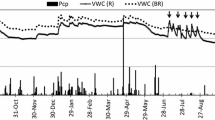
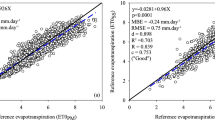
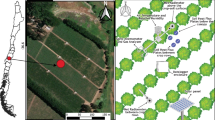
Abstract
In this paper, based on the analysis of a long-term energy balance monitoring programme, a Bowen ratio-based method (BR) was proposed to resolve the lack of closure of the eddy covariance technique to obtain reliable sensible (H) and latent heat fluxes (λE). Evapotranspiration (ET) values determined from the BR method (ETc,corr) were compared with the upscaled transpiration data determined by the sap flow heat pulse (HP) technique, evidencing the degree of correspondence between instantaneous transpirational flux at tree level and the micrometeorological measurement of ET at orchard level. Using the BR-corrected λE fluxes, a crop ET model implementing the Penman–Monteith approach, where the canopy surface resistance was determined from standard microclimatic variables, was applied to determine the crop coefficient values. The performance of the model was evaluated by comparing it with the sap flow HP data. The results of the comparison were satisfactory, and therefore, the proposed methodology may be considered valid for characterizing the ET process for orange orchards grown in a Mediterranean climate. By contrast to reports in the FAO 56 paper, the crop growth coefficient of the orange orchard being studied was not constant throughout the growing season.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Allen RG, Pereira LS, Raes D, Smith M (1998) Crop evapotranspiration, guidelines for computing crop water requirements. Paper No. 56, Rome
Arya SP (1988) Introduction to micrometeorology. Academic Press, London
Aubinet M, Grelle A, Ibrom A, Rannik U, Moncrieff J, Foken T, Kowalski AS, Martin PH, Berbigier P, Bernhofer C, Clement R, Elbers J, Granier A, Grunwald T, Morgenstern K, Pilegaard K, Rebmann C, Snijders W, Valentini R, Vesala T (2000) Estimates of the annual net carbon and water exchange of European forests: the EUROFLUX methodology. Adv Ecol Res 30:114–175
Ayars JE, Johnson RS, Phene CJ et al (2003) Water use by drip-irrigated late-season peaches. Irrig Sci 22:94
Azevedo PV, Silva BB, da Silva VPR (2003) Water requirements of irrigated mango orchards in northeast Brazil. Agric Water Manage 58:241–254
Baldocchi DD (2003) Assessing ecosystem carbon balance: problems and prospects of the Eddy covariance technique. Glob Change Biol 9:479–492
Barr AG, King KM, Gillespie TJ, denHartog G, Neumann HH (1994) A comparison of Bowen ratio and eddy correlation sensible and latent heat flux measurements above deciduous forest. Bound Layer Meteorol 71:21–41
Bethenod O, Katerji N, Goujet R, Bertolini JM, Rana G (2000) Determination and validation of corn crop transpiration by sap flow measurement under field conditions. Theor Appl Climatol 67:153–160
Blanken PD, Black TA, Yang PC, Newmann HH, Nesic Z, Staebler R, denHartog G, Novak MD, Lee X (1997) Energy balance and canopy conductance of a boreal aspen forest: partitioning overstory and understory components. J Geophys Res 102(D24):28915–28928
Brutsaert W (1988) Evaporation into the atmosphere. D Reidel Publishing Company, Dordrecht
Burman RD, Wright JL, Nixon PR, Hill RW (1980) Irrigation management-water requirements and water balance. In: Irrigation, challenges of the 80’s. Proceedings of the second national irrigation symposium, American Society of Agricultural Engineers, St. Joseph, MI, pp 141–153
Campbell GS, Norman JM (1998) An introduction to environmental biophysics, 2nd edn. Springer, New York
Castellví F, Consoli S, Papa R (2012) Sensible heat flux estimates using two different methods based on Surface renewal analysis. A study case over an orange orchard in Sicily. Agric For Meteorol 152:58–64
Cohen Y (1991) Determination of orchard water requirement by a combined trunk sap flow and meteorological approach. Irrig Sci 12(2):93–98
Cohen M, Girona J, Valancogne C, Ameglio T, Cruizat P, Archer P (1993) Water consumption and optimisation of the irrigation in orchards. Acta Hort 335:34–357
Consoli S, O’Connell N, Snyder R (2006) Estimation of evapotranspiration of different-sized navel-orange tree orchards using energy balance. J Irrig Drain Eng 132(1):2–8
de Teixeira AHC, Bastiaanssen WGM, Moura MSB, Soares JM, Ahmad MD, Bos MG (2008) Energy and water balance measurements for water productivity analysis in irrigated mango trees, Northeast Brazil. Agric For Meteorol 148:1524–1537
Doorenbos J, Pruitt WO (1975) Guidelines for predicting crop water requirements. Irrigation and Drainage Paper no. 24, FAO-ONU, Rome, Italy
Doorenbos J, Pruitt WO (1977) Guidelines for predicting crop water requirements, FAO-ONU, Rome. Irrigation and Drainage Paper no. 24 (rev.)
El Maayar M, Chen JM, Price DT (2008) On the use of field measurements of energy fluxes to evaluate land surface models. Ecol Model 214:293–304
Finnigan JJ (2004) A revaluation of long-term flux measurement techniques. Part II: coordinate systems. Bound Layer Meteorol 113:1–41
Foken T (2008) Micrometeorology. Springer, New York
Green SR, Clothier B (1988) Water use of kiwifruit vines and apple trees by the heat-pulse technique. J Exp Bot 39:115–123
Green SR, McNaughton KG, Clothier BE (1989) Observations of night-time water use in kiwifruit vines and apple trees. Agric For Meteorol 48:251–261
Green S, Clothier B, Jardine B (2003) Theory and practical application of heat pulse to measure sap flow. Agron J 95:1371–1379
Guo JX, Bian LG, Dai YJ (2009) Multiple time scale evaluation of the energy balance during the maize growing season, and a new reason of energy imbalance. Sci China Ser D Earth Sci 52:108–117
Hamdy A (1999) water resources in the Mediterranean region: from ideas to action. In: Background documentation for thematic session. Consultation of experts from MENA region on: World Water Vision-Water for Food and Rural Development. CIHEAM-IAMB, Valenzano, 27–29 May 1999, pp 1–23
Han H, Felker P (1997) Field validation of water-use efficiency of the CAM plant Opuntia ellisiana in south Texas. J Arid Environ 36:133–148
Heilman JL, McInnes KJ, Gesch RW, Lacano RJ, Savage MJ (1996) Effects of trellising on the energy balance of a vineyard. Agric For Meteorol 81:79–93
Jara J, Stockle CO, Kjelgaard J (1998) Measurement of evapotranspiration and its components in a corn (Zea Mays L) field. Agric For Meteorol 92:131–145
Jensen ME (1968) Water consumption by agricultural plants. In: Kozlowski TT (ed) Water deficits and plant growth, vol II. Academic Press, Inc., New York, pp 1–22
Ju W, Chen JM, Black TA, Barr AG, Liu J, Chen B (2006) Modelling multi-year coupled carbon and water fluxes in a boreal aspen forest. Agric For Meteorol 140:136–151
Katerji N, Perrier A (1983) Modélisation de l’évapotranspiration réelle ETR d’une parcelle de luzerne: rŏle d’un coefficient cultural. Agronomie 3(6):513–521
Katul G, Hsieh C-I, Bowling D, Clark K, Shurpali N, Turnipseed A, Albertson J, Tu K, Hollinger D, Evans B, Offerle B, Anderson D, Ellsworth D, Vogel C, Oren R (1999) Spatial variability of turbulent fluxes in the roughness sublayer of an even-aged pine forest. Bound Layer Meteorol 93:1–28
Kucharik C, Barford C, El Maayar M, Wofsy SC, Monson RK, Baldocchi DD (2006) Evaluation of a dynamic global vegetation model (DGVM) at the forest stand-level: vegetation structure, phenology, and seasonal and inter-annual CO2 and H2O vapor exchange at three AmeriFlux study sites. Ecol Model 196:1–31
Kustas WP, Prueger JR, Humes KS, Starks PJ (1999) Estimation of surface heat fluxes at field scale using surface layer versus mixed layer atmospheric variables with radiometric temperature observations. J Appl Meteorol 38:224–238
Liu H, Randerson JT, Lindfors J, Massman W, Foken T (2006) Consequences of incomplete surface energy balance closure for CO2 fluxes from open-path CO2/H2O infrared gas analyzers. Bound Layer Meteorol 120:65–85
Mahrt L (1998) Flux sampling errors for aircraft and towers. J Atmos Ocean Technol 15:416–429
Mauder M, Foken T (2004) Documentation and instruction manual of the eddy covariance software package TK2. Universität Bayreuth, Abt.Mikrometeorologie, Arbeitsergebnisse 26-44. http://www.geo.unibayreuth.de/mikrometeorologie/ARBERG
Mauder M, Foken T, Clement R, Elbers JAEW, Grünwald T, Heusinkveld B, Kolle O (2007) Quality control of CarboEurope flux data—part 2: inter-comparison of eddy-covariance software. Biogeosciences 5:4067–4099
Monteith JL (1965) Evaporation and environment. In: Fogg GE (ed) The state and movement of water in living organism. Proceedings of the XIX symposium on society for experimental biology. Academic Press, New York, pp 205–234
Moreno F, Ferna′ndez JE, Clothier BE, Green SR (1996) Transpiration and root water uptake by olive trees. Plant Soil 184:85–96
Moreshet S, Cohen Y, Fuchs M (1983) Response of mature "Shamouti" orange trees to irrigation of different soil volumes at similar levels of available water. Irr Sci 3:223–236
Moriana A, Villalobos FJ, Fereres E (2002) Stomatal and photosynthetic responses of olive (Olea europaea L.) leaves to water deficits. Plant Cell Environ 25(3):395–405
Motisi A, Consoli S, Rossi F, Minacapilli M, Cammalleri C, Papa R, Rallo G, D’urso G (2012) Eddy covariance and sap flow measurement of energy and mass exchange of woody crops in a Mediterranean environment. In: 8th international workshop on sap flow. Volterra (Italy), May 8–12
Oncley SP, Foken T, Vogt R et al (2007) The energy balance experiment EBEX-2000. Part I: overview and energy balance. Bound Layer Meteorol 123:1–28
Orgaz F, Testi L, Villalobos FJ, Fereres E (2006) Water requirements of olive orchards. II. Determination of crop coefficients for irrigation scheduling. Irrig Sci 24(2):77–84
Paco TA, Ferreira MI, Conceicao N (2006) Peach orchard evapotranspiration in a sandy soil: comparison between eddy covariance measurements and estimates by the FAO 56 approach. Agric Water Manag 85(3):305–313
Rana G, Katerji N, de Lorenzi F (2005) Measurements and modelling of evapotranspiration of irrigated citrus orchard under Mediterranean conditions. Agric For Meteorol 128:199–209
Sammis TW, Mexal JG, Miller D (2004) Evapotranspiration of flood-irrigated pecans. Agric Water Manage 69:179–190
Smith DM, Allen SJ (1996) Measurement of sap flow in plant stems. J Exp Bot 47:1833–1844
Snyder RL, O’Connell NV (2007) Crop coefficients for microsprinkler-irrigated, clean-cultivated, mature citrus in an arid climate. J Irrig Drain Eng 133(1):43–52
Stanghellini C, Bosma AH, Gabriels PCJ, Werkoven C (1990) The water consumption of agricultural crops: how crop coefficient are affected by crop geometry and microclimate. Acta Hortic 278:509–516
Swanson RH, Whitfield DWA (1981) A numerical analysis of heat-pulse velocity theory and practice. J Exp Bot 32:221–239
Tarantino E, Onofrii M (1991) Determinazione dei coefficienti colturali mediante lisimetri. Bonifica 7:119–136 (in Italian)
Testi L, Villalobos FJ, Orgaz F (2004) Evapotranspiration of a young irrigated olive orchard in southern Spain. Agric For Meteorol 121:1–18
Testi L, Orgaz F, Villalobos FJ (2006) Variations in bulk canopy conductance of an irrigated olive (Olea europaea L.) orchard. Environ Exp Bot 55:15–28
Trambouze W, Bertuzzi P, Voltz M (1998) Comparison of methods for estimating actual evapotranspiration in a row cropped vineyard. Agric For Meteorol 91:193–208
Twine TE, Kustas WP, Norman JM et al (2000) Correcting eddy-covariance flux underestimates over a grass land. Agric For Meteorol 103:279–300
Villalobos FJ, Orgaz F, Testi L, Fereres E (2000) Measurement and modeling of evapotranspiration of olive (Olea europea L.) orchards. Agric For Meteorol 13:155–163
Villalobos FJ, Testi L, Moreno-Perez MF (2009) Evaporation and canopy conductance of citrus orchards. Agric Water Manag 96:565–573
Williams DG, Cable W, Hultine K, Yepez EA, Er-Raki S, Hoedjes JCB, Boulet G, de Bruin HAR, Chehbouni A, Timouk F (2003) Suivi de la repartition de l’evapotranspiration dans une oliveraie (Olea europaea L.) a l’aide des techniques de l’eddy covariance, des flux de seve et des isotopes stables. Vemes Journees de l’Ecologie Fonctionnelle, 12 au 14 Mars 2003 a Nancy
Wilson K, Goldstein A, Falge E et al (2002) Energy balance closure at fluxnet sites. Agric For Meteorol 113:223–243
Wright JL (1982) New evapotranspiration crop coefficients. J Irrig Drain Div ASCE 108:57–74
Wullschleger SD, Wilson KB, Hanson PJ (2000) Environmental control of whole-plant transpiration, canopy conductance and estimates of the decoupling coefficient for large red maple trees. Agric For Meteorol 104:157–168
Zhang H, Simmonds LP, Morison JIL, Payne D (1997) Estimation of transpiration by single trees: comparison of sap flow with combination equation. Agric For Meteorol 87:155–169
Zhang Y, Grant RF, Flanagan LB, Wang S, Verseghy DL (2005) Modelling CO2 and energy exchanges in a northern semiarid grassland using the carbon- and nitrogen-coupled Canadian Land Surface Scheme (C-CLASS). Ecol Model 181:591–614
Acknowledgments
This work was carried out under the auspices of the Project Innovazioni e strumenti per l’adattamento dell’agricoltura ai cambiamenti climatici (ISAACC) (Innovations and tools for adapting agriculture to climatic change) under grant no. 594/2011 of the Sicilian Region. The authors wish to thank Azienda Tribulato (Lentini, SR) for its hospitality. The authors are also grateful to the Agrometeorological Service (SIAS) of the Sicilian Region and to CSEI Catania for their cooperation and support.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Communicated by J. Li.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Consoli, S., Papa, R. Corrected surface energy balance to measure and model the evapotranspiration of irrigated orange orchards in semi-arid Mediterranean conditions. Irrig Sci 31, 1159–1171 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00271-012-0395-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00271-012-0395-4