Abstract
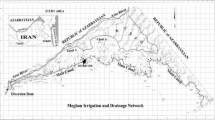
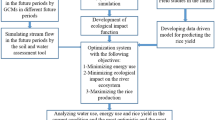
The present study proposes and evaluates an integrated optimization framework for agricultural planning in which an environmental flow model, drought analysis, cropping pattern model, and deficit irrigation functions are linked. Fuzzy physical habitat simulation was used to assess the environmental flow regime. A regression model was applied to develop the deficit irrigation functions. Average river flow time series in three hydrological conditions (dry, normal, and wet) were obtained using drought analysis. The environmental flow model, cropping pattern model, deficit irrigation functions, and river flow time series were then used in the structure of the optimization model. The goal of the optimization model is to provide an agricultural plan, including optimal cropping patterns and irrigation supply that minimizes ecological impacts on the river ecosystem. A genetic algorithm was used in the optimization process. Based on case study results, the proposed model is able to minimize ecological impacts on the river ecosystem in all hydrological conditions and propose an optimal plan for cropping patterns and irrigation supply. The difference between average revenue in the optimal plan and current conditions in all simulated hydrological conditions is less than 10%, which means the optimization system provides a sustainable plan for agricultural and environmental management.














Similar content being viewed by others
Availability of data and materials
Some or all data and materials that support the findings of this study are available from the corresponding author upon reasonable request. However, some parts are not free of charge.
References
Afshar A, Marino MA (1989) Optimization models for wastewater reuse in irrigation. J Irrig Drain Eng ASCE 115:185–202
Afshar A, Massoumi F, Afshar A, Mariño MA (2015) State of the art review of ant colony optimization applications in water resource management. Water Resour Manage 29(11):3891–3904
Akbari H, Rakhshandehroo G, Sharifloo AH, Ostadzadeh E (2015) Drought analysis based on standardized precipitation index (SPI) and streamflow drought index (SDI) in Chenar Rahdar river basin, Southern Iran. EWRI Watershed Management Symposium, ASCE Headquarters, Reston, VA, USA.
Amir I, Fisher FM (1999) Analyzing agricultural demand for water with an optimizing model. Agric Syst 61(1):45–56
Arthington AH, Bunn SE, Poff NL, Naiman RJ (2006) The challenge of providing environmental flow rules to sustain river ecosystems. Ecol Appl 16(4):1311–1318
Birhanu K, Alamirew T, Dinka MO, Ayalew S, Aklog D (2014) Optimizing reservoir operation policy using chance constraint nonlinear programming for Koga irrigation Dam Ethiopia. Water Resour Manage 28(14):4957–4970
Boman R, Warren J (2014) Understanding Cotton Irrigation Requirements in Oklahoma, Oklahoma Cooperative Extension Service, Fact Sheet PSS-2406.
Cervantes-Godoy D, Dewbre J (2010) Economic importance of agriculture for poverty reduction. OECD Food, Agriculture and Fisheries Papers, No. 23, OECD Publishing, Paris, https://doi.org/10.1787/5kmmv9s20944-en.
Dokeroglu T, Sevinc E, Kucukyilmaz T, Cosar A (2019) A survey on new generation metaheuristic algorithms. Comput Ind Eng 137:106040
Ehteram M, Karami H, Mousavi SF, Farzin S, Kisi O (2017) Optimization of energy management and conversion in the multi-reservoir systems based on evolutionary algorithms. J Clean Prod 168:1132–1142
Ehteram M, Karami H, Mousavi SF, Farzin S, Celeste AB, Shafie AE (2018) Reservoir operation by a new evolutionary algorithm: Kidney algorithm. Water Resour Manage 32(14):4681–4706
Garg K, Dadhich SM (2014) Integrated non-linear model for optimal cropping pattern and irrigation scheduling under deficit irrigation. Agric Water Manag 140:1–13
Ghahraman B, Sepaskhah AR (2004) Linear and non-linear optimization models for allocation of a limited water supply. J Irrig Drain Eng ASCE 53(1):39–54
Gorantiwar SD, Smout IK (2003) Allocation of scarce water resources using deficit irrigation in rotational systems. J Irrig Drain Eng ASCE 129(3):155–163
Haghnegahdar A, Razavi S (2017) Insights into sensitivity analysis of Earth and environmental systems models: on the impact of parameter perturbation scale. Environ Model Softw 95:115–131
Han Y, Huang YF, Wang GQ, Maqsood I (2011) A multi-objective linear programming model with interval parameters for water resources allocation in Dalian city. Water Resour Manage 25(2):449–463
Jahandideh-Tehrani M, Bozorg-Haddad O, Loáiciga HA (2021) A review of applications of animal-inspired evolutionary algorithms in reservoir operation modelling. Water Environ J 35(2):628–646
Jorde K, Schneider M, Zöllner F (2020) Invited lecture: Analysis of instream habitat quality–Preference functions and fuzzy models. In: Wang ZY, Hu S-X (eds) Stochastic Hydraulics 2000. CRC Press, pp 671–680
Karami H, Ehteram M, Mousavi SF, Farzin S, Kisi O, El-Shafie A (2019) Optimization of energy management and conversion in the water systems based on evolutionary algorithms. Neural Comput Appl 31(10):5951–5964
Kipkorir EC, Sahli A, Raes D (2002) MIOS: a decision tool for determination of optimal irrigated cropping pattern of a multicrop system under water scarcity constraints. Irrig Drain 51(1):155–166
Kuo M-H, Vom-Baur E, Struhl K, Allis CD (2000) Gcn4 activator targets Gcn5 histone acetyltransferase to specific promoters independently of transcription. Mol Cell 6(6):1309–1320
Li QS, Willardson LS, Deng W, LiLiu XJCJ (2005) Crop water deficit estimation and irrigation scheduling in western Jilin province North East China. Agric Water Manag 71(1):47–60
Mainuddin M, Das-Gupta A, Raj-Onta P (1997) Optimal crop planning model an existing groundwater irrigation project in Thailand. Agric Water Manag 33(1):43–62
Mayya SG, Prasad R (1989) System analysis of tank irrigation: I. Crop staggering. J Irrig Drain Eng ASCE 115:384–405
Memon SA, Sheikh IA, Talpur MA, Mangrio MA (2021) Impact of deficit irrigation strategies on winter wheat in semi-arid climate of sindh. Agric Water Manag 243:106389
Mirjalili S (2019) Genetic algorithm. In Evolutionary Algorithms and Neural Networks (pp. 43–55). Springer, Cham.
Nestler JM, Milhous RT, Layzer JB (2018) Instream habitat modeling techniques. In Gore, J.a. (Ed.), Alternatives in Regulated River Management (p. 295–314). CRC Press.
Noack M, Schneider M, Wieprecht S (2013) The Habitat modelling system CASiMiR: a multivariate fuzzy-approach and its applications. In: Maddock I, Harby A, Kemp P, Wood P (eds) Ecohydraulics: An Integrated Approach. John Wiley and Sons, pp 75–91
Oliveira IDC, Silva DDD, Guedes HA, Dergam JA, Ribeiro CBDM (2016) One-and two-dimensional ecohydraulic modeling of Formoso River (MG). Engenharia Agrícola 36:1050–1062
Onta PR, Loof R, Banskota M (1995) Performance based irrigation planning underwater shortage. Irrig Drain Syst 9:143–162
Paudyal GN, Gupta AD (1990) Irrigation planning by multilevel optimization. J Irrig Drain Eng ASCE 116:273–291
Postel SL (1998) Water for food production: will there be enough in 2025? Bioscience 48(8):629–637
Railsback SF (2016) Why it is time to put PHABSIM out to pasture. Fisheries 41(12):720–725
Rani D, Mourato S, Moreira M (2020) A generalized dynamic programming modelling approach for integrated reservoir operation. Water Resour Manage 34:1335–1351
Sedighkia M, Abdoli A (2021) Efficiency of coupled invasive weed optimization-adaptive neuro fuzzy inference system method to assess physical habitats in streams. SN Appl Sci 3(2):1–13
Sedighkia M, Ayyoubzadeh SA, Hajiesmaeli M (2017) Modification of Tennant and wetted perimeter methods in Simindasht basin Tehran Province. Civil Eng Infrastruct J 50(2):221–231
Sedighkia M, Abdoli A, Datta B (2021) Optimizing monthly ecological flow regime by a coupled fuzzy physical habitat simulation–genetic algorithm method. Environ Syst Decision 41:425–436
Sheikholeslami R, Yassin F, Lindenschmidt KE, Razavi S (2017) Improved understanding of river ice processes using global sensitivity analysis approaches. J Hydrol Eng 22(11):04017048
Shyam R, Chauhan HS, Sharma JS (1994) Optimal operation scheduling model for a canal system. Agric Water Manag 26:213–225
Singh DK, Jaiswal CS, Reddy KS, Singh RM, Bhandarkar DM (2001) Optimal cropping pattern in a canal command area. Agric Water Manag 50(1):1–8
Stajkowski S, Kumar D, Samui P, Bonakdari H, Gharabaghi B (2020) Genetic-algorithm-optimized sequential model for water temperature prediction. Sustainability 12(13):5374
Tharme RE (2003) A global perspective on environmental flow assessment: emerging trends in the development and application of environmental flow methodologies for rivers. River Res Appl 19(5–6):397–441
Wang Y, Zhang Y, Zhang R, Li J, Zhang M, Zhou S, Wang Z (2018) Reduced irrigation increases the water use efficiency and productivity of winter wheat-summer maize rotation on the North China Plain. Sci Total Environ 618:112–120
Yaseen ZM, Allawi MF, Karami H, Ehteram M, Farzin S, Ahmed AN, Koting SB, Mohd NS, Jaafar WZB, Afan HA, El-Shafie A (2019) A hybrid bat–swarm algorithm for optimizing dam and reservoir operation. Neural Comput Appl 31(12):8807–8821
Yawson DO, Adu MO, Armah FA, Chiroro C (2014) Virtual water and phosphorus gains through rice imports to Ghana: implications for food security policy. Int J Agric Resour Gov Ecol 10(4):374–393
Yu Y, Wang P, Wang C, Wang X (2018) Optimal reservoir operation using multi-objective evolutionary algorithms for potential estuarine eutrophication control. J Environ Manage 223:758–770
Funding
Not applicable.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
Not applicable.
Ethical approval
Not applicable.
Consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent to publish
Not applicable.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Sedighkia, M., Fathi, Z., Razavi, S. et al. Optimal agricultural plan for minimizing ecological impacts on river ecosystems. Irrig Sci 41, 93–106 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00271-022-00834-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00271-022-00834-7