacoustic signals in comparison with WM signals, subsequent measurements were taken in AM fashion and at total gas pressures of 1000 mbar.
The resulting calibration curve in the range from 0 to 180 ppmv H2S was recorded with the 20-mW laser, with an amplitude modulation frequency of 20 Hz, 100 mA injection current and FFT time constant of 778.9 ms. Each point of the calibration curve correlates to an averaging of 10 gas samples which were individually drawn from the gas mixing setup. After successful measurement of the PA signal at the respective H2S concentration step, the photoacoustic cell was purged, new sample gas volume was drawn in and the valves were closed for data acquisition.
The resulting calibration curve of the photoacoustic detection of H2S yielded a limit of detection (3σ) of 8 ppmv H2S in the gas stream. Analysis of the residuals provided a convenient means of confirming the linearity of the calibration data.
5.4 Long-term stability
In spectroscopic measurements, the stability of the system is an important issue, as long-term signal averaging is an effective means to improve the sensitivity and detection limit. One way to characterize the stability and long-term drifts is to measure the Allan variance of the signal. The Allan variance is a time-domain analysis technique developed in 1966 originally used for the assessment of frequency stability of precision oscillators [53]. The application of the Allan method to optical sensors has been discussed by Werle et al. [54] where the Allan variance is measured for equally timed sequences of the signal. In this context, the Allan variance can be expressed as:
where τ is the integration time, N is the number of consecutive observations, and variable \(\overline{y}_{i}\) is the average of i consecutives of the recorded signal.
The stability test of our setup was made with the DFB laser with pure N2 and with H2S concentrations of 1000 ppmv with total pressures of 300 and 1000 mbar.
When working with a H2S concentration of 1000 ppmv in N2, minimum Allan deviation was observed with 50-s averaging time for 1000 mbar, whereas a minimum Allan deviation could be observed with up to 100-s averaging time for 300 mbar.
In the case of pure N2 in the PA chamber, minimum Allan deviation was surveyed with 50-s averaging time for 1000 mbar and up to 100 s for the reduced pressure measurements as well, while the Allan deviation itself could be nearly reduced by the order of one magnitude.
For comparison, trace gas sensors based on direct optical absorption detection usually exhibit drifts that do not allow useful data averaging for time periods longer than 100–200 s [55].
The performance of the detection system is influenced by various noise sources. Measurements by Kauppinen et al. indicated that the ambient acoustic noise is the dominant noise source present in cantilever-enhanced PA arrangements. Lowering the pressure reduces the influence of the acoustic noise but also tends to decrease the signal amplitude. At low pressures, the limiting noise source is thermal noise. Compared to acoustic and thermal noise sources, the electric noise of the system is vanishingly small [36].
6 Conclusion
In conclusion, the compact and commercially available cantilever-enhanced photoacoustic unit PA201 from Gasera was used for sensitive H2S detection. A 20-mW DFB laser emitting near 1601 nm was used as the excitation source. Our results show that 8 ppmv H2S levels can be detected with this method when employing amplitude modulation with a chopping frequency of 20 Hz.
As compared to simulated spectra, the cantilever-enhanced photoacoustic detection approach in combination with the sufficiently stable and narrow bandwidth NIR laser is able to reproduce the rotationally resolved H2S spectrum at low pressures of 300 mbar. Slowly scanning over the H2S peak of interest and recording the nth harmonic component of the Fourier-transformed interferometer signal yielded in the nth derivative like H2S spectrum.
The sensitivity of the system is expected to improve when employing laser sources in the Mid-IR as quantum cascades (QC) lasers or interband cascade (IC) lasers. Considering the constant improvement regarding the quality and power of IC and QC laser sources, an excess of 50 mW in optical power can be achieved in monomode continuous wave operation. For example, the intrinsic linestrengths of the H2S ro-vibrational features in the 2.7-µm (~3800 cm−1) region are up to a factor of 16 higher than compared to the linestrengths in the NIR region. Addressing the 8-µm (1300 cm−1) region, an improvement up to a factor of 11 can be expected.
To facilitate process implementation of the CEPAS sensor system, further modifications to the sampling system might be required. These should focus on a continuous operation and achieving pressure levels of 100 mbar or lower as this could attribute for a pronounced matrix resolution due to spectral narrowing. In the case of complex sample matrices, it would be crucial to balance between improved peak resolution accompanied with an enhanced detection selectivity and decreased signal amplitude when performing measurements at reduced pressure.
References
European Agency for Safety and Health at Work, Occupational Exposure Limits OSHA (online). http://osha.europa.eu/en/topics/ds/oel
NIOSH, NIOSH Pocket Guide to Chemical Hazards, DHHS (NIOS, no. 2005) (National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health, 2007)
EPA, Health Assessment Document for Hydrogen Sulfide (US Environmental Protection Agency, 1986)
B.R. Weiner, H.B. Levene, J.J. Valentini, A.P. Baronavski, Ultraviolet photodissociation dynamics of H2S and D2S. J. Chem. Phys. 90(1989), 1403 (1989)
B. Chawla, F. Di Sanzo, Determination of sulfur components in light petroleum streams by high-resolution gas chromatography with chemiluminescence detection. J. Chromatogr. 589(1–2), 271–279 (1992)
E. Kuester, S.T. Williams, Production of hydrogen sulfide by streptomycetes and methods for its detection. Appl. Microbiol. 12(1), 46–52 (1964)
C.D. Pearson, W.J. Hines, Determination of hydrogen sulfide, carbonyl sulfide, carbon disulfide, and sulfur dioxide in gases and hydrocarbon streams by gas chromatography/flame photometric detection. Anal. Chem. 49(1), 123–126 (1977)
N.S. Lawrence, J. Davis, R.G. Compton, Analytical strategies for the detection of sulfide: a review. Talanta 52, 771–784 (2000)
P. Werle, F. Slemr, K. Maurer, R. Kormann, Near- and mid-infrared laser-optical sensors for gas analysis. Opt. Lasers Eng. 37(2–3), 101–114 (2002)
U. Willer, M. Saraji, A. Khorsandi, P. Geiser, W. Schade, Near- and mid-infrared laser monitoring of industrial processes, environment and security applications. Opt. Lasers Eng. 44(7), 699–710 (2006)
I. Linnerud, P. Kaspersen, T. Jæger, T. Jaeger, Gas monitoring in the process industry using diode laser spectroscopy. Appl. Phys. B Lasers Opt. 305(3), 297–305 (1998)
S.W. Sharpe, T.J. Johnson, R.L. Sams, P.M. Chu, G.C. Rhoderick, P.A. Johnson, Gas-phase databases for quantitative infrared spectroscopy. Appl. Spectrosc. 58(12), 1452–1461 (2004)
J.B. McManus, P.L.P. Kebabian, M.S.M. Zahniser, Astigmatic mirror multipass absorption cells for long-path-length spectroscopy. Appl. Opt. 34(18), 3336–3348 (1995)
A. Manninen, B. Tuzson, H. Looser, Y. Bonetti, L. Emmenegger, Versatile multipass cell for laser spectroscopic trace gas analysis. Appl. Phys. B 109(3), 461–466 (2012)
J.A. Silver, Simple dense-pattern optical multipass cells. Appl. Opt. 44(31), 6545–6556 (2005)
D. Kaur, A.M. de Souza, J. Wanna, S.A. Hammad, L. Mercorelli, D.S. Perry, Multipass cell for molecular beam absorption spectroscopy. Appl. Opt. 29(1), 119–124 (1990)
P. Vogel, V. Ebert, Near shot noise detection of oxygen in the A-band with vertical-cavity surface-emitting lasers. Appl. Phys. B 72(1), 127–135 (2001)
G.B. Rieker, J.B. Jeffries, R.K. Hanson, Calibration-free wavelength-modulation spectroscopy for measurements of gas temperature and concentration in harsh environments. Appl. Opt. 48(29), 5546–5560 (2009)
B.H. King, M.J. Sailor, Medium-wavelength infrared gas sensing with electrochemically fabricated porous silicon optical rugate filters. J. Nanophotonics 5(1), 051510 (2011)
W. Chen, A.A. Kosterev, F.K. Tittel, X. Gao, W. Zhao, H2S trace concentration measurements using off-axis integrated cavity output spectroscopy in the near-infrared. Appl. Phys. B Lasers Opt. 90(2), 311–315 (2008)
F. Schmidt, Laser-based Absorption Spectrometry—Development of NICE-OHMS Towards Ultra-sensitive Trace Species Detection, Doctoral thesis, Department of Physics, Umeå University, Sweden (2007)
A. Foltynowicz, F.M. Schmidt, W. Ma, O. Axner, Noise-immune cavity-enhanced optical heterodyne molecular spectroscopy: current status and future potential. Appl. Phys. B 92(3), 313–326 (2008)
A. Varga, Z. Bozóki, M. Szakáll, G. Szabó, Photoacoustic system for on-line process monitoring of hydrogen sulfide (H2S) concentration in natural gas streams. Appl. Phys. B Lasers Opt. 85(2–3), 315–321 (2006)
Z. Bozóki, A. Pogány, G. Szabó, Photoacoustic instruments for practical applications: present, potentials, and future challenges. Appl. Spectrosc. Rev. 46(1), 1–37 (2011)
A. Szabó, Á. Mohácsi, G. Gulyás, Z. Bozóki, G. Szabó, In situ and wide range quantification of hydrogen sulfide in industrial gases by means of photoacoustic spectroscopy. Meas. Sci. Technol. 24(6), 065501 (2013)
H. Wu, L. Dong, H. Zheng, X. Liu, X. Yin, W. Ma, L. Zhang, W. Yin, S. Jia, F.K. Tittel, Enhanced near-infrared QEPAS sensor for sub-ppm level H2S detection by means of a fiber amplified 1582 nm DFB laser. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 221, 666–672 (2015)
J. Kauppinen, K. Wilcken, I. Kauppinen, V. Koskinen, High sensitivity in gas analysis with photoacoustic detection. Microchem. J. 76(1–2), 151–159 (2004)
T.H. Edwards, Ground-state molecular constants of hydrogen sulfide. J. Chem. Phys. 46(6), 2139 (1967)
L. Lechuga-Fossat, J.-M. Flaud, C. Camy-Peyret, P. Arcas, M. Cuisenier, The H2S spectrum in the 1.6 μm spectral region. Mol. Phys. 61(1), 23–32 (1987)
R. McClatchey, W. Benedict, S. Clough, AFCRL Atmospheric Absorption Line Parameters Compilation. Environ. Res. Pap. (434), 1–86 (1973)
A. Elia, P.M. Lugarà, C. Di Franco, V. Spagnolo, Photoacoustic techniques for trace gas sensing based on semiconductor laser sources. Sensors 9(12), 9616–9628 (2009)
J. Li, W. Chen, B. Yu, Recent progress on infrared photoacoustic spectroscopy techniques. Appl. Spectrosc. Rev. 46(6), 440–471 (2011)
A.A. Kosterev, F.K. Tittel, D.V. Serebryakov, A.L. Malinovsky, I.V. Morozov, Applications of quartz tuning forks in spectroscopic gas sensing. Rev. Sci. Instrum. 76(4), 043105 (2005)
V. Koskinen, J. Fonsen, K. Roth, J. Kauppinen, Progress in cantilever enhanced photoacoustic spectroscopy. Vib. Spectrosc. 48(1), 16–21 (2008)
K. Wilcken, J. Kauppinen, Optimization of a microphone for photoacoustic spectroscopy. Appl. Spectrosc. 57(9), 1087–1092 (2003)
J. Kauppinen, V. Koskinen, Extremely sensitive CWA analyzer based on a novel optical pressure sensor in photoacoustic gas analysis. in Proceedings of the SPIE 5617, Opt. Based Biol. Chem. Sens. Def., vol. 5617 (2004), pp. 115–127
R.E. Lindley, A.M. Parkes, K.A. Keen, E.D. McNaghten, A.J. Orr-Ewing, A sensitivity comparison of three photoacoustic cells containing a single microphone, a differential dual microphone or a cantilever pressure sensor. Appl. Phys. B 86(4), 707–713 (2006)
H. Cattaneo, T. Laurila, R. Hernberg, Photoacoustic detection of oxygen using cantilever enhanced technique. Appl. Phys. B 85(2–3), 337–341 (2006)
T. Laurila, H. Cattaneo, V. Koskinen, J. Kauppinen, R. Hernberg, Diode laser-based photoacoustic spectroscopy with interferometrically-enhanced cantilever detection. Opt. Express 14(9), 4195 (2006)
J. Peltola, T. Hieta, M. Vainio, Parts-per-trillion-level detection of nitrogen dioxide by cantilever-enhanced photo-acoustic spectroscopy. Opt. Lett. 40(13), 2933 (2015)
J. Saarela, J. Toivonen, A. Manninen, T. Sorvajärvi, R. Hernberg, Wavelength modulation waveforms in laser photoacoustic spectroscopy. Appl. Opt. 48(4), 743–747 (2009)
P. Kluczynski, J. Gustafsson, Å.M. Lindberg, O. Axner, Wavelength modulation absorption spectrometry—an extensive scrutiny of the generation of signals. Spectrochim. Acta Part B At. Spectrosc. 56(8), 1277–1354 (2001)
M. Angelmahr, A. Miklos, P. Hess, Wavelength-and amplitude-modulated photoacoustics: comparison of simulated and measured spectra of higher harmonics. Appl. Opt. 47(15), 2806–2812 (2008)
S. Schilt, L. Thévenaz, Wavelength modulation photoacoustic spectroscopy: theoretical description and experimental results. Infrared Phys. Technol. 48, 154–162 (2006)
T. Kuusela, J. Kauppinen, Photoacoustic gas analysis using interferometric cantilever microphone. Appl. Spectrosc. Rev. 42(5), 443–474 (2007)
L.S. Rothman, I.E. Gordon, Y. Babikov, A. Barbe, D.C. Benner, P.F. Bernath, M. Birk, L. Bizzocchi, V. Boudon, L.R. Brown, A. Campargue, K. Chance, E.A. Cohen, L.H. Coudert, V.M. Devi, B.J. Drouin, A. Fayt, J.-M. Flaud, R.R. Gamache, J.J. Harrison, J.-M. Hartmann, C. Hill, J.T. Hodges, D. Jacquemart, A. Jolly, J. Lamouroux, R.J. Le Roy, G. Li, D.A. Long, O.M. Lyulin, C.J. Mackie, S.T. Massie, S. Mikhailenko, H.S.P. Müller, O.V. Naumenko, A.V. Nikitin, J. Orphal, V. Perevalov, A. Perrin, E.R. Polovtseva, C. Richard, M.A.H. Smith, E. Starikova, K. Sung, S. Tashkun, J. Tennyson, G.C. Toon, V.G. Tyuterev, G. Wagner, The HITRAN2012 molecular spectroscopic database. J. Quant. Spectrosc. Radiat. Transf. 130, 4–50 (2013)
I.G. Calasso, M.W. Sigrist, Selection criteria for microphones used in pulsed nonresonant gas-phase photoacoustics. Rev. Sci. Instrum. 70(12), 4569 (1999)
A. Miklos, H. Sauren, D. Bicanic, An experimental methodology for characterizing the responsivity of the photoacoustic cell for gases at reduced pressure by means of the vibrating strip as the calibrating sound source. Meas. Sci. Technol. 2, 957–962 (1999)
B.J. Schattka, D.M. Turnbull, H.G. Kjaergaard, B.R. Henry, Dependence of an acoustically nonresonant intracavity photoacoustic signal on sample and buffer gas pressure. J. Phys. Chem. 99(17), 6327–6332 (1995)
J. Henningsen, N. Melander, Sensitive measurement of adsorption dynamics with nonresonant gas phase photoacoustics. Appl. Opt. 36(27), 7037–7045 (1997)
V.A. Kapitanov, Y.N. Ponomarev, K. Song, H.K. Cha, J. Lee, Resonance photoacoustic spectroscopy and gas analysis of gaseous flow at reduced pressure. Appl. Phys. B Lasers Opt. 73(7), 745–750 (2001)
M. Szakáll, H. Huszár, Z. Bozóki, G. Szabó, On the pressure dependent sensitivity of a photoacoustic water vapor detector using active laser modulation control. Infrared Phys. Technol. 48(3), 192–201 (2006)
D. Allan, Statistics of atomic frequency standards. Proc. IEEE 54(2), 221–230 (1966)
P. Werle, F. Slemr, Signal-to-noise ratio analysis in laser absorption spectrometers using optical multipass cells. Appl. Opt. 30(4), 430–434 (1991)
P. Werle, R. Mücke, F. Slemr, The limits of signal averaging in atmospheric trace-gas monitoring by tunable diode-laser absorption spectroscopy (TDLAS). Appl. Phys. B Lasers Opt. 139, 131–139 (1993)
Acknowledgments
The authors acknowledge funding of this work by the Austrian Research Promotion Agency (FFG) within the K-project imPACts (Contract No. 843546).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/), which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons license, and indicate if changes were made.
About this article
Cite this article
Moser, H., Lendl, B. Cantilever-enhanced photoacoustic detection of hydrogen sulfide (H2S) using NIR telecom laser sources near 1.6 µm. Appl. Phys. B 122, 83 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00340-016-6355-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00340-016-6355-6