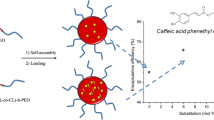
Abstract
In this study, boronic acid-functionalized methacrylate-based nanoparticles were synthesized via surfactant-free emulsion polymerization in one pot. Uniform (polydispersity index <0.05) sub-100 nm nanoparticles were obtained. The changes of average hydrodynamic diameter and polydispersity index of nanoparticles against boronic acid content in total monomer and acetone percentage in the solvent mixture were investigated. Polymerization kinetics in terms of monomer conversion rate was monitored by gravimetric method. The nanoparticles were characterized by scanning electron microscopy and dynamic light scattering. The boron content in the nanoparticles was confirmed by electron-dispersive X-ray spectroscopy. Further, the nanoparticles were combined with caffeic acid. Caffeic acid carrying nanoparticles were titrated against glucose or fructose in which caffeic acid is released by the displacement reaction in a controlled manner. The displacement of caffeic acid and glucose was monitored by UV–visible spectral change. Furthermore, in vitro biocompatibility of nanoparticles was tested in NIH-3T3 cells, which resulted no significant toxicity effect on the cells.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Kim JK, Jung KH, Jang JH, Huh DS (2014) Hydrophobic interaction-mediated reversible adsorption–desorption of nanoparticles in the honeycomb-patterned thermoresponsive poly(N-isopropylamide) hydrogel surface. Polym Bull 71:1375–1388. doi:10.1007/s00289-014-1129-y
Facundo IA, Soria MJ, Rosales MG, Elizalde LE, Leo´n RD, Saade H, Lo´pez RG (2011) Synthesis and characterization of thermosensitive core–shell polymeric nanoparticles. Polym Bull 67:985–995. doi:10.1007/s00289-010-0440-5
Fu X, Yang H, Zhang X, Li X, Xu L, Jia Y (2011) One-step method for preparation of pH-responsive gold nanoparticles with block copolymer shell structures by UV irradiation. Polym Bull 67:1059–1072. doi:10.1007/s00289-011-0524-x
Wang G, Yang S, Wei Z, Dong X, Wang H, Qi M (2013) Facile preparation of poly(e-caprolactone)/Fe3O4@graphene oxide superparamagnetic nanocomposites. Polym Bull 70:2359–2371. doi:10.1007/s00289-013-0957-5
Bootdee K, Nithitanakul M, Grady BP (2012) Synthesis and encapsulation of magnetite nanoparticles in PLGA: effect of amount of PLGA on characteristics of encapsulated nanoparticles. Polym Bull 69:795–806. doi:10.1007/s00289-012-0773-3
Yavuz MS, Cheng Y, Chen J, Cobley MC, Zhang Q, Rycenga M, Xie J, Kim C, Song KH, Schwartz AG, Wang LV, Xia Y (2009) Gold nanocages covered by smart polymers for controlled release with near-infrared light. Nat Mater 8:935–938
Tan BH, Tam KC, Lam YC, Tan CB (2004) Microstructure and rheology of stimuliresponsive nanocolloidal systems effect of ionic strength. Langmuir 20:11380–11386
Ulasan M, Yavuz E, Bagriacik EU, Cengeloglu Y, Yavuz MS (2015) Biocompatible thermoresponsive PEGMA nanoparticles crosslinked with cleavable disulfide-based crosslinker for dual drug release. J Biomed Mater Res A 103(1):243–251. doi:10.1002/jbm.a.35146
Kim JK, Basavaraja C, Yamaguchi T, Do Sung Huh DS (2013) Preparation and characterization of smart hydrogel nanocomposites sensitive to oxidation–reduction. Polym Bull 70:207–220. doi:10.1007/s00289-012-0825-8
Thornton PD, Mart RJ, Ulijn RV (2007) Enzyme-responsive polymer hydrogel particles for controlled release. Adv Mater 19:1252–1256
Liu YS, Chu CH, Tsai CA, Chen YH, Lee CF (2012) Synthesis and characteristics of poly(methyl methacrylate-methacrylic acid-3,3-(trimethoxysilyl) propyl methacrylate) hollow latex particles and their application to drug carriers. Polym Bull 69:699–714. doi:10.1007/s00289-012-0758-2
Hu Y, Yang T, Hu X (2012) Novel polysaccharides-based nanoparticle carriers prepared by polyelectrolyte complexation for protein drug delivery. Polym Bull 68:1183–1199. doi:10.1007/s00289-011-0683-9
Tang Y, Zhao Y, Li Y, Du Y (2010) A thermosensitive chitosan/poly(vinyl alcohol) hydrogel containing nanoparticles for drug delivery. Polym Bull 64:791–804. doi:10.1007/s00289-009-0214-0
Xiong XB, Binkhathlan Z, Molavi O, Lavasanifar A (2012) Amphiphilic block copolymers: preparation and application in nanodrug and gene delivery. Acta Biomater 8:2017–2033
Xu XD, Lin BB, Feng J, Wang Y, Cheng SX, Zhang XZ, Zhuo RX (2012) Biological glucose metabolism regulated peptide self-assembly as a simple visual biosensor for glucose detection. Macromol Rapid Commun 33:426–431
Nguyen VQ, Ishihara M, Mori Y, Nakamura S, Kishimoto S, Hattori H, Fujita M, Kanatani Y, Ono T, Miyahira Y, Matsui T (2013) Preparation of size-controlled silver nanoparticles and chitin-based composites and their antimicrobial activities. J Nanomater. 2013. doi:10.1155/2013/693486 (Article ID 693486)
Oishi M, Nagasaki Y (2010) Stimuli-responsive smart nanogels for cancer diagnostics and therapy. Nanomedicine 5:451–468
Chen YC, Lo CL, Hsiue GH (2014) Multifunctional nanomicellar systems for delivering anticancer drugs. J Biomed Mater Res A 102(6):2024–2038. doi:10.1002/jbm.a.34850
Urban MW (2011) Handbook of stimuli responsive materials. ePDF: 978-3-527-63374-6 (Chapter 2.2.1.3.)
Striegler S (2003) Selective carbohydrate recognition by synthetic receptors in aqueous solution. Curr Org Chem 7(1):82–102
Springsteen G, Wang BA (2002) Detailed examination of boronic acid-diol complexation. Tetrahedron 58:5291–5300
Huang YJ, Jiang YB, Fossey JS, James TD, Marken F (2010) Assembly of N-hexadecyl-pyridinium-4-boronic acid hexafluorophosphate monolayer films with catechol sensing selectivity. J Mater Chem 20:8305–8310
Cannizzo C, Sonia AG, Larpent C (2005) Boronic acid-functionalized nanoparticles: synthesis by microemulsion polymerization and application as a re-usable optical nanosensor for carbohydrates. Polymer 46(4):1269–1279
Li S, Davis EN, Anderson J, Lin Q, Wang Q (2008) Development of boronic acid grafted random copolymer sensing fluid for continuous glucose monitoring. Biomacromolecules 10(1):113–118
Shiino D, Murata Y, Kubo A, Kim YJ, Kataoka K, Koyama Y, Kikuchi A, Yokoyama M, Sakurai Y, Okano T (1995) Amine containing phenylboronic acid gel for glucose-responsive insulin release under physiological Ph. J Controlled Rel. 37(3):269–276
Zhang L, Lin Y, Wang J, Yao W, Wu W, Jiang X (2011) A facile strategy for constructing boron-rich polymer nanoparticles via a boronic acid-related reaction. Macromol Rapid Commun 32(6):534–539
Mulla HR, Agard NJ, Basu A (2004) 3-Methoxycarbonyl-5-nitrophenyl boronic acid: high affinity diol recognition at neutral Ph. Bioorg Med Chem Lett 14(1):25–27
Senel S, Camli ST, Tuncel M, Tuncel A (2002) Nucleotide adsorption-desorption behaviour of boronic acid functionalized uniform-porous particles. J Chromatogr B 769(2):283–295
Elmas B, Onur MA, Senel S, Tuncel A (2004) Thermosensitive N-isopropylacrylamidevinylphenyl boronic acid copolymer latex particles for nucleotide isolation. Colloids Surf A 232:253–259
Koyama T, Terauchi KI (1996) Synthesis and application of boronic acid-immobilized porous polymer particles: a novel packing for high-performance liquid affinity chromatography. J Chromatogr B 679:31–40
Gao S, Wang W, Wang B (2001) Building fluorescent sensors for carbohydrates using template-directed polymerizations. Bioorg Chem 29(5):308–320
Cianga I, Yagci Y (2001) Polystyrene macromonomer with boronic acid propanediol diester functionality prepared by ATRP for synthesis of comb-like polyphenylenes. Polym Bull 47:17–24
He L, Fullenkamp DE, Rivera JG, Messersmith PB (2011) pH Responsive self-healing hydrogels formed by boronate-catechol complexation. Chem Commun 47:7497–7499
Camli ST, Senel S, Tuncel A (2002) Nucleotide isolation by boronic acid functionalized hydrophilic supports. Colloids Surf A 207:127–137
Sahiner N (2014) One step poly(rutin) particle preparation as biocolloid and its characterization. Mater Sci Eng C 44:9–16
Li Y, Xiao W, Xiao K, Berti L, Luo J, Tseng HP, Fung G, Lam KS (2012) Well-defined, reversible boronate crosslinked nanocarriers for targeted drug delivery in response to acidic ph values and cis-diols. Angew Chem Int Ed 51:2864–2869
Shahidi F, Naczk M (2003) Food phenolics: sources, chemistry, effects, applications. Taylor & Francis, London
Lebo SE, Gargulak JD, Timothy MJ (2001) Lignin. Kirk-Othmer encyclopedia of chemical technology, vol 15. John Wiley & Sons, Inc. doi:10.1002/0471238961
Olthof MR, Hollman PC, Katan MB (2001) Chlorogenic acid and caffeic acid are absorbed in humans. J Nutr 131(1):66–71
Ou S, Kwok K (2004) Ferulic acid: pharmaceutical functions, preparation and applications in foods. J Sci Food Agric 84(11):1261–1269
Rajendra PN, Karthikeyan A, Karthikeyan S, Reddy BV (2011) Inhibitory effect of caffeic acid on cancer cell proliferation by oxidative mechanism in human HT-1080 fibrosarcoma cell line. Mol Cell Biochem 349:11–19
Saija A, Tomaino A, Cascio RL, Trombetta D, Proteggente A, Pasquale AD, Uccella N, Bonina F (1999) Ferulic and caffeic acids as potential protective agents against photooxidative skin damage. J Sci Food Agric 79(3):476–480
Coussens LM, Werb Z (2002) Inflammation and cancer. Nature 420:860–867
Gupta SC, Kim JH, Kannappan R, Reuter S, Dougherty PM, Aggarwal BB (2011) Role of nuclear factor-{kappa}B-mediated inflammatory pathways in cancer-related symptoms and their regulation by nutritional agents. Exp Biol Med 236(6):658–671
Hirose M, Takesada Y, Tanaka H, Tamano S, Kato T, Shirai T (1998) Carcinogenicity of antioxidants BHA, caffeic acid, sesamol, 4-methoxyphenol and catechol at low doses, either alone or in combination, and modulation of their effects in a rat medium-term multi-organ carcinogenesis model. Carcinogenesis 19(1):207–212
Kang NJ, Shin SH, Lee HJ, Lee KW (2011) Polyphenols as small molecular inhibitors of signaling cascades in carcinogenesis. Pharmacol Ther 130:310–324
Jus S, Stachel I, Schloegl W, Pretzler M, Friess W, Meyer M, Birner-Gruenberger R, Guebitz GM (2011) Cross-linking of collagen with laccases and tyrosinases. Mater Sci Eng C 31:1068–1077
Fathi M, Mirlohi M, Varshosaz J, Madani G (2013) Novel caffeic acid nanocarrier: production, characterization, and release modeling. J Nanomater. 2013. doi:10.1155/2013/434632 (Article ID 434632)
Huo J, Li J, Li Q (2013) Study on electrochemical behaviors and the reaction mechanisms of dopamine and epinephrine at the pre-anodized inlaying ultrathin carbon paste electrode with nichrome as a substrate. Mater Sci Eng C 33:507–511
Paini M, Aliakbarian B, Casazza AA, Perego P, Ruggiero C, Pastorino L (2015) Chitosan/dextran multilayer microcapsules for polyphenols co-delivery. Mater Sci Eng C 46:374–380. doi:10.1016/j.msec.2014.10.047
Catauro M, Papale F, Roviello G, Ferone C, Bollino F, Trifuoggi M, Aurilio C (2014) Synthesis of SiO2 and CaO rich calcium silicate systems via sol-gel process: bioactivity, biocompatibility, and drug delivery tests. J Biomed Mater Res A 102(9):3087–3092. doi:10.1002/jbm.a.34978
Yang X, Bakaic E, Hoare T, Cranston ED (2013) Injectable polysaccharide hydrogels reinforced with cellulose nanocrystals: morphology, rheology, degradation, and cytotoxicity. Biomacromolecules 14(12):4447–4455
Yavuz MS, Buyukserin F, Zengin Z, Camli ST (2011) Thermoresponsive oligo(ethylene glycol) methacrylate colloids with antifouling surface properties. J Polym Sci A Polym Chem 49:4800–4808
Camli ST, Buyukserin F, Balci O, Budak GG (2010) Size controlled synthesis of sub-100 nm monodisperse poly(methylmethacrylate) nanoparticles, using surfactant-free emulsion polymerization. J Colloid Interface Sci 344:528–532
Chen KY, Chen YW (2003) Synthesis of spherical titanium dioxide particles by homogeneous precipitation in acetone solution. J Sol Gel Sci Technol 27:111–117
Camli ST, Buyukserin F, Yavuz MS, Budak GG (2010) Fine-tuning of functional poly(methylmethacrylate) nanoparticle size at the sub-100 nm scale using surfactant-free emulsion polymerization. Colloids Surf A 366:141–146
Choi CH, Jung JH, Hwang TS, Lee CS (2009) In situ microfluidic synthesis of monodisperse PEG microspheres. Macromol Res 17(3):163–167
Choi CH, Jung JH, Rhee YW, Kim DP, Shim SE, Lee CS (2007) Generation of monodisperse alginate microbeads and in situ encapsulation of cell in microfluidic device. Biomed Microdevices 9(6):855–862
Goldshtein J, Margel S (2009) Synthesis and characterization of new UV absorbing microspheres of narrow size distribution by dispersion polymerization of 2-(2′-hydroxy-5′-methacryloxyethylphenyl)-2H-benzotriazole. Polymer 50(15):3422–3430
Vollrath A, Pretzel D, Pietsch C, Perevyazko I, Schubert S, Pavlov GM, Schubert US (2012) Preparation, cellular internalization, and biocompatibility of highly fluorescent PMMA nanoparticles. Macromol Rapid Commun 33(20):1791–1797
Ormsby R, McNally T, O’Hare P, Burke G, Mitchell C, Dunne N (2012) Fatigue and biocompatibility properties of a poly(methyl methacrylate) bone cement with multi-walled carbon nanotubes. Acta Biomater 8(3):1201–1212
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by Selcuk University Scientific Research Fund (S.U. BAP No. 12201077) and TUBITAK (Project No.112M096, COST TD1004). The authors are grateful to Advanced Technology Research and Application Center of Selcuk University for their kind help regarding with analysis studies (SEM, EDX, DLS, UV–Vis). The authors thank to Dr. Pembegul UYAR for providing 3T3 cells as a kind gift and her valuable guidance and to Huseyin Sakalak for his help in experimental studies.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ulasan, M., Yavuz, E., Cengeloglu, Y. et al. Facile synthesis of boronic acid-functionalized nanocarriers for glucose-triggered caffeic acid release. Polym. Bull. 72, 2127–2142 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00289-015-1393-5
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00289-015-1393-5