Abstract
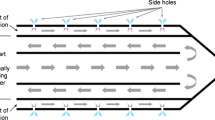
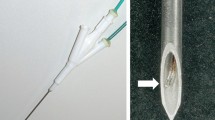
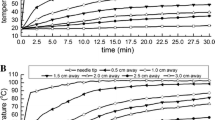
The purpose of this study was to assess the efficacy of a new perfused-cooled electrode that uses a single pump for creating a large ablation zone in explanted bovine liver. This was done by comparing with the radiofrequency (RF) ablation zones that were created with a monopolar cooled electrode to the RF ablation zones that were created by the new perfused-cooled electrode. We developed a new perfused-cooled electrode that uses a single pump by modifying a 17-gauge cooled electrode (Radionics) with a 2.5-cm outer metallic sheath (15-gauge) in order to allow use of the internal cooling water (5.85 % hypertonic saline) for the infused saline. Thirty ablation zones were created in explanted bovine livers (12-min ablation cycle; pulsed technique; 2000 mA, maximum) with three different regimens: group A, RF ablation with the 17-gauge cooled electrode; group B, RF ablation with the 15-gauge cooled electrode; group C, RF ablation with the perfused-cooled electrode. T2-weighted magnetic resonance (MR) imaging was obtained immediately after RF ablation for calculating volumes of the ablation zone. Following MR imaging, the ablation zones were excised and measured for transverse diameters and vertical diameters. The transverse diameter, vertical diameter, and the calculated volumes of the ablation zones on MR imaging were compared among the groups. Ablation zones created with the perfused-cooled electrode (group C) were significantly larger than those created with the 17-gauge cooled electrode (group A) and the 15-gauge cooled electrode (group B) according to the transverse diameter and vertical diameter on the gross specimens (p < 0.05): 3.6 ± 0.38 cm and 4.4 ± 0.20 cm in group A, 3.7 ± 0.08 cm and 4.6 ± 0.16 cm in group B, and 5.4 ± 0.65 cm and 6.0 ± 0.56 cm in group C, respectively. On the MR imaging, the calculated volumes of the ablation zones in group C were significantly larger than those in groups A and B (p < 0.05): 23.1 ± 8.7 cm3 in group A, 28.9 ± 5.7 cm3 in group B, and 80.0 ± 34 cm3 in group C, respectively. A new perfused-cooled electrode using a single pump could efficiently increase the size of the ablation zone in liver compared with a monopolar cooled electrode, and this was due to its simultaneous use of internal cooling and saline infusion.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
McGahan JP, Brock JM, Tesluk H, et al. (1992) Hepatic ablation with use of radio-frequency electrocautery in the animal model. J Vasc Intervent Radiol 3:291–297
Goldberg SN, Gazelle GS, Dawson SL, et al. (1995) Tissue ablation with radiofrequency: effect of probe size, gauge, duration, and temperature on lesion volume. Acad Radiol 2:399–404
Solbiati L, Ierace T, Goldberg SN, et al. (1997) Percutaneous US-guided radio-frequency tissue ablation of liver metastases: treatment and follow-up in 16 patients. Radiology 202:195–203
Livraghi T, Goldberg SN, Monti F, et al. (1997) Saline-enhanced radio frequency tissue ablation in the treatment of liver metastases. Radiology 202:205–210
Solbiati L, Goldberg SN, Ierace T, et al. (1997) Hepatic metastases: percutaneous radio-frequency ablation with cooled-tip electrodes. Radiology 205:367–373
Livraghi T, Goldberg SN, Lazzaroni S, et al. (2000) Hepatocellular carcinoma: radiofrequency ablation of medium and large lesions. Radiology 214:761–768
Curley SA, Izzo F, Delrio P, et al. (1999) Radiofrequency ablation of unresectable primary and metastatic hepatic malignancies: results in 123 patients. Ann Surg 230:1–8
Lorentzen T (1996) A cooled needle electrode for radiofrequency tissue ablation: thermodynamic aspects of improved performance compared with conventional needle design. Acad Radiol 3:556–563
Goldberg SN, Gazelle GS, Solbiati L, et al. (1996) Radiofrequency tissue ablation: increased lesion diameter with a perfusion electrode. Acad Radiol 3:636–644
Miao Y, Ni Y, Mulier S, et al. (1997) Ex vivo experiment on radio-frequency liver ablation with saline infusion through a screw-tip cannulated electrode. J Surg Res 71:19–24
Burdio F, Guemes A, Burdio JM, et al. (2003) Bipolar saline-enhanced electrode for radiofrequency ablation: results of experimental study of in vivo porcine liver. Radiology 229:447–456
Giorgio A, Tarantino L, de Stefano G, et al. (2003) Percutaneous sonographically guided saline-enhanced radiofrequency ablation of hepatocellular carcinoma. Am j Roentgenol 181:479–484
Goldberg SN, Gazelle GS, Dawson SL, et al. (1995) Tissue ablation with radiofrequency using multiprobe arrays. Acad Radiol 2:670–674
McGahan JP, Gu WZ, Brock J, et al. (1996) Hepatic ablation using bipolar radiofrequency electrocautery. Acad Radiol 3:418–422
Rossi S, Buscarini E, Garbagnati F, et al. (1998) Percutaneous treatment of small hepatic tumors by an expandable RF needle electrode. Am J Roentgenol 170:1015–1022
de Baere T, Denys A, Johns Wood B, et al. (2001) Radiofrequency liver ablation: experimental comparative study of water-cooled versus expandable systems. Am J Roentgenol 176:187–192
Goldberg SN, Solbiati L, Hahn PF, et al. (1999) Large-volume tissue ablation with radio-frequency by using a clustered internally cooled electrode technique: laboratory and clinical experience in liver metastases. Radiology 209:371–379
Miao Y, Ni Y, Yu J, et al. (2000) A comparative study on validation of a novel cooled-wet electrode for radiofrequency liver ablation. Invest Radiol 35:438–444
Ni Y, Miao Y, Mulier S, Yu J, et al. (2000) A novel “cooled-wet” electrode for radiofrequency ablation. Eur Radiol 10:852–854
Lee JM, Han JK, Kim SH, et al. (2004) Saline-enhanced hepatic radiofrequency ablation using a perfused-cooled electrode: comparison of dual probe bipolar mode with monopolar and single probe bipolar modes. Korean J Radiol 5:121–127
Goldberg SN, Stein M, Gazelle GS, et al. (1999) Percutanous radiofrequency tissue ablation: optimization of pulsed-RF technique to increase coagulation necrosis. J Vasc Intervent Radiol 10:907–916
Choi D, Lim HK, Kim MJ, et al. (2003) Overlapping ablation using a coaxial radiofrequency electrode and multiple cannulae system: experimental study in ex-vivo bovine liver. Korean J Radiol 4:117–123
Breiman RS, Beck JW, Korobkin M, et al. (1982) Volume determinations using computed tomography. Am J Roentgenol 138:329–333
Raman SS, Lu DS, Vodopich DJ, et al. (2000) Creation of radiofrequency lesions in a porcine model: correlation with sonography, CT, and histopathology. Am J roentgenol 175:1253–1258
Lee JD, Lee JM, Kim SW, et al. (2001) MR maginghistopathologic correlation of radiofrequency thermal ablation lesion in a rabbit liver model: observation during acute and chronic stages. Korean J Radiol 2:151–158
Schmidt D, Trubenbach J, Brieger J, et al. (2003) Automated saline-enhanced radiofrequency thermal ablation: initial results in ex vivo bovine livers. Am J Roentgenol 180:163–165
Denys AL, De Baere T, Mahe C, et al. (2001) Radio-frequency tissue ablation of the liver: effects of vascular occlusion on lesion diameter and biliary and portal damages in a pig model. Eur Radiol 11:2102–2108
Marchal F, Elias D, Rauch P, et al. (2004) Biliary lesions during radiofrequency ablation in liver. Study on the pig. Eur Surg Res 36:88–94
Boehm T, Malich A, Goldberg SN, et al. (2002) Radio-frequency tumor ablation: internally cooled electrode versus saline-enhanced technique in an aggressive rabbit tumor model. Radiology 222:805–813
Kettenbach J, Kostler W, Rucklinger E, et al. (2003) Percutaneous saline-enhanced radiofrequency ablation of unresectable hepatic tumors: initial experience in 26 patients. Am J Roentgenol 180:1537–1545
Denys AL, De Baere T, Kuoch V, et al. (2003) Radio-frequency tissue ablation of the liver: in vivo and ex vivo experiments with four different systems. Eur Radiol 13:2346–2352
Pereira PL, Trubenbach J, Schenk M, et al. (2004) Radiofrequency ablation: in vivo comparison of four commercially available devices in pig livers. Radiology 232:482–490
Goldberg SN, Ahmed M, Gazelle GS, et al. (2001) Radiofrequency thermal ablation with NaCl solution injection: effect of electrical conductivity on tissue heating, and coagulation-phantom and porcine liver study. Radiology 219:157–165
Acknowledgments
The author thanks the fine people at Sehwa Medical Systems for their technical and intellectual assistance. This work was supported by the 2003 Inje University research grant.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kim, S.K., Seo, J.W. Radiofrequency Ablation with a New Perfused-Cooled Electrode Using a Single Pump: An Experimental Study in Ex Vivo Bovine Liver. Cardiovasc Intervent Radiol 28, 779–788 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00270-005-0047-7
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00270-005-0047-7