Abstract
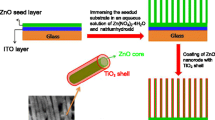
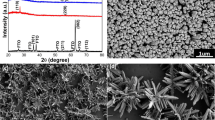
Growth of ZnO nanowires within TiO2 mesoporous structures is carried out by hydrothermal method. Structural, optical and thermal characterizations have been carried out by SEM, XRD, EDAX, DTG, TG, PL and UV–Vis spectroscopy. XRD characterization shows that the all diffraction peaks of the tandem nanostructures films can be well indexed to a mixture of hexagonal wurtzite ZnO and anatase TiO2 structures. The UV–Visible absorbance spectrum indicates that the tandem nanostructures based on TiO2 mesoporous/ZnO nanowire arrays have 3.13 eV band gap energy while pure ZnO nanowire and bare TiO2 mesoporous show 3.37 and 3.22 eV band gap energy, respectively. The PL spectra of tandem nanostructures show that the UV, violet and yellow emission peaks appeared at 3.1, 2.6 and 2.3 eV, respectively. It has been shown that from the PL spectra, the enhanced ultraviolet emission of TiO2/ZnO tandem structures is related to the fluorescence resonance energy transfer between TiO2 mesoporous and ZnO nanowires. Thermogravimetric analysis from room temperature to 800 °C has been performed to identify the thermal stability and the amount of tandem TiO2/ZnO structures.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Z. Yunyan, M. Jin, Controllable synthesis of flower-and rod-like ZnO nanostructures by simply tuning the ratio of sodium hydroxide to zinc acetate. Nanotechnology 7, 075606 (2007)
C. Cheng, A. Amini, C. Zhu, Z. Xu, H. Song, N. Wang, Enhanced photocatalytic performance of TiO2–ZnO hybrid nanostructures. Sci. Rep. 4, 4181 (2014)
C. Lao, Y. Li, C.P. Wong, Z.L. Wang, Enhancing the electrical and optoelectronic performance of nanobelt devices by molecular surface functionalization. Nano Lett. 7(5), 1323–1328 (2007)
B. KiliC, L. Wang, O. Ozdemir, M. Lu, S. Tüzemen, One dimensional (1D) ZnO nanowires dye sensitized solar cell. J. Nanosci. Nanotechnol 13, 333–338 (2013)
Y. Tak, S.J. Hong, J.S. Lee, K. Yong, Solution-based synthesis of a CdS nanoparticle/ZnO nanowire heterostructure array. Cryst. Growth Des. 9(6), 2627–2632 (2009)
M.R. Mohammadi, R.R.M. Louca, D.J. Fray, M.E. Welland, Dye-sensitized solar cells based on a single layer deposition of TiO2 from a new formulation paste and their photovoltaic performance. Sol. Energy 86(9), 2654–2664 (2012)
B. Kılıç, E. Gür, S. Tüzemen, Nanoporous ZnO photoelectrode for dye-sensitized solar cell. J. Nanomater. 7, 474656 (2012)
S.H. Lee, H.J. Lee, H. Goto, M. Cho, T. Yao, Fabrication of Porous ZnO nanostructures and morphology control. Phys Status Solidi C 4(5), 1747–1750 (2007)
Q. Zhang, C.S. Dandeneau, X. Zhou, G. Cao, ZnO nanostructures for dye sensitized solar cell. Adv. Mater. 21, 4087–4108 (2009)
Z.L. Wang, J. Song, Piezoelectric nanogenerators based on zinc oxide nanowire arrays. Science 312(5771), 242–246 (2006)
J. Zhou, N.S. Xu, Z.L. Wang, Dissolving behavior and stability of ZnO wires in biofluids: a study on biodegradability and biocompatibility of ZnO nanostructures. Adv. Mater. 18(18), 2432–2435 (2006)
G. Tang, S. Liu, H. Tang, D. Zhang, C. Li, X. Yang, Template-assisted hydrothermal synthesis and photocatalytic activity of novel TiO2 hollow nanostructures. Ceram Int. 39, 4969–4974 (2013)
T. Yu, X. Tan, L. Zhao, Y. Yin, P. Chen, J. Wei, Characterization, activity and kinetics of a visible light driven photocatalyst: cerium and nitrogen co-doped TiO2 nanoparticles. Chem. Eng. J. 157, 86–92 (2010)
S. Kim, D. Kim, H. Choi, M.S. Kang, K. Song, S.O. Kang, J. Ko, Enhanced photovoltaic performances and long-term stability of quasi solid state dye sensitized solar cell via molecular engineering. Chem. Commun. 40, 4951–4953 (2008)
S.H. Kang, J.Y. Kim, Y.Y. Kim, H.S. Kim, Y.E. Sung, Surface modification of stretched TiO2 nanotubes for solid-state dye-sensitized solar cells. J. Phys. Chem. C 111, 9614–9623 (2007)
J.J. Qiu, F.W. Zhuge, K. Lou, X.M. Li, X.D. Gao, X.Y. Gan, W.D. Yu, H.K. Kim, Y.H. Hwang, A facile route to aligned TiO2 nanotube arrays on transparent conducting oxide substrates for dye-sensitized solar cells. J. Mater. Chem. 21, 5062–5068 (2011)
K.E. Kim, S.R. Jang, J. Park, R. Vittal, K.J. Kim, Enhancement in the performance of dye-sensitized solar cells containing ZnO-covered TiO2 electrodes prepared by thermal chemical vapor deposition Sol. Energy Mater. Sol. Cells 91, 366–370 (2007)
T.R. Andersen, T.T. Larsen-Olsen, B. Andreasen, A.P.L. Böttiger, J.E. Carlé, M. Helgesen, E. Bundgaard, K. Norrman, J.W. Andreasen, M. Jørgensen, F.C. Krebs, Aqueous processing of low-band-gap polymer solar cells using roll-to-roll methods. ACS Nano 5, 4188–4196 (2011)
C-Shii Chou, F-Cheng Chou, J-Yuan Kang, Preparation of ZnO-coated TiO2 electrodes using dip coating and their applications in dye-sensitized solar cells. Powder Technol. 215–216, 38–45 (2012)
C.Y. Jiang, X.W. Sun, G.Q. Lo, D.L. Kwong, J.X. Wang, Improved dye-sensitized solar cells with a ZnO-nanoflower photoanode. Appl. Phys. Lett. 90(26), 263501–263503 (2007)
F. Yueping, P. Qi, W. Xiaogang, W. Jiannong, Y. Shihe, Synthesis of ultrathin ZnO nanofibers aligned on a zinc substrate. Small 2(5), 612–615 (2006)
S. Baruah, J. Dutta, Hydrothermal growth of ZnO nanostructures. Sci. Technol. Adv. Mater. 10(1), 013001 (2009)
N. Wang, X.Y. Li, Y.X. Wang, Y. Hou, X.J. Zou, G.H. Chen, Synthesis of ZnO/TiO2 nanotube composite film by a two-step route. Mater. Lett. 62, 3691–3693 (2008)
A. Irannejad, K. Janghorban, O.K. Tan, H. Huang, C.K. Lim, P.Y. Tan, X. Fang, C.S. Chua, S. Maleksaeedi, S.M.H. Hejazi, M.M. Shahjamali, M. Ghaffari, Effect of the TiO2 shell thickness on the dye-sensitized solar cells with ZnO–TiO2 core–shell nanorod electrodes. Electrochim. Acta 58, 19–24 (2011)
Bayram Kilic, Taylan Günes, Ilknur Besirli, Merve Sezginer, Sebahattin Tuzemen, Construction of 3-dimensional ZnO-nanoflower structures for high quantum and photocurrent efficiency in dye sensitized solar cell. Appl. Surf. Sci. 318, 32–36 (2014)
C.W. Zou, X.D. Yan, J. Han, R.Q. Chen, J.M. Bian, E. Haemmerle, W. Gao, Preparation and enhanced photoluminescence property of ordered ZnO/TiO2 bottlebrush nanostructures. Chem. Phys. Lett. 476, 84–88 (2009)
L. Xu, H. Shen, X. Li, R. Zhu, Influence of annealing temperature on the photoluminescence property of ZnO thin film covered by TiO2 nanoparticles. J. Lumin. 130, 2123–2127 (2010)
D. Ma, J. Huang, Z. Ye, L. Wang, B. Zhao, Relationship between photoluminescence and structural properties of the sputtered Zn1−xCdxO films on Si substrates. Opt. Mater. 25, 367 (2004)
K. Prabakar, C. Kim, C. Lee, UV, violet and blue-green luminescence from RF sputter deposited ZnO: Al thin films. Cryst. Res. Technol. 40, 1150 (2005)
H.Y. Lin, Y.Y. Chou, C.L. Cheng, Y.F. Chen, Giant enhancement of band edge emission based on ZnO/TiO2 nanocomposites. Opt. Express 15, 13832 (2007)
A. Leelavathi, G. Madrasa, N. Ravishankar, Origin of enhanced photocatalytic activity and photoconduction in high aspect ratio ZnO nanorods. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 15, 10795–10802 (2013)
T. Ohsaka, F. Izumi, Y. Fujiki, Raman spectrum of anatase, TiO2. J. Raman Spectrosc. 7, 321–324 (1978)
A. Umar, Y.B. Hahn, ZnO nanosheet networks and hexagonal nanodiscs grown on silicon substrate: growth mechanism and structural and optical properties. Nanotechnology 17, 2174 (2006)
Acknowledgments
This project was supported by The Scientific and Technological Research Council of Turkey (TUBITAK, Project Number: 114F292) and the Research found of Yalova University, Project Number 2013/BAP/085.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kılıç, B., Çelik, V. Self-assembled growth of tandem nanostructures based on TiO2 mesoporous/ZnO nanowire arrays and their optoelectronic and photoluminescence properties. Appl. Phys. A 119, 783–790 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00339-015-9030-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00339-015-9030-6