Abstract
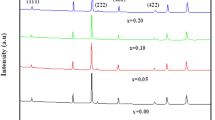
Manganese–zinc ferrite nanoparticles with composition MnyZn1-yFe2O4 (0 ≤ x ≤ 1) were synthesized using the coprecipitation technique. The formation of cubic spinel structures with average crystallite sizes less than 16 nm is confirmed by X-ray diffraction. On replacing Zn2+ ions with Mn2+ ions, compressive lattice strain is produced which lowers the lattice parameter. Thermogravimetric analysis (TGA) demonstrates superior thermal stability of ZnFe2O4 nanoparticles. The superparamagnetic nature of Mn-Zn ferrites was revealed by vibrating sample magnetometer (VSM). The specific magnetization lies between 14.6 and 21.7 emug−1. The optical bandgap energy ranges from 2.34 to 2.84 eV. With increasing Mn2+ ions, the dc electrical resistivity shows a preliminary increase followed by a steady decline. The exposure of ferrite pellets to humidity facilitates the conduction mechanism. Resistivity significantly decreases with increasing relative humidity. Among Mn-Zn ferrites, ZnFe2O4 nanoparticles possess superior humidity sensing properties.








Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The authors declare that all the data supporting the findings of this study are available within the article.
References
R. Srivastava, B.C. Yadav, Ferrite materials: introduction, synthesis techniques, and applications as sensors. International Journal of Green Nanotechnology 4(2), 141–154 (2012)
M. Sugimoto, The past, present, and future of ferrites. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 82(2), 269–280 (1999)
K.I. Arshak, A. Ajina, D. Egan, Development of screen-printed polymer thick film planner transformer using Mn–Zn ferrite as core material. Microelectron. J. 32(2), 113–116 (2001)
K. Arshaka, K. Twomey, D. Egan, A ceramic thick film humidity sensor based on MnZn ferrite. Sensors 2(2), 50–61 (2002)
R. Lebourgeois, C. Coillot, Mn–Zn ferrites for magnetic sensor in space applications. J. Appl. Phys. 103(7), 07E510 (2008)
M. Singh, S.P. Sud, Mg–Mn–Al ferrites for high frequency applications. Mod. Phys. Lett. B 14(14), 531–537 (2000)
B.P. Rao, K.H. Rao, K. Trinadh, O.F. Caltun, Dielectric behaviour of niobium doped Ni-Zn ferrites. J. Optoelectron. Adv. Mater. 6, 951–954 (2004)
L. Li, Y.K. Fang, Y.J. Liu, Preparation and application on antenna of soft ferrite core for wireless sensor networks. IEEE Trans. Magn. 51(11), 1–3 (2015)
Hussain, M. I., Xia, M., Akhtar, K., Nawaz, A., Sharma, S. K., & Javed, Y. (2020). Ferrite Nanoparticles for Biomedical Applications. In Magnetic Nanoheterostructures (pp. 243–265). Springer, Cham.
M. Pardavi-Horvath, Microwave applications of soft ferrites. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 215, 171–183 (2000)
A. Verma, M.I. Alam, R. Chatterjee, T.C. Goel, R.G. Mendiratta, Development of a new soft ferrite core for power applications. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 300(2), 500–505 (2006)
E. Roess, Soft magnetic ferrites and applications in telecommunication and power converters. IEEE Trans. Magn. 18(6), 1529–1534 (1982)
A.R. Kumar, K.V.G.R. Kumar, C.S. Chakra, K.V. Rao, Silver doped manganese–zinc–ferrite nano flowers for biomedical applications. Int. J. Emerg. Technol. Adv. Eng 5, 2250–2459 (2014)
K.S. Chou, T.K. Lee, F.J. Liu, Sensing mechanism of a porous ceramic as humidity sensor. Sens. Actuators, B Chem. 56(1–2), 106–111 (1999)
E. Traversa, Ceramic sensors for humidity detection: the state-of-the-art and future developments. Sens. Actuators, B Chem. 23(2–3), 135–156 (1995)
V. Jeseentharani, M. George, B. Jeyaraj, A. Dayalan, K.S. Nagaraja, Synthesis of metal ferrite (MFe2O4, M= Co, Cu, Mg, Ni, Zn) nanoparticles as humidity sensor materials. J. Exp. Nanosci. 8(3), 358–370 (2013)
E.R. Kumar, P.S.P. Reddy, G.S. Devi, S. Sathiyaraj, Structural, dielectric and gas sensing behavior of Mn substituted spinel MFe2O4 (M= Zn, Cu, Ni, and Co) ferrite nanoparticles. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 398, 281–288 (2016)
N.S. Chen, X.J. Yang, E.S. Liu, J.L. Huang, Reducing gas-sensing properties of ferrite compounds MFe2O4 (M= Cu, Zn, Cd and Mg). Sens. Actuators, B Chem. 66(1–3), 178–180 (2000)
X. Xu, L. Xiao, N.O. Haugen, Z. Wu, Y. Jia, W. Zhong, J. Zou, High humidity response property of sol–gel synthesized ZnFe2O4 films. Mater. Lett. 213, 266–268 (2018)
J. Zhang, J.M. Song, H.L. Niu, C.J. Mao, S.Y. Zhang, Y.H. Shen, ZnFe2O4 nanoparticles: Synthesis, characterization, and enhanced gas sensing property for acetone. Sens. Actuators, B Chem. 221, 55–62 (2015)
X. Zhou, J. Liu, C. Wang, P. Sun, X. Hu, X. Li, G. Lu, Highly sensitive acetone gas sensor based on porous ZnFe2O4 nanospheres. Sens. Actuators, B Chem. 206, 577–583 (2015)
R. Cristina de Oliveira, R.A. Pontes Ribeiro, G.H. Cruvinel, R.A. CiolaAmoresi, M.H. Carvalho, A.J. Aparecido de Oliveira, E. Longo, Role of Surfaces in the Magnetic and Ozone Gas-Sensing Properties of ZnFe2O4 Nanoparticles: Theoretical and Experimental Insights. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces. 13(3), 4605–4617 (2021)
K. Wu, J. Li, C. Zhang, Zinc ferrite based gas sensors: A review. Ceram. Int. 45(9), 11143–11157 (2019)
C. Mukherjee, R. Mondal, S. Dey, S. Kumar, J. Das, Nanocrystalline CopperNickelZinc Ferrite: efficient sensing materials for ethanol and acetone at room temperature. IEEE Sens. J. 17(9), 2662–2669 (2017)
K. Wu, Y. Lu, Y. Liu, Y. Liu, M. Shen, M. Debliquy, C. Zhang, Synthesis and acetone sensing properties of copper (Cu2+) substituted zinc ferrite hollow micro-nanospheres. Ceram. Int. 46(18), 28835–28843 (2020)
A.V. Kadu, S.V. Jagtap, G.N. Chaudhari, Current Appl. Phys. 9(6), 1246–1251 (2009)
M. Deepty, S. Ch, P.N. Ramesh, N.K. Mohan, M.S. Singh, C.L. Prajapat, D.L. Sastry, Evaluation of structural and dielectric properties of Mn2+-substituted Zn-spinel ferrite nanoparticles for gas sensor applications. Sensors and Actuators B: Chemical 316, 128127 (2020)
R.R. Powar, V.D. Phadtare, V.G. Parale, S. Pathak, K.R. Sanadi, H.H. Park, D.N. Zambare, Effect of zinc substitution on magnesium ferrite nanoparticles: Structural, electrical, magnetic, and gas-sensing properties. Mater. Sci. Eng.: B 262, 114776 (2020)
H. Farahani, R. Wagiran, M.N. Hamidon, Humidity sensors principle, mechanism, and fabrication technologies: a comprehensive review. Sensors 14(5), 7881–7939 (2014)
Y. Jin, F. Wang, M. Carpenter, R.B. Weller, D. Tabor, S.R. Payne, The effect of indoor thermal and humidity condition on the oldest-old people’s comfort and skin condition in winter. Build. Environ. 174, 106790 (2020)
Khatri, J., Sharma, N., Dahlander, P., & Koopmans, L. (2020). Effect of relative humidity on water injection technique in downsized spark ignition engines. International Journal of Engine Research, 1468087420940854.
Alfaresi, B., Nawawi, Z., Malik, R. F., Anwar, K., & Nur, L. O. (2020). HUMIDITY EFFECT TO 5G PERFORMANCES UNDER PALEMBANG CHANNEL MODEL AT 28 GHZ. traffic, 5(6), 7.
Albuquerque, F. B., & Shea, H. (2020, April). Effect of humidity, temperature, and elastomer material on the lifetime of silicone-based dielectric elastomer actuators under a constant DC electric field (Conference Presentation). In Electroactive Polymer Actuators and Devices (EAPAD) XXII (Vol. 11375, p. 113751E). International Society for Optics and Photonics.
C. Amitrano, C. Arena, S. De Pascale, V. De Micco, Light and low relative humidity increase antioxidants content in mung bean (Vigna radiata L) Sprouts. Plants 9(9), 1093 (2020)
S.S. Pati, J. Philip, in Enhancement in maghemite to hematite phase transition temperature with very low fraction of Co (II) doping. International Conference on Nanoscience, Engineer- ing and Technology (ICONSET 2011) (IEEE, 2011, November), pp. 323–325
Thermally stable ferrous-doped CoFe2O4 ferromagnetic nanoparticles with high quality factor for the use in electronic devices
Yashpreet, & Chudasama, B. (2020). Effect of annealing on structural and magnetic properties of manganese ferrite nanoparticles. In AIP Conference Proceedings (Vol. 2265, No. 1, p. 030179). AIP Publishing LLC.
Du, S., & Li, Y. (2015). Effect of annealing on microstructure and mechanical properties of magnetron sputtered Cu thin films. Advances in Materials science and Engineering, 2015.
Cullity, B. D. (1956). Elements of X-ray Diffraction. Addison-Wesley Publishing.
Bharati, V. A., Patade, S. R., Bajaj, S., Parlikar, R., Keche, A. P., & Sondur, V. V. (2020, October). Structural and magnetic properties of nickel ferrite nanoparticles prepared by solution combustion method. In Journal of Physics: Conference Series (Vol. 1644, No. 1, p. 012005). IOP Publishing.
T. Tatarchuk, M. Myslin, I. Mironyuk, M. Bououdina, A.T. Pędziwiatr, R. Gargula, P. Kurzydło, Synthesis, morphology, crystallite size and adsorption properties of nanostructured Mg–Zn ferrites with enhanced porous structure. J. Alloys Compounds 819, 152945 (2020)
K.E. Sickafus, J.M. Wills, N.W. Grimes, Structure of spinel. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 82(12), 3279–3292 (1999)
Singh, R., & Thirupathi, G. (2017). Manganese-zinc spinel ferrite nanoparticles and ferrofluids. Magnetic Spinels-Synthesis, Properties and Applications, 140–159.
C. Klein, A.R. Philpotts, Earth Materials: Introduction to Mineralogy and Petrology (Cambridge University Press, 2013)
M.M. Rashad, M.I. Nasr, Controlling the microstructure and magnetic properties of Mn-Zn ferrites nanopowders synthesized by co-precipitation method. Electron. Mater. Lett. 8(3), 325–329 (2012)
M.M.L. Sonia, S. Anand, V.M. Vinosel, M.A. Janifer, S. Pauline, A. Manikandan, Effect of lattice strain on structure, morphology and magneto-dielectric properties of spinel NiGdxFe2− xO4 ferrite nano-crystallites synthesized by sol-gel route. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 466, 238–251 (2018)
R. Iyer, R. Desai, R.V. Upadhyay, Low temperature synthesis of nanosized Mn 1–x Zn x Fe 2 O 4 ferrites and their characterizations. Bull. Mater. Sci. 32(2), 141–147 (2009)
N. Kumari, V. Kumar, S. Khasa, S.K. Singh, Chemical synthesis and magnetic investigations on Cr3+ substituted Zn-ferrite superparamagnetic nano-particles. Ceram. Int. 41(1), 1907–1911 (2015)
R. Topkaya, A. Baykal, A. Demir, Yafet–Kittel-type magnetic order in Zn-substituted cobalt ferrite nanoparticles with uniaxial anisotropy. J. Nanopart. Res. 15(1), 1–18 (2013)
R.G. Kulkarni, V.G. Panicker, Study of canted spin structure in Cu-Cd ferrites. J. Mater. Sci. 19(3), 890–894 (1984)
S.D. Oberdick, A. Abdelgawad, C. Moya, S. Mesbahi-Vasey, D. Kepaptsoglou, V.K. Lazarov, S.A. Majetich, Spin canting across core/shell Fe 3 O 4/Mn x Fe 3–x O 4 nanoparticles. Sci. Rep. 8(1), 1–12 (2018)
I.C. Masthoff, A. Gutsche, H. Nirschl, G. Garnweitner, Oriented attachment of ultra-small Mn (1–x) Zn x Fe 2 O 4 nanoparticles during the non-aqueous sol–gel synthesis. CrystEngComm 17(12), 2464–2470 (2015)
S.E. Shirsath, B.G. Toksha, R.H. Kadam, S.M. Patange, D.R. Mane, G.S. Jangam, A. Ghasemi, Doping effect of Mn2+ on the magnetic behavior in Ni–Zn ferrite nanoparticles prepared by sol–gel auto-combustion. J. Phys. Chem. Solids 71(12), 1669–1675 (2010)
Srinivasamurthy, K. M., Angadi, V. J., Kubrin, S. P., Matteppanavar, S., Sarychev, D. A., & Rudraswamy, B. (2019). 32(3), 693–704.
E.C. Stoner, E.P. Wohlfarth, A mechanism of magnetic hysteresis in heterogeneous alloys Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society of London. Series A, Math. Phys. Sci. 240(826), 599–642 (1948)
G.P. Joshi, N.S. Saxena, R. Mangal, A. Mishra, T.P. Sharma, Band gap determination of Ni-Zn ferrites. Bull. Mater. Sci. 26(4), 387–389 (2003)
A. Manohar, C. Krishnamoorthi, Photocatalytic study and superparamagnetic nature of Zn-doped MgFe2O4 colloidal size nanocrystals prepared by solvothermal reflux method. J. Photochem. Photobiol., B 173, 456–465 (2017)
Singh, J. P., Srivastava, R. C., & Agrawal, H. M. (2010, October). Optical behaviour of zinc ferrite nanoparticles. In AIP Conference Proceedings (Vol. 1276, No. 1, pp. 137–143). American Institute of Physics.
Fontijn, W. F. J. (1998). Magneto-optical spectroscopy of spinel type ferrites in bulk materials and layered structures.
Tauc, J. (Ed.). (2012). Amorphous and liquid semiconductors. Springer Science & Business Media.
C. Belkhaoui, N. Mzabi, H. Smaoui, P. Daniel, Enhancing the structural, optical and electrical properties of ZnO nanopowders through (Al+ Mn) doping. Results in Physics 12, 1686–1696 (2019)
M.N. Ashiq, M.F. Ehsan, M.J. Iqbal, I.H. Gul, Synthesis, structural and electrical characterization of Sb3+ substituted spinel nickel ferrite (NiSbxFe2− xO4) nanoparticles by reverse micelle technique. J. Alloy. Compd. 509(16), 5119–5126 (2011)
C.S. Lakshmi, C.S. Sridhar, G. Govindraj, S. Bangarraju, D.M. Potukuchi, Structural, magnetic and dielectric investigations in antimony doped nano-phased nickel-zinc ferrites. Physica B 459, 97–104 (2015)
M. El-Shabasy, DC electrical properties of Zn Ni ferrites. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 172(1–2), 188–192 (1997)
N. Chandamma, B.M. Manohara, B.S. Ujjinappa, G.J. Shankarmurthy, M.S. Kumar, Structural and electrical properties of Zinc doped Nickel ferrites nanoparticles prepared via facile combustion technique. J. Alloy. Compd. 702, 479–488 (2017)
T. Nitta, S. Hayakawa, Ceramic humidity sensors. IEEE Transactions on Components, Hybrids, and Manufacturing Technology 3(2), 237–243 (1980)
S. Muthurani, M. Balaji, S. Gautam, K.H. Chae, J.H. Song, D.P. Padiyan, K. Asokan, Magnetic and Humidity-Sensing Properties of Nanostructured Cu x Co1− x Fe2O4 Synthesized via Autocombustion. J. Nanosci. Nanotechnol. 11(7), 5850–5855 (2011)
E. McCafferty, A.C. Zettlemoyer, Adsorption of water vapour on α-Fe 2 O 3. Discuss. Faraday Soc. 52, 239–254 (1971)
N. Agmon, The grotthuss mechanism. Chem. Phys. Lett. 244(5–6), 456–462 (1995)
K. Manjunatha, K.M. Srininivasamurthy, C.S. Naveen, Y.T. Ravikiran, E.I. Sitalo, S.P. Kubrin, V.J. Angadi, Observation of enhanced humidity sensing performance and structure, dielectric, optical and DC conductivity studies of scandium doped cobalt chromate. J. Mater. Sci.: Mater. Electron. 30(18), 17202–17217 (2019)
Bagum, N., Gafur, M. A., Bhuiyan, A. H., & Saha, D. K. (2010). MgCl2 doped CuxZn1− xFe2O4 ferrite humidity sensors. physica status solidi (a), 207(4), 986–992.
I.C. Sathisha, K. Manjunatha, A. Bajorek, B.R. Babu, B. Chethan, T.R.K. Reddy, V.J. Angadi, Enhanced humidity sensing and magnetic properties of bismuth doped copper ferrites for humidity sensor applications. J. Alloys Compounds 848, 156577 (2020)
Funding
None to declare.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Anu Rana contributed to supervision, software, validation, writing-reviewing, and editing; Nitika contributed to data curation, writing-original draft preparation, investigation, formal analysis; Vinod Kumar contributed to conceptualization, methodology, visualization, resources.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflicts of interest
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Nitika, Rana, A. & Kumar, V. Evaluation of structural, magnetic, optical, electrical, and humidity sensing properties of manganese-substituted zinc ferrite nanoparticles. Appl. Phys. A 127, 860 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00339-021-05016-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00339-021-05016-4