Abstract
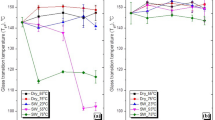
The environmental issue derived from petroleum-based plastic has brought wide attention on biodegradable plastic. The enforcement of new regulation on the requirement of environmentally friendly plastics has increased the demand of polylactic acid (PLA). Considering the increasing application of PLA, the accumulation of PLA wastes is also expected to increase. Recycling of PLA wastes is one of the promising alternatives in the minimization and sustainability of resources. However, the properties of the recycled PLA (RPLA) are deteriorated. This work intended to study the mechanical properties degradation of virgin PLA (VPLA) and RPLA aging in natural weathering and seawater environment. The degradation in mechanical properties was analyzed by tensile strength, transverse rupture strength (TRS), impact energy, and hardness. The samples were exposed to natural weathering and seawater environments for 150 days, and the mechanical properties degradation was monitored every 30 days. The results showed that the tensile strength, TRS, impact energy, and hardness properties degraded faster in RPLA than in VPLA. It was also noted that the degradation in tensile strength, TRS, impact energy, and hardness properties was more accelerated in seawater environment than in natural weathering environment, which suggested that hydrolysis degradation was a more predominant phenomenon than thermal degradation. No alteration on the surface and physical morphology was observed on the samples for both VPLA and RPLA in natural weathering and seawater environment, which indicated that the samples had undergone bulk degradation. No significant differences were observed in the thermal stability of VPLA and RPLA after aging in both environments.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Lv S, Zhang Y, Gu J, Tan H (2017) Biodegradation behaviour and modelling of soil burial effect on degradation rate of PLA blended with starch and wood flour. Colloids Surf, B 159:800–808. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.colsurfb.2017.08.056
Deroine M, Le Duigou A, Corre YM, Le Gac PY, Davies P, Cesay G, Bruzaud S (2014) Accelerated ageing of polylactide in aqueous environments: Comparative study between distilled water and seawater. Polym Degrad Stab 108:319–329. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.polymdegradstab.2014.01.020
Lv S, Liu X, Gu J, Jiang Y, Tan H, Zhang Y (2017) Microstructure analysis of polylactic acid-based composites during degradation in soil. Int Biodeterior Biodegradation 122:53–60. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ibiod.2017.04.017
Wan L, Li C, Sun C, Zhou S, Zhang Y (2019) Conceiving a feasible degradation model of polylactic acid-based composites through hydrolysis study to polylactic acid/wood flour/polymethyl mechacrylate. Compos Sci Technol 181:107675. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compscitech.2019.06.002
de Rosario SSM, Campo-Erazo SD, Villada-Castillo HS, Solanilla-Duque JF (2019) Structural changes of cassava starch and polylactic acid films submitted to biodegradation process. Int J Biol Macromol 129:442–447. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2019.01.187
Fahim IS, Chbib H, Mohamed Mahmoud H (2019) The synthesis, production & economic feasibility of manufacturing PLA from agricultural waste. Sustain Cities Soc 12:100142. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scp.2019.100142
Chuensangjun C, Pechyen C, Sirisansaneeyakul S (2013) Degradation behaviours of different blends of polylactic acid buries in soil. Energy Procedia 34:73–82. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.egypro.2013.06.735
Farah S, Anderson DG, Langer R (2016) Physical and mechanical properties of PLA, and their functions in widespread applications — a comprehensive review. Adv Drug Deliv Rev 107:367–392. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.addr.2016.06.012
Hamad K, Kaseem M, Deri F (2010) Rheological and mechanical properties of poly(lactic acid)/polystyrene polymer blend. Polym Bull 65:509–519. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00289-010-0354-2
Kong J, Li Y, Bai Y, Li Z, Cao Z, Yu Y, Han C, Dong L (2018) High-performance biodegradable polylactide composites fabricated using a novel plasticizer and functionalized eggshell powder. Int J Biol Macromol 112:46–53. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2018.01.153
Janczak K, Hrynkiewicz K, Znzjewska Z, Dabrowska G (2018) Use of rhizosphere microorganisms in the biodegradation of PLA and PET polymers in compost soil. Int Biodeterior Biodegrad 130:65–75. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ibiod.2018.03.017
Wan L, Zhang Y (2018) Jointly modified mechanical properties and accelerated hydrolytic degradation of PLA by interface reinforcement of PLA-WF. J Mech Behav Biomed Mater 88:223–230. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmbbm.2018.08.016
Chen H, Wang Y, Sun X, Peng P, Xiao L (2020) Mixing effect of polylactic acid microplastic and straw residue on soil property and ecological function. Chemosphere 243:125271. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2019.125271
Maga D, Hiebel M, Thonemann N (2019) Life cycle assessment of recycling options for polylactic acid. Resour Conserv Recycl 149:86–96. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.resconrec.2019.05.018
La Mantia FP, Morreale M (2011) Green composites: a brief review. Compos A Appl Sci Manuf 42:579–588. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compositesa.2011.01.017
Rudnik E, Briassoulis D (2011) Degradation behaviour of poly(lactic acid) films and fibres in soil under Mediterranean field conditions and laboratory simulations testing. Ind Crops Prod 33:648–658. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.indcrop.2010.12.031
Codari F, Lazzari S, Soos M, Storti G, Morbidelli M, Moscatelli D (2012) Kinetics of the hydrolytic degradation of poly(lactic acid). Polym Degrad Stab 97:2460–2466. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.polymdegradstab.2012.06.026
Sailema-Palate GP, Vidaurre A, Campillo-Fernandez AJ, Castilla-Cortazar I (2016) A comparative study on Poly(ε-caprolactone) film degradation at extreme pH values. Polym Degrad Stab 130:118–125. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.polymdegradstab.2016.06.005
Elsawy MA, Kim KH, Park JW, Deep A (2017) Hydrolytic degradation of polylactic acid (PLA) and its composites. Renew Sustain Energy Rev 79:1346–1352. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rser.2017.05.143
Varsavas SD, Kaynak C (2018) Weathering degradation performance of PLA and its glass fiber reinforced composite. Mater Today Commun 15:344–353. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mtcomm.2017.11.008
Spiridon I, Darie RN, Kangas H (2016) Influence of fiber modifications on PLA/fiber composites. Behavior to accelerated weathering. Compos B 92:19–27. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compositesb.2016.02.032
Beltran FR, Lorenzo V, de la Orden MU, Martinez-Urreaga J (2016) Effect of different mechanical recycling processes on the hydrolytic degradation of poly(L-lactic acid). Polym Degrad Stab 133:339–348. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.polymdegradstab.2016.09.018
Kaynak C, Sari B (2016) Accelerated weathering performance of polylactide and its montmorillonite nanocomposite. Appl Clay Sci 121:86–94. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.clay.2015.12.025
Techawinyutham L, Siengchin S, Dangtungee R, Parameswaranpillai J (2019) Influence of accelerated weathering on the thermo-mechanical, antibactirial, and rheological properties of polylactic acid incorporated with porous silica-containing varying amount of capsium oleoresin. Compos B 175:107108. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compositesb.2019.107108
Ho M, Lau K, Wang H, Hui D (2015) Improvement on the properties of polylactic acid (PLA) using bamboo charcoal particles. Compos B 8:14–25. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compositesb.2015.05.048
Man C, Zhang C, Liu Y, Wang W, Ren W, Jiang L, Reisdorffer F, Nguyen TP, Yi D (2012) Poly (lactic acid)/titanium dioxide composites : preparation and performance under ultraviolet irradiation. Polym Degrad Stab 97:856–862. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.polymdegradstab.2012.03.039
Pires M, Murariu M, Cardoso AM, Bonnaud L, Dubois P (2019) Thermal degradation of poly(lactic acid)–zeolite composites produced by melt-blending. Polym Bull. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00289-019-02846-4
Budin S, Maideen NC, Koay MH, Ibrahim D, Yusoff H (2019) A comparison study on mechanical properties of virgin and recycled polylactic acid (PLA). J Phys: Conf Ser 1349:012002. https://doi.org/10.1088/1742-6596/1349/1/012002
Mohammad ST, Al-Kayiem HH, Aurybi MA, Khlief AK (2020) Measurement of global and direct normal solar energy radiation in Seri Iskandar and comparison with other cities of Malaysia. Case Stud Therm Eng 18:100591. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.csite.2020.100591
Chavez-Montes WM, Gonzalez-Sanchez G, Lopez-Martinez EI, de Lira-gomez P, Ballinas-Casarrubias L, Flores-Gallardo S (2015) Effect of artificial weathering on PLA/nanocomposite molecular weight distribution. Polymers 7:760–776. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym7040760
Zhang X, Espiritu M, Bilyk A, Kurniawan L (2008) Morphological behaviour of poly(lactic acid) during hydrolytic degradation. Polym Degrad Stab 93:1964–1970. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.polymdegradstab.2008.06.007
Budin S, Hyie KH, Yussof H, Ishak A, Ginting R (2020) Investigation on mechanical properties of blend virgin and recycled acrylonitrile-butadiene-styrene (ABS) in injection molding. Key Eng Mater 833:8–12
Gorrasi G, Pantani R (2013) Effect of PLA grades and morphologies on hydrolytic degradation at composting temperature: Assessment of structural modification and kinetic parameters. Polym Degrad Stab 98:1006–1014. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.polymdegradstab.2013.02.005
Torres-Huerta AM, Palma-Ramirez D, Dominguez-Crespo MA, Del Angel-Lopez D, de la Fuente D (2014) Comparative assessment of miscibility and degradability on PET/PLA and PET/chitosan blends. Eur Polymer J 61:285–299. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eurpolymj.2014.10.016
Beltran-Sanahuja A, Casado-Coy N, Simo-Cabrera L, Sanz-Lazaro C (2020) Monitoring polymer degradation under different conditions in the marine environment. Environ Pollut 259:113836. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2019.113836
Zhou X, Yang R, Wang B, Chen K (2019) Development and characterization of bilayer films based on pea starch/polylactic acid and use in cherry tomatoes packaging. Carbohyd Polym 222:114912. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2019.05.042
Ngaowthong C, Boruvka M, Behalek L, Lenferd P, Svec M, Dangtungee R, Siengchin S, Rangappa RM, Parameswaranpillai J (2019) Recycling of sisal reinforced polypropylene and polylactic acid composites : thermo-mechanical properties, morphology and water absorption behavior. Waste Manag 97:71–81. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.wasman.2019.07.038
Acknowledgements
This research is supported by Faculty of Mechanical Engineering, Universiti Teknologi MARA, Cawangan Pulau Pinang.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Budin, S., Jaafar, M. Comparative study on mechanical properties of virgin and recycled polylactic acid aging in natural weathering and seawater environment. Polym. Bull. 79, 4841–4858 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00289-021-03756-0
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00289-021-03756-0