Abstract
Purposes
Temporary hemiepiphysiodesis (TH) using eight-plates is one of the most frequently performed surgeries for correcting angular deformities of the lower extremities in adolescents. Rarely have studies examined children with X-linked hypophosphataemic rickets (X-LHPR) treated with TH using eight-plates. This study was conducted to investigate the efficacy, the endpoint, and the complications of TH using eight-plates to correct angular deformities of the lower extremities in skeletally immature children.
Methods
We reviewed a total of 26 children (86 physes, 52 knees) with X-LHPR (mean age of 6.2 years, range from 2 to 13 years) who underwent TH using eight-plate to correct angular deformities of the lower extremities. Radiographs and clinical records of these patients were evaluated for demographic data and related clinical factors.
Results
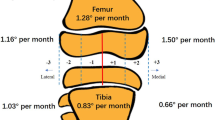
The average correction of the mechanical lateral distal femoral angle (mLDFA) was 11.7 ± 8.7° (range from 1.0 to 29.7°), and the average correction of the mechanical medial proximal tibial angle (mMPTA) was 8.4 ± 5.0° (range from 0.3 to 16.7°). The mean deformity correction time was 22.7 months (range from 7 to 60 months), and the mean follow-up after eight-plate removal was 43.9 months (range from 24 to 101 months). Overall, 76.9% (20/26 patients) of the angular deformities of the knee were completely corrected and 15.4% (4/26) of the patients received osteotomy surgery. The femoral correction velocity (0.9° per month) was significantly higher than the proximal tibial (0.6° per month) (p = 0.02). The correction velocity of the mLDFA and mMPTA with the TH procedure was faster than that in the absence of intervention (0.9° vs. 0.2°, 0.7° vs. 0.4° per month, p < 0.05). The correction velocity of the mLDFA (1.2° vs. 0.5° per month, \(p<0.001\)) and mMPTA (0.7° vs. 0.5° per month, p = 0.04) of patients whose age ≤ five years old was faster than that of patients whose age > five years old. A total of 69.2% (18/26) patients experienced one TH procedure using eight-plates only. Two patients had screw loosening (2/26, 7.7%). One patient (1/26, 3.8%) had a rebound phenomenon after the removal of eight-plate and had the TH procedure again. There was no breakage, infection, physis preclosure, or limited range of movement found in the follow-up.
Conclusion
TH using eight-plates is a safe and effective procedure with a relatively low incidence of complication and rebound, and it could be used as part of a streamlined treatment for younger X-LHPR patients with resistant or progressive lower limb deformity despite optimal medical treatment. Early intervention can achieve better results.




Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The datasets analyzed in this study are available from the corresponding author upon reasonable request.
Code availability
Not applicable.
References
Horn A, Wright J, Bockenhauer D, Van’t Hoff W, Eastwood DM (2017) The orthopaedic management of lower limb deformity in hypophosphataemic rickets. J Child Orthop 11:298–305. https://doi.org/10.1302/1863-2548.11.170003
Bitzan M, Goodyer PR (2019) Hypophosphatemic rickets. Pediatr Clin North Am 66:179–207. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pcl.2018.09.004
Baroncelli GI, Mora S (2021) X-linked hypophosphatemic rickets: multisystemic disorder in children requiring multidisciplinary management. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne) 12:688309. https://doi.org/10.3389/fendo.2021.688309
Novais E, Stevens PM (2006) Hypophosphatemic rickets: the role of hemiepiphysiodesis. J Pediatr Orthop 26:238–244. https://doi.org/10.1097/01.bpo.0000218531.66856.b7
Kulkarni RM, Ilyas Rushnaiwala FM, Kulkarni GS, Negandhi R, Kulkarni MG, Kulkarni SG (2015) Correction of coronal plane deformities around the knee using a tension band plate in children younger than 10 years. Indian J Orthop 49:208–218. https://doi.org/10.4103/0019-5413.152484
Kumar A, Gaba S, Sud A, Mandlecha P, Goel L, Nayak M (2016) Comparative study between staples and eight plate in the management of coronal plane deformities of the knee in skeletally immature children. J Child Orthop 10:429–437. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11832-016-0758-0
Dai Z-Z, Liang Z-P, Li H, Ding J, Wu Z-K, Zhang Z-M, Li H (2021) Temporary hemiepiphysiodesis using an eight-plate implant for coronal angular deformity around the knee in children aged less than 10 years: efficacy, complications, occurrence of rebound and risk factors. BMC Musculoskel Dis 22:53. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12891-020-03915-w
Stevens PM (2007) Guided growth for angular correction: a preliminary series using a tension band plate. J Pediatr Orthop 27:253–259. https://doi.org/10.1097/BPO.0b013e31803433a1
Danino B, Rodl R, Herzenberg JE, Shabtai L, Grill F, Narayanan U, Segev E, Wientroub S (2019) Growth modulation in idiopathic angular knee deformities: is it predictable? J Child Orthop 13:318–323. https://doi.org/10.1302/1863-2548.13.190033
Ding J, Zhu T, Jin FC, Wu ZK, Li H (2019) The effect of temporary hemiepiphysiodesis in the treatment of skeleton immature posttraumatic genu angular deformity: a retrospective study of 27 cases. J Orthop Surg Res 14:381. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13018-019-1426-0
Lee HJ, Oh CW, Song KS, Kyung HS, Min WK, Park BC (2012) Guided growth with a noncannulated screw-plate system for angular deformity of the knee: a preliminary report. J Pediatr Orthop B 21:339–347. https://doi.org/10.1097/BPB.0b013e3283547198
Park SS, Kang S, Kim JY (2016) Prediction of rebound phenomenon after removal of hemiepiphyseal staples in patients with idiopathic genu valgum deformity. Bone Joint J 98-B:1270–1275. https://doi.org/10.1302/0301-620X.98B9.37260
Mielke CH, Stevens PM (1996) Hemiepiphyseal stapling for knee deformities in children younger than 10 years: a preliminary report. J Pediatr Orthop 16:423–429
Stevens PM, Pease F (2006) Hemiepiphysiodesis for posttraumatic tibial valgus. J Pediatr Orthop 26:385–392
Stevens PM, Maguire M, Dales MD, Robins AJ (1999) Physeal stapling for idiopathic genu valgum. J Pediatr Orthop 19:645–649
Eltayeby HH, Iobst CA, Herzenberg JE (2019) Hemiepiphysiodesis using tension band plates: does the initial screw angle influence the rate of correction? J Child Orthop 13:62–66. https://doi.org/10.1302/1863-2548.13.180086
Kumar S, Sonanis SV (2018) Growth modulation for coronal deformity correction by using eight plates-systematic review. J Orthop 15:168–172. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jor.2018.01.022
Burghardt RD, Herzenberg JE, Standard SC, Paley D (2008) Temporary hemiepiphyseal arrest using a screw and plate device to treat knee and ankle deformities in children: a preliminary report. J Child Orthop 2:187–197. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11832-008-0096-y
Burghardt RD, Herzenberg JE (2010) Temporary hemiepiphysiodesis with the eight-Plate for angular deformities: mid-term results. J Orthop Sci 15:699–704. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00776-010-1514-9
Stevens PM, Klatt JB (2008) Guided growth for pathological physes: radiographic improvement during realignment. J Pediatr Orthop 28:632–639. https://doi.org/10.1097/BPO.0b013e3181841fda
Zajonz D, Schumann E, Wojan M, Kübler FB, Josten C, Bühligen U, Heyde CE (2017) Treatment of genu valgum in children by means of temporary hemiepiphysiodesis using eight-plates: short-term findings. BMC Musculoskel Dis 18:456. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12891-017-1823-7
Narayana Kurup JK, Shah HH (2020) Hemiepiphysiodesis using 2-holed reconstruction plate for correction of angular deformity of the knee in children. J Orthop 20:54–59. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jor.2020.01.001
El-Sobky TA, Samir S, Baraka MM, Fayyad TA, Mahran MA, Aly AS, Amen J, Mahmoud S (2020) Growth modulation for knee coronal plane deformities in children with nutritional rickets a prospective series with treatment algorithm. J Am Acad Orthop Surg Glob Res Rev 4(1):e19.00009. https://doi.org/10.5435/JAAOSGlobal-D-19-00009
Bonnet-Lebrun A, Linglart A, De Tienda M, Ouchrif Y, Berkenou J, Assi A, Wicart P, Skalli W (2021) Quantitative analysis of lower limb and pelvic deformities in children with X-linked hypophosphatemic rickets. Orthop Traumatol Surg Res:103187. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.otsr.2021.103187.
Gigante C, Borgo A, Corradin M (2017) Correction of lower limb deformities in children with renal osteodystrophy by guided growth technique. J Child Orthop 11:79–84. https://doi.org/10.1302/1863-2548-11-160172
Danino B, Rödl R, Herzenberg JE, Shabtai L, Grill F, Narayanan U, Segev E, Wientroub S (2018) Guided growth: preliminary results of a multinational study of 967 physes in 537 patients. J Child Orthop 12:91–96. https://doi.org/10.1302/1863-2548.12.170050
Alkhatib N, Bouri F, Hegazy A, Ibrahim T (2018) Vitamin D and tibiofemoral joint orientation angles in children. J Pediatr Orthop B 27:467–471. https://doi.org/10.1097/BPB.0000000000000457
Shabtai L, Herzenberg JE (2016) Limits of growth modulation using tension band plates in the lower extremities. J Am Acad Orthop Surg 24:691–701. https://doi.org/10.5435/JAAOS-D-14-00234
Burghardt RD, Specht SC, Herzenberg JE (2010) Mechanical failures of eight-plateguided growth system for temporary hemiepiphysiodesis. J Pediatr Orthop 30:594–597. https://doi.org/10.1097/BPO.0b013e3181e4f591
Burghardt RD, Herzenberg JE, Andre S, Bernius P, Kazim MA (2018) Treatment failures and complications in patients with Blount disease treated with temporary hemiepiphysiodesis: a critical systematic literature review. J Pediatr Orthop B 27:522–529. https://doi.org/10.1097/BPB.0000000000000523
Griswold BG, Shaw KA, Houston H, Bertrand S, Cearley D (2020) Guided growth for the treatment of infantile Blount’s disease: is it a viable option? J Orthop 20:41–45. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jor.2020.01.007
Jain MJ, Inneh IA, Zhu H, Phillips WA (2020) Tension band plate (TBP)-guided hemiepiphysiodesis in blount disease: 10-year single-center experience with a systematic review of literature. J Pediatr Orthop 40:e138–e143. https://doi.org/10.1097/BPO.0000000000001393
Funding
This work was supported by High-level Hospital Construction Research Project of Maoming People’s Hospital, and Maoming Science and Technology Project (2022166).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
All authors participated in the design, interpretation of the studies, and analysis of the data and review of the manuscript. Feng WJ and Wu ZK did the design of the study; Xiong QG, Dai ZZ, and Feng WJ reviewed the patients and analyzed the data; Feng WJ and Wu ZK wrote the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval
This study was performed in line with the principles of the Declaration of Helsinki. Approval was granted by the Ethics Committee of Xin Hua Hospital Affiliated to Shanghai Jiao Tong University School of Medicine (Approval number: XHEC-D-2022–192).
Consent to participate
Written informed consent was obtained from the parents.
Consent for publication
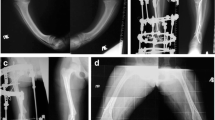
The authors affirm that human research participants provided informed consent for publication of the images in Figs. 2, 3, and 4.
Competing interests
Financial interests: Feng WJ, Dai ZZ, and Wu ZK declare they have no financial interests. Xiong QG has received research funding from High-level Hospital Construction Research Project of Maoming People’s Hospital and Maoming Science and Technology Project (2022166).
Additional information
Publisher's note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Feng, WJ., Dai, ZZ., Xiong, QG. et al. Temporary hemiepiphysiodesis using eight-plates for angular deformities of the lower extremities in children with X-linked hypophosphataemic rickets. International Orthopaedics (SICOT) 47, 763–771 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00264-023-05688-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00264-023-05688-y