Abstract
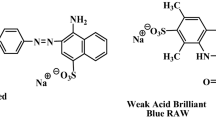
In this study, novel blend hydrogel beads were prepared for the use in removal of anionic textile dyes due to their hazardous impact to nature. Sodium alginate and sodium alginate/poly(N-vinyl-2-pyrrolidone) beads were prepared by gelation method into calcium chloride solution. Prepared blend beads were characterized by TGA and FTIR analysis, and they were successfully used in adsorption of the reactive red-120 (RR), cibacron brilliant red 3B-A (CBR) and remazol brilliant blue R (RBB) in batch system. The effects of various parameters such as pH, initial dye concentration, contact time and temperature onto adsorption were investigated. The maximum adsorption capacities were found 116.8, 73.3 and 55.3 mg g−1 for RR, CBR and RBB, respectively. The adsorption of dyes was well described by pseudo-second-order kinetics and Langmuir isotherm. Thermodynamic parameters indicated that the adsorption is spontaneous and exothermic. These results have shown that blend hydrogel beads can be effectively used as adsorbent in the removal of dyes from harmful wastewaters.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Vijayaraghavan K, Yun YS (2008) Biosorption of C.I. reactive black 5 from aqueous solution using acid treated biomass of brown seaweed Laminaria sp. Dyes Pigments 76:726–732
Aksu Z (2005) Application of biosorption for the removal of organic pollutants: a review. Process Biochem 40:997–1026
Çelekli A, İlgün G, Bozkurt H (2012) Sorption equilibrium, kinetic, thermodynamic, and desorption studies of reactive red 120 on Characontraria. Chem Eng J 191:228–235
Arıca MY, Bayramoğlu G (2007) Biosorption of reactive red-120 dye from aqueous solution by native and modified fungus biomass preparations of Lentinussajor-caju. J Hazard Mater 149:499–507
Acar I, Bal A, Güçlü G (2012) Adsorption of basic dyes from aqueous solutions by depolymerization products of post-consumer PET bottles. Clean Soil Air Water 40:325–333
Khaled A, El Nemr A, El-Sikaily A, Abdelwahap O (2009) Removal of direct N-Blue-106 from artificial textile dye effluent using activated carbon from orange peel: adsorption isotherm and kinetic studies. J Hazard Mater 165:100–110
Jesus AMD, Romão LPC, Araújo BR, Costa AS, Marques JJ (2011) Use of humin as an alternative material for adsorption/desorption of reactive dyes. Desalination 274:13–21
Sadettin S, Donmez G (2006) Bioaccumulation of reactive dyes by thermophilic cyanobacteria. Process Biochem 41:836–841
Aksu Z, Tezer S (2005) Biosorption of reactive dyes on the green alga Chlorella vulgaris. Process Biochem 40:1347–1361
Bhatti HN, Arkam N, Asgher M (2008) Optimization of culture conditions for enhanced decolorization of cibacron red FN-2BL by Schizophyllum commune IBL-6. Appl Biochem Biotechnol 149:255–264
Çelekli A, Yavuzatmaca M, Bozkurt H (2009) Kinetic and equilibrium studies on the adsorption of reactive red 120 from aqueous solution on Spirogyra majuscule. Chem Eng J 152:139–145
Asgher M, Bhatti HN (2012) Evaluation of thermodynamics and effect of chemical treatments on sorption potential of Citrus waste biomass for removal of anionic dyes from aqueous solutions. Ecol Eng 38:79–85
Chowdhury AK, Sarkar AD, Bandyopadhyay A (2009) Rice husk ash as a low cost adsorbent for the removal of methylene blue and congo red in aqueous phases. Clean Soil Air Water 37:581–591
Vimonses V, Lei S, Jin B, Chris WKC, Chris S (2009) Kinetic study and equilibrium isotherm analysis of Congo red adsorption by clay materials. Chem Eng J 148:354–364
Babu VR, Sairam M, Hosamani KM, Aminabhavi TM (2007) Preparation of sodium alginate–methylcellulose blend microspheres for controlled release of nifedipine. Carbohydr Polym 69:241–250
Akamatsu K, Maruyama K, Chen W, Nakao A, Nakao S (2011) Drastic difference in porous structure of calcium alginate microspheres prepared with fresh or hydrolyzed sodium alginate. J Colloid Interface Sci 363:707–710
Blackburn R (2004) Natural polysaccharides and their interactions with dye molecules: applications in effluent treatment. Environ Sci Technol 38:4905–4909
Zhu HY, Fu YQ, Jiang R, Yao J, Xiao L, Zeng GM (2012) Novel magnetic chitosan/poly(vinyl alcohol) hydrogel beads: preparation, characterization and application for adsorption of dye from aqueous solution. Bioresour Technol 105:24–30
Yan L, Chang PR, Zheng P, Yan XML, Chang PR, Zheng P, Ma X (2012) Characterization of magnetic guar gum-grafted carbon nanotubes and the adsorption of the dyes. Carbohydr Polym 87:1919–1924
Fan J, Shi Z, Lian M, Li H, Yin J (2013) Mechanically strong graphene oxide/sodium alginate/polyacrylamide nanocomposite hydrogel with improved dye adsorption capacity. J Mater Chem A 1:7433–7443
Bhattacharyya R, Ray SK (2014) Adsorption of industrial dyes by semi-IPN hydrogels of acrylic copolymers and sodium alginate. J Ind Eng Chem. doi:10.1016/j.jiec.2014.06.029
Wang W, Wang A (2010) Synthesis and swelling properties of pH-sensitive semi-IPN superabsorbent hydrogels based on sodium alginate-g-poly(sodium acrylate) and polyvinylpyrrolidone. Carbohydr Polym 80:1028–1036
Lu Q, Yu J, Gao J, Yang W, Li Y (2011) Glow-discharge electrolysis plasma induced synthesis of polyvinylpyrrolidone/acrylic acid hydrogel and its adsorption properties for heavy-metal ions. Plasma Process Polym 8:803–814
Wang W, Wang Q, Wang A (2011) pH-responsive carboxymethylcellulose-g-poly(sodium acrylate)/polyvinylpyrrolidone semi-IPN hydrogels with enhanced responsive and swelling properties. Macromol Res 19:57–65
Saraydın D, Karadağ E (2000) Binding of some dyes onto crosslinked poly (N-vinylpyrrolidone). Polym Bull 44:501–508
Şenkal BF, Erkal D, Yavuz E (2006) Removal of dyes from water by poly(vinyl pyrrolidone) hydrogel. Polym Adv Technol 17:924–927
Rocher V, Siaugue JM, Cabuil V, Bee A (2008) Removal of organic dyes by magnetic alginate beads. Water Res 42:1290–1298
Pathak TS, Kim JS, Lee SJ, Baek DJ, Paeng J (2008) Preparation of alginic acid and metal alginate from algae and their comparative study. J Polym Environ 16:198–204
Işıklan N, Kurşun F, İnal M (2010) Graft copolymerization of itaconic acid onto sodium alginate using benzoyl peroxide. Carbohydr Polym 79:665–672
Moharram MA, Khafagi MG (2006) Thermal behavior of poly(acrylic acid)–poly(vinyl pyrrolidone) and poly(acrylic acid)–metal–poly(vinyl pyrrolidone) complexes. J Appl Polym Sci 102:4049–4057
Xue Y, Hou H, Zhu S (2009) Adsorption removal of reactive dyes from aqueous solution by modified basic oxygen furnace slag: isotherm and kinetic study. Chem Eng J 147:272–279
Çelekli A, Tanrıverdi B, Bozkurt H (2011) Predictive modeling of removal of Lanaset Red G on Chara contraria; kinetic, equilibrium, and thermodynamic studies. Chem Eng J 169:166–172
Cheng R, Jiang Z, Ou S, Li Y, Xiang B (2009) Investigation of acid black 1 adsorption onto amino-polysaccharides. Polym Bull 62:69–77
Min M, Shen L, Hong G, Zhu M, Zhang Y, Wang X, Chen Y, Hsiao BS (2012) Micro-nano structure poly(ether sulfones)/poly(ethyleneimine) nanofibrous affinity membranes for adsorption of anionic dyes and heavy metal ionsin aqueous solution. Chem Eng J 197:88–100
Zhao S, Zhou F, Li L, Cao M, Zuo D, Liu H (2012) Removal of anionic dyes from aqueous solutions by adsorption of chitosan-based semi-IPN hydrogel composites. Composites B 43:1570–1578
Absalan G, Asadi M, Kamran S, Sheikhian L, Goltz DM (2011) Removal of reactive red-120 and 4-(2-pyridylazo) resorcinol from aqueous samples by Fe3O4 magnetic nanoparticles using ionic liquid as modifier. J Hazard Mater 192:476–484
Ahmad MA, Rahman NK (2011) Equilibrium, kinetics and thermodynamic of remazol brilliant orange 3R dye adsorption on coffee husk-based activated carbon. Chem Eng J 170:154–161
Çelekli A, Tanrıverdi B, Bozkurt H (2012) Lentil straw: a novel adsorbent for removing of hazardous dye–sorption behavior studies. Clean Soil Air Water 40:515–522
Aravindhan R, Rao JR, Nair BU (2007) Removal of basic yellow dye from aqueous solution by sorption on green alga Caulerpa scalpelliformis. J Hazard Mater 142:68–76
Chu BS, Baharin BS, Man YBC, Quek SY (2004) Separation of vitamin E from palm fatty acid distillate using silica: I equilibrium of batch adsorption. J Food Eng 62:97–103
Zhong ZY, Yang Q, Li XM, Luo K, Liu Y, Zeng GM (2012) Preparation of peanut hull-based activated carbon by microwave-induced phosphoric acid activation and its application in remazol brilliant blue R adsorption. Ind Crop Prod 37:178–185
Wang S, Wei J, Lv S, Guo Z, Jiang F (2013) Removal of organic dyes in environmental water onto magnetic-sulfonic graphene nanocomposite. Clean Soil Air Water 41:992–1001
Naveen N, Saravanan P, Baskar G, Renganathan S (2011) Equilibrium and kinetic modeling on the removal of reactive red 120 using positively charged Hydrillaverticillata. J Taiwan Inst Chem E 42:463–469
Saha TK, Bhoumik NC, Karmaker S, Ahmed MG, Ichikawa H, Fukumori Y (2011) Adsorption characteristics of reactive black 5 from aqueous solution onto chitosan. Clean Soil Air Water 39:984–993
Sathishkumara P, Arulkumarb M, Palvannan T (2012) Utilization of agro-industrial waste Jatropha curcas pods as an activated carbon for the adsorption of reactive dye remazol brilliant blue R (RBBR). J Clean Prod 22:67–75
Luo X, Zhang L (2009) High effective adsorption of organic dyes on magnetic cellulose beads entrapping activated carbon. J Hazard Mater 171:340–347
Ayan EM, Toptaş A, Kıbrıslıoğlu G, Yalçınkaya EES, Yanık J (2011) Biosorption of dyes by natural and activated vine stem. Interaction between biosorbent and dye. Clean Soil Air Water 39:406–412
Vijayakumar G, Dharmendirakumar M, Renganathan S, Sivanesan S, Baskar G, Elango KP (2009) Removal of Congo Red from aqueous solutions by Perlite. Clean Soil Air Water 37:355–364
Eren E (2010) Adsorption performance and mechanism in binding of azo dye by raw bentonite. Clean Soil Air Water 38:758–763
Suteu D, Bilba D, Aflori M, Doroftei F, Lisa G, Badeanu M, Malutan T (2012) The seashell wastes as biosorbent for reactive dye removal from textile effluents. Clean Soil Air Water 40:198–205
Nawi MA, Sabar S, Sheilatina AHJ, Ngah WSW (2010) Adsorption of Reactive Red 4 by immobilized chitosan on glass plates: towards the design of immobilized TiO2–chitosan synergistic photocatalyst-adsorption bilayer system. Biochem Eng J 49:317–325
Won SW, Wu G, Ma H, Liu Q, YanY Cui L, Liu C, Yun YS (2006) Adsorption performance and mechanism in binding of reactive red 4 by coke waste. J Hazard Mater 138:370–377
Junxiong C, Longzhe C, Yanxin W, Chengfu L (2009) Effect of functional groups on sludge for biosorption of reactive dyes. J Environ Sci 21:534–538
Dizge N, Aydiner C, Demirbaş E, Kobya M, Kara S (2008) Adsorption of reactive dyes from aqueous solutions by fly ash: kinetic and equilibrium studies. J Hazard Mater 150:737–746
Uğurlu M (2009) Adsorption of a textile dyes onto activated sepiolite. Microporous Mesoporous Mater 119:276–283
Acknowledgments
The authors gratefully acknowledge the financial support provided by the Kırıkkale University Research Fund through Project 2011/2.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
İnal, M., Erduran, N. Removal of various anionic dyes using sodium alginate/poly(N-vinyl-2-pyrrolidone) blend hydrogel beads. Polym. Bull. 72, 1735–1752 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00289-015-1367-7
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00289-015-1367-7