Abstract
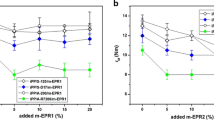
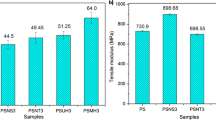
In this study, attempts have been made to assess the influence of interfacial compatibilizer and functionality of the elastomeric phase on micromorphology development and mechanical properties of polypropylene (PP)/ethylene propylene diene terpolymer (EPDM)/silicon dioxide (SiO2) ternary composites, containing 10 wt% of PP grafted with maleic anhydride (PP-g-MA) as a compatibilizer. Samples are fabricated by melt compounding of materials in a laboratory internal mixer. It is shown that the melt viscoelastic as well as developing micromorphology of nanocomposites is affected by the functionality of EPDM and incorporating compatibilizer. Morphological/mechanical features and fracture behavior of the nanocomposites are studied via diverse characterization methods including field-emission scanning electron microscopy, rheological trails and mechanical testing. The results are obviously demonstrative of the dependence of micromorphology on SiO2 nanoparticles’ positioning. The highly enhanced tensile properties in nanocomposites are achieved by coincident utilizing of compatibilizer and unfunctionalized rubber rather than functionalized EPDM due to the finer and more homogeneous dispersion of elastomer particles and SiO2 nanoparticles in EPDM-contained sample. In stark contrast, however, the core–shell structure of uncompatibilized PP/EPDM/nano-SiO2, which facilitates overlapping of the stress fields between the elastomer droplets along the PP matrix, contributes to its highest impact-resistant properties in great concordance to its shear-yielding toughening mechanism.





Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
Not applicable.
Code availability
Not applicable.
References
Fenouillot F, Cassagnau P, Majesté JC (2009) Uneven distribution of nanoparticles in immiscible fluids: morphology development in polymer blends. Polymer (Guildf) 50:1333–1350. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.polymer.2008.12.029
Elias L, Fenouillot F, Majesté JC et al (2008) Immiscible polymer blends stabilized with nano-silica particles: rheology and effective interfacial tension. Polymer (Guildf) 49:4378–4385. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.polymer.2008.07.018
de Oliveira AG, Moreno JF, de Sousa AMF et al (2019) Composites based on high-density polyethylene, polylactide and calcium carbonate: effect of calcium carbonate nanoparticles as co-compatibilizers. Polym Bull. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00289-019-02887-9
Hoseini M, Haghtalab A, Famili MHN (2017) Rheology and morphology study of immiscible linear low-density polyethylene/poly(lactic acid) blends filled with nanosilica particles. J Appl Polym Sci 134:1–12. https://doi.org/10.1002/app.45526
Meer S, Kausar A, Iqbal T (2016) Attributes of polymer and silica nanoparticle composites: a review. Polym-Plast Technol Eng 55:826–861. https://doi.org/10.1080/03602559.2015.1103267
Yang H, Zhang Q, Guo M et al (2006) Study on the phase structures and toughening mechanism in PP/EPDM/SiO 2 ternary composites. Polymer (Guildf) 47:2106–2115. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.polymer.2006.01.076
Yang H, Zhang X, Qu C et al (2007) Largely improved toughness of PP/EPDM blends by adding nano-SiO2 particles. Polymer (Guildf) 48:860–869. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.polymer.2006.12.022
Yang H, Li B, Wang K et al (2008) Rheology and phase structure of PP/EPDM/SiO2 ternary composites. Eur Polym J 44:113–123. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eurpolymj.2007.10.028
Bazgir S, Katbab AA, Nazockdast H (2004) Silica-reinforced dynamically vulcanized ethylene-propylene-diene monomer/polypropylene thermoplastic elastomers: morphology, rheology and dynamic mechanical properties. J Appl Polym Sci 92:2000–2007. https://doi.org/10.1002/app.20057
Javidi Z, Tarashi Z, Rostami A, Nazockdast H (2017) Role of nanosilica localization on morphology development of HDPE/PS/PMMA immiscible ternary blends. Express Polym Lett 11:362–373. https://doi.org/10.3144/expresspolymlett.2017.35
Gong L, Chen SH, Hou WM et al (2016) Fracture toughness of PP/EPDM/nano-ternary composites: the role of distribution of inorganic particles. Int Polym Process 31:224–232. https://doi.org/10.3139/217.3174
Helal E, Pottier C, David E et al (2018) Polyethylene/thermoplastic elastomer/zinc oxide nanocomposites for high voltage insulation applications: dielectric, mechanical and rheological behavior. Eur Polym J 100:258–269. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eurpolymj.2018.02.004
Zoukrami F, Haddaoui N, Sclavons M et al (2018) Rheological properties and thermal stability of compatibilized polypropylene/untreated silica composites prepared by water injection extrusion process. Polym Bull 75:5551–5566. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00289-018-2344-8
Panigrahi H, Sreenath PR, Bhowmick AK, Dinesh Kumar K (2019) Unique compatibilized thermoplastic elastomer from polypropylene and epichlorohydrin rubber. Polymer (Guildf) 183:121866. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.polymer.2019.121866
Zoukrami F, Haddaoui N, Vanzeveren C et al (2008) Effect of compatibilizer on the dispersion of untreated silica in a polypropylene matrix. Polym Int 57:756–763. https://doi.org/10.1002/pi.2406
Aso O, Eguiazábal JI, Nazábal J (2007) The influence of surface modification on the structure and properties of a nanosilica filled thermoplastic elastomer. Compos Sci Technol 67:2854–2863. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compscitech.2007.01.021
Uotila R, Hippi U, Paavola S, Seppälä J (2005) Compatibilization of PP/elastomer/microsilica composites with functionalized polyolefins: effect on microstructure and mechanical properties. Polymer (Guildf) 46:7923–7930. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.polymer.2005.06.099
El-Midany AA, Ibrahim SS (2011) Interfacial role of compatabilizers to improve mechanical properties of silica-polypropylene composites. Physicochem Probl Miner Process 46:295–305
Martin G, Barres C, Sonntag P et al (2009) Co-continuous morphology and stress relaxation behaviour of unfilled and silica filled PP/EPDM blends. Mater Chem Phys 113:889–898. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matchemphys.2008.08.069
Hajibabazadeh S, Palahang M, Razavi Aghjeh MK (2019) Effect of morphology development on mechanical properties and fracture behavior of PP/EPDM/SiO2 blend-nanocomposites. Polym Test 73:124–134. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.polymertesting.2018.11.029
Hajibabazadeh S, Razavi Aghjeh MK, Palahang M (2020) Study on the fracture toughness and deformation micro-mechanisms of PP/EPDM/SiO2 ternary blend-nanocomposites. J Compos Mater 54:591–605. https://doi.org/10.1177/0021998319863475
Wang H, Yang X, Fu Z et al (2017) Rheology of nanosilica-compatibilized immiscible polymer blends: formation of a “heterogeneous network” facilitated by interfacially anchored hybrid nanosilica. Macromolecules 50:9494–9506. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.macromol.7b02143
Pustak ASS, Denac M, Leskovac M et al (2015) Polypropylene/silica micro-and nanocomposites modified with poly(styrene-b-ethylene-co-butylene-b-styrene). J Appl Polym Sci 132:12–22. https://doi.org/10.1002/app.41486
Pustak A, Denac M, Leskovac M et al (2015) Morphology and mechanical properties of iPP/silica composites modified with (styrene-b-ethylene-co-butylene-b-styrene) grafted with maleic anhydride. Polym-Plast Technol Eng 54:647–660. https://doi.org/10.1080/03602559.2014.979495
Sghari Dilmani MA, Mor Z, Erdoğan A (2017) Preparation and characterization of thermoplastic elastomers/plasticizer-compatibilizer/organoclay nanocomposites by reactive extrusion system. Chem Sci J. https://doi.org/10.4172/2150-3494.1000166
Ahmadlouydarab M, Chamkouri M, Chamkouri H (2019) Compatibilization of immiscible polymer blends (R-PET/PP) by adding PP-g-MA as compatibilizer: analysis of phase morphology and mechanical properties. Polym Bull. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00289-019-03054-w
Gharzouli N, Doufnoune R, Riahi F, Bouchareb S (2019) Effects of nanosilica filler surface modification and compatibilization on the mechanical, thermal and microstructure of PP/EPR blends. J Adhes Sci Technol 33:445–467. https://doi.org/10.1080/01694243.2018.1539157
Li W, Karger-Kocsis J, Schlarb AK (2009) Dispersion of TiO2 particles in PET/PP/TiO2 and PET/PP/PP-g-MA/TiO2 composites prepared with different blending procedures. Macromol Mater Eng 294:582–589. https://doi.org/10.1002/mame.200900123
Maani A, Carreau PJ (2016) Rheological and morphological properties of thermoplastic olefin blends containing nanosilica. J Nonnewton Fluid Mech 233:95–106. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jnnfm.2016.01.017
Risite H, Oualid HA, Mabrouk K El (2018) Effects of vinyltriethoxysilane and maleic anhydride grafted polypropylenes on the morphological, thermal, rheological, and mechanical properties of polypropylene/clay nanocomposites. Proceedings 3:6. https://doi.org/10.3390/iocn_2018-1-05500
Khosrokhavar R, Bakhshandeh GR, Ghoreishy MHR, Naderi G (2009) PP/EPDM blends and their developments up to nanocomposites. J Reinf Plast Compos 28:613–639. https://doi.org/10.1177/0731684408096850
Khodabandelou M, Razavi Aghjeh MK, Khonakdar HA, Mehrabi Mazidi M (2017) Effect of localization of carbon nanotubes on fracture behavior of un-vulcanized and dynamically vulcanized PP/EPDM/MWCNT blend-nanocomposites. Compos Sci Technol 149:134–148. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compscitech.2017.06.003
Antunes CF, Van Duin M, MacHado AV (2011) Morphology and phase inversion of EPDM/PP blends-effect of viscosity and elasticity. Polym Test 30:907–915. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.polymertesting.2011.08.013
Huang C, Yu W (2016) Rheology and processing of nanoparticle filled polymer blend nanocomposites. Rheol Process Polym Nanocomposites. https://doi.org/10.1002/9781118969809.ch15
Jeddi J, Yousefzade O, Babaei A et al (2017) Morphology, microstructure and rheological properties of SAN (styrene-acrylonitrile)/EPDM (ethylene-propylene-diene monomer) nanocomposites: investigating the role of organoclay type and order of mixing. Mater Chem Phys 187:191–202. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matchemphys.2016.12.001
Soares BG, Santos DM, Sirqueira AS (2008) A novel thermoplastic elastomer based on dynamically vulcanized polypropylene/acrylic rubber blends. Express Polym Lett 2:602–613. https://doi.org/10.3144/expresspolymlett.2008.72
Soares BG, de Oliveira M, Meireles D, Sirqueira AS, Mauler RS (2008) Dynamically vulcanized polypropylene/nitrile rubber blends: the effect of peroxide/bis-maleimide curing system and different compatibilizing systems. Wiley Intersci 110:3566–3573
Mazidi MM, Razavi Aghjeh MK, Khonakdar HA, Reuter U (2016) Structure-property relationships in super-toughened polypropylene-based ternary blends of core-shell morphology. RSC Adv 6:1508–1526. https://doi.org/10.1039/c5ra24125a
Chow WS, Abu Bakar A, Mohd Ishak ZA et al (2005) Effect of maleic anhydride-grafted ethylene-propylene rubber on the mechanical, rheological and morphological properties of organoclay reinforced polyamide 6/polypropylene nanocomposites. Eur Polym J 41:687–696. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eurpolymj.2004.10.041
Tarawneh MA, Yu LJ, Tarawni MA et al (2015) High performance thermoplastic elastomer (TPE) nanocomposite based on graphene nanoplates (GNPs). World J Eng 12:437–442. https://doi.org/10.1260/1708-5284.12.5.437
Eriksson M, Peijs T, Goossens H (2018) The effect of polymer molar mass and silica nanoparticles on the rheological and mechanical properties of poly(Ε-caprolactone) nanocomposites. Nanocomposites 4:112–126. https://doi.org/10.1080/20550324.2018.1534792
Ling Z, Zhenghua W, Rui H et al (2002) PP/elastomer/calcium, carbonate composites: Effect of elastomer and calcium carbonate contents on the deformation and impact behavior. J Mater Sci 37:2615–2621. https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1015848528564
Odent J, Raquez JM, Thomassin JM et al (2015) Mechanistic insights on nanosilica self-networking inducing ultra-toughness of rubber-modified polylactide-based materials. Nanocomposites 1:113–125. https://doi.org/10.1179/2055033215Y.0000000005
Mahajan DK, Hartmaier A (2012) Mechanisms of crazing in glassy polymers revealed by molecular dynamics simulations. Phys Rev E-Stat Nonlinear Soft Matter Phys. https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevE.86.021802
Tjong SC (2006) Structural and mechanical properties of polymer nanocomposites. Mater Sci Eng R Rep 53:73–197. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mser.2006.06.001
Dompas D, Groeninckx G, Isogawa M, Hasegawa T, Kadokura M (1995) Cavitation versus debonding during deformation of rubber-modified poly(vinyl chloride). Polymer (Guildf) 36:437–441
Funding
No funding was received for conducting this study.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Not applicable.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that there is no conflict of interest.
Ethics approval
Not applicable.
Consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mokhtari Dizaji, S., Katbab, A.A. & Hajibabazadeh, S. Role of interfacial compatibilizer and functionality of rubber phase on micromorphology development and mechanical properties of PP/EPDM/nanosilica ternary nanocomposite. Polym. Bull. 80, 1353–1368 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00289-022-04112-6
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00289-022-04112-6