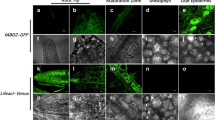
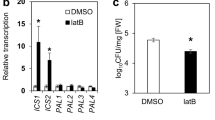
Abstract
Changes in actin dynamics represent the primary response of the plant cell to extracellular signaling. Recent studies have now revealed that actin remodeling is involved in abiotic stress tolerance in plants. In our current study, the relationship between the changes in actin dynamics and the reactive oxygen species (ROS) level at the initial stages of salt stress was investigated in the elongation zone of the Arabidopsis root tip. We found that a 200 mM NaCl treatment disrupted the dynamics of the actin filaments within 10 min and increased the ROS levels in the elongation zone cells of the Arabidopsis root tip. We further found that the NADPH oxidase activity inhibitor, diphenyleneiodonium, treatment blocked this ROS increase under salt stress conditions. The roles of actin dynamics and the NADPH oxidases in ROS generation were further analyzed using the actin-specific agents, latrunculin B (Lat-B) and jasplakinolide (Jasp), and mutants of Arabidopsis NADPH oxidase AtrbohC. Lat-B and Jasp promote actin depolymerization and polymerization, respectively, and both were found to enhance the ROS levels following NaCl treatment. However, this response was abolished in the atrbohC mutants. Our present results thus demonstrate that actin dynamics are involved in regulating the ROS level in Arabidopsis root under salt stress conditions.
Key message Salt stress disrupts the dynamics of the actin filaments in Arabidopsis in the short term which are involved in regulating the ROS levels that arise under salt stress conditions via the actions of the AtrbohC.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bubb MR, Spector I, Beyer BB, Fosen KM (2000) Effects of jasplakinolide on the kinetics of actin polymerization. An explanation for certain in vivo observations. J Biol Chem 275:5163–5170
Chhabra ES, Higgs HN (2007) The many faces of actin: matching assembly factors with cellular structures. Nat Cell Biol 9:1110–1121
D’Angeli S, Altamura M (2007) Osmotin induces cold protection in olive trees by affecting programmed cell death and cytoskeleton organization. Planta 225:1147–1163
Era A, Tominaga M, Ebine K, Awai C, Saito C, Ishizaki K, Yamato KT, Kohchi T, Nakano A, Ueda T (2009) Application of Lifeact reveals F-actin dynamics in Arabidopsis thaliana and the liverwort, Marchantia polymorpha. Plant Cell Physiol 50:1041–1048
Foreman J, Demidchik V, Bothwell JH, Mylona P, Miedema H, Torres MA, Linstead P, Costa S, Brownlee C, Jones JD, Davies JM, Dolan L (2003) Reactive oxygen species produced by NADPH oxidase regulate plant cell growth. Nature 422:442–446
Franklin-Tong VE, Gourlay CW (2008) A role for actin in regulating apoptosis/programmed cell death, evidence spanning yeast, plants and animals. Biochem J 413:389–404
Gourlay CW, Carpp LN, Timpson P, Winder SJ, Ayscough KR (2004) A role for the actin cytoskeleton in cell death and aging in yeast. J Cell Biol 164:803–809
Hussey PJ, Ketelaar T, Deeks MJ (2006) Control of the actin cytoskeleton in plant cell growth. Annu Rev Plant Biol 57:109–125
Jiang M, Zhang J (2003) Cross-talk between calcium and reactive oxygen species originated from NADPH oxidase in abscisic acid-induced antioxidant defense in leaves of maize seedlings. Plant, Cell Environ 26:929–939
Kwak JM, Mori IC, Pei ZM, Leonhardt N, Torres MA, Dangl JL, Bloom RE, Bodde S, Jones JDG, Schroeder JI (2003) NADPH oxidase AtrbohD and AtrbohF genes function in ROS-dependent ABA signaling in Arabidopsis. EMBO J 22:2623–2633
Leshem Y, Serie L, Levine A (2007) Induction of phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase-mediated endocytosis by salt stress leads to intracellular production of reactive oxygen species and salt tolerance. Plant J 51:185–197
MacRobbie EA, Kurup S (2007) Signalling mechanisms in the regulation of vacuolar ion release in guard cells. New Phytol 175:630–640
Malerba M, Crosti P, Cerana R (2010) Effect of heat stress on actin cytoskeleton and endoplasmic reticulum of tobacco BY-2 cultured cells and its inhibition by Co2+. Protoplasma 239:23–30
Mazars C, Thion L, Thuleau P, Graziana A, Knight MR, Moreau M, Ranjeva R (1997) Organization of cytoskeleton controls changes in cytosolic calcium of cold-shocked Nicotiana plumbaginifolia protoplasts. Cell Calcium 22:413–420
Mazel A, Leshem Y, Tiwari BS, Levine A (2004) Induction of salt and osmotic stress tolerance by overexpression of an intracellular vesicle trafficking protein AtRab7 (AtRabG3e). Plant Physiol 134:118–128
Michelot A, Berro J, Guerin C, Boujemaa-Paterski R, Staiger CJ, Martiel JL, Blanchoin L (2007) Actin-filament stochastic dynamics mediated by ADF/cofilin. Curr Biol 17:825–833
Miller G, Suzuki N, Ciftci-Yilmaz S, Mittler R (2010) Reactive oxygen species homeostasis and signalling during drought and salinity stresses. Plant Cell Environ 33:453–467
Mittler R, Vanderauwera S, Gollery M, Van Breusegem F (2004) Reactive oxygen gene network of plants. Trends Plant Sci 9:490–498
Monshausen GB, Bibikova TN, Weisenseel MH, Gilroy S (2009) Ca2+ regulates reactive oxygen species production and pH during mechanosensing in Arabidopsis roots. Plant Cell 21:2341–2356
Morley SC, Sun GP, Bierer BE (2003) Inhibition of actin polymerization enhances commitment to and execution of apoptosis induced by withdrawal of trophic support. J Cell Biochem 88:1066–1076
Müller J, Menzel D, Samaj J (2007) Cell-type-specific disruption and recovery of the cytoskeleton in Arabidopsis thaliana epidermal root cells upon heat shock stress. Protoplasma 230:231–242
Müller K, Carstens AC, Linkies A, Torres MA, Leubner-Metzger G (2009) The NADPH-oxidase AtrbohB plays a role in Arabidopsis seed after ripening. New Phytol 184:885–897
Ogasawara Y, Kaya H, Hiraoka G, Yumoto F, Kimura S, Kadota Y, Hishinuma H, Senzaki E, Yamagoe S, Nagata K, Nara M, Suzuki K, Tanokura M, Kuchitsu K (2008) Synergistic activation of the Arabidopsis NADPH oxidase AtrbohD by Ca2+ and phosphorylation. J Biol Chem 283:8885–8892
Orvar BL, Sangwan V, Omann F, Dhindsa RS (2000) Early steps in cold sensing by plant cells, the role of actin cytoskeleton and membrane fluidity. Plant J 23:785–794
Ou GS, Chen ZL, Yuan M (2002) Jasplakinolide reversibly disrupts actin filaments in suspension-cultured tobacco BY-2 cells. Protoplasma 219:168–175
Pokorna J, Schwarzerova K, Zelenkova S, Petrasek J, Janotova I, Capkova V, Opatrny Z (2004) Sites of actin filament initiation and reorganization in cold treated tobacco cells. Plant Cell Environ 27:641–653
Posey SC, Bierer BE (1999) Actin stabilization by jasplakinolide enhances apoptosis induced by cytokine deprivation. J Biol Chem 274:4259–4265
Rasmussen I, Pedersen LH, Byg L, Suzuki K, Sumimoto H, Vilhardt F (2010) Effects of F/G-actin ratio and actin turn-over rate on NADPH oxidase activity in microglia. BMC Immunol 11:44
Sagi M, Fluhr R (2006) Production of reactive oxygen species by plant NADPH oxidases. Plant Physiol 141:336–340
Sheppard FR, Kelher MR, Moore EE, McLaughlin NJ, Banerjee A, Silliman CC (2005) Structural organization of the neutrophil NADPH oxidase, phosphorylation and translocation during priming and activation. J Leukocyte Biol 78:1025–1042
Smertenko AP, Deeks MJ, Hussey PJ (2010) Strategies of actin reorganisation in plant cells. J Cell Sci 123:3019–3028
Staiger CJ, Sheahan MB, Khurana P, Wang X, McCurdy DW, Blanchoin L (2009) Actin filament dynamics are dominated by rapid growth and severing activity in the Arabidopsis cortical array. J Cell Biol 184:269–280
Takeda S, Gapper C, Kaya H, Bell E, Kuchitsu K, Dolan L (2008) Local positive feedback regulation determines cell shape in root hair cells. Science 319:1241–1244
Tamura M, Kai T, Tsunawaki S, Lambeth JD, Kameda K (2000) Direct interaction of actin with p47phox of neutrophil NADPH oxidase. Biochem Bioph Res Co 276:1186–1190
Thomas SG, Huang S, Li S, Staiger CJ, Franklin-Tong VE (2006) Actin depolymerization is sufficient to induce programmed cell death in self-incompatible pollen. J Cell Biol 174:221–229
Torres MA, Onouchi H, Hamada S, Machida C, Hammond-Kosack KE, Jones JD (1998) Six Arabidopsis thaliana homologues of the human respiratory burst oxidase gp91phox. Plant J 14:365–370
Usatyuk PV, Romer LH, He D, Parinandi NL, Kleinberg ME, Zhan S, Jacobson JR, Dudek SM, Pendyala S, Garcia JG, Natarajan V (2007) Regulation of hyperoxia-induced NADPH oxidase activation in human lung endothelial cells by the actin cytoskeleton and cortactin. J Biol Chem 282:23284–23295
Verbelen JP, De Cnodder T, Le J, Vissenberg K, Baluska F (2006) The root apex of Arabidopsis thaliana consists of four distinct zones of growth activities, meristematic zone, transition zone, fast elongation zone and growth terminating zone. Plant Signal Behav 1:296–304
Vidali L, Rounds CM, Hepler PK, Bezanilla M (2009) Lifeact-mEGFP reveals a dynamic apical F-actin network in tip growing plant cells. PLoS ONE 4:e5744
Wang P, Song CP (2008) Guard-cell signalling for hydrogen peroxide and abscisic acid. New Phytol 178:703–718
Wang YF, Fan LM, Zhang WZ, Zhang W, Wu WH (2004) Ca2+-permeable channels in the plasma membrane of Arabidopsis pollen are regulated by actin microfilaments. Plant Physiol 136:3892–3904
Wang YS, Yoo CM, Blancaflor EB (2007) Improved imaging of actin filaments in transgenic Arabidopsis plants expressing a green fluorescent protein fusion to the C- and N-termini of the fimbrin actin-binding domain 2. New Phytol 177:525–536
Wang C, Zhang L, Yuan M, Ge Y, Liu Y, Fan J, Ruan Y, Cui Z, Tong S, Zhang S (2009) The microfilament cytoskeleton plays a vital role in salt and osmotic stress tolerance in Arabidopsis. Plant Biol 12:70–98
Wang XL, Gao XQ, Wang XC (2011) Stochastic dynamics of actin filaments in guard cells regulating chloroplast localization during stomatal movement. Plant Cell Environ 34:1248–1257
Wasteneys GO, Yang Z (2004) New views on the plant cytoskeleton. Plant Physiol 136:3884–3891
Wientjes FB, Reeves EP, Soskic V, Furthmayr H, Segal AW (2001) The NADPH oxidase components p47phox and p40phox bind to moesin through their PX domain. Biochem Biophy Res Co 289:382–388
Wilkins KA, Bancroft J, Bosch M, Ings J, Smirnoff N, Franklin-Tong VE (2011) Reactive oxygen species and nitric oxide mediate actin reorganization and programmed cell death in the self-incompatibility response of Papaver. Plant Physiol 156:404–416
Xie YJ, Xu S, Han B, Wu MZ, Yuan XX, Han Y, Gu Q, Xu DK, Yang Q, Shen WB (2011) Evidence of Arabidopsis salt acclimation induced by up-regulation of HY1 and the regulatory role of RbohD-derived reactive oxygen species synthesis. Plant J 66:280–292
Yao H, Xu Q, Yuan M (2008) Actin dynamics mediates the changes of calcium level during the pulvinus movement of Mimosa pudica. Plant Signal Behav 3:954–960
Zhang W, Fan LM, Wu WH (2007) Osmo-sensitive and stretch activated calcium-permeable channels in Vicia faba guard cells are regulated by actin dynamics. Plant Physiol 143:1140–1151
Zhou Y, Yang Z, Guo G, Guo Y (2010) Microfilament dynamics is required for root growth under alkaline stress in Arabidopsis. J Integr Plant Biol 52:952–958
Acknowledgments
We thank Dr. Elison B. Blancaflor (Samuel Roberts Noble Foundation, Ardmore, Oklahoma, USA) for providing the transgenic line expressing GFP-ABD2-GFP, and the Arabidopsis Biological Resource Center (Ohio State University, www.arabidopsis.org/abrc) for kindly providing the Arabidopsis mutant seeds. This study is funded by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (31170293; 31000652), and the Opening Project of the State Key Laboratory of Plant Physiology and Biochemistry (SKLPPBKF09005).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Communicated by K. Chong.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, S.G., Zhu, D.Z., Chen, G.H. et al. Disrupted actin dynamics trigger an increment in the reactive oxygen species levels in the Arabidopsis root under salt stress. Plant Cell Rep 31, 1219–1226 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00299-012-1242-z
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00299-012-1242-z