Abstract
Purpose
This retrospective study evaluated the feasibility, efficacy, and safety of combining transcatheter arterial embolization (TAE) with radiofrequency thermal ablation (RFA) in a single session for the treatment of technically unresectable liver-only malignancies.
Methods
From May 2006 to January 2011, a total of 30 patients affected by liver metastases with single or multiple unresectable liver-only lesions underwent a combined treatment with TAE followed by RFA in the same session, for a total of 36 treated lesions. Patients were extrapolated from a cohort of patients discussed within the weekly institutional tumor board. TAE was performed by using 100 μm microspheres; RFA was performed immediately after TAE by positioning the electrode needle via ultrasound and/or computed tomographic guidance. Local tumor responses and procedure-related complications were evaluated.
Results
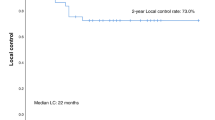
Completion of both procedures was obtained in all patients for all 36 lesions. Liver lesions had a maximum axial diameter ranging 16–59 mm. Postintervention unenhanced ablated areas ranged 28–104 mm in maximum axial diameter. Safety margins ranged 1–30.5 mm. Complete response, defined as complete devascularization at computed tomography, was obtained in all treated lesions for a maximum period of 12 months. Tumor relapse was observed in one patient at 12 months. Sixteen patients developed new liver lesions or progressive systemic disease during follow-up. Nine patients were still disease-free. Seven patients died as a result of systemic progressive disease. One major treatment-related complication was observed.
Conclusions
In patients with technically unresectable liver-only malignancies, single-session combined TAE-RFA is an effective and safe treatment.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Olnes MJ, Erlich R (2004) A review and update on cholangiocarcinoma. Oncology 66:167–179
Sasson AR, Sigurdson ER (2002) Surgical treatment of liver metastases. Semin Oncol 29:107–118
Biasco G, Derenzini E, Grazi G et al (2006) Treatment of hepatic metastases from colorectal cancer: many doubts, some certainties. Cancer Treat Rev 32:214–228
Meyerhardt JA, Mayer RY (2005) Systemic therapy for colorectal cancer. N Engl J Med 352:476–487
Goldberg SN, Gazelle GS (2001) Radiofrequency tissue ablation: physical principles and techniques for increasing coagulation necrosis. Hepatogastroenterology 48:359–367
Goldberg SN, Hahn PF, Tanabe KK et al (1998) Percutaneous radiofrequency tissue ablation: does perfusion-mediated tissue cooling limit coagulation necrosis? J Vasc Interv Radiol 9:101–111
Nakai M, Sato M, Sahara S et al (2007) Radiofrequency ablation in a porcine liver model: effects of transcatheter arterial embolization with iodized oil on ablation time, maximum output, and coagulation diameter as well as angiographic characteristics. World J Gastroenterol 13:2841–2845
Mostafa EM, Ganguli S, Faintuch S et al (2008) Optimal strategies for combining transcatheter arterial chemoembolization and radiofrequency ablation in rabbit VX2 hepatic tumors. J Vasc Interv Radiol 19:1740–1748
Cheng BQ, Jia CQ, Liu CT et al (2008) Chemoembolization combined with radiofrequency ablation for patients with hepatocellular carcinoma larger than 3 cm. JAMA 299:1669–1677
Takaki H, Yamakado K, Uraki J et al (2009) Radiofrequency ablation combined with chemoembolization for the treatment of hepatocellular carcinomas larger than 5 cm. J Vasc Interv Radiol 20:217–224
Liu CH, Arellano RS, Uppot RN et al (2010) Radiofrequency ablation of hepatic tumours: effect of post-ablation margin on local tumour progression. Eur Radiol 20:877–885
Brown DB, Cardella JF, Sacks D et al (2006) Quality improvement guidelines for transhepatic arterial chemoembolization, embolization and chemiotherapeutic infusion for hepatic malignancy. J Vasc Interv Radiol 17:225–232
Goldberg SN, Grassi CJ, Cardella JF et al (2009) Image-guided tumor ablation: standardization of terminology and reporting criteria. J Vasc Interv Radiol 20:s377–s390
Curley SA, Izzo F, Ellis LM et al (2000) Radiofrequency ablation of hepatocellular cancer in 110 patients with cirrhosis. Ann Surg 232:381–391
Solbiati L, Livraghi T, Goldberg SN et al (2001) Percutaneous radiofrequency ablation of hepatic metastases from colorectal cancer: long-term results in 111 patients. Radiology 221:159–166
Lin SM, Lin CJ, Lin CC et al (2005) Randomised controlled trial comparing percutaneous radiofrequency thermal ablation, percutaneous ethanol injection, and percutaneous acetic acid injection to treat hepatocellular carcinoma of 3 cm or less. Gut 54:1151–1156
Primrose JN (2002) Treatment of colorectal metastases: surgery, cryotherapy, or radiofrequency ablation. Gut 50:1–5
O’Rourke AP, Haemmerich D, Prakash P et al (2007) Current status of liver tumor ablation devices. Expert Rev Med Devices 4:523–537
Flanders VL, Gervais DA (2010) Ablation of liver metastases: current status. J Vasc Interv Radiol 21:S214–S222
Nesbitt C, Glendinning RJ, Byrne C et al (2007) Factors that influence treatment strategies in advanced colorectal cancer. Eur J Surg Oncol 33:s88–s94
Llovet JM, Bruix J (2008) Novel advancements in the management of hepatocellular carcinoma in 2008. J Hepatol 48:S20–S37
Livraghi T, Meloni F, Goldberg SN et al (2000) Hepatocellular carcinoma: radiofrequency ablation of medium and large lesions. Radiology 214:761–768
Liapi E, Geschwind JFH (2007) Transcatheter and ablative therapeutic approaches for solid malignancies. J Clin Oncol 25:978–986
Takaki H, Yamakado K, Uraki J et al (2009) Radiofrequency ablation combined with chemoembolization for the treatment of hepatocellular carcinoma larger than 5 cm. J Vasc Interv Radiol 20:217–224
Liao GS, Yu CY, Chan DC et al (2009) Radiofrequency ablation after transarterial embolization as therapy for patients with unresectable hepatocellular carcinoma. Eur J Surg Oncol 34:61–66
Veltri A, Moretto P, Doriguzzi A et al (2006) Radiofrequency thermal ablation (RFA) after transarterial chemoembolization (TACE) as a combined therapy for unresectable non-early hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC). Eur Radiol 16:661–669
Vogl TJ, Mack MG, Balzer JO et al (2003) Liver metastases: neoadjuvant downsizing with trans-arterial chemoembolization before laser-induced thermotherapy. Radiology 229:457–464
Nakai M, Sato M, Sahara S et al (2007) Radiofrequency ablation in a porcine liver model: effects on transcatheter arterial embolization with iodized oil on ablation time, maximum output, and coagulation diameter as well as angiographic characteristics. World J Gastreoenterol 13:2841–2845
Cady B, Jenkins R, Steele GD et al (1998) Surgical margin in hepatic resection for colorectal metastasis: a critical and improvable determinant outcome. Ann Surg 227:566–571
Poston GJ (2004) Surgical strategies for colorectal liver metastases. Surg Oncol 13:125–136
Ekberg H, Tranberg KG, Andersson R et al (1986) Determinants of survival in liver resection for colorectal secondaries. Br J Surg 73:727–731
Scheele J, Stang R, Altendorf-Hofmann A et al (1995) Resection of colorectal liver metastases. World J Surg 19:59–71
Kokudo N, Miki Y, Sugai S et al (2002) Genetic and histological assessment of surgical margins in resected liver metastases from colorectal carcinoma: minimum surgical margins for successful resection. Arch Surg 137:833–840
Cheng BQ, Jia CQ, Liu CT et al (2008) Chemoembolization combined with radiofrequency ablation for patients with hepatocellular carcinoma larger than 3 cm. A randomized controlled trial. JAMA 299:1669–1677
Kang SG, Yoon CJ, Jeong SH et al (2009) Single-session combined therapy with chemoembolization and radiofrequency ablation in hepatocellular carcinoma less than or equal to 5 cm: a preliminary study. J Vasc Interv Radiol 20:1570–1577
Simmonds PC, Primrose JN, Colquitt JL et al (2006) Surgical resection of hepatic metastases from colorectal cancer: systematic review of published studies. Br J Cancer 94:982–999
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bonomo, G., Della Vigna, P., Monfardini, L. et al. Combined Therapies for the Treatment of Technically Unresectable Liver Malignancies: Bland Embolization and Radiofrequency Thermal Ablation within the Same Session. Cardiovasc Intervent Radiol 35, 1372–1379 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00270-012-0341-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00270-012-0341-0