Abstract
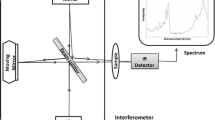
A silver nanoparticle ensemble was prepared under ultrahigh vacuum (UHV) conditions by Volmer–Weber growth on a quartz substrate for surface-enhanced Raman scattering (SERS) investigations of pyrene molecules. To tune the surface plasmon resonance frequency in the vicinity of the excitation wavelength of 488 nm of the diode laser, the morphology of the silver nanoparticles was optimized. The substrates were mounted in a flow-through cell as part of the optical Raman set-up. A microsystem diode laser generates two slightly different emission wavelengths (λ=487.61 nm and λ=487.91 nm) with a spectral width <10 pm and an optical power of 20 mW, i.e. SERS experiments are possible but also shifted excitation Raman difference spectroscopy (SERDS) can be carried out. For trace analysis of pyrene in water we demonstrate SERS/SERDS experiments which lead to a limit of detection of 2 nmol/l for pyrene. These results suggest that with silver nanoparticle ensembles excited at their plasmon resonance at 488 nm combined SERS/SERDS measurements can be effectively performed for in-situ trace analysis of pollutant chemicals in water.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
R.L. McCreery, Raman Spectroscopy for Chemical Analysis (Wiley, New York, 2000)
L.P. Choo-Smith, H.G.M. Edwards, H.P. Endtz, J.M. Kros, F. Heule, H. Barr, J.S. Robinson, H.A. Bruining, G.J. Puppels, Biopolymers 67, 1 (2002)
A. Oust, T. Moretro, K. Naterstad, G. Kowalwska, G.D. Sockalingum, I. Adt, M. Manfait, A. Kohler, Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 72, 228 (2006)
M. Fleischmann, P.J. Hendra, A.J. McQuillan, Chem. Phys. Lett. 26, 163 (1974)
T. Baussant, S. Sanni, A. Skadsheim, G. Jonsson, J.F. Borseth, B. Gaudebert, Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 20, 1185 (2001)
G. Witt, Mar. Chem. 79, 49 (2002)
H. Schmidt, N.B. Ha, J. Pfannkuche, H. Amann, H.-D. Kronfeldt, G. Kowalwska, Mar. Pollut. Bull. 49, 229 (2004)
T. Murphy, H. Schmidt, H.-D. Kronfeldt, Appl. Phys. B 69, 147 (1999)
F. Hubenthal, D. Blázques Sánchez, N. Borg, H. Schmidt, H.-D. Kronfeldt, F. Träger, Appl. Phys. B 95, 351 (2009)
O. Péron, E. Rinnert, M. Lehaitre, P. Crassous, C. Compére, Talanta 79, 199 (2009)
C.L. Jones, K.C. Bantz, C.L. Haynes, Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 394, 303 (2009)
L. Guerrini, J.V. Garcia-Ramos, C. Domingo, S. Sanchez-Cortes, Anal. Chem. 81, 953 (2009)
K. Kneipp, H. Kneipp, I. Itzkan, R.R. Dasari, M.S. Feld, J. Phys., Condens. Matter 14, R597 (2002)
F.J. Garcia-Vidal, J.B. Pendry, Phys. Rev. Lett. 77, 1163 (1996)
H. Xu, J. Aizpura, M. Käll, P. Apell, Phys. Rev. E 62, 4318 (2000)
L.G. Olson, Y.-S. Lo, T.P. Beebe, Jr., J.M. Harris, Anal. Chem. 73, 4268 (2001)
H. Ouacha, C. Hendrich, F. Hubenthal, F. Träger, Appl. Phys. B 81, 663 (2005)
J. Zhao, M.M. Carrabba, F.S. Allen, Appl. Spectrosc. 56, 834 (2002)
M. Maiwald, H. Schmidt, B. Sumpf, R. Güther, G. Erbert, H.-D. Kronfeldt, G. Tränkle, Appl. Spectrosc. 63, 1283 (2009)
F. Hubenthal, Eur. J. Phys. 30, S49 (2009)
F. Hubenthal, Nobel metal nanoparticles: synthesis and optical properties, in Comprehensive Nanoscience and Technology, ed. by D.L. Andrews, G.D. Scholes, G.P. Wiederecht, vol. 1 (Academic Press, San Diego, 2011), pp. 375–435
F. Hubenthal, N. Borg, F. Träger, Appl. Phys. B 93, 39 (2008)
M. Maiwald, D. Jedrzejczyk, A. Sahm, K. Paschke, R. Güther, B. Sumpf, G. Erbert, G. Tränkle, Opt. Lett. 34, 217 (2009)
H. Schmidt, D. Perez Kaiser, M. Maiwald, Method for generating and for detecting a Raman spectrum. International patent, WO 2011/033017 A1 (2011)
D.M. Carey, G.M. Korenowski, J. Chem. Phys. 108, 2669 (1998)
S. Nah, D. Kim, H. Chung, S.-H. Han, M.-Y. Yoon, J. Raman Spectrosc. 38, 475 (2007)
Acknowledgements
The authors acknowledge the support by the European Community in the framework of the EU project “SENSEnet” under the contract number PITN-GA-2009-237868.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ossig, R., Kwon, YH., Hubenthal, F. et al. Naturally grown Ag nanoparticles on quartz substrates as SERS substrate excited by a 488 nm diode laser system for SERDS. Appl. Phys. B 106, 835–839 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00340-011-4866-8
Received:
Revised:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00340-011-4866-8