Abstract
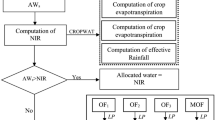
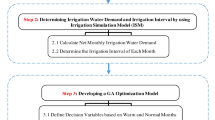
Attaining sustainable agriculture requires water consumption management. A water allocation optimization model was developed for the Moghan irrigation network (northwest of Iran) based on the AquaCrop plug-in model. The genetic algorithm was applied to optimize water allocation for five main crops, including wheat, first-cultivation maize, second-cultivation maize, soybeans, and alfalfa. The heuristic economic utility (EU) function was used as the objective function to optimize water allocation. In this function, drained water salinity was applied as a penalty factor to the total benefit, and soil salinity deterioration due to irrigation was also considered as a factor in each crop’s benefit. The results showed that the optimal allocated water depth was 17% less than the normal water consumption. Moreover, the application of soil water salinity coefficients did not affect the ratio of EU to EB (economic benefits) for wheat and alfalfa. However, first-cultivation maize, second-cultivation maize, and soybeans cultivation led to a reduction in EU within the study area. A combination of the crops cultivation led to a change in river water quality and an 8.2% reduction in the ratio of EU to EB function.






Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
The data that support this study will be shared upon reasonable request to the corresponding author.
References
Adabi, V., Azizian, A., Ramezani Etedali, H., Kaviani, A., & Ababaei, B. (2020). Local sensitivity analysis of AquaCrop model for wheat and maize in qazvin plain and Moghan Pars-Abad in Iran. Iran J Irrig Drain, 6(13), 1565–1579.
Alizade Govarchin, G. Y., Baykara, M., & Unal, A. (2017). Analysis of decadal land cover changes and salinization in Urmia Lake Basin using remote sensing techniques. Nat Hazards Earth Syst Discuss. https://doi.org/10.5194/nhess-2017-212
Allen, R. G., Pereira, L. S., Raes, D., & Smith, M. (1998). Crop evapotranspiration: guidelines for computing crop water requirements FAO Irrigation and drainage paper (pp. 1–300). Rome: FAO.
Bastiaanssen, W. G., Allen, R. G., Droogers, P., D’Urso, G., & Steduto, P. (2007). Twenty five years modeling irrigated and drained soils: State of the art. Agricult Water Manag, 92(3), 111–125. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.agwat.2007.05.013
Chu, L., & Grafton, R. Q. (2020). Water pricing and the value-add of irrigation water in Vietnam: Insights from a crop choice model fitted to a national household survey. Agricult Water Manag, 228, 105881. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.agwat.2019.105881
Connor, J. D., Schwabe, K., King, D., & Knapp, K. (2012). Irrigated agriculture and climate change: the influence of water supply variability and salinity on adaptation. Ecological Economics, 77, 149–157. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecolecon.2012.02.021
Cortignani, R., & Severini, S. (2009). Modeling farmlevel adoption deficit irrigation using positive mathematical programming. Agricult Water Manag, 96(12), 1785–1791.
Doorenbos, J., & Kassam, A. H. (1979). Yieid response to water. FAO irrigation and drainage paper 33. Rome: FAO.
Douaik, A., Van Meirvenne, M., & Toth, T. (2006). Temporal stability of spatial patterns of soil salinity determined from laboratory and field electrolytic conductivity. Arid Land Research and Management, 20(1), 1–13. https://doi.org/10.1080/15324980500369392
García-Vilaa, M., & Fereres, E. (2012). Combining the simulation crop model AquaCrop with an economic model for the optimization of irrigation management at farm level. Euro J Agron, 36(1), 21–31. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eja.2011.08.003
Goldberg, D. E. (1989). Genetic algorithms in search, optimization, and machine learning. Addison-Wesley-Longman, Publishing Co Inc.
Guo, D., Olesen, J. E., Manevski, K., & Ma, X. (2021). Optimizing irrigation schedule in a large agricultural region under different hydrologic scenarios. Agricult Water Manag, 245, 106575. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.agwat.2020.106575
Hanks, R. J., Dudley, L. M., Cartee, R. L., Mace, W. R., Pomela, E., Kidman, R. L., & McCurdy, G. D. (1990). Use of saline waste water from electrical power plants for irrigation. 1989 report. Part 1. Utah Agricultural Experiment Station, 133.
Huang, Q., Rozelle, S., Howitt, R., Wang, J., & Huang, J. (2010). Irrigation water demand and implications for water pricing policy in rural China. Environ Develop Econ, 15(3), 293–319. https://doi.org/10.1017/S1355770X10000070
Izadfard, A., Sarmadian, F., Jahansooz, M. R., & Asadi Oskouei, E. (2021). Optimum cropping pattern based on irrigation water productivity using AquaCrop simulation model. J Agricult Sci Technol, 23(5), 1163–1178.
Jahin, H. S., Abuzaid, A. S., & Abdellatif, A. D. (2020). Using multivariate analysis to develop irrigation water quality index for surface water in Kafr El Sheikh Governorate Egypt. Environ Technol Innovat, 17, 100532. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eti.2019.100532
Kanooni, A. (2013). Development of an Integrated Optimal Water Allocation and Distribution Model at Different Levels of Irrigation Networks. Ph.D. thesisin. Tehran: Tarbiat Modares University, Department of water structures engineering, (In Persian) pp. 177.
Kanooni, A., & Monem, M. J. (2014). Integrated stepwise approach for optimal water allocation in irrigation canal. Irrigation and Drainage, 63, 12–21. https://doi.org/10.1002/ird.1798
Kheir, A. M., Alkharabsheh, H. M., Seleiman, M. F., Al-Saif, A. M., Ammar, K. A., Attia, A., Zoghdan, M. G., Shabana, M. M. A., Aboelsoud, H., & Schillaci, C. (2021). Calibration and validation of AQUACROP and APSIM models to optimize wheat yield and water saving in arid regions. Land, 10(12), 1375. https://doi.org/10.3390/land10121375
Kumar, V., & Yadav, S. M. (2019). Optimization of cropping patterns using elitist-Jaya and elitist- TLBO algorithms. Water Resour Manag, 33(5), 1817–1833. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11269-019-02204-z
Li, J., Jiao, X., Jiang, H., Song, J., & Chen, L. (2020). Optimization of irrigation scheduling for maize in an arid oasis based on simulation–optimization model. Agronomy, 10(7), 935. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy10070935
Li, J., Song, J., Li, M., Shang, S., Mao, X., Yang, J., & Adeloye, A. J. (2018). Optimization of irrigation scheduling for spring wheat based on simulation-optimization model under uncertainty. Agricult Water Manag, 208, 245–260. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.agwat.2018.06.029
Linker, R., Ioslovich, I., Sylaios, G., Plauborg, F., & Battilani, A. (2016). Optimal model-based deficit irrigation scheduling using AquaCrop: a simulation study with cotton, potato and tomato. Agricult Water Manag, 163, 236–243. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.agwat.2015.09.011
Liu, B., Wang, S., Kong, X., Liu, X., & Sun, H. (2019). Modeling and assessing feasibility of long-term brackish water irrigation in vertically homogeneous and heterogeneous cultivated lowland in the North China Plain. Agricult Water Manag, 211, 98–110.
Martinez-Romero, A., Lopez-Urrea, R., Montoya, F., Pardo, J. J., & Dominguez, A. (2021). Optimization of irrigation scheduling for barley crop, combining AquaCrop and MOPECO models to simulate various water-deficit regimes. Agricult Water Manag, 258, 107219. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.agwat.2021.107219
Mathur, Y. P., Sharma, G., & Pawde, A. W. (2009). Optimal operation scheduling of irrigation canals using genetic algorithm. Int J Recent Trends Eng, 1(6), 11–15.
McBride, G. B. (2002). Calculating stream reaeration coefficients from oxygen profiles. Journal of Environmental Engineering, 128(4), 384–386. https://doi.org/10.1061/(ASCE)0733-9372(2002)128:4(384)
Minhas, P. S., & Gupta, R. K. (1993). Conjunctive use of saline and non-saline waters. I. Response of wheat to initial salinity profiles and salinization patterns. Agricult Water Manag, 23, 125–137. https://doi.org/10.1016/0378-3774(93)90036-A
Mohammadi, M., Ghahraman, B., Davary, K., Ansari, H., Shahidi, A., & Bannayan, M. (2016). Nested validation of aquacrop model for simulation of winter wheat grain yield, soil moisture and salinity profiles under simultaneous salinity and water stress. Irrigation and Drainage, 65, 112–128.
Monem, M. J., & Namdariyan, R. (2005). Application of Simulated Annealing (SA) Techniques for Optimal Water Distribution in Irrigation Canals. Irrigation and Drainage, 54(4), 365–373. https://doi.org/10.1002/ird.199
Nemoto, Y., & Sasakuma, T. (2002). Differential stress responses of early salt stress responding genes in common wheat. Phytochemistry, 61(2), 129–133. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0031-9422(02)00228-5
Oad, R., Garcia, L., Kinzli, K. D., Patterson, D., & Shafike, N. (2009). Decision support systems for efficient irrigation in the Middle Rio Grande Valley. Journal of Irrigation and Drainage Engineering, 135(2), 177–185. https://doi.org/10.1061/(ASCE)0733-9437(2009)135:2(177)
Osroosh, Y., Peters, R. T., Campbell, C. S., & Zhang, Q. (2016). Comparison of irrigation automation algorithms for drip-irrigated apple trees. Comput Electron Agricult, 128, 87–99. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compag.2016.08.013
Pourgholam-Amiji, M., Liaghat, A., Ghameshlou, A. N., & Khoshravesh, M. (2021). The evaluation of DRAINMOD-S and AquaCrop models for simulating the salt concentration in soil profiles in areas with a saline and shallow water table. Journal of Hydrology, 598, 126259.
Quinn, N. W. (2011). Adaptive implementation of information technology for real-time, basin-scale salinity management in the San Joaquin Basin, USA and Hunter River Basin Australia. Agricult Water Manag, 98(6), 930–940. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.agwat.2010.11.013
Rabie, Z., Honar, T., & Bateni, M. (2015). Determination of optimal and water allocation under limited water resources using soil water balance in ordibehesht canal of doroodzan water district. Iran Agricult Res, 34(2), 21–28. https://doi.org/10.22099/IAR.2016.3454
Raes, D., Steduto, P., Hsiao, T. C., & Fereres, E. (2012). Reference Manual: AquaCrop (Version 4.0). FAO Land and Water Division, Rome. Italy (pp. 1–164). http://www.fao.org/nr/water/aquacrop.html. Accessed Nov 2013
Rath, A., Samantary, S., Biswal, S., & Swain, P. C. (2018). Application of genetic algorithm to derive an optimal cropping pattern, in part of Hirakud command. Progress in computing, analytics and networking: proceedings of ICCAN 2017 (pp. 711–721). Singapore: Springer Singapore.
Sandhu, R., & Irmak, S. (2019). Performance of AquaCrop model in simulating maize growth, yield, and evapotranspiration under rainfed, limited and full Irrigation. Agricult Water Manag, 223, 105687. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.agwat.2019.105687
Shen, H., Jiang, K., Sun, W., Xu, Y., & Ma, X. (2021). Irrigation decision method for winter wheat growth period in a supplementary irrigation area based on a support vector machine algorithm. Comput Electron Agricult, 182, 106032. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compag.2021.106032
Somlyody, L., Henze, M., Koncsos, L., Rauch, W., Reichert, P., Shanahan, P., & Vanrolleghem, P. (1998). River water quality modeling: III. Future of the atr. Water Science and Technology, 38(11), 253–260. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0273-1223(98)00662-3
Steduto, P., Hsiao, T. C., Fereres, E., & Raes, D. (2012). Crop yield response to water. FAO Irrigation and drainage paper 66. Rome: United Nations FAO.
Vaughan, L. V., MacAdam, J. W., Smith, S. E., & Dudley, L. M. (2002). Root growth and yield of differing alfalfa rooting populations under increasing salinity and zero leaching. Crop Science, 42(6), 2064–2071.
Villacampa, Y., Navarro-González, F. J., Compañ-Rosique, P., & Satorre-Cuerda, R. (2019). A guided genetic algorithm for diagonalization of symmetric and Hermitian matrices. Applied Soft Computing, 75, 180–189. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.asoc.2018.11.004
Wabela, K., Hammani, A., Abdelilah, T., Tekleab, S., & El-Ayachi, M. (2022). Optimization of irrigation scheduling for improved irrigation water management in Bilate watershed, Rift valley Ethiopia. Water, 14(23), 3960. https://doi.org/10.3390/w14233960
Wang, H. R., Dong, Y. Y., Wang, Y., & Liu, Q. (2008). Water right institution and strategies of the Yellow River valley. Water Resour Manag, 22, 1499–1519. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11269-008-9239-7
Wang, Y., Zhang, H., He, Z., Li, F., Wang, Z., Zhou, C., Han, Y., & Lei, L. (2022). Effects of regulated deficit irrigation on yield and quality of isatis indigotica in a cold and arid environment. Water, 14(11), 1798. https://doi.org/10.3390/w14111798
Wilcox, L. V. (1955). Classification and use of irrigation waters (No. 969). US Departement of Agriculture, Washington D. C. USA.
Wilkinson, R. E. (2000). Plant-Environment Interactions; Marcel dekker: New York, NY, USA, ISBN 0824703774.
Yao, W., Ma, X., & Chen, Y. (2019). Optimization of canal water in an irrigation network based on a genetic algorithm: A case study of the north china plain canal system. Irrigation and Drainage, 68(4), 629–636. https://doi.org/10.1002/ird.2345
Zhai, Y., Huang, M., Zhu, C., Xu, H., & Zhang, Z. (2022). Evaluation and application of the AquaCrop model in simulating soil salinity and winter wheat yield under saline water irrigation. Agronomy, 12(10), 2313. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy12102313
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Kahkhamoghaddam, P., Ziaei, A.N., Davary, K. et al. Optimal land allocation and irrigation scheduling to maximize the economic utility. Int. J. Plant Prod. (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s42106-024-00283-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s42106-024-00283-6