Abstract
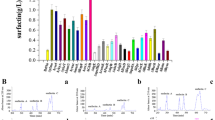
Surfactin is a promising microbial lipopeptide with wide applications in food, environmental, agricultural, and pharmaceutical fields. However, its high cost caused by low productivity largely limits the commercial application. In this study, genome shuffling was employed to improve surfactin production in Bacillus velezensis strain LM3403 via recursive protoplast fusion. RT-qPCR analysis was employed to evaluate the transcriptional variance of surfactin synthase genes and surfactin efflux gene to insight into the variance underlying the recombinant strain. After three rounds of genome shuffling, a high-yield and genetic stable recombinant F34 was obtained, exhibiting dramatic improvement in surfactin production (from 229.60 ± 7.10 mg/L to 908.15 ± 5.65 mg/L) with high proportion of long carbon chain homologues. Scale-up fermentation confirmed that F34 had good growth performance and reached the yield of 917.05 ± 10.25 mg/L in a 30 L fermenter, which was 3.99-fold that of the initial strain. RT-qPCR analysis showed that the transcriptional levels of surfactin synthase genes srfAA and sfp, and surfactin efflux gene swrC in F34 were 8.12-fold, 9.27-fold, and 8.45-fold higher than those of LM3403, respectively. The upregulation of genes were consistent with the high surfactin yield in F34, indicating the increased capability of surfactin biosynthesis and transmember efflux in F34. To our knowledge, this is the first attempt to employ genome shuffling to breeding a B. velezensis strain to improve surfactin yield. The research helps us to understand the mechanisms underlying surfactin overproduction and provide references for further rational strain improvement.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
K Arima A Kakinuma G Tamura 1968 Surfactin, a crystalline peptidelipid surfactant produced by Bacillus subtilis: isolation, characterization and its inhibition of fibrin clot formation Biochem Biophys Res Commun 31 488 494
F Peypoux JM Bonmatin J Wallach 1999 Recent trends in the biochemistry of surfactin Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 51 553 563
Y Zhi Q Wu Y Xu 2017 Genome and transcriptome analysis of surfactin biosynthesis in Bacillus Amyloliquefaciens MT45 Sci Rep 7 40976
NS Shaligram RS Singhal 2010 Surfactin-a review on biosynthesis, fermentation, purification and applications Food Technol Biotechnol 48 119 134
WC Chen RS Juang YH Wei 2015 Applications of a lipopeptide biosurfactant, surfactin, produced by microorganisms Biochem Eng J 103 158 169
Q Wu Y Zhi Y Xu 2019 Systematically engineering the biosynthesis of a green biosurfactant surfactin by Bacillus subtilis 168 Metab Eng 52 87 97
IM Banat A Franzetti I Gandolfi G Bestetti MG Martinotti L Fracchia TJ Smyth R Marchant 2010 Microbial biosurfactants production, applications and future potential Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 87 427 444
SM Mandal AE Barbosa OL Franco 2013 Lipopeptides in microbial infection control: scope and reality for industry Biotechnol Adv 31 338 345
GV Moro RTR Almeida AP Napp C Porto EJ Pilau DS Ludtke AV Moro MH Vainstein 2018 Identification and ultra-high-performance liquid chromatography coupled with high-resolution mass spectrometry characterization of biosurfactants, including a new surfactin, isolated from oil-contaminated environments Microb Biotechnol 11 759 769
A Bartal A Vigneshwari B Boka M Voros I Takacs L Kredics L Manczinger M Varga C Vagvolgyi A Szekeres 2018 Effects of different cultivation parameters on the production of surfactin variants by a Bacillus subtilis strain Molecules 23 2675
FX Hu YY Liu S Li 2019 Rational strain improvement for surfactin production: enhancing the yield and generating novel structures Microb Cell Factories 18 42
MS Yeh YH Wei JS Chang 2005 Enhanced production of surfactin from Bacillus subtilis by addition of solid carriers Biotechnol Prog 21 1329 1334
J Willenbacher T Mohr M Henkel S Gebhard T Mascher C Syldatk R Hausmann 2016 Substitution of the native srfA promoter by constitutive Pveg in two B. subtilis strains and evaluation of the effect on surfactin production J Biotechnol 224 14 17
M Henkel M Geissler F Weggenmann R Hausmann 2017 Production of microbial biosurfactants: status quo of rhamnolipid and surfactin towards large-scale production Biotechnol J 12 1600561
JQ Wang RJ Guo WC Wang GZ Ma SD Li 2018 Insight into the surfactin production of Bacillus velezensis B006 through metabolomics analysis J Ind Microbiol Biotechnol 45 1033 1044
YX Zhang K Perry VA Vinci K Powell WP Stemmer SB Cardayre del 2002 Genome shuffling leads to rapid phenotypic improvement in bacteria Nature 415 644 646
TA Magocha H Zabed MM Yang JH Yun HH Zhang XH Qi 2018 Improvement of industrially important microbial strains by genome shuffling: current status and future prospects Bioresour Technol 257 281 289
J Sun H Li Y Ni XM Zhang JS Shi ZH Xu 2017 Genome shuffling of Colletotrichum lini for improving 3β, 7α, 15α-trihydroxy-5-androsten-17-one production from dehydroepiandrosterone J Ind Microbiol Biotechnol 44 937 947
QG Huang BD Zeng L Liang SG Wu JZ Huang 2018 Genome shuffling and high-throughput screening of Brevibacterium flavum MDV1 for enhanced L-valine production World J Microbiol Biotechnol 34 121
Y Wang G Zhang X Zhao J Ling 2017 Genome shuffling improved the nucleosides production in Cordyceps kyushuensis J Biotechnol 260 42 47
M Kordowska-Wiater U Lisiecka K Kostro 2018 Improvement of Candida parapsilosis by genome shuffling for the efficient production of arabitol from L-arabinose Food Sci Biotechnol 27 1395 1403
R Patnaik S Louie V Gavrilovic K Perry WP Stemmer CM Ryan S Cardayre del 2002 Genome shuffling of Lactobacillus for improved acid tolerance Nat Biotechnol 20 707 712
S Hu Y You F Xia J Liu W Dai J Liu Y Wang 2019 Genome shuffling improved acid-tolerance and succinic acid production of Actinobacillus succinogenes Food Sci Biotechnol 28 817 822
KD Jetti RGNS Reddy D Garlapab SK Nammi 2019 Improved ethanol productivity and ethanol tolerance through genome shuffling of Saccharomyces cerevisiae and Pichia stipitis Int Microbiol 22 247 254
L Chen JY Heng SY Qin K Bian 2018 A comprehensive understanding of the biocontrol potential of Bacillus velezensis LM2303 against Fusarium head blight PLoS ONE 13 e0198560
KJ Livak TD Schmittgen 2001 Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2−ΔΔCT method Methods 25 402 408
E Jourdan G Henry F Duby J Dommes JP Barthelemy P Thonart M Ongena 2009 Insights into the defense-related events occurring in plant cells following perception of surfactin-type lipopeptide from Bacillus subtilis Mol Plant Microbe Interact 22 456 468
G Henry M Deleu E Jourdan P Thonart M Ongena 2011 The bacterial lipopeptide surfactin targets the lipid fraction of the plant plasma membrane to trigger immune-related defence responses Cell Microbiol 13 1824 1837
C Carrillo JA Teruel FJ Aranda A Ortiz 2003 Molecular mechanism of membrane permeabilization by the peptide antibiotic surfactin Biochim et Biophys Acta 1611 91 97
MM Nakano MA Marahiel P Zuber 1988 Identification of a genetic locus required for biosynthesis of the lipopeptide antibiotic surfactin in Bacillus subtilis J Bacteriol 170 5662 5668
LE Quadri PH Weinreb M Lei MM Nakano P Zuber CT Walsh 1998 Characterization of Sfp, a Bacillus subtilis phosphopantetheinyl transferase for peptidyl carrier protein domains in peptide synthetases Biochemistry 37 1585 1595
X Li H Yang D Zhang X Li H Yu Z Shen 2015 Overexpression of specific proton motive force-dependent transporters facilitate the export of surfactin in Bacillus subtilis J Ind Microbiol Biotechnol 42 93 103
H Nikaido 1998 Multiple antibiotic resistance and efflux Curr Opin Microbiol 1 516 523
K Tsuge Y Ohata M Shoda 2001 Gene yerP, involved in surfactin self-resistance in Bacillus subtilis Antimicrob Agents Chemother 45 3566 3573
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by National natural science foundation project of China (31401543, U1304332), National top youth talent support program for grain industry (LQ2016101), Natural science foundation project of Henan province (182300410042), Innovative Research Team in University of Henan Province (19IRTSTHN008).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Research Involving Human Participants and/or Animals
This article does not contain any studies with human participants or animals performed by any of the authors.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chen, L., Chong, Xy., Zhang, YY. et al. Genome Shuffling of Bacillus velezensis for Enhanced Surfactin Production and Variation Analysis. Curr Microbiol 77, 71–78 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00284-019-01807-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00284-019-01807-4