Abstract
Key message
Wheat MAPK member TaMPK4 responds to abiotic stresses of Pi and N deprivations and high salinity and is crucial in regulating plant tolerance to aforementioned stresses.
Abstract
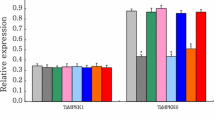
Mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) cascades are important signal transduction modules in regulating plant responses to various environmental stresses. In this study, a wheat MAPK member referred to TaMPK4 was characterized for its roles in mediating plant tolerance to diverse stresses. TaMPK4 shares conserved domains generally identified in plant MAPKs and possesses in vitro kinase activity. Under stresses of Pi and N deprivations and high salinity, TaMPK4 was strongly upregulated and its expressions were restored upon recovery treatments from above stresses. Sense- and antisense-expressing TaMPK4 in tobacco significantly modified plant growth under the stress conditions and dramatically modified the root architecture through transcriptional regulation of the auxin transport-associated genes NtPIN3 and NtPIN9, whose downregulated expressions dramatically reduced the root growth. Compared with wild type (WT), the antioxidant enzymatic activities under the stress conditions, P accumulation under P deprivation, and N amount under N deficiency were altered dramatically in the transgenic plants, showing higher in the TaMPK4-overexpressing and lower in the TaMPK4-knockout plants, which were in concordance with the modified expressions of a set of antioxidant enzyme genes (NtPOD2;1, NtPOD9, NtSOD2, NtFeSOD, and NtCAT), two phosphate transporter genes (NtPT and NtPT2), and two nitrate transporter genes (NtNRT1.1-s and NtNRT1.1-t), respectively. Downregulated expression of above genes in tobacco largely reduced the plant growth, and Pi and N acquisitions under the stress conditions. TaMPK4 also involved regulations of plant K+ and osmolyte contents under high salinity. Thus, TaMPK4 is functional in regulating plant tolerance to diverse stresses through modifying various biological processes.










Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- ABA:
-
Abscisic acid
- CAT:
-
Catalase
- EASA:
-
Effective absorption surface area
- IAA:
-
Indole-3-acetic acid
- LR:
-
Lateral root
- MAPK:
-
Mitogen-activated protein kinases
- MDA:
-
Malondialdehyde
- NPQ:
-
Nonphotochemical quenching
- NRT:
-
Nitrate transporter
- ORF:
-
Open reading frame
- PT:
-
Phosphate transporter
- POD:
-
Peroxidase
- PSII:
-
Photosystem II
- P n :
-
Photosynthetic rate
- PR:
-
Primary root
- qPCR:
-
Quantitative polymerism chain reaction
- ROS:
-
Reactive oxidative species
- RSA:
-
Root system architecture
- SOD:
-
Superoxide dismutase
- TASA:
-
Total absorption surface area
- WT:
-
Wild type
References
Alemán F, Caballero F, Ródenas R, Rivero RM, Martínez V, Rubio F (2014) The F130S point mutation in the Arabidopsis high-affinity K(+) transporter AtHAK5 increases K(+) over Na(+) and Cs(+) selectivity and confers Na(+) and Cs(+) tolerance to yeast under heterologous expression. Front Plant Sci 5:430
Bohnert HJ, Nelson DE, Jensen RG (1995) Adaptations to environmental stresses. Plant Cell 7:1099–1111
Brader G, Djamei A, Teige M, Palva ET, Hirt H (2007) The MAP kinase kinase MKK2 affects disease resistance in Arabidopsis. Mol Plant Microbe Interact 20:589–596
Chen AQ, Hu J, Sun SB, Xu GH (2007) Conservation and divergence of both phosphate- and mycorrhiza-regulated physiological responses and expression patterns of phosphate transporters in solanaceous species. New Phytol 173:817–831
Colcombet J, Hirt H (2008) Arabidopsis MAPKs: a complex signalling network involved in multiple biological processes. Biochem J 413:217–226
Corpas FJ, Palma JM, Sandalio LM, Lopez-Huertas E, Romero-Puertas MC, Barroso JB, Del Rio LA (1999) Purification of catalase from pea leaf peroxisomes: identification of five different isoforms. Free Radical Res 31(Suppl):S235–S241
De Smet I, White PJ, Bengough AG et al (2012) Analyzing lateral root development: how to move forward. Plant Cell 24:15–20
Dechorgnat J, Nguyen CT, Armengaud P, Jossier M, Diatloff E, Filleur S, Daniel-Vedele F (2011) From the soil to the seeds: the long journey of nitrate in plants. J Exp Bot 62:1349–1359
Ding HD, Zhang XH, Xu SC, Sun LL, Jiang MY, Zhang AY, Jin YG (2009) Induction of protection against paraquat-induced oxidative damage by abscisic acid in maize leaves is mediated through mitogen-activated protein kinase. J Integr Plant Biol 51:961–972
Droillard M, Boudsocq M, Barbier-Brygoo H, Laurière C (2002) Different protein kinase families are activated by osmotic stresses in Arabidopsis thaliana cell suspensions. Involvement of the MAP kinases AtMPK3 and AtMPK6. FEBS Lett 527:43–50
Droillard MJ, Boudsocq M, Barbier-Brygoo H, Lauriere C (2004) Involvement of MPK4 in osmotic stress response pathways in cell suspensions and plantlets of Arabidopsis thaliana: activation by hypoosmolarity and negative role in hyperosmolarity tolerance. FEBS Lett 574:42–48
Du X, Zhao X, Liu X, Guo C, Lu W, Gu J, Xiao K (2013) Overexpression of TaSRK2C1, wheat SNF1-related protein kinase gene, increases tolerance to dehydration, salt, and low temperature in transgenic tobacco. Plant Mol Biol Rep 31:810–821
Fukaki H, Tasaka M (2009) Hormone interactions during lateral root formation. Plant Mol Biol 69:437–449
Gu L, Liu Y, Zong X, Liu L, Li DP, Li DQ (2010) Overexpression of maize mitogen-activated protein kinase gene, ZmSIMK1 in Arabidopsis increases tolerance to salt stress. Mol Biol Rep 37:4067–4073
Guo C, Li J, Chang W, Zhang L, Cui X, Xiao K (2011) Effects of chromosome substitution on the utilization efficiency of nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium in wheat. Front Agric China 5:253–261
Guo C, Zhao X, Liu X, Zhang L, Gu J, Li X, Lu W, Xiao K (2013) Function of wheat phosphate transporter gene TaPHT2;1 in Pi translocation and plant growth regulation under replete and limited Pi supply conditions. Planta 237:1163–1178
Hasegawa PM, Bressan RA, Zhu J-K, Bohnert H (2000) Plant cellular and molecular responses to high salinity. Ann Rev Plant Physiol Plant Mol Biol 51:463–499
Huang XS, Liu JH, Chen XJ (2010) Overexpression of PtrABF gene, a bZIP transcription factor isolated from Poncirus trifoliata, enhances dehydration and drought tolerance in tobacco via scavenging ROS and modulating expression of stress-responsive genes. BMC Plant Biol 10:230
Huang XS, Luo T, Fu XZ, Fan QJ, Liu JH (2011) Cloning and molecular characterization of a mitogen-activated protein kinase gene from Poncirus trifoliata whose ectopic expression confers dehydration/drought tolerance in transgenic tobacco. J Exp Bot 62:5191–5206
Ichimura K, Mizoguchi T, Yoshida R, Yuasa T, Shinozaki K (2000) Various abiotic stresses rapidly activate Arabidopsis MAP kinases ATMPK4 and ATMPK6. Plant J 24:655–665
Kim J, Malladi A, Iersel MW (2012) Physiological and molecular responses to drought in Petunia: the importance of stress severity. J Exp Bot 63:6335–6345
Kong D, Li M, Dong Z, Ji H, Li X (2015) Identification of TaWD40D, a wheat WD40 repeat-containing protein that is associated with plant tolerance to abiotic stresses. Plant Cell Rep 34:395–410
Kovtun Y, Chiu WL, Tena G, Sheen J (2000) Functional analysis of oxidative stress-activated mitogen-activated protein kinase cascade in plants. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 97:2940–2945
Li W, Wang Y, Okamoto M, Crawford NM, Siddiqi MY, Glass ADM (2007) Dissection of the AtNRT2.1:AtNRT2.2 inducible high-affinity nitrate transporter gene cluster. Plant Physiol 143:425–433
Li X, Guo C, Gu J, Duan W, Zhao M, Ma C, Du X, Lu W, Xiao K (2014) Overexpression of TaVP, a vacuolar H+-pyrophosphatase gene in wheat (Triticum aestivum L.), improves tobacco plant growth under Pi and N deprivations, high salinity, and drought. J Exp Bot 65:683–696
Li J, Yu G, Sun X, Liu Y, Liu J, Zhang X, Jia C, Pan H (2015) AcPIP2, a plasma membrane intrinsic protein from halophyte Atriplex canesens, enhances plant growth rate and abiotic stress tolerance when overexpressed in Arabidopsis thaliana. Plant Cell Rep 34:1401–1415
Liang YC, Chen Q, Liu Q, Zhang W, Ding R (2003) Exogenous silicon (Si) increases antioxidant enzyme activity and reduces lipid peroxidation in roots of salt-stressed barley (Hordeum vulgare L.). J Plant Physiol 160:1157–1164
Liu X, Zhao X, Zhang L, Lu W, Li X, Xiao K (2013) TaPht1;4, a high-affinity phosphate transporter gene in wheat (Triticum aestivum L.), plays an important role in plant phosphate acquisition under phosphorus deprivation. Funct Plant Biol 40:329–341
López-Bucio J, Cruz-Ramírez A, Herrera-Estrella L (2003) The role of nutrient availability in regulating root architecture. Curr Opin Plant Biol 6:280–287
Lumbreras V, Vilela B, Irar S, Solé M, Capellades M, Valls M et al (2010) MAPK phosphatase MKP2 mediates disease responses in Arabidopsis and functionally interacts with MPK3 and MPK6. Plant J 63:1017–1030
Meszaros T, Helfer A, Hatzimasoura E et al (2006) The Arabidopsis MAP kinase kinase MKK1 participates in defence responses to the bacterial elicitor flagellin. Plant J 48:485–498
Moustafa K, AbuQamar S et al (2014) MAPK cascades and major abiotic stresses. Plant Cell Rep 33:1217–1225
Musick GJ, Fairchild ML, Fergason VL, Zuber MS (1965) A method of measuring root volume in corn (Zea mays L.). Crop Sci 5:601–602
Nakagami H, Kiegerl S, Hirt H (2004) OMTK1, a novel MAPKKK, channels oxidative stress signaling through direct MAPK interaction. J Biol Chem 279:26959–26966
Nakagami H, Soukupova H, Schikora A, Zarsky V, Hirt H (2006) A mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase kinase mediates reactive oxygen species homeostasis in Arabidopsis. J Biol Chem 281:38697–38704
Ning J, Li X, Hicks LM, Xiong L (2010) A raf-like MAPKKK gene DSM1 mediates drought resistance through reactive oxygen species scavenging in rice. Plant Physiol 152:876–890
Nussaume L, Kanno S, Javot H, Marin E, Pochon N, Ayadi A, Nakanishi TM, Thibaud MC (2011) Phosphate import in plants: focus on the PHT1 transporters. Front Plant Sci 13:83
Orsel M, Eulenburg K, Krapp A, Daniel-Vedele F (2004) Disruption of the nitrate transporter genes AtNRT2.1 and AtNRT2.2 restricts growth at low external nitrate concentration. Planta 219:714–721
Ortiz-Masia D, Perez-Amador MA, Carbonell P, Aniento F, Carbonell J, Marcote MJ (2008) Characterization of PsMPK2, the first C1 subgroup MAP kinase from pea (Pisum sativum L.). Planta 227:1333–1342
Peever TL, Higgins VJ (1989) Electrolyte leakage, lipoxygenase, and lipid peroxidation induced in tomato leaf tissue by specific and nonspecific elicitors from Cladosporium fulvum. Plant Physiol 90:867–875
Pei L, Wang J, Li K, Li Y, Li B, Gao F, Yang A (2012) Overexpression of Thellungiella halophila H+-pyrophosphatase gene improves low phosphate tolerance in maize. PLoS One 7:e43501
Pitzschke A, Hirt H (2009) Disentangling the complexity of mitogen-activated protein kinases and reactive oxygen species signaling. Plant Physiol 149:606–615
Pitzschke A, Schikora A, Hirt H (2009) MAPK cascade signalling networks in plant defence. Curr Opin Plant Biol 12:421–426
Romeis T (2001) Protein kinases in the plant defence response. Curr Opin Plant Biol 4:407–414
Shalata A, Mittova V, Volokita M, Guy M, Tal M (2001) Response of the cultivated tomato and its wild salt-tolerant relative Lycopersicon pennellii to salt-dependent oxidative stress: the root antioxidative system. Physiol Plantarum 112:487–494
Shan DP, Huang JG, Yang YT, Guo YH, Wu CA, Yang GD, Gao Z, Zheng CC (2007) Cotton GhDREB1 increases plant tolerance to low temperature and is negatively regulated by gibberellic acid. New Phytol 176:70–81
Sharp RE, LeNoble ME (2002) ABA, ethylene and the control of shoot and root growth under water stress. J Exp Bot 53:33–37
Sharp RE, Poroyko V, Hejlek LG, Spollen WG, Springer GK, Bohnert HJ, Nguyen HT (2004) Root growth maintenance during water deficits: physiology to functional genomics. J Exp Bot 55:2343–2351
Shi J, Fu XZ, Peng T, Huang XS, Fan QJ, Liu JH (2010) Spermine pretreatment confers dehydration tolerance of citrus in vitro plants via modulation of antioxidative capacity and stomatal response. Tree Physiol 30:914–922
Shin H, You MK, Jeung JU, Shin JS (2014) OsMPK3 is a TEY-type rice MAPK in Group C and phosphorylates OsbHLH65, a transcription factor binding to the E-box element. Plant Cell Rep 33:1343–1353
Sinha AK, Jaggi M, Raghuram B, Tuteja N (2011) Mitogen-activated protein kinase signaling in plants under abiotic stress. Plant Sign Behav 2:196–203
Sun Z, Ding C, Li X, Xiao K (2012) Molecular characterization and expression analysis of TaZFP15, a C2H2- type zinc finger transcription factor gene in wheat (Triticum aestivum L.). J Integr Agric 11:31–42
Teige M, Scheikl E, Eulgem T, Dóczi R, Ichimura K, Shinozaki K et al (2004) The MKK2 pathway mediates cold and salt stress signaling in Arabidopsis. Mol Cell 15:141–152
Tena G, Asai T, Chiu WL, Sheen J (2001) Plant mitogen-activated protein kinase signaling cascades. Curr Opin Plant Biol 4:392–400
Xiang Y, Huang Y, Xiong L (2007) Characterization of stress responsive CIPK genes in rice for stress tolerance improvement. Plant Physiol 144:1416–1428
Xing Y, Jia W, Zhang J (2007) AtMEK1 mediates stress-induced gene expression of CAT1 catalase by triggering H2O2 production in Arabidopsis. J Exp Bot 58:2969–2981
Xing Y, Jia W, Zhang J (2008) AtMKK1 mediates ABA-induced CAT1 expression and H2O2 production via AtMPK6-coupled signaling in Arabidopsis. Plant J 54:440–451
Xiong L, Yang Y (2003) Disease resistance and abiotic stress tolerance in rice are inversely modulated by an abscisic acid-inducible mitogen-activated protein kinase. Plant Cell 15:745–759
Yang T, Zhang S, Hu Y, Wu F, Hu Q, Chen G, Cai J, Wu T, Moran N, Yu L, Xu G (2014) The role of a potassium transporter OsHAK5 in potassium acquisition and transport from roots to shoots in rice at low potassium supply levels. Plant Physiol 166:945–959
Zhu M, Chen G, Zhang J, Zhang Y, Xie Q, Zhao Z, Pan Y, Hu Z (2014) The abiotic stress-responsive NAC-type transcription factor SINAC4 regulates salt and drought tolerance and stress-related genes in tomato (Solanum lycopersicum). Plant Cell Rep 33:1851–1863
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 31,371,618), the Natural Science Foundation of Hebei (No. C2015204048), the National Transgenic Major Program (No. 2011ZX08008) and the Key Laboratory of Crop Growth Regulation of Hebei Province.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Communicated by E. Benvenuto.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hao, L., Wen, Y., Zhao, Y. et al. Wheat mitogen-activated protein kinase gene TaMPK4 improves plant tolerance to multiple stresses through modifying root growth, ROS metabolism, and nutrient acquisitions. Plant Cell Rep 34, 2081–2097 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00299-015-1853-2
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00299-015-1853-2