Abstract
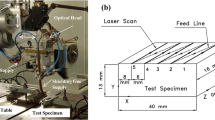
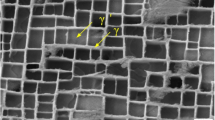
The aim of the study was to investigate the effect of laser shock peening (LSP) on surface topography evolution of metallic targets. Samples manufactured by a Ni-based single crystal superalloy with polished finish were treated by LSP, and the surface topographies before and after LSP were examined by non-contact White-Light Interferometer (WLI). Results showed the following three aspects: (a) By taking advantage of WLI, the shrinkage porosities and the interdendritic structures were observed simultaneously. (b) With the increasing impact times, the round pit induced by laser shock became deeper. (c) The nano-scale surface reliefs were found on the bottom of round pit induced by LSP, and the specific plastic flow of metallic materials under the action of compressive stresses was deemed as the primary contributor to the formation of surface reliefs. It revealed a novel microscale plastic deformation phenomenon of metallic materials in surface strengthening.










Similar content being viewed by others
References
M. Thomas, T. Lindley, D. Rugg, M. Jackson, The effect of shot peening on the microstructure and properties of a near-alpha titanium alloy following high temperature exposure. Acta Mater. 60, 5040–5048 (2012)
R.K. Nalla, I. Altenberger, U. Noster, G.Y. Liu, B. Scholtes, R.O. Ritchie, On the influence of mechanical surface treatments—deep rolling and laser shock peening—on the fatigue behavior of Ti–6Al–4 V at ambient and elevated temperatures. Mater. Sci. Eng. A. 355, 216–230 (2003)
F.A. Guo, N. Trannoy, J. Lu, Microstructural analysis by scanning thermal microscopy of a nanocrystalline Fe surface induced by ultrasonic shot peening. Superlattices Microstruct. 35, 445–453 (2004)
A. Azhari, C. Schindler, K. Hilbert, C. Godard, E. Kerscher, Influence of waterjet peening and smoothing on the material surface and properties of stainless steel 304. Surf. Coat. Technol. 258, 1176–1182 (2014)
I. Nikitin, B. Scholtes, H. Maier, I. Altenberger, High temperature fatigue behavior and residual stress stability of laser-shock peened and deep rolled austenitic steel AISI 304. Scripta Mater. 50, 1345–1350 (2004)
J.Z. Lu, K.Y. Luo, Y.K. Zhang, C.Y. Cui, G.F. Sun, J.Z. Zhou, L. Zhang, J. You, K.M. Chen, J.W. Zhong, Grain refinement of LY2 aluminum alloy induced by ultra-high plastic strain during multiple laser shock processing impacts. Acta Mater. 58, 3984–3994 (2010)
L. Wagner, G. Luetjering, Influence of shot peening on the fatigue behavior of titanium alloys, In: Proceedings of the First International Conference on Shot Peening, Paris, 1996, pp. 453–460
S. Zabeen, M. Preuss, P.J. Withers, Evolution of a laser shock peened residual stress field locally with foreign object damage and subsequent fatigue crack growth. Acta Mater. 83, 216–226 (2015)
M.P. Sealy, Y.B. Guo, Surface integrity and process mechanics of laser shock peening of novel biodegradable magnesium–calcium (Mg–Ca) alloy. J. Mech. Behav. Biomed. Mater. 3, 488–496 (2010)
M. Dorman, M.B. Toparli, N. Smyth, A. Cini, M.E. Fitzpatrick, P.E. Irving, Effect of laser shock peening on residual stress and fatigue life of clad 2024 aluminium sheet containing scribe defects, Mater. Sci. Eng. A. 548, 142–151 (2012)
S. Zabeen, M. Preuss, P.J. Withers, Residual stresses caused by head-on and 45° foreign object damage for a laser shock peened Ti–6Al–4 V alloy aerofoil. Mater. Sci. Eng. A. 560, 518–527 (2013)
Y. Liao, G.J. Cheng, Controlled precipitation by thermal engineered laser shock peening and its effect on dislocation pinning: multiscale dislocation dynamics simulation and experiments. Acta Mater. 61, 1957–1967 (2013)
C.-H. Lu, B. Remington, B. Maddox, B. Kad, H.-S. Park, S. Prisbrey, M. Meyers, Laser compression of monocrystalline tantalum. Acta Mater. 60, 6601–6620 (2012)
M.A. Meyers, F. Gregori, B. Kad, M. Schneider, D. Kalantar, B. Remington, G. Ravichandran, T. Boehly, J. Wark, Laser-induced shock compression of monocrystalline copper: characterization and analysis. Acta Mater. 51, 1211–1228 (2003)
G.J. Cheng, M.A. Shehadeh, Multiscale dislocation dynamics analyses of laser shock peening in silicon single crystals. Int. J. Plast. 22, 2171–2194 (2006)
B.Y. Cao, D.H. Lassila, M.S. Schneider, B.K. Kad, C.X. Huang, Y.B. Xu, D.H. Kalantar, B.A. Remington, M.A. Meyers, Effect of shock compression method on the defect substructure in monocrystalline copper. Mater. Sci. Eng. A. 409, 270–281 (2005)
F. Pusavec, H. Hamdi, J. Kopac, I. Jawahir, Surface integrity in cryogenic machining of nickel based alloy—Inconel 718. J. Mater. Process. Technol. 211, 773–783 (2011)
E. Brinksmeier, T. Brockhoff, Utilization of grinding heat as a new heat treatment process, CIRP Ann. Manuf. Technol. 45, 283–286 (1996)
S. Vukelić, J.W. Kysar, Y.L. Yao, Grain boundary response of aluminum bicrystal under micro scale laser shock peening. Int. J. Solids Struct. 46, 3323–3335 (2009)
Y.K. Zhang, X.D. Ren, J.Z. Zhou, J.Z. Lu, L.C. Zhou, Investigation of the stress intensity factor changing on the hole crack subject to laser shock processing. Mater. Des. 30, 2769–2773 (2009)
I. Metrology, The scanning probe image processor, SPIPTM, user’s and reference guide version, 4 (2002)
O. Arora, S. Dapkunas, Interdendritic structures of a directionally solidified cobalt-base alloy. Metall. Mater. Trans. B. 3, 3033–3035 (1972)
L. Liu, T. Jin, N. Zhao, Z. Wang, X. Sun, H. Guan, Z. Hu, Effect of carbon additions on the microstructure in a Ni-base single crystal superalloy. Mater. Lett. 58, 2290–2294 (2004)
A. Osma, E. Kayali, M. Öveçoglu, The effect of elevated temperature and silicon addition on a cobalt-based wear resistant superalloy. J. Mater. Sci. 31, 4603–4608 (1996)
G.X. Lu, J.D. Liu, Y.Z. Zhou, T. Jin, X.F. Sun, Z.Q. Hu, Differences in the micromechanical properties of dendrites and interdendritic regions in superalloys. Philos. Mag. Lett. (2016) 1–8.
D. Argence, C. Vernault, Y. Desvallees, D. Fournier, MC-NG, Generation single crystal superalloy for future aeronautical turbine blades and vanes. In: Superalloys, TMS, Warrendale, 2000, pp. 829–837.
G.X. Lu, J.D. Liu, H.C. Qiao, Y.Z. Zhou, T. Jin, X.F. Sun, Z.Q. Hu, Nonuniformity of morphology and mechanical properties on the surface of single crystal superalloy subjected to laser shock peening. J. Alloy. Compd. 658, 721–725 (2016)
L.K. Gillespie, P. Blotter, The formation and properties of machining burrs. J. Manuf. Sci. Eng. 98, 66–74 (1976)
S. Malayappan, R. Narayanasamy, An experimental analysis of upset forging of aluminium cylindrical billets considering the dissimilar frictional conditions at flat die surfaces. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 23, 636–643 (2004)
Acknowledgements
This work was partly supported by the High Technology Research and Development Program of China (No. 2014AA041701) and the National Natural Science Foundation of China (NSFC) under Grant Nos. 51171179, 51271174, 51331005, and 11332010. In addition, the authors thank S. Guan and Z.W. Shi for valuable advices, and thank S. Gao for manufacturing of samples.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Deceased: Z. Q. Hu.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lu, G.X., Liu, J.D., Qiao, H.C. et al. Surface topography evolution of Ni-based single crystal superalloy under laser shock: Formation of the nano-scale surface reliefs. Appl. Phys. A 123, 213 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00339-017-0814-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00339-017-0814-8