Abstract
Background
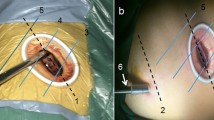
Robot-assisted lobectomy has been used to treat non-small cell lung cancer and usually uses 3 or 4 ports and 3 or 4 robotic arms. We recently developed a two-port approach for robotic lobectomy using three robotic arms and performed a propensity score-matched analysis to compare the feasibility of the two-port and three-port techniques.
Methods
Data on robotic lobectomy for non-small cell lung cancer were retrospectively reviewed. Patients were matched using propensity score based on age, sex, smoking, diabetes, hypertension, forced expiratory volume per 1 s, neoadjuvant chemotherapy, clinical stage, lobe involved, tumor size, and cell types. Overall, 53 and 89 patients who underwent the two-port and three-port approaches, respectively, were matched (1:1 ratio; caliper distance, 0.2). We analyzed the perioperative outcomes and postoperative pain to evaluate the feasibility and safety.
Results
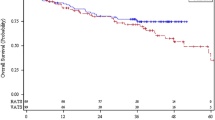
The matched group included 37 patients each who underwent two-port and three-port robotic lobectomy. The operation time was shorter in the two-port group (P = .01). The number of lymph nodes resected (P = .70), conversion to multiport or thoracotomy (P > .99), morbidity and mortality (P = .31), drain indwelling time (P = .32), and hospital stay (P = .11) were not significantly different between the groups. The postoperative pain was less at 0–3 postoperative days (P < .01) in the two-port group. The total medical cost was not markedly increased after transitioning to the two-port technique.
Conclusions
Two-port approach in robotic lobectomy is a safe and feasible alternative approach for treating non-small cell lung cancer.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Rocco G, Internullo E, Cassivi SD et al (2008) The variability of practice in minimally invasive thoracic surgery for pulmonary resections. Thorac Surg Clin 18:235–247. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.thorsurg.2008.06.002
Park SY, Kim HK, Jang DS et al (2019) Initial experiences with robotic single-site thoracic surgery for mediastinal masses. Ann Thorac Surg 107:242–247. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.athoracsur.2018.08.016
Cadiere GB, Himpens J, Vertruyen M et al (1999) The world’s first obesity surgery performed by a surgeon at a distance. Obes Surg 9:206–209. https://doi.org/10.1381/096089299765553539
Melfi FM, Menconi GF, Mariani AM et al (2002) Early experience with robotic technology for thoracoscopic surgery. Eur J Cardiothorac Surg 21:864–868. https://doi.org/10.1016/s1010-7940(02)00102-1
Reddy RM, Gorrepati ML, Oh DS et al (2018) Robotic-assisted versus thoracoscopic lobectomy outcomes from high-volume thoracic surgeons. Ann Thorac Surg 106:902–908. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.athoracsur.2018.03.048
Veronesi G, Galetta D, Maisonneuve P et al (2010) Four-arm robotic lobectomy for the treatment of early-stage lung cancer. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg 140:19–25. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jtcvs.2009.10.025
Wei B, Cerfolio RJ (2017) Robotic lobectomy and segmentectomy: technical details and results. Surg Clin North Am 97:771–782. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.suc.2017.03.008
Kernstine KH, Anderson CA, Falabella A (2008) Robotic lobectomy. Oper Tech Thorac Cardiovasc Surg 13:204. https://doi.org/10.1053/j.optechstcvs.2008.09.001
Park BJ, Flores RM, Rusch VW (2006) Robotic assistance for video-assisted thoracic surgical lobectomy: technique and initial results. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg 131:54–59. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jtcvs.2005.07.031
Peng M, Wang X, Chen C et al (2020) Report on 153 sequential three-incision robotic-assisted pulmonary resections by a single surgeon: technical details and learning curve. J Thorac Dis 12:741–748. https://doi.org/10.21037/jtd.2019.12.116
Han KN, Kim HK, Choi YH (2017) Midterm outcomes of single port thoracoscopic surgery for major pulmonary resection. PLoS ONE 12:e0186857. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0186857
Bokhari MB, Patel CB, Ramos-Valadez DI et al (2011) Learning curve for robotic-assisted laparoscopic colorectal surgery. Surg Endosc 25:855–860. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00464-010-1281-x
Park SY, Han KN, Hong JI et al (2020) Subxiphoid approach for robotic single-site-assisted thymectomy. Eur J Cardiothorac Surg 58:i34–i38. https://doi.org/10.1093/ejcts/ezaa036
Bae SU, Jeong WK, Baek SK (2016) Single-port plus an additional port robotic complete mesocolic excision and intracorporeal anastomosis using a robotic stapler for right-sided colon cancer. Ann Surg Treat Res 91:212–217. https://doi.org/10.4174/astr.2016.91.4.212
Lee JH, Son T, Kim J et al (2018) Intracorporeal delta-shaped gastroduodenostomy in reduced-port robotic distal subtotal gastrectomy: technical aspects and short-term outcomes. Surg Endosc 32:4344–4350. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00464-018-6244-7
Kim SH, Kang CM, Lee WJ (2017) Robotic single-site plus ONE port distal pancreatectomy. Surg Endosc 31:4258–4259. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00464-017-5476-2
Morelli L, Guadagni S, Caprili G et al (2013) Robotic right colectomy using the Da Vinci Single-Site® platform: case report. Int J Med Robot 9:258–261. https://doi.org/10.1002/rcs.1488
Kim JJ, Choi C, Nam SH et al (2017) Feasibility of reduced-port robotic surgery for myomectomy with the da vinci surgical system. J Minim Invasive Gynecol 24:926–931. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmig.2017.04.025
Lee JH, Hong JI, Kim HK (2021) Robot-assisted thoracic surgery in non-small cell lung cancer. J Chest Surg 54(4):266–278. https://doi.org/10.5090/jcs.21.070
Funding
This study was supported by Nano-Material Technology Development Program through the National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF) funded by Ministry of Science and ICT (2021M3H4A4079630) and Korea Medical Device Development Fund grant funded by the Korean government (the Ministry of Science and ICT, Ministry of Trade, Industry and Energy, Ministry of Health & Welfare, Ministry of Food and Drug Safety) (Project Number: 1711138151, KMDF_PR_20200901_0094_02).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
None declared.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Supplementary file1 (MP4 32842 KB)
Supplementary file2 (MP4 59117 KB)
Supplementary file3 (MP4 22431 KB)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Han, K.N., Lee, J.H., Hong, J.I. et al. Comparison of Two-Port and Three-Port Approaches in Robotic Lobectomy for Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer. World J Surg 46, 2517–2525 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00268-022-06660-4
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00268-022-06660-4