Abstract
A clinical trial was initiated to evaluate the recommended dose of cyclophosphamide in combination with bortezomib and dexamethasone as induction treatment before stem cell transplantation for younger patients with newly diagnosed multiple myeloma (MM). Thirty patients were treated with three 21-day cycles of bortezomib 1.3 mg/m2 on days 1, 4, 8, and 11 plus dexamethasone 40 mg on the day of bortezomib injection and the day after plus cyclophosphamide at 900, 1,200, or 1,500 mg/m2 on day 1. The maximum tolerated dose of cyclophosphamide was defined as 900 mg/m2. At this dose level, 92% of patients achieved at least a partial response. The overall response rate [complete response (CR) plus partial response (PR)] across all dose levels was 77%, with a 10% CR rate. No patient experienced progressive disease. The most frequent adverse events were hematological and gastrointestinal toxicities as well as neuropathy. The results suggest that bortezomib in combination with cyclophosphamide at 900 mg/m2 and dexamethasone is an effective induction treatment for patients with newly diagnosed MM that warrants further investigation.
Similar content being viewed by others
Avoid common mistakes on your manuscript.
Introduction
For patients younger than 65 years with newly diagnosed multiple myeloma (MM), high-dose melphalan followed by stem cell transplantation (SCT) is considered the standard of care. Induction treatment before SCT typically consists of vincristine, doxorubicin, and dexamethasone. With this regimen, response rates are in the range of 50–60% with a generally low incidence of complete responses (CRs; <10%) [1]. It has been suggested that the inclusion of novel agents, such as thalidomide, lenalidomide, and bortezomib, in induction treatments improves response rates over those achieved with traditional regimen and may improve overall outcomes for patients [2].
Bortezomib (Velcade®; Millennium Pharmaceuticals, Cambridge, MA, USA and Johnson & Johnson Pharmaceutical Research and Development LLC, La Jolla, CA, USA) is a selective and reversible inhibitor of the proteasome that has demonstrated efficacy in the relapsed and relapsed/refractory setting. In patients with a relapse after one to three prior therapies, an overall response rate of 43% was noted, with a 16% complete response (CR) + near CR rate [3]. Moreover, the overall survival with single-agent bortezomib for relapsed myeloma was 29.8 months. The combination of bortezomib with conventional cytotoxic therapy suggested synergistic anti-myeloma activity in preclinical studies [4, 5]. Furthermore, a number of trials have shown increased overall and complete response rates when bortezomib is combined with conventional chemotherapy and steroids [6–9].
Bortezomib is currently undergoing investigation in frontline treatment in both the transplant and non-transplant setting. A number of phase 2 studies and, more recently, two phase 3 studies are demonstrating that inclusion of bortezomib in induction regimen increases response rates pre- as well as post-transplant [2, 10–12].
We have previously shown that bortezomib in combination with cyclophosphamide and dexamethasone results in a high overall response rate with manageable adverse events in patients with relapsed/refractory MM, prompting the investigation of this three-drug combination in the frontline setting [6]. These results in relapsed myeloma have recently been confirmed by others [13, 14]. The current trial was initiated to examine the combination of fixed doses of bortezomib and dexamethasone with varying doses of cyclophosphamide, with the objective of defining a recommended dose of cyclophosphamide, which then will be further investigated. The results of this dose-finding study are reported in this paper.
Materials and methods
Patients
From March 2006 to February 2007, 31 patients were enrolled at five study centers in Germany. Major inclusion criteria were newly diagnosed MM requiring therapy, age 18–60 years, leukocytes ≥3.0 × 103/mm3, absolute neutrophil count ≥1.5 × 103/mm3, platelets ≥75 × 103/mm3, creatinine clearance >30 ml/min, aspartate aminotransferase and alanine aminotransferase <2.5 × upper limit of normal (ULN), bilirubin <1.5 × ULN. Prior localized radiotherapy and short-course dexamethasone were allowed.
The following were major exclusion criteria: non-secretory myeloma; prior systemic treatment for symptomatic myeloma; hypersensitivity to bortezomib, boron, mannitol, or cyclophosphamide; pre-existing peripheral neuropathy of grade 2 or greater intensity; cancer other than MM within 5 years before enrollment, with the exception of basal cell carcinoma or cervical cancer in situ; active hepatitis; and HIV infection. Females of childbearing potential were required to have a negative pre-treatment urine pregnancy test and contraception throughout treatment.
The study was conducted in accordance with the Declaration of Helsinki including all current amendments. It has been registered at the European Clinical Trials Database (EudraCT no. 2005-003907-27). The study protocol was approved by the local ethics committee at each participating site. All patients provided written informed consent. Data were controlled by an independent clinical research organization.
Study design and treatment schedule
This open-label, prospective trial was designed to evaluate the maximum tolerated dose of cyclophosphamide in combination with bortezomib and dexamethasone. Thirty patients with newly diagnosed MM were scheduled to receive a maximum of three 21-day cycles of bortezomib 1.3 mg/m2 as a single bolus i.v. twice weekly (on days 1, 4, 8, and 11) plus dexamethasone 40 mg p.o. on the day of and the day after bortezomib plus cyclophosphamide i.v. on day 1 (Fig. 1). The following cyclophosphamide dose levels were scheduled to be examined: 600, 900, 1,200, and 1,500 mg/m2. The initial dose of cyclophosphamide was 1,200 mg/m2. If no dose-limiting toxicity (DLT) occurred, cyclophosphamide was to be increased to 1,500 mg/m2. An extension to six patients was to be done if DLT was documented in one out of three patients at 1,200 mg/m2. If more than two sixths of the patients experienced a DLT, cyclophosphamide was to be reduced to 900 mg/m2 and then to 600 mg/m2.
If two out of three patients experienced a DLT, an immediate dose reduction was mandatory.
DLT was defined as either hematological toxicity grade 4, non-hematological toxicity ≥ grade 3 (except nausea, vomiting, and alopecia) or neuropathy grade 2 with pain occurring during the first treatment cycle.
The maximum tolerated dose for cyclophosphamide was defined as the dose level at which the incidence of DLTs was less than 33%.
Recommended concomitant medication consisted of prophylactic antiviral medication, prophylaxis against pneumocystis carinii, oral non-absorbable antifungal medication, and bisphosphonates. In addition, anti-emetics, cytokines, uromitexan, and intravenous immunoglobulins were allowed.
Assessment of efficacy and safety
Response was evaluated following the European Group for Blood and Marrow Transplantation criteria [15]. Briefly, a partial response (PR) was defined as >50% reduction of monoclonal immunoglobulin and >90% reduction of light chain proteinuria; for a minor response (MR), the corresponding cut points were 25% and 50%, respectively. CR required a negative immunofixation in serum and urine. PD without prior CR was determined by a ≥25% increase in monoclonal gammopathy or light chain proteinuria or the occurrence of new lytic bone lesions.
Baseline evaluations included physical examination, blood counts, hepatic and renal function tests, bone marrow aspirate for centrally performed (PL) molecular cytogenetic analyses (fluorescence in situ hybridization) and biopsy, serum and urine protein electrophoreses, and quantitation of serum immunoglobulins and urinary light chains, β2M and C reactive protein. A chest X-ray and a complete radiological bone survey were also performed. Safety was assessed throughout the study by physical examinations, recording of vital signs, toxicity assessments, and laboratory tests (hematology, clinical chemistry). All patients that received at least one dose of the study drugs were included in the toxicity evaluation.
Study objectives and statistical analysis
The primary objective of this study was to establish the optimal dose of cyclophosphamide in combination with fixed doses of bortezomib and dexamethasone.
Secondary objectives were to evaluate the safety and tolerability of an induction therapy with bortezomib, dexamethasone, and cyclophosphamide.
Outcome was analyzed on an intention-to-treat basis.
Results
Patient characteristics
Of 31 patients enrolled, one patient had to be excluded from the study for not meeting eligibility criteria. Baseline characteristics of the 30 patients who entered the active treatment phase are shown in Table 1. A number of patients had received supportive treatment for myeloma before study enrollment: 21 patients had received single pulses of dexamethasone, and nine patients had undergone localized radiotherapy.
In total, 13 (43.3%) patients were treated with an initial dose of cyclophosphamide 900 mg/m2, 13 (43.3%) patients with 1,200 mg/m2, and four (13.3%) patients with 1,500 mg/m2. Twenty-two patients (73.3%) completed all three scheduled treatment cycles. Twenty-seven patients are evaluable for cyclophosphamide dose definition. Three patients had to be excluded from evaluation for dose definition because of major protocol deviations.
Results of the cyclophosphamide dose-finding study
Three patients were treated with cyclophosphamide at an initial dose of 1,200 mg/m2 without any DLT occurring in the first treatment cycle. Therefore, the dose of cyclophosphamide was increased to 1,500 mg/m2. At this dose level, two DLTs (both leukopenia) occurred in two of three treated patients. As a result, the cyclophosphamide dose was reduced to 1,200 mg/m2, and six further patients were treated at this dose level (in addition to the three patients who were initially treated at 1,200 mg/m2). In two of the six patients, a DLT was observed (one leukopenia and one neutropenia). To test this dose level further, four additional patients were treated with cyclophosphamide 1,200 mg/m2. In two of these patients, a DLT occurred (leukopenia in both cases), and as a result, the dose of cyclophosphamide was reduced to 900 mg/m2. A total of 13 patients were treated at 900 mg/m2 with one DLT (pneumonia) occurring. The dose of 900 mg/m2 was therefore defined as the maximum tolerated dose for cyclophosphamide in combination with bortezomib and dexamethasone.
Efficacy
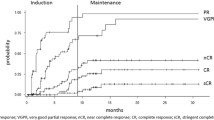
All 30 patients in the intent-to-treat population were evaluable for response. Overall, the response rate (CR + PR) was 77%, with three patients achieving CR (10%), 20 PR (67%), and three (10%) MR (Table 2). No patient experienced progressive disease.
In the subgroup of patients who received the maximum tolerated dose, the overall response rate was 92% with one CR, 11 PRs, and one MR, with a median time to best response of 46 days.
Patients with high-risk cytogenetics (t[4;14], or 17p deletion, n = 8) showed a slightly inferior overall response rate compared to patients without these changes (n = 15; 62.5% versus 86.5% ≥PR); when patients with 13q deletion were included in the high-risk group, the overall response rate was inferior compared to patients with standard-risk cytogenetics (61.5% versus 100% ≥PR).
To date, stem cell harvest has been carried out within the subsequent trial, the DSMM XI study in 28 patients. All patients mobilized well with a median of one collection procedure. Following subsequent high-dose melphalan therapy, median time to neutrophil engraftment was 13 days (range, 1–20); median time to platelet engraftment was 15 days (range, 8–30).
Safety
All patients experienced at least one adverse event. The most frequent adverse events were myelosuppression, gastrointestinal disorders, fatigue, and neuropathy (Table 3). In addition, one patient who had not received antiviral prophylaxis experienced grade 2 herpes zoster. Most adverse events were National Cancer Institute Common Toxicity Criteria grades 1–2.
Adverse events leading to premature discontinuation of bortezomib or cyclophosphamide were documented in five (16.7%) patients.
Serious adverse events occurred in eight of 30 (26.7%) patients. In the 900 mg/m2 group, serious adverse events were dose-limiting pneumonia, cholelithiasis, and neuralgia. In the 1,200 mg/m2 group, the following serious adverse events were noted: two cases of dose-limiting leukopenia, one case of pneumonia, and one case of intervertebral disc protrusion. In the 1,500 mg/m2 group, serious adverse events included thrombocytopenia, urethral hemorrhage, acute renal failure, dose-limiting infection (which was subsequently corrected as being just a serious adverse event but not DLT since the patient was classified as drop out and therefore not evaluable for DLT) and two cases of leukopenia.
Two cases of dose-limiting leukopenia were not considered to be serious adverse events.
No deaths were reported during the conduct of the study.
Discussion
We initiated a trial to evaluate the optimal dose of cyclophosphamide in combination with fixed dose bortezomib and dexamethasone as induction treatment before SCT and to evaluate efficacy and safety. This combination obviates the risks associated with the repeated placing and maintenance of indwelling central venous catheters for phlebotoxic drugs, such as vincristine or doxorubicin, which are widely used for pre-transplant induction in myeloma. Instead this treatment can be administered on an outpatient basis. The study defined that cyclophosphamide at 900 mg/m2 in combination with standard doses of bortezomib and dexamethasone is the recommended dose that should be investigated further. At the maximum tolerated dose of cyclophosphamide, a high overall response rate was achieved with a short time to response. The lower response rates observed at the higher cyclophosphamide doses may be due to the fact that in patients with a DLT response was assessed early after the first cycle corresponding to the end of study treatment. Patients in the 900 mg/m2 group, on the other hand, typically received all three cycles of therapy before response was assessed.
The high response rate achieved at the maximum tolerated dose is in line with the results of other bortezomib combination studies in the frontline setting [2, 10–12, 16]. The recently presented Canadian phase 2 trial investigating the combination of bortezomib, cyclophosphamide, and dexamethasone as induction treatment differed from that in our study in that cyclophosphamide was given at 300 mg/m2 weekly (on days 1, 8, 15, and 22) and dexamethasone 40 mg was administered on days 1–4, 9–12, and 17–20 [16]. Nevertheless, the results of the Canadian study agree with those of our own study, suggesting that the combination of bortezomib, cyclophosphamide, and dexamethasone is effective, inducing rapid and deep responses.
Consistent with previous data, our results demonstrate that bortezomib-based regimen lead to responses even in patients with cytogenetic abnormalities [17–19]. The response rate appears to be reduced compared with that in patients with standard-risk cytogenetics; however, the small number of patients precludes a meaningful comparison.
Adverse events in our study were in line with those observed in previous studies involving bortezomib, cyclophosphamide, and dexamethasone [6]. Notably, no deep vein thrombosis was seen, and only a single patient, who did not receive antiviral prophylaxis, experienced herpes zoster.
Induction therapy with bortezomib/dexamethasone/cyclophosphamide neither adversely affected subsequent stem cell mobilization nor engraftment after high-dose melphalan, which is in accordance with previous reports of bortezomib-based induction regimen [20].
Our results demonstrate that bortezomib in combination with cyclophosphamide and dexamethasone is an effective outpatient induction treatment for newly diagnosed MM. The recommended dose of cyclophosphamide in this combination is 900 mg/m2. This schedule is currently being evaluated as pre-transplant induction therapy in a prospective trial of the Deutsche Studiengruppe Multiples Myelom.
References
Palumbo A, Rajkumar SV (2009) Treatment of newly diagnosed myeloma. Leukemia (in press)
Harousseau JL, Attal M, Leleu X, Troncy J, Pegourie B, Stoppa AM, Hulin C, Benboubker L, Fuzibet JG, Renaud M, Moreau P, Avet-Loiseau H (2006) Bortezomib plus dexamethasone as induction treatment prior to autologous stem cell transplantation in patients with newly diagnosed multiple myeloma: results of an IFM phase II study. Haematologica 91:1498–1505
Richardson PG, Sonneveld P, Schuster M, Irwin D, Stadtmauer E, Facon T, Harousseau JL, Ben-Yehuda D, Lonial S, Goldschmidt H, Reece D, Miguel JS, Bladé J, Boccadoro M, Cavenagh J, Alsina M, Rajkumar SV, Lacy M, Jakubowiak A, Dalton W, Boral A, Esseltine DL, Schenkein D, Anderson KC (2007) Extended follow-up of a phase 3 trial in relapsed multiple myeloma: final time-to-event results of the APEX trial. Blood 110:3557–3560
Ma MH, Yang HH, Parker K, Manyak S, Friedman JM, Altamirano C, Wu ZQ, Borad MJ, Frantzen M, Roussos E, Neeser J, Mikail A, Adams J, Sjak-Shie N, Vescio RA, Berenson JR (2003) The proteasome inhibitor PS-341 markedly enhances sensitivity of multiple myeloma tumor cells to chemotherapeutic agents. Clin Cancer Res 9:1136–1144
Mitsiades N, Mitsiades CS, Richardson PG, Poulaki V, Tai YT, Chauhan D, Fanourakis G, Gu X, Bailey C, Joseph M, Libermann TA, Schlossman R, Munshi NC, Hideshima T, Anderson KC (2003) The proteasome inhibitor PS-341 potentiates sensitivity of multiple myeloma cells to conventional chemotherapeutic agents: therapeutic implications. Blood 101:2377–2380
Kropff M, Bisping G, Schuck E, Liebisch P, Lang N, Hentrich M, Dechow T, Kröger N, Salwender H, Metzner B, Sezer O, Engelhardt M, Wolf HH, Einsele H, Volpert S, Heinecke A, Berdel WE, Kienast J (2007) Bortezomib in combination with intermediate-dose dexamethasone and continuous low-dose oral cyclophosphamide for relapsed multiple myeloma. Br J Haematol 138:330–337
Orlowski RZ, Nagler A, Sonneveld P, Bladé J, Hajek R, Spencer A, San Miguel J, Robak T, Dmoszynska A, Horvath N, Spicka I, Sutherland HJ, Suvorov AN, Zhuang SH, Parekh T, Xiu L, Yuan Z, Rackoff W, Harousseau JL (2007) Randomized phase III study of pegylated liposomal doxorubicin plus bortezomib compared with bortezomib alone in relapsed or refractory multiple myeloma: combination therapy improves time to progression. J Clin Oncol 25:3892–3901
Berenson JR, Yang HH, Vescio RA, Nassir Y, Mapes R, Lee SP, Wilson J, Yellin O, Morrison B, Hilger J, Swift R (2008) Safety and efficacy of bortezomib and melphalan combination in patients with relapsed or refractory multiple myeloma: updated results of a phase 1/2 study after longer follow-up. Ann Hematol 87:623–631
Palumbo A, Ambrosini MT, Benevolo G, Pregno P, Pescosta N, Callea V, Cangialosi C, Caravita T, Morabito F, Musto P, Bringhen S, Falco P, Avonto I, Cavallo F, Boccadoro M, Italian Multiple Myeloma Network, Gruppo Italiano Malattie Ematologicche dell’Adulto (2007) Bortezomib, melphalan, prednisone, and thalidomide for relapsed multiple myeloma. Blood 109:2767–2772
Harousseau JL, Mathiot C, Attal M, Marit G, Caillot D, Mohty MMM, Hullin C, Facon TTF, Webb IIW, Moreau P (2007) VELCADE/Dexamethasone (Vel/D) versus VAD as induction treatment prior to autologous stem cell transplantion (ASCT) in newly diagnosed multiple myeloma: updated results of the IFM 2005/01 trial. Blood 110:450
Cavo M, Patriarca F, Tacchetti P, Galli M, Perrone G, Petrucci MT, Brioli A, Bringhen S, Pantani L, Tosi P, Crippa C, Zamagni E, Di Raimondo F, Narni F, Cellini C, Ceccolini M, Pescosa N, Goldaniga MC, Montefusco V, Callea V, De Stefano V, Caravita T, Boccadoro M, Baccarani M (2007) Bortezomib (Velcade)–thalidomide–dexamethasone (VTD) vs thalidomide–dexamethasone (TD) in preparation for autologous stem-cell transplantation (ASCT) in newly diagnosed multiple myeloma. Blood 110:73
Popat R, Oakervee HE, Hallam S, Curry N, Odeh L, Foot N, Esseltine DL, Drake M, Morris C, Cavenagh JD (2008) Bortezomib, doxorubicin and dexamethasone (PAD) front-line treatment of multiple myeloma: updated results after long-term follow-up. Br J Haematol 141:512–516
Davies FE, Wu P, Jenner M, Srikanth M, Saso R, Morgan GJ (2007) The combination of cyclophosphamide, velcade, and dexamethasone (CVD) induces high response rates with comparable toxicity to velcade alone (V) and velcade plus dexamethasone (VD). Haematologica 92:1149–1150
Reece DE, Rodriguez GP, Chen C, Trudel S, Kukreti V, Mikhael J, Pantoja M, Xu W, Stewart AK (2008) Phase I-II trial of bortezomib plus oral cyclophosphamide and prednisone in relapsed and refractory multiple myeloma. J Clin Oncol 26:4777–4783
Bladé J, Samson D, Reece D, Apperley J, Björkstrand B, Gahrton G, Gertz M, Giralt S, Jagannath S, Vesole D (1998) Criteria for evaluating disease response and progression in patients with multiple myeloma treated by high-dose therapy and haemopoietic stem cell transplantation. Br J Haematol 102:1115–1123
Reeder CB, Reece DE, Fonseca R, Bergsagel PL, Hentz J, Pirooz NA, Boesiger JE, Pisa JG, Kukreti V, Chen C, Trudel S, Mikhael JR, Lacy M, Rajkumar SV, Stewart AK (2007) A phase II trial of myeloma induction therapy with cyclophosphamide, bortezomib, and dexamethasone (Cybor-D): improved response over historical lenalidomide-dexamethasone controls. Blood 110:3601
Chang H, Trieu Y, Qi X, Xu W, Stewart KA, Reece D (2007) Bortezomib therapy response is independent of cytogenetic abnormalities in relapsed/refractory multiple myeloma. Leuk Res 31:779–782
Sagaster V, Ludwig H, Kaufmann H, Odelga V, Zojer N, Ackermann J, Küenburg E, Wieser R, Zielinski C, Drach J (2007) Bortezomib in relapsed multiple myeloma: response rates and duration of response are independent of a chromosome 13q-deletion. Leukemia 21:164–168
Rosiñol L, Oriol A, Mateos MV, Sureda A, García-Sánchez P, Gutiérrez N, Alegre A, Lahuerta JJ, de la Rubia J, Herrero C, Liu X, Van de Velde H, San Miguel J, Bladé J (2007) Phase II PETHEMA trial of alternating bortezomib and dexamethasone as induction regimen before autologous stem-cell transplantation in younger patients with multiple myeloma: efficacy and clinical implications of tumor response kinetics. J Clin Oncol 25:4452–4458
Oakervee H, Popat R, Cavenagh JD (2007) Use of bortezomib as induction therapy prior to stem cell transplantation in frontline treatment of multiple myeloma: impact on stem cell harvesting and engraftment. Leuk Lymphoma 48:1910–1921
Acknowledgement
The authors thank Pia Sondergeld for editorial assistance in the development of the manuscript.
Open Access
This article is distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution Noncommercial License which permits any noncommercial use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author(s) and source are credited.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Consortia
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
Open Access This is an open access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution Noncommercial License (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/2.0), which permits any noncommercial use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author(s) and source are credited.
About this article
Cite this article
Kropff, M., Liebisch, P., Knop, S. et al. DSMM XI study: dose definition for intravenous cyclophosphamide in combination with bortezomib/dexamethasone for remission induction in patients with newly diagnosed myeloma. Ann Hematol 88, 1125–1130 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00277-009-0726-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00277-009-0726-6