Abstract
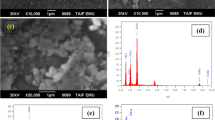
Quaternary Cu2ZnSnS4 (CZTS) nanoparticles of high quality have been synthesized utilizing rotary evaporation technique. The volume of the solvent, oleylamine (OLM), was found to affect the morphological, structural and electrical characteristics of the synthesized structures. The materials were characterized using various analytical techniques. XRD patterns and Raman measurements reveal that CZTS nanoparticles exist in a crystalline state with a kesterite structure. For OLM of 6 mL, transmission electron microscopy reveals the formation of spherical CZTS nanoparticles. Scanning electron microscopy analysis of the nanocrystal thin films clearly shows a crack-free, uniform-grain thin film with a particle size in the range between 1 and 2 µm. Ultraviolet–visible–near infrared (UV–Vis–NIR) spectra showed a direct band gap of 1.47 eV, which is close to the optimum value required for photovoltaic applications. The current synthetic strategy is rapid and simple, and it can be utilized for commercial application. Solar cells were built using the structure glass/Mo/CZTS/CdS/i-ZnO/AZO/Ag and were found to exhibit a conversion efficiency of about 2%.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
T.K. Todorov, K.B. Reuter, D.B. Mitzi, High efficiency solar cell with earth abundant liquid processed absorber. Adv. Mater. 22, E156–E159 (2010)
M. Valentini, C. Malerba, F. Menchini, D. Tedeschi, A. Polimeni, M. Capizzi, A. Mittiga, Effect of the order-disorder transition on the optical properties of Cu2ZnSnS4. Appl. Phys. Lett. 108, 211909 (2016)
A. Inamdar, S. Lee, K.-Y. Jeon, C.H. Lee, S. Pawar, R. Kalubarme, C.J. Park, H. Im, W. Jung, H. Kim, Optimized fabrication of sputter deposited Cu2ZnSnS4 (CZTS) thin films. Sol. Energy 91, 196–203 (2013)
B. Shin, O. Gunawan, Y. Zhu, N.A. Bojarczuk, S.J. Chey, S. Guha, Thin film solar cell with 8.4% power conversion efficiency using an earth-abundant Cu2ZnSnS4 absorber. Prog. Photovolt. Res. Appl. 21, 72–76 (2013)
M. Ravindiran, C. Praveenkumar, Status review and the future prospects of CZTS based solar cell–a novel approach on the device structure and material modeling for CZTS based photovoltaic device. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 94, 317–329 (2018)
C. Yan, J. Huang, K. Sun, S. Johnston, Y. Zhang, H. Sun, A. Pu, M. He, F. Liu, K. Eder, Cu2ZnSnS4 solar cells with over 10% power conversion efficiency enabled by heterojunction heat treatment. Nat. Energy 3, 764 (2018)
S.H. Hadke, S. Levcenko, S. Lie, C.J. Hages, J.A. Márquez, T. Unold, L.H. Wong, Synergistic effects of double cation substitution in solution-processed CZTS solar cells with over 10% efficiency. Adv. Energy Mater. 8, 1802540 (2018)
C. Zhang, J. Tao, J. Chu, An 8.7% efficiency co-electrodeposited Cu2ZnSnS4 photovoltaic device fabricated via a pressurized post-sulfurization process. J. Mater. Chem. C 6, 13275–13282 (2018)
N. Bao, X. Qiu, Y.-H.A. Wang, Z. Zhou, X. Lu, C.A. Grimes, A. Gupta, Facile thermolysis synthesis of CuInS2 nanocrystals with tunable anisotropic shape and structure. Chem. Commun. 47, 9441–9443 (2011)
E.M. Mkawi, K. Ibrahim, M.K.M. Ali, K.A.M. Saron, M.A. Farrukh, A.S. Mohamed, N.K. Allam, Aqueous synthesis of visible-light photoactive cuboid Cu2ZnSnS4 nanocrystals using rotary evaporation. Mater. Lett. 125, 195–197 (2014)
E.M. Mkawi, K. Ibrahim, M.K.M. Ali, M.A. Farrukh, N.K. Allam, Solvent solution-dependent properties of nonstoichiometric cubic Cu2ZnSnS4 nanoparticles. Chem. Phys. Lett. 608, 393–397 (2014)
E. Mkawi, K. Ibrahim, M. Ali, M. Farrukh, A. Mohamed, Dependence of the properties of copper zinc tin sulfide thin films prepared by electrochemical deposition on sulfurization temperature. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electr. 25, 857–863 (2014)
S.S. Mali, B.M. Patil, C.A. Betty, P.N. Bhosale, Y.W. Oh, S.R. Jadkar, R.S. Devan, Y.-R. Ma, P.S. Patil, Novel synthesis of kesterite Cu2ZnSnS4 nanoflakes by successive ionic layer adsorption and reaction technique: characterization and application. Electrochim. Acta 66, 216–221 (2012)
K.-C. Hsu, J.-D. Liao, J.-R. Yang, Y.-S. Fu, Cellulose acetate assisted synthesis and characterization of kesterite quaternary semiconductor Cu2ZnSnS4 mesoporous fibers by an electrospinning process. CrystEngComm 15, 4303–4308 (2013)
Y. Wang, H. Gong, Low temperature synthesized quaternary chalcogenide Cu2ZnSnS4 from nano-crystallite binary sulfides. J. Electrochem. Soc. 158, H800–H803 (2011)
P. Fernandes, P. Salomé, A. Da Cunha, Growth and Raman scattering characterization of Cu2ZnSnS4 thin films. Thin Solid Films 517, 2519–2523 (2009)
M. Jiang, X. Yan, Cu 2ZnSnS 4 Thin Film Solar Cells: Present Status and Future Prospects (INTECH Open Access Publisher, London, 2013)
K. Mokurala, P. Bhargava, S. Mallick, Single step synthesis of chalcogenide nanoparticles Cu2ZnSnS4, Cu2FeSnS4 by thermal decomposition of metal precursors. Mater. Chem. Phys. 147, 371–374 (2014)
A. Khare, B. Himmetoglu, M. Johnson, D.J. Norris, M. Cococcioni, E.S. Aydil, Calculation of the lattice dynamics and Raman spectra of copper zinc tin chalcogenides and comparison to experiments. J. Appl. Phys. 111, 083707 (2012)
S.W. Shin, S. Pawar, C.Y. Park, J.H. Yun, J.-H. Moon, J.H. Kim, J.Y. Lee, Studies on Cu2ZnSnS4 (CZTS) absorber layer using different stacking orders in precursor thin films. Sol. Energy Mater. Sol. Cells 95, 3202–3206 (2011)
S.W. Shin, J.H. Han, C.Y. Park, S.-R. Kim, Y.C. Park, G. Agawane, A. Moholkar, J.H. Yun, C.H. Jeong, J.Y. Lee, A facile and low cost synthesis of earth abundant element Cu2ZnSnS4 (CZTS) nanocrystals: effect of Cu concentrations. J. Alloys Compd. 541, 192–197 (2012)
W. Wang, M.T. Winkler, O. Gunawan, T. Gokmen, T.K. Todorov, Y. Zhu, D.B. Mitzi, Device characteristics of CZTSSe thin-film solar cells with 12.6% efficiency. Adv. Energy Mater. 4, 1301465 (2014)
A. Redinger, S. Siebentritt, Coevaporation of Cu2ZnSnSe4 thin films. Appl. Phys. Lett. 97, 092111 (2010)
S. Chen, X. Gong, A. Walsh, S.-H. Wei, Defect physics of the kesterite thin-film solar cell absorber Cu2ZnSnS4. Appl. Phys. Lett. 96, 021902 (2010)
M. Kumar, A. Dubey, N. Adhikari, S. Venkatesan, Q. Qiao, Strategic review of secondary phases, defects and defect-complexes in kesterite CZTS–Se solar cells. Energy Environ. Sci. 8, 3134–3159 (2015)
S. Bourdais, C. Choné, B. Delatouche, A. Jacob, G. Larramona, C. Moisan, A. Lafond, F. Donatini, G. Rey, S. Siebentritt, Is the Cu/Zn disorder the main culprit for the voltage deficit in kesterite solar cells? Adv. Energy Mater. 6, 1502276 (2016)
S. Siebentritt, S. Schorr, Kesterites—a challenging material for solar cells. Prog. Photovolt. Res. Appl. 20, 512–519 (2012)
X. Liu, J. Huang, F. Zhou, F. Liu, K. Sun, C. Yan, J.A. Stride, X. Hao, Understanding the key factors of enhancing phase and compositional controllability for 6% efficient pure-sulfide Cu2ZnSnS4 solar cells prepared from quaternary wurtzite nanocrystals. Chem. Mater. 28, 3649–3658 (2016)
Acknowledgements
This project was funded by the Deanship of Scientific Research (DSR) at King Abdulaziz University, Jeddah, under Grant No. D1439-52-130. The authors, therefore, acknowledge with thanks DSR for technical and financial support.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mkawi, E.M., Al-Hadeethi, Y., Shalaan, E. et al. Solution-processed sphere-like Cu2ZnSnS4 nanoparticles for solar cells: effect of oleylamine concentration on properties. Appl. Phys. A 126, 50 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00339-019-3233-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00339-019-3233-1