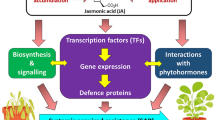
Abstract
Charcoal rot (CR) is a major disease of soybean, which is caused by Macrophomina phaseolina (Mp). Increasing temperatures and low rainfall in recent years have immensely benefitted the pathogen. Hence, the search for genetically acquired resistance to this pathogen is essential. The pathogen is a hemibiotroph, which germinates on the root surface and colonizes epidermal tissue. Several surface receptors initiate pathogenesis, followed by the secretion of various enzymes that provide entry to host tissue. Several enzymes and other converging cascades in the pathogen participate against host defensive responses. β-glucan of the fungal cell wall is recognized as MAMPs (microbe-associated molecular patterns) in plants, which trigger host immune responses. Kinase receptors, resistance, and pathogenesis-related genes correspond to host defense response. They work in conjunction with hormone-mediated defense pathway especially, the systemic acquired resistance, calcium-signaling, and production of phytoalexins. Due to its quantitative nature, limited QTLs have been identified in soybean for CR resistance. The present review attempts to provide a functional link between M. phaseolina pathogenicity and soybean responses. Elucidation of CR resistance responses would facilitate improved designing of breeding programs, and may help in the selection of corresponding genes to introgress CR resistant traits.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abbas HK, Bellaloui N, Accinelli C, Smith JR, Shier WT (2019) Toxin production in soybean (Glycine max L.) plants with charcoal rot disease and by Macrophomina phaseolina, the fungus that causes the disease. Toxins. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins11110645
Adeyanju A, Little C, Yu J, Tesso T (2015) Genome-wide association study on resistance to stalk rot diseases in grain sorghum. Genes Genomes Genet 5(6):1165–1175
Akbar MT, Habib AM, Chowdhury DU, Bhuiyan MI, Mostafa KM, Mondol S, Mosleh IM (2013) An insight into the lignin peroxidase of Macrophomina phaseolina. Bioinformation 9:730
Almeida ÁM, Abdelnoor RV, Arias CA, Carvalho VP, Jacoud Filho DS, Marin SR, Benato LC, Pinto MC, Carvalho CG (2003a) Genotypic diversity among Brazilian isolates of Macrophomina phaseolina revealed by RAPD. Fitopatol Bras 28:279–285
Almeida ÁM, Amorim L, Bergamin Filho A, Torres E, Farias JR, Benato LC, Pinto MC, Valentim N (2003b) Progress of soybean charcoal rot under tillage and no-tillage systems in Brazil. Fitopatol Bras 28:131–135
Ammon V, Wyllie TD, Brown MF Jr (1974) An ultrastructural investigation of pathological alterations induced by Macrophomina phaseolina (Tassi) Goid in seedlings of soybean, Glycine max (L.) Merrill. Physiol Plant Pathol 4:1–4
Ammon V, Wyllie TD, Brown MF (1975) Investigation of the infection process of Macrophomina phaseolina on the surface of soybean roots using scanning electron microscopy. Mycopathologia 55:77–81
Arasimowicz-Jelonek M, Floryszak-Wieczorek J (2014) Nitric oxide: an effective weapon of the plant or the pathogen? Mol Plant Pathol 15:406–416
Arfaoui A, El Hadrami A, Daayf F (2018) Pre-treatment of soybean plants with calcium stimulates ROS responses and mitigates infection by Sclerotinia sclerotiorum. Plant Physiol Biochem 122:121–128
Arias MM, Leandro LF, Munkvold GP (2013a) Aggressiveness of Fusarium species and impact of root infection on growth and yield of soybeans. Phytopathology 103:822–832
Arias RS, Ray JD, Mengistu A, Scheffler BE (2011) Discriminating microsatellites from Macrophomina phaseolina and their potential association to biological functions. Plant Pathol 60:709–718
Arias SG, Pons RR, Stowasser V, Sanfuentes E (2013b) Temporal analysis of charcoal root rot in forest nurseries under different pathogen inoculum densities and soil moisture content. Tropical Plant Pathol 38:179–187
Arora NK, Khare E, Verma A, Sahu RK (2008) In vivo control of Macrophomina phaseolina by a chitinase and β-1,3-glucanase-producing pseudomonad NDN1. Symbiosis 46:129–135
Attia M, Awad NM, Turky AS, Hamed HA (2011) Induction of defense responses in soybean plants against Macrophomina phaseolina by some strains of plant growth promoting rhizobacteria. J Appl Sci Response 7:1507–1517
Aylward J, Steenkamp ET, Dreyer LL, Roets F, Wingfield BD, Wingfield MJ (2017) A plant pathology perspective of fungal genome sequencing. IMA Fungus 8:1–45
Babu BK, Saxena AK, Srivastava AK, Arora DK (2007) Identification and detection of Macrophomina phaseolina by using species-specific oligonucleotide primers and probe. Mycologia 99:797–803
Bandara YA, Weerasooriya DK, Liu S, Little CR (2018) The necrotrophic fungus Macrophomina phaseolina promotes charcoal rot susceptibility in grain sorghum through induced host cell wall-degrading enzymes. Phytopathology. https://doi.org/10.1094/PHYTO-12-17-0404-R
Bellaloui N, Mengistu A, Paris RL (2008) Soybean seed composition in cultivars differing in resistance to charcoal rot (Macrophomina phaseolina). J Agric Sci 146:667–675
Bellaloui N, Mengistu A, Zobiole LH, Shier WT (2012) Resistance to toxin-mediated fungal infection: role of lignins, isoflavones, other seed phenolics, sugars, and boron in the mechanism of resistance to charcoal rot disease in soybean. Toxin Rev 31:16–26
Bhattacharya D, Dhar TK, Siddiqui KA, Ali E (1994) Inhibition of seed germination by Macrophomina phaseolina is related to phaseolinone production. J Appl Bacteriol 77:129–133
Bhattacharya DI, Dhar TK, Ali ES (1992) An enzyme immunoassay of phaseolinone and its application in estimation of the amount of toxin in Macrophomina phaseolina infected seeds. Appl Environ Microbiol 58:1970–1974
Bhattacharya G, Dhar TK, Bhattacharya FK, Siddiqui KA (1987) Mutagenic action of phaseolinone, a mycotoxin isolated from Macrophomina phaseolina. Aust J Biol Sci 40:349–354
Bhattacharya G, Roy AK, Siddiqui KA, Bhadra R (1990) Phaseolinone, a new mycotoxin, inhibits RNA polymerase (s) other than RNA polymerase II. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 168:51–57
Bhowal J, Ghosh S, Guha AK, Chaterjee BP (2010) Infection of jute seedlings by the phytopathogenic fungus Macrophomina phaseolina mediated by endogenous lectin. Res J Microbiol 5:657–666
Bhowal J, Guha AK, Chatterjee BP (2005) Purification and molecular characterization of a sialic acid specific lectin from the phytopathogenic fungus Macrophomina phaseolina. Carbohydr Res 340:1973–1982
Boudsocq M, Sheen J (2013) CDPKs in immune and stress signaling. Trends Plant Sci 18:30–40
Bressano M, Giachero ML, Luna CM, Ducasse DA (2010) An in vitro method for examining infection of soybean roots by Macrophomina phaseolina. Physiol Mol Plant Pathol 74:201–204
Cao H, Glazebrook J, Clarke JD, Volko S, Dong X (1997) The Arabidopsis NPR1 gene that controls systemic acquired resistance encodes a novel protein containing ankyrin repeats. Cell 88:57–63
Castanera R, Lopez-Varas L, Borgognone A, LaButti K, Lapidus A, Schmutz J, Grimwood J, Perez G, Pisabarro AG, Grigoriev IV et al (2016) Transposable elements versus the fungal genome: impact on whole-genome architecture and transcriptional profiles. PLoS Genet. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pgen.1006108
Chang KF, Hwang SF, Ahmed HU, Strelkov SE, Harding MW, Conner RL, McLaren DL, Gossen BD, Turnbull GD (2017) Disease reaction to Rhizoctonia solani and yield losses in soybean. Can J Plant Sci 98:115–124
Choudhary DK (2011) Plant growth-promotion (PGP) activities and molecular characterization of rhizobacterial strains isolated from soybean (Glycine max L. Merril) plants against charcoal rot pathogen Macrophomina phaseolina. Biotechnol Lett 33:2287
Chowdhury S, Basu A, Kundu S (2017) Biotrophy-necrotrophy switch in pathogen evoke differential response in resistant and susceptible sesame involving multiple signaling pathways at different phases. Sci Rep 7:17251
Cloud GL, Rupe JC (1994) Influence of nitrogen, plant growth stage, and environment on charcoal rot of grain sorghum caused by Macrophomina phaseolina (Tassi) Goid. Plant Soil 158:203–210
Cook GE, Boosalis MG, Dunkle LD, Odvody GN (1973) Survival of Macrophomina phaseoli in corn and sorgum stalk residue. Plant Disease Reporter 57:873–875
Coser SM, Chowda Reddy RV, Zhang J, Mueller DS, Mengistu A, Wise KA, Allen TW, Singh A, Singh AK (2017) Genetic architecture of charcoal rot (Macrophomina phaseolina) resistance in soybean revealed using a diverse panel. Front Plant Sci 8:1626
Cruz DRJ (2011) Influence of soils, nutrition, and water relations upon charcoal rot disease processes in Kansas (dissertation): Kansas State University
Cummings JA, Bergstrom GC (2013) First report of charcoal rot caused by Macrophomina phaseolina in soybean in New York. Plant Dis 97:1506
D’ovidio R, Roberti S, DiGiovanni M, Capodicasa C, Melaragni M, Sella L, Tosi P, Favaron F (2006) The characterization of the soybean polygalacturonase-inhibiting proteins (Pgip) gene family reveals that a single member is responsible for the activity detected in soybean tissues. Planta 224:633–645
da Silva MP (2018) Genetic and Phytopathological Studies on Charcoal Rot Resistance in Soybean Glycine max (L) Merr. dissertation: University of Arkansas
Del Giudice J, Cam Y, Damiani I, Fung-Chat F, Meilhoc E, Bruand C, Brouquisse R, Puppo A, Boscari A (2011) Nitric oxide is required for an optimal establishment of the Medicago truncatula–Sinorhizobium meliloti symbiosis. New Phytol 191:405–417
Del Poeta M, Nimrichter L, Rodrigues ML, Luberto C (2014) Synthesis and biological properties of fungal glucosylceramide. PLoS Pathog. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.ppat.1003832
Delledonne M, Xia Y, Dixon RA, Lamb C (1998) Nitric oxide functions as a signal in plant disease resistance. Nature 394:585
Dhar TK, Siddiqui KA, Ali E (1982) Structure of phaseolinone, a novel phytotoxin from Macrophomina phaseolina. Tetrahedron Lett 23:5459–5462
Dhingra OD, Sinclair JB (1977) An annotated bibliography of Macrophomina phaseolina, 1908-1975. ImprensaUniversit aria, UniversidadeFeederal de Vicosa, Minas Gerais
Dhingra OD, Sinclair JB (1978) Biology and pathology of Macrophomina phaseolina. ImprensaUniversit aria UniversidadeFeederal de Vicosa, Minas Gerais
Dong H, Shi S, Zhang C, Zhu S, Li M, Tan J, Yu Y, Lin L, Jia S, Wang X, Wu Y (2018) Transcriptomic analysis of genes in soybean in response to Peronospora manshurica infection. BMC Genomics 19:366
Dorrance AE, Mills D, Robertson AE, Draper MA, Giesler L, Tenuta A (2007) Phytophthora root and stem rot of soybean. The Plant Health Instructor. https://doi.org/10.1094/PHI-I-2007-0830-07
Doubledee MD (2012) Effects of environment and genotype on charcoal rot development on soybeans. University of Arkansas, Fayetteville
Eckardt NA (2008) Oxylipin signaling in plant stress responses. Plant Cell 20:495–497
Fesel PH, Zuccaro A (2016) β-glucan: crucial component of the fungal cell wall and elusive MAMP in plants. Fungal Genet Biol 90:53–60
Gangopadhyay S, Wyllie TD, Luedders VD (1970) Charcoal rot disease of soybean transmitted by seeds. Plant Dis Rep 54(10):1088–1091
García-Olivares JG, López-Salinas E, Cumpián-Gutiérrez J, Cantú-Almaguer MA, Zavala-García F, Mayek-Pérez N (2012) Grain yield and charcoal rot resistance stability in common beans under terminal drought conditions. J Phytopathol 160:98–105
George HL, Hirschi KD, VanEtten HD (1998) Biochemical properties of the products of cytochrome P450 genes (PDA) encoding pisatin demethylase activity in Nectria haematococca. Arch Microbiol 170:147–154
Gfeller A, Dubugnon L, Liechti R, Farmer EE (2010) Jasmonate biochemical pathway. Sci Signal 3:3
Ghorbanipour A, Rabiei B, Rahmanpour S, Khodaparast SA (2019) Association analysis of charcoal rot disease resistance in soybean. Plant Pathol J 35:189
Gill SS, Tuteja N (2010) Reactive oxygen species and antioxidant machinery in abiotic stress tolerance in crop plants. Plant Physiol Biochem 48:909–930
Goidanish G (1947) Revisione del genere Macrophomina Petrak. Species tipica: Macrophomina phaseolina (Tass.) Goid. nov. comb. nec. M. phaseoli (Maubl.). Ashby Annali Della Sperimentazione Agraria 1:449–461
Gowda DSS (2014) Molecular mapping of charcoal rot resistance in soybean (Glycine max L. Merr.) (dissertation). Division of Genetics: Indian Agricultural Research Institute New Delhi
Gupta GK, Sharma SK, Ramteke R (2012) Biology, epidemiology and management of the pathogenic fungus Macrophominaphaseolina (Tassi) Goid with special reference to charcoal rot of soybean (Glycine max (L.) Merrill). J Phytopath 160:167–180
Hefel A (2015) The link between susceptibility to Macrophomina phaseolina and three phytohormones in Medicago truncatula [dissertation]. Wichita State University
Hemmati P, Zafari D, Mahmoodi SB, Hashemi M, Gholamhoseini M, Dolatabadian A, Are A (2018) Histopathology of charcoal rot disease (Macrophomina phaseolina) in resistant and susceptible cultivars of soybean. Rhizosphere 7:27–34
Homrich MS, Wiebke-Strohm B, Weber RL, Bodanese-Zanettini MH (2012) Soybean genetic transformation: a valuable tool for the functional study of genes and the production of agronomically improved plants. Genet Mol Biol 35:998–1010
Islam MS, Haque MS, Islam MM, Emdad EM, Halim A, Hossen QM, Hossain MZ, Ahmed B, Rahim S, Rahman MS et al (2012) Tools to kill: genome of one of the most destructive plant pathogenic fungi Macrophomina phaseolina. BMC Genomics 13:493
Jennings DB, Ehrenshaft M, Pharr DM, Williamson JD (1998) Roles for mannitol and mannitol dehydrogenase in active oxygen-mediated plant defense. Proc Natl Acad Sci 95:15129–15133
Joshi RK, Nayak S (2011) Functional characterization and signal transduction ability of nucleotide-binding site-leucine-rich repeat resistance genes in plants. Genet Mol Res 10:2637–2652
Kang YJ, Kim KH, Shim S, Yoon MY, Sun S, Kim MY, Van K, Lee SH (2012) Genome-wide mapping of NBS-LRR genes and their association with disease resistance in soybean. BMC Plant Biol 12:139
Kaur S, Dhillon GS, Brar SK, Vallad GE, Chand R, Chauhan VB (2012) Emerging phytopathogen Macrophomina phaseolina: biology, economic importance and current diagnostic trends. Crit Rev Microbiol 38:136–151
Khaledi N, Taheri P (2016) Biocontrol mechanisms of Trichoderma harzianum against soybean charcoal rot caused by Macrophomina phaseolina. J Plant Prot Res 56:21–31
Khan KA, Shoaib A, Arshad Awan Z, Basit A, Hussain M (2018) Macrophomina phaseolina alters the biochemical pathway in Vigna radiata chastened by Zn2+ and FYM to improve plant growth. J Plant Interact 13:131–140
Kim KH, Kang YJ, Kim DH, Yoon MY, Moon JK, Kim MY, Van K, Lee SH (2011) RNA-Seq analysis of a soybean near-isogenic line carrying bacterial leaf pustule-resistant and susceptible alleles. DNA Res 18:483–497
Kiprovski B, Malencic D, Popovic M, Budakov D, Stojšin V, Baleševic-Tubic S (2012) Antioxidant systems in soybean and maize seedlings infected with Rhizoctonia solani. J Plant Pathol 94:313–324
Kombrink E, Schmelzer E (2001) The hypersensitive response and its role in local and systemic disease resistance. Eur J Plant Pathol 107:69–78
Kumar K, Singh J (2000) Location, survival, transmission and management of seed-borne Macrophomina phaseolina, causing charcoal rot in soybean. Ann Plant Protect Sci 8:44–46
Lamb C, Dixon RA (1997) The oxidative burst in plant disease resistance. Annu Rev Plant Biol 48:251–275
Lawaju BR, Lawrence KS, Lawrence GW, Klink VP (2018) Harpin-inducible defense signaling components impair infection by the ascomycete Macrophomina phaseolina. Plant Physiol Biochem 129:331–348
Levine A, Tenhaken R, Dixon R, Lamb C (1994) H2O2 from the oxidative burst orchestrates the plant hypersensitive disease resistance response. Cell 79:583–593
Lin F, Zhao M, Baumann DD, Ping J, Sun L, Liu Y, Zhang B, Tang Z, Hughes E, Doerge RW, Hughes TJ (2014) Molecular response to the pathogen Phytophthora sojae among ten soybean near isogenic lines revealed by comparative transcriptomics. BMC Genomics 15:18
Liu J, Horstman HD, Braun E, Graham MA, Zhang C, Navarre D, Qiu WL, Lee Y, Nettleton D, Hill JH, Whitham SA (2011) Soybean homologs of MPK4 negatively regulate defense responses and positively regulate growth and development. Plant Physiol 157:1363–1378
Liu JZ, Braun E, Qiu WL, Shi YF, Marcelino-Guimarães FC, Navarre D, Hill JH, Whitham SA (2014) Positive and negative roles for soybean MPK6 in regulating defense responses. Mol Plant Microbe Interact 27:824–834
Lygin AV, Zernova OV, Hill CB, Kholina NA, Widholm JM, Hartman GL, Lozovaya VV (2013) Glyceollin is an important component of soybean plant defense against Phytophthora sojae and Macrophomina phaseolina. Phytopathology 103:984–994
Lyne RL, Mulheirn LJ, Leworthy DP (1976) New pterocarpinoid phytoalexins of soybean. J Chem Soc Chem Commun 13:497–498
Magnin-Robert M, Le Bourse D, Markham J, Dorey S, Clément C, Baillieul F, Dhondt-Cordelier S (2015) Modifications of sphingolipid content affect tolerance to hemibiotrophic and necrotrophic pathogens by modulating plant defense responses in Arabidopsis. Plant Physiol 169:2255–2274
Mathieu C, Moreau S, Frendo P, Puppo A, Davies MJ (1998) Direct detection of radicals in intact soybean nodules: presence of nitric oxide-leghemoglobin complexes. Free Radic Biol Med 24:1242–1249
Mayék-Pérez N, López-Castañeda C, González-Chavira M, Garcia-Espinosa R, Acosta-Gallegos J, de la Vega OM, Simpson J (2001) Variability of Mexican isolates of Macrophomina phaseolina based on pathogenesis and AFLP genotype. Physiol Mol Plant Pathol 59:257–264
Mazarei M, Elling AA, Maier TR, Puthoff DP, Baum TJ (2007) GmEREBP1 is a transcription factor activating defense genes in soybean and Arabidopsis. Mol Plant Microbe Interact 20:107–119
Meena M, Prasad V, Zehra A, Gupta VK, Upadhyay RS (2015) Mannitol metabolism during pathogenic fungal–host interactions under stressed conditions. Front Microbiol 6:1019
Mengistu A, Arelli P, Bond J, Nelson R, Rupe J, Shannon G, Wrather A (2013) Identification of soybean accessions resistant to Macrophomina phaseolina by field screening and laboratory validation. Plant Health Progress 14:25
Mengistu A, Arelli PA, Bond JP, Shannon GJ, Wrather AJ, Rupe JB, Chen P, Little CR, Canaday CH, Newman MA, Pantalone VR (2011) Evaluation of soybean genotypes for resistance to charcoal rot. Plant Health Progress 10:26–31
Mengistu A, Ray JD, Smith JR, Arelli PR, Bellaloui N, Chen P, Shannon G, Boykin D (2018) Effect of charcoal rot on selected putative drought tolerant soybean genotypes and yield. Crop Prot 105:90–101
Mengistu A, Ray JD, Smith JR, Paris RL (2007) Charcoal rot disease assessments of soybean genotypes using a colony forming unit index. Crop Sci 47:2453–2461
Meyer WA, Sinclair JB, Khare MN (1974) Factors affecting charcoal rot of soybean seedlings. Phytopathology 64:845–849
Mohammadi M, Karr AL (2002) Beta-1, 3-glucanase and chitinase activities in soybean root nodules. J Plant Physiol 159:245
Mur LA, Mandon J, Persijn S, Cristescu SM, Moshkov IE, Novikova GV, Hall MA, Harren FJ, Hebelstrup KH, Gupta KJ (2013) Nitric oxide in plants: an assessment of the current state of knowledge. AoB Plants. https://doi.org/10.1093/aobpla/pls052
Pawlowski ML, Hill CB, Hartman GL (2015) Resistance to charcoal rot identified in ancestral soybean germplasm. Crop Sci 55:1230–1235
Porta H, Rocha-Sosa M (2002) Plant lipoxygenases physiological and molecular features. Plant Physiol 130:15–21
Raffaele S, Kamoun S (2012) Genome evolution in filamentous plant pathogens: why bigger can be better. Nat Rev Microbiol 10:417
Ramezani M, Shier WT, Abbas HK, Tonos JL, Baird RE, Sciumbato GL (2007) Soybean charcoal rot disease fungus Macrophomina phaseolina in Mississippi produces the phytotoxin (−) botryodiplodin but no detectable phaseolinone. J Nat Prod 70:128–129
Ramos AM, Gally M, Szapiro G, Itzcovich T, Carabajal M, Levin L (2016) In vitro growth and cell wall degrading enzyme production by Argentinean isolates of Macrophomina phaseolina, the causative agent of charcoal rot in corn. Rev Argent Microbiol 48:267–273
Rayatpanah S, Nanagulyan SG, Alav SV, Razavi M, Ghanbari-Malidarreh A (2012) Diversidad Patogénica y Genética entre Aislamientos Iraníes de Macrophomina phaseolina. Chil J Agr Response 72:40–44
Reis EM, Boaretto C, Danelli AL (2014) Macrophomina phaseolina: density and longevity of microsclerotia in soybean root tissues and free on the soil, and competitive saprophytic ability. Summa Phytopathol 40:128–133
Reznikov S, Bleckwedel J, Claps MP, De Lisi V, González V, Escobar M, Ledesma F, Devani M, Castagnaro AP, Ploper LD (2020) Nuevas fuentes de resistencia a la podredumbre carbonosa de la soja causada por Macrophomina phaseolina. Rev Ind y Agríc De Tucumán 97(1):35–42
Reznikov S, Chiesa MA, Pardo EM, De Lisi V, Bogado N, González V, Ledesma F, Morandi EN, Ploper LD, Castagnaro AP (2019) Soybean-Macrophomina phaseolina-specific interactions and identification of a novel source of resistance. Phytopathology 19:63–73
Reznikov S, Vellicce GR, Mengistu A, Arias RS, González V, De Lisi V, García MG, Rocha CM, Pardo EM, Castagnaro AP, Ploper LD (2018) Disease incidence of charcoal rot (Macrophomina phaseolina) on soybean in north-western Argentina and genetic characteristics of the pathogen. Can J Plant Pathol 40:423–433
Romero Luna MP, Mueller D, Mengistu A, Singh AK, Hartman GL, Wise KA (2017) Advancing our understanding of charcoal rot in soybeans. J Integr Pest Manag 8:8
Sandhu D, Tasma IM, Frasch R, Bhattacharyya MK (2009) Systemic acquired resistance in soybean is regulated by two proteins, orthologous to Arabidopsis NPR1. BMC Plant Biol 9:105
Sarkar TS, Biswas P, Ghosh SK, Ghosh S (2014) Nitric oxide production by necrotrophic pathogen Macrophomina phaseolina and the host plant in charcoal rot disease of jute: complexity of the interplay between necrotroph–host plant interactions. PLoS ONE. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0107348
Sarr MP, Ndiaye MB, Groenewald JZ, Crous PW (2014) Genetic diversity in Macrophomina phaseolina, the causal agent of charcoal rot. Phytopathol Mediterr 53:250–268
Schmutz J, Cannon SB, Schlueter J, Ma J, Mitros T, Nelson W, Hyten DL, Song Q, Thelen JJ, Cheng J, Xu D (2010) Genome sequence of the palaeopolyploid soybean. Nature 463:178
Serrano M, Coluccia F, Torres M, L’Haridon F, Métraux JP (2014) The cuticle and plant defense to pathogens. Frontiers Plant Sci 5:274
Sexton ZF, Hughes TJ, Wise KA (2016) Analyzing isolate variability of Macrophomina phaseolina from a regional perspective. Crop Prot 1(81):9–13
Sharma I, Kumari N, Sharma V (2014) Defense gene expression in Sorghum bicolor against Macrophomina phaseolina in leaves and roots of susceptible and resistant cultivars. J Plant Interact 9:315–323
Shier WT, Abbas HK, Baird RE, Ramezani M, Sciumbato GL (2007) (−) Botryodiplodin, a unique ribose-analog toxin. Toxin Rev 26:343–386
Shin J, Kim JE, Lee YW, Son H (2018) Fungal Cytochrome P450s and the P450 complement (CYPome) of Fusarium graminearum. Toxins 10:112
Shokes FM, Lyda SD, Jordan WR (1977) Effect of water potential on the growth and survival of Macrophomina phaseolina. Phytopathology 67:239–241
Short GE, Wyllie TD (1978) Inoculum potential of Macrophomina phaseolina. Phytopathology 68:742–746
Siddiqui KA, Gupta AK, Paul AK, Banerjee AK (1979) Purification and properties of a heat-resistant exotoxin produced by Macrophomina phaseolina (Tassi) Goid in culture. Experientia 35:1222–1223
Small W (1927) Further notes on Rhizoctonia bataticola (Taub) Butler. Trop Agriculturist 71:77–80
Smith G, Wyllie TD (1999) Charcoal rot. In: Paul St (ed) Compendium of soybean diseases, 4th Edn. American Phytopathological Society, Minnesota, MN, pp 29–31
Su G, Suh SO, Schneider RW, Russin JS (2001) Host specialization in the charcoal rot fungus, Macrophomina phaseolina. Phytopathology 91:120–126
Talukdar A, Verma K, Gowda DS, Lal SK, Sapra RL, Singh R, Singh KP, Sinha P (2009) Molecular breeding of charcoal rot in soybean. I. Screening and mapping population development. Indian J Genet 69:367–370
Tenkouano A, Miller FR, Frederiksen RA, Rosenow DT (1993) Genetics of nonsenescence and charcoal rot resistance in sorghum. Theor Appl Genet 85:644–648
Thakur S, Jana T (2017) Computational analysis reveals industrial natural products and toxins in charcoal rot pathogen Macrophomina phaseolina. Curr Sci. https://doi.org/10.18520/cs/v112/i02/322-331
Thuleau P, Aldon D, Cotelle V, Brière C, Ranty B, Galaud JP, Mazars C (2013) Relationships between calcium and sphingolipid-dependent signalling pathways during the early steps of plant–pathogen interactions. Biochim Biophys Acta 1833:1590–1594
Umemoto N, Kakitani M, Iwamatsu A, Yoshikawa M, Yamaoka N, Ishida I (1997) The structure and function of a soybean β-glucan-elicitor-binding protein. Proc Natl Acad Sci 94:1029–1034
Underhill DM (2007) Escape mechanisms from the immune response. Immunology of fungal infections. Springer, Dordrecht, pp 429–442
Upchurch RG (2011) Soybean fatty acid desaturation pathway: responses to temperature changes and pathogen infection. Soybean-Genetics and Novel Techniques for Yield Enhancement. InTech, Croatia. https://doi.org/10.5772/19079
Vaughn SF, Gardner HW (1993) Lipoxygenase-derived aldehydes inhibit fungi pathogenic on soybean. J Chem Ecol 19(10):2337–2345
Verma S, Tomar RS, Rathode V, Thakker J, Bhagwaat N (2018) Genome sequencing analysis of Macrophomina Phaseolina resistant and susceptible castor genotype. Biosci Biotechnol Res Asia 15(1):195–215
Vibha (2016) Macrophomina phaseolina. The most destructive soybean fungal pathogen of global concern. In: Kumar P, Gupta V, Tiwari A, Kamle M (eds) Current trends in plant disease diagnostics and management practices fungal biology. Springer, New York. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-27312-9_8
Vidić M, Đorđević V, Petrović K, Miladinović J (2013) Review of soybean resistance to pathogens. Ratarstvoipovrtarstvo 50(2):52–61
Walker JC (1994) Structure and function of the receptor-like protein kinases of higher plants. Plant Mol Biol 26(5):1599–1609
Wang H, Jones RW (1995) A unique endoglucanase-encoding gene cloned from the phytopathogenic fungus Macrophomina phaseolina. Appl Environ Microbiol 61(5):2004–2006
Wrather A, Shannon G, Balardin R, Carregal L, Escobar R, Gupta GK, Ma Z, Morel W, Ploper D, Tenuta A (2010) Effect of diseases on soybean yield in the top eight producing countries in 2006. Plant Health Progress 10:1094
Wrather JA, Elrod JM (1990) Apparent systemic effect of Colletotrichum truncatum and C. lagenarium on the interaction between soybean and C. truncatum. Phytopathology 80(5):472–474
Yang Y, Zhou Y, Chi Y, Fan B, Chen Z (2017) Characterization of soybean WRKY gene family and identification of soybean WRKY genes that promote resistance to soybean cyst nematode. Sci Rep 7(1):17804
Yi J, Derynck MR, Li X, Telmer P, Marsolais F, Dhaubhadel S (2010) A single-repeat MYB transcription factor, GmMYB176, regulates CHS8 gene expression and affects isoflavonoid biosynthesis in soybean. Plant J 62(6):1019–1034
Yoshimi A, Miyazawa K, Abe K (2017) Function and biosynthesis of cell wall α-1, 3-glucan in fungi. J Fungi 3:63
Young PA (1949) Charcoal rot of plants in east Texas. Bull Tex Agric Exp Stat 31–33
Zhou F, Guo Y, Qiu LJ (2016) Genome-wide identification and evolutionary analysis of leucine-rich repeat receptor-like protein kinase genes in soybean. BMC Plant Biol 16(1):58
Zilli CG, Carmona MA, Simonetti E, Santa-Cruz DM, Yannarelli GG, Balestrasse KB (2018) Biocontrol of Macrophomina phaseolina (Tassi) Goid: differential production of H2O2 and in the relationship pathogen–PGPR in soybean seedling. Biocontrol Sci Tech 28(4):416–422
Zipfel C, Felix G (2005) Plants and animals: a different taste for microbes? Curr Opin Plant Biol 8(4):353–360
Zipfel C, Robatzek S (2010) Pathogen-associated molecular pattern-triggered immunity: veni, vidi…? Plant Physiol 154:551–554
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to thank the Science and Engineering Research Board, India for the financial support to RD (Grant number PDF/2016/000064). The authors would also like to thank the members of the laboratory for their technical help and suggestions during the writing of the manuscript.
Funding
This study was funded by Science and Engineering Research Board (grant number. PDF/2016/000064) to RD under the National Post-Doctoral Fellowship scheme.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflicts of interest
The authors declare that they have no competing interest.
Ethical approval
None.
Consent to participate
None.
Consent for publication
Permission granted post-acceptance.
Additional information
Communicated by Wusheng Liu.
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Deshmukh, R., Tiwari, S. Molecular interaction of charcoal rot pathogenesis in soybean: a complex interaction. Plant Cell Rep 40, 1799–1812 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00299-021-02747-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00299-021-02747-9