Abstract
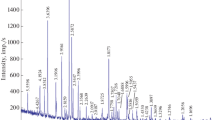
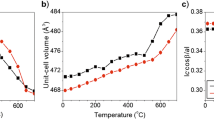
Premelting effects in gehlenite (Ca2Al2SiO7) have been studied by Raman spectroscopy and calorimetry, and in gehlenite and pseudowollastonite (CaSiO3) by electrical conductivity. The enthalpy of premelting of gehlenite is 17.3 kJ mol−1 and represents 9% of the reported enthalpy of fusion, which is in the range of the reported fraction of other minerals. The Raman and electrical conductivity experiments at high temperatures, for gehlenite and pseudowollastonite, show that the premelting effects of both compositions are associated with enhanced dynamics of calcium atoms near the melting point. This conclusion agrees with the results obtained for other minerals like diopside, but contrasts with those found for sodium metasilicate in which the weaker bonding of sodium allows the silicate framework to distort near the melting temperature and deform in such a way to prefigure the silicate entities present in the melt.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Received: 30 April 2002 / Accepted: 7 August 2002
Acknowledgements We thank Y. Linard for help with DSC measurements and two anonymous reviewers for their constructive comments. This work has been partly supported by the EU Marie-Curie fellowship contract no. HPMF-CT-1999-00329, the CNRS-Carnegie Institution of Washington program PICS no.192, and the NSF grants EAR-9614432 and EAR-9901886 to B.O.M.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bouhifd, M., Gruener, G., Mysen, B. et al. Premelting and calcium mobility in gehlenite (Ca2Al2SiO7) and pseudowollastonite (CaSiO3). Phys Chem Min 29, 655–662 (2002). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00269-002-0276-0
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00269-002-0276-0