Abstract
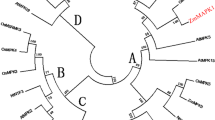
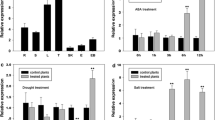
Mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) cascades play a remarkably crucial role in plants. It has been studied intensively in model plants Arabidopsis, tobacco and rice. However, the function of MAPKs in maize (Zea mays L.) has not been well documented. ZmSIMK1 (Zea mays salt-induced mitogen-activated protein kinase 1) is a previously identified MAPK gene in maize. In this research, we charactered ZmSIMK1 and showed that ZmSIMK1 was involved in Arabidopsis salt stress. The genomic organization of ZmSIMK1 gene and its expression in maize have been analyzed. In order to investigate the function of ZmSIMK1, we generated transgenic Arabidopsis constitutively overexpressing ZmSIMK1. Ectopic expression of ZmSIMK1 in Arabidopsis resulted in increased resistance against salt stress. Importantly, ZmSIMK1-overexpressing Arabidopsis exhibited constitutive expression of stress-responsive marker genes, RD29A and P5CS1. Furthermore, RD29A and P5CS1 were upregulated under salt stress. These results suggest that ZmSIMK1 may play an important role in plant salt stress.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ai J, Wang Y, Tan K, Deng Y, Luo N, Yuan W, Wang Z, Li Y, Wang Y, Mo X, Zhu C, Yin Z, Liu M, Wu X (2008) A human homolog of mouse Lbh gene, hLBH, expresses in heart and activates SRE and AP-1 mediated MAPK signaling pathway. Mol Biol Rep 35:179–187
Mishra NS, Tuteja R, Tuteja N (2006) Signaling through MAP kinase networks in plants. Arch Biochem Biophys 452:55–68
Colcombet J, Hirt H (2008) Arabidopsis MAPKs: a complex signalling network involved in multiple biological processes. Biochem J 413:217–226
Pitzschke A, Schikora A, Hirt H (2009) MAPK cascade signalling networks in plant defence. Curr Opin Plant Biol 12:421–426
Xu H, Li K, Yang F, Shi Q, Wang X (2009) Overexpression of CsNMAPK in tobacco enhanced seed germination under salt and osmotic stresses. Mol Biol Rep. doi: 10.1007/s11033-009-9895-6
Ghawana S, Kumar S, Ahuja PS (2010) Early low-temperature responsive mitogen activated protein kinases RaMPK1 and RaMPK2 from Rheum australe D. Don respond differentially to diverse stresses. Mol Biol Rep 37:933–938
Peng S, Zhang Y, Zhang J, Wang H, Ren B (2009) Effect of ketamine on ERK expression in hippocampal neural cell and the ability of learning behavior in minor rats. Mol Biol Rep. doi: 10.1007/s11033-009-9892-9
Zhu N, Shao Y, Xu L, Yu L, Sun L (2009) Gadd45-alpha and Gadd45-gamma utilize p38 and JNK signaling pathways to induce cell cycle G2/M arrest in Hep-G2 hepatoma cells. Mol Biol Rep 36:2075–2085
Agarwal PK, Gupta K, Jha B (2010) Molecular characterization of the Salicornia brachiata SbMAPKK gene and its expression by abiotic stress. Mol Biol Rep 37:981–986
Group MAPK (2002) Mitogen-activated protein kinase cascades in plants: a new nomenclature. Trends Plant Sci 7:301–308
Duerr B, Gawienowski M, Ropp T, Jacobs T (1993) MsERK1: a mitogen-activated protein kinase from a flowering plant. Plant Cell 5:87–96
Reyna NS, Yang Y (2006) Molecular analysis of the rice MAP kinase gene family in relation to Magnaporthe grisea infection. Mol Plant Microbe Interact 19:530–540
Nicole MC, Hamel LP, Morency MJ, Beaudoin N, Ellis BE, Seguin A (2006) MAP-ping genomic organization and organ-specific expression profiles of poplar MAP kinases and MAP kinase kinases. BMC Genomics 7:223
Zhang T, Liu Y, Yang T, Zhang L, Xu S, Xue L, An L (2006) Diverse signals converge at MAPK cascades in plant. Plant Physiol Biochem 44:274–283
Berberich T, Sano H, Kusano T (1999) Involvement of a MAP kinase, ZmMPK5, in senescence and recovery from low-temperature stress in maize. Mol Gen Genet 262:534–542
Lalle M, Visconti S, Marra M, Camoni L, Velasco R, Aducci P (2005) ZmMPK6, a novel maize MAP kinase that interacts with 14-3-3 proteins. Plant Mol Biol 59:713–722
Wang Q, Zhai S, Zhang Y, Yin X, Zhang J (2005) Cloning and molecular characterization of a gene encoding MAP kinase from maize and its expression in E. coli. High Technol Lett 11:315–319
Zong XJ, Li DP, Gu LK, Li DQ, Liu LX, Hu XL (2009) Abscisic acid and hydrogen peroxide induce a novel maize group C MAP kinase gene, ZmMPK7, which is responsible for the removal of reactive oxygen species. Planta 229:485–495
Zhang A, Jiang M, Zhang J, Tan M, Hu X (2006) Mitogen-activated protein kinase is involved in abscisic acid-induced antioxidant defense and acts downstream of reactive oxygen species production in leaves of maize plants. Plant Physiol 141:475–487
Zhang A, Jiang M, Zhang J, Ding H, Xu S, Hu X, Tan M (2007) Nitric oxide induced by hydrogen peroxide mediates abscisic acid-induced activation of the mitogen-activated protein kinase cascade involved in antioxidant defense in maize leaves. New Phytol 175:36–50
Ding H, Zhang A, Wang J, Lu R, Zhang H, Zhang J, Jiang M (2009) Identity of an ABA-activated 46 kDa mitogen-activated protein kinase from Zea mays leaves: partial purification, identification and characterization. Planta 230:239–251
Lin F, Ding H, Wang J, Zhang H, Zhang A, Zhang Y, Tan M, Dong W, Jiang M (2009) Positive feedback regulation of maize NADPH oxidase by mitogen-activated protein kinase cascade in abscisic acid signalling. J Exp Bot 60:3221–3238
Alexandrov NN, Brover VV, Freidin S, Troukhan ME, Tatarinova TV, Zhang H, Swaller TJ, Lu YP, Bouck J, Flavell RB, Feldmann KA (2009) Insights into corn genes derived from large-scale cDNA sequencing. Plant Mol Biol 69:179–194
Zhu JK (2002) Salt and drought stress signal transduction in plants. Annu Rev Plant Biol 53:247–273
Mizoguchi T, Irie K, Hirayama T, Hayashida N, Yamaguchi-Shinozaki K, Matsumoto K, Shinozaki K (1996) A gene encoding a mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase kinase is induced simultaneously with genes for a mitogen-activated protein kinase and an S6 ribosomal protein kinase by touch, cold, and water stress in Arabidopsis thaliana. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 93:765–769
Ichimura K, Mizoguchi T, Irie K, Morris P, Giraudat J, Matsumoto K, Shinozaki K (1998) Isolation of ATMEKK1 (a MAP kinase kinase kinase)-interacting proteins and analysis of a MAP kinase cascade in Arabidopsis. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 253:532–543
Ichimura K, Mizoguchi T, Yoshida R, Yuasa T, Shinozaki K (2000) Various abiotic stresses rapidly activate Arabidopsis MAP kinases ATMPK4 and ATMPK6. Plant J 24:655–665
Teige M, Scheikl E, Eulgem T, Doczi R, Ichimura K, Shinozaki K, Dangl JL, Hirt H (2004) The MKK2 pathway mediates cold and salt stress signaling in Arabidopsis. Mol Cell 15:141–152
Ulm R, Ichimura K, Mizoguchi T, Peck SC, Zhu T, Wang X, Shinozaki K, Paszkowski J (2002) Distinct regulation of salinity and genotoxic stress responses by Arabidopsis MAP kinase phosphatase 1. EMBO J 21:6483–6493
Liu L, Hu X, Song J, Zong X, Li DP, Li D (2009) Over-expression of a Zea mays L. protein phosphatase 2C gene (ZmPP2C) in Arabidopsis thaliana decreases tolerance to salt and drought. J Plant Physiol 166:531–542
Xu Y, Li DP, Gu L, Hu X, Zong X, Li D (2005) Cloning and expression characteristics of protein phosphatase gene ZmPP2C of Zea mays roots. J Plant Physiol Mol Biol 31:183–189
Clough SJ, Bent AF (1998) Floral dip: a simplified method for Agrobacterium-mediated transformation of Arabidopsis thaliana. Plant J 16:735–743
Koo SC, Yoon HW, Kim CY, Moon BC, Cheong YH, Han HJ, Lee SM, Kang KY, Kim MC, Lee SY, Chung WS, Cho MJ (2007) Alternative splicing of the OsBWMK1 gene generates three transcript variants showing differential subcellular localizations. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 360:188–193
Liu H, He R, Zhang H, Huang Y, Tian M, Zhang J (2010) Analysis of synonymous codon usage in Zea mays. Mol Biol Rep 37:677–684
Lai J, Dey N, Kim CS, Bharti AK, Rudd S, Mayer KF, Larkins BA, Becraft P, Messing J (2004) Characterization of the maize endosperm transcriptome and its comparison to the rice genome. Genome Res 14:1932–1937
Dembinsky D, Woll K, Saleem M, Liu Y, Fu Y, Borsuk LA, Lamkemeyer T, Fladerer C, Madlung J, Barbazuk B, Nordheim A, Nettleton D, Schnable PS, Hochholdinger F (2007) Transcriptomic and proteomic analyses of pericycle cells of the maize primary root. Plant Physiol 145:575–588
Gao L, Xiang CB (2008) The genetic locus At1g73660 encodes a putative MAPKKK and negatively regulates salt tolerance in Arabidopsis. Plant Mol Biol 67:125–134
Cao Z, Jia Z, Liu Y, Wang M, Zhao J, Zheng J, Wang G (2010) Constitutive expression of ZmsHSP in Arabidopsis enhances their cytokinin sensitivity. Mol Biol Rep 37:1089–1097
Acknowledgments
Many thanks to Professor Juren Zhang for providing helpful suggestions. This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Nos. 30471052, 30871457) and the State Key Basic Research and Development Plan of China (No. 2009CB118500), and also was supported by the Program for Changjiang Scholars and Innovative Research Team in University (No. IRT0635).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Lingkun Gu and Yukun Liu have contributed equally to this work.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gu, L., Liu, Y., Zong, X. et al. Overexpression of maize mitogen-activated protein kinase gene, ZmSIMK1 in Arabidopsis increases tolerance to salt stress. Mol Biol Rep 37, 4067–4073 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11033-010-0066-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11033-010-0066-6