Abstract
Key message
We provide evidence that nucleotide sequence and methylation status changes occur in the Arabidopsis genome during in vitro tissue culture at a frequency high enough to represent an important source of variation.
Abstract
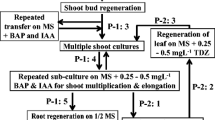
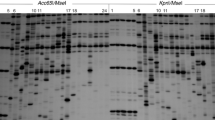
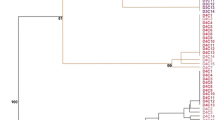
Somaclonal variation is a general consequence of the tissue culture process that has to be analyzed specifically when regenerated plants are obtained in any plant species. Currently, there are few studies about the variability comprising sequence changes and methylation status at the DNA level, generated by the culture of A. thaliana cells and tissues. In this work, two types of highly reproducible molecular markers, modified methylation sensitive AFLP (metAFLP) and transposon methylation display (TMD) have been used for the first time in this species to analyze the nucleotide and cytosine methylation changes induced by transformation and tissue culture protocols. We found significantly higher average methylation values (7.5%) in regenerated and transgenic plants when compared to values obtained from seed derived plants (3.2%) and that the main component of the somaclonal variation present in Arabidopsis clonal plants is genetic rather than epigenetic. However, we have found that the Arabidopsis regenerated and transgenic plants had a higher number of non-fully methylated sites flanking transposable elements than the control plants, and therefore, their mobilization can be facilitated. These data provide further evidence that changes in nucleotide sequence and methylation status occur in the Arabidopsis genome during in vitro tissue culture frequently enough to be an important source of variation in this species.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Altmann T, Damm B, Frommer WB et al (1994) Easy determination of ploidy level in Arabidopsis thaliana plants by means of pollen size measurement. Plant Cell Rep 13:652–656
Arabidopsis Genome Initiative (2000) Analysis of the genome sequence of the flowering plant Arabidopsis thaliana. Nature 408:96–815
Azman A, Mhiri C, Grandbastien M et al (2014) Transposable elements and the detection of somaclonal variation in plant tissue culture. Malayas Appl Biol 43:1–12
Bairu MW, Aremu AO, Van Staden J (2011) Somaclonal variation in plants: causes and detection methods. Plant Growth Regul 63:147–173
Barkla BJ, Vera-Estrella R, Pantoja O (2014) Growing Arabidopsis in vitro: cell suspensions, in vitro culture, and regeneration. Methods Mol Biol 1062:53–62
Bednarek PT, Orlowska R, Koebner RMD et al (2007) Quantification of the tissue-culture induced variation in barley (Hordeum vulgare L.). BMC Plant Biol 7:10
Bednarek PT, Orlowska R, Niedziela A (2017) A relative quantitative methylation-sensitive amplified polymorphism (MSAP) method for the analysis of abiotic stress. BMC Plant Biol 17:79
Cervera MT, Ruiz-Garcia L, Martinez-Zapater J (2002) Analysis of DNA methylation in Arabidopsis thaliana based on methylation-sensitive AFLP markers. Mol Genet Genomics 268:543–552
Cokus SJ, Feng S, Zhang X et al (2008) Shotgun bisulphite sequencing of the Arabidopsis genome reveals DNA methylation patterning. Nature 452:215–219
Feng S, Cokus SJ, Zhang X et al (2010) Conservation and divergence of methylation patterning in plants and animals. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 107:8689–8694
Fiuk A, Bednarek P, Rybczyński J (2010) Flow cytometry, HPLC-RP, and metAFLP analyzes to assess genetic variability in somatic embryo-derived plantlets of Gentiana pannonica Scop. Plant Mol Biol Rep 28:413–420
Fras A, Machczyńska J (2004) The correlation between the chromosome variation in callus and genotype of explants of Arabidopsis thaliana. Genetica 121:145–154
Fulneček J, Kovařík A (2014) How to interpret methylation sensitive amplified polymorphism (MSAP) profiles? BMC Genet 15:2
Gaj MD (2001) Direct somatic embryogenesis as a rapid and efficient system for in vitro regeneration of Arabidopsis thaliana. Plant Cell Tiss Org 64:39–46
Gaj MD, Maluszynski M (1987) Genetic variation in callus culture of Arabidopsis thaliana (L.) Heynh Arabidopsis Inf Serv 23:1–8
Galbraith DW, Harkins KR, Knapp S (1991) Systemic endopolyploidy in Arabidopsis thaliana. Plant Physiol 96:985–989
Gamborg OL, Miller RA, Ojima K (1968) Nutrient requirements of suspension cultures of soybean root cells. Exp Cell Res 50:151–158
Gao D, Vallejo VA, He B et al (2009) Detection of DNA changes in somaclonal mutants of rice using SSR markers and transposon display. Plant Cell Tiss Org 98:187–196
González AI, Sáinz A, Acedo A, Ruiz ML, Polanco C (2013) Analysis of genomic DNA methylation patterns in regenerated and control plants of rye (Secale cereale L.). Plant Growth Regul 70:227–236
Gunn JS, Piekarowicz A, Chien R et al (1992) Cloning and linkage analysis of Neisseria gonorrhoeae DNA methyltransferases. J Bacteriol 174:5654–5660
Guo W, Wu R, Zhang Y et al (2007) Tissue culture-induced locus-specific alteration in DNA methylation and its correlation with genetic variation in Codonopsis lanceolata Benth. et Hook. f. Plant Cell Rep 26:1297–1307
Henderson IR, Jacobsen SE (2007) Epigenetic inheritance in plants. Nature 447:418–424
Hoekema A, Hirsch P, Hooykaas P et al (1983) A binary plant vector strategy based on separation of vir-and T-region of the Agrobacterium tumefaciens Ti-plasmid. Nature 303:179–180
Hofmeister BT, Lee K, Rohr NA et al (2017) Stable inheritance of DNA methylation allows creation of epigenome maps and the study of epiallele inheritance patterns in the absence of genetic variation. Genome Biol 18:155
Ito H, Kakutani T (2014) Control of transposable elements in Arabidopsis thaliana. Chromosome Res 22:217–223
Jiang C, Mithani A, Gan X et al (2011) Regenerant Arabidopsis lineages display a distinct genome-wide spectrum of mutations conferring variant phenotypes. Cur Biol 21:1385–1390
Joly-Lopez Z, Bureau TE (2014) Diversity and evolution of transposable elements in Arabidopsis. Chromosome Res 22:203–216
Kaeppler SM, Phillips RL (1993) Tissue culture-induced DNA methylation variation in maize. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 90:8773–8776
Kantama L, Junbuathong S, Sakulkoo J et al (2013) Epigenetic changes and transposon reactivation in Thai rice hybrids. Mol Breed 31:815–827
Kashkush K, Khasdan V (2007) Large-scale survey of cytosine methylation of retrotransposons and the impact of readout transcription from long terminal repeats on expression of adjacent rice genes. Genetics 177:1975–1985
Kato M, Miura A, Bender J et al (2003) Role of CG and non-CG methylation in immobilization of transposons in Arabidopsis. Curr Biol 13:421–426
Korch C, Hagblom P (1986) In-vivo-modified gonococcal plasmid pJD1. Eur J Biochem 161:519–524
Kubis S, Castilho A, Vershinin A et al (2003) Retroelements, transposons and methylation status in the genome of oil palm (Elaeis guineensis) and the relationship to somaclonal variation. Plant Mol Biol 52:69–79
Labra M, Vannini C, Grassi F et al (2004) Genomic stability in Arabidopsis thaliana transgenic plants obtained by floral dip. Theor Appl Genet 109:1512–1518
Larkin P, Scowcroft W (1981) Somaclonal variation—a novel source of variability from cell-cultures for plant improvement. Theor Appl Genet 60:197–214
Law JA, Jacobsen SE (2010) Establishing, maintaining and modifying DNA methylation patterns in plants and animals. Nat Rev Genet 11:204–220
Li J, Chory J (1998) Preparation of DNA from Arabidopsis. In: Martinez-Zapater JM, Salinas J (eds) Arabidopsis protocols. Humana Press Inc, Totowa, pp 55–60
Li X, Yu X, Wang N et al (2007) Genetic and epigenetic instabilities induced by tissue culture in wild barley (Hordeum brevisubulatum (Trin.) Link). Plant Cell Tiss Org 90:153–168
Lister R, O’Malley RC, Tonti-Filippini J et al (2008) Highly integrated single-base resolution maps of the epigenome in Arabidopsis. Cell 133:523–536
Machczyńska J, Orłowska R, Zimny J et al (2014) Extended metAFLP approach in studies of tissue culture induced variation (TCIV) in triticale. Mol Breed 34:845–854
Machczyńska J, Zimny J, Bednarek PT (2015) Tissue culture-induced genetic and epigenetic variation in triticale (× Triticosecale spp. Wittmack ex A Camus 1927) regenerants. Plant Mol Biol 89:279–292
MacKenzie JL, Saadé FE, Le QH et al (2005) Genomic mutation in lines of Arabidopsis thaliana exposed to ultraviolet-B radiation. Genetics 171:715–723
Matthes M, Singh R, Cheah S et al (2001) Variation in oil palm (Elaeis guineensis Jacq.) tissue culture-derived regenerants revealed by AFLPs with methylation-sensitive enzymes. Theor Appl Genet 102:971–979
McCourt P, Keith K (1998) Sterile techniques in Arabidopsis. Method Mol Cell Biol 82:13‑17
Mirouze M, Reinders J, Bucher E et al (2009) Selective epigenetic control of retrotransposition in Arabidopsis. Nature 461:427–430
Murashige T, Skoog F (1962) A revised medium for rapid growth and bio assays with tobacco tissue cultures. Physiol Plant 15:473–497
Nelson PS, Papas TS, Schweinfest CW (1993) Restriction endonuclease cleavage of 5-methyl-deoxycytosine hemimethylated DNA at high enzyme-to-substrate ratios. Nucleic Acids Res 21:681–686
Orlowska R, Machczyńska J, Oleszczuk S et al (2016) DNA methylation changes and TE activity induced in tissue cultures of barley (Hordeum vulgare L.). J of Biol Res Thessaloniki 23:19
Parra R, Pastor MT, Pérez-Payá E et al (2001) Effect of in vitro shoot multiplication and somatic embryogenesis on 5-methylcytosine content in DNA of Myrtus communis L. Plant Growth Regul 33:131–136
Peraza-Echeverria S, Herrera-Valencia V, James-Kay A (2001) Detection of DNA methylation changes in micropropagated banana plants using methylation-sensitive amplification polymorphism (MSAP). Plant Sci 161:359–367
Polanco C, Ruiz ML (2002) AFLP analysis of somaclonal variation in Arabidopsis thaliana regenerated plants. Plant Sci 162:817–824
Quemada H, Roth EJ, Lark KG (1987) Changes in methylation of tissue cultured soybean cells detected by digestion with the restriction enzymes HpaII and MspI. Plant Cell Rep 6:63 66
Reyna-Lopez G, Simpson J, Ruiz Herrera J (1997) Differences in DNA methylation patterns are detectable during the dimorphic transition of fungi by amplification of restriction polymorphisms. Mol Gen Genet 253:703–710
Roberts RJ, Vincze T, Posfai J et al (2015) REBASE-a database for DNA restriction and modification: enzymes, genes and genomes. Nucleic Acids Res 43(D1):D298-D299
Ruiz-García L, Cervera MT, Martínez-Zapater JM (2005) DNA methylation increases throughout Arabidopsis development. Planta 222:301–306
Sangwan RS, Bourgeois Y, Brown S et al (1992) Characterization of competent cells and early events of Agrobacterium-mediated genetic transformation in Arabidopsis thaliana. Planta 188:439–456
Scheid OM, Jakovleva L, Afsar K et al (1996) A change of ploidy can modify epigenetic silencing. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 93:7114–7119
Schrey AW, Álvarez M, Foust CM et al (2013) Ecological epigenetics: beyond MS-AFLP. Integr Comp Biol 53:340‑350
Schulz B, Eckstein RL, Durka W (2013) Scoring and analysis of methylation-sensitive amplification polymorphisms for epigenetic population studies. Mol Ecol 13:642–653
Sedov KA, Fomenkov AA, Solovyova AI et al (2014) The level of genetic variability of cells in prolonged suspension culture of Arabidopsis thaliana. Biol Bull 41:493–499
Shemer O, Landau U, Candela H et al (2015) Competency for shoot regeneration from Arabidopsis root explants is regulated by DNA methylation. Plant Sci 238:251–261
Smulders M, RusKortekaas W, Vosman B (1995) Tissue culture-induced DNA methylation polymorphisms in repetitive DNA of tomato calli and regenerated plants. Theor Appl Genet 91:1257–1264
Smýkal P, Valledor L, Rodriguez R et al (2007) Assessment of genetic and epigenetic stability in long-term in vitro shoot culture of pea (Pisum sativum L.). Plant Cell Rep 26:1985–1998
Stroud H, Ding B, Simon SA et al (2013) Plants regenerated from tissue culture contain stable epigenome changes in rice. eLIFE 2:e00354
Takagi K, Ishikawa N, Maekawa M et al (2007) Transposon display for active DNA transposons in rice. Genes Genet Syst 82:109–122
Tsukahara S, Kobayashi A, Kawabe A et al (2009) Bursts of retrotransposition reproduced in Arabidopsis. Nature 461:423–426
Valvekens D, Van Montagu M, Van Lijsebettens M (1988) Agrobacterium tumefaciens-mediated transformation of Arabidopsis thaliana root explants by using kanamycin selection. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 85:5536–5540
Wang X, Wu R, Lin X et al (2013) Tissue culture-induced genetic and epigenetic alterations in rice pure-lines, F1 hybrids and polyploids. BMC Plant Biol 13:77
Wu Y, Wu R, Zhang B et al (2012) Epigenetic instability in genetically stable micropropagated plants of Gardenia jasminoides Ellis. Plant Growth Regul 66:137 143
Xu ML, Li XQ, Korban SS (2004) DNA-methylation alterations and exchanges during in vitro cellular differentiation in rose (Rosa hybrida L.). Theor Appl Genet 109:899–910
Yu XM, Li X, Zhao XX et al (2011) Tissue culture- induced genomic alteration in maize (Zea mays) inbred lines and F1 hybrids. Ann Appl Biol 158:237–247
Zhang X, Yazaki J, Sundaresan A et al (2006) Genome-wide high-resolution mapping and functional analysis of DNA methylation in Arabidopsis. Cell 126:1189–1201
Zhang M, Xu C, Yan H et al (2009) Limited tissue culture-induced mutations and linked epigenetic modifications in F1 hybrids of sorghum pure lines are accompanied by increased transcription of DNA methyltransferases and 5-methylcytosine glycosylases. Plant J 57:666–679
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the Spanish DGICYT grant AGL2066-14249-C02-02 and by the Junta de Castilla y León grant LE052A06.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Communicated by Tarek Hewezi.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
299_2017_2217_MOESM1_ESM.pptx
Supplementary Figure 1. Grouped column scatter graph depicting the number of different types of metAFLP markers detected in each plant analyzed corresponding to the CCGN and CCWG primer clusters. Red horizontal lines represent mean values and blue horizontal lines represent standard deviations. 208R0 and 211R0: regenerated cell lines; 261T0 and 291T0: transformed cell lines; R0s: grouped regenerated lines; T0s: grouped transformed lines; R0s+T0s: grouped cell lines (PPTX 428 KB)
299_2017_2217_MOESM2_ESM.pptx
Supplementary Figure 2. Grouped column scatter graph depicting the number of different types of TMD markers detected in each plant analyzed associated to copia transposable elements. Red horizontal lines represent mean values and blue horizontal lines represent standard deviations. 208R0 and 211R0: regenerated cell lines; 261T0 and 291T0: transformed cell lines; R0s: grouped regenerated lines; T0s: grouped transformed lines; R0s+T0s: grouped cell lines (PPTX 164 KB)
299_2017_2217_MOESM3_ESM.pptx
Supplementary Figure 3. Grouped column scatter graph depicting the number of different types of TMD markers detected in each plant analyzed associated to TRIM transposable elements. Red horizontal lines represent mean values and blue horizontal lines represent standard deviations. 208R0 and 211R0: regenerated cell lines; 261T0 and 291T0: transformed cell lines; R0s: grouped regenerated lines; T0s: grouped transformed lines; R0s+T0s: grouped cell lines (PPTX 190 KB)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Coronel, C.J., González, A.I., Ruiz, M.L. et al. Analysis of somaclonal variation in transgenic and regenerated plants of Arabidopsis thaliana using methylation related metAFLP and TMD markers. Plant Cell Rep 37, 137–152 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00299-017-2217-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00299-017-2217-x