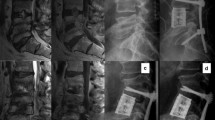
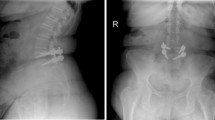
Abstract
Introduction
Postoperative spondylodiscitis is a primary infection of the nucleus pulposus with secondary involvement of the cartilaginous endplate and vertebral bone. Although uncommon, postoperative spondylodiscitis causes major morbidity and may be associated with serious long-term sequelae. Several risk factors had been identified, including immunosuppression, obesity, alcohol, smoking, diabetes and malnutrition.
Materials and methods
A review of the literature was done to analyse the diagnosis, treatment and prevention of postoperative spondylodiscitis.
Results
We found that the principles of conservative treatment are to establish an accurate microbiological diagnosis, treat with appropriate antibiotics, immobilise the spine, and closely monitor for spinal instability and neurological deterioration. The purpose of surgical treatment is to obtain multiple cultures of bone and soft tissue, perform a thorough debridement of infected tissue, decompress neural structures, and reconstruct the unstable spinal column with bone graft with or without concomitant instrumentation.
Conclusions
Appropriate management requires aggressive medical treatment and, at times, surgical intervention. If recognised early and treated appropriately, a full recovery can often be expected. Therefore, clinicians should be aware of the clinical presentation of such infections to improve patient outcome. A review of the literature was done to advance our understanding of the diagnosis, treatment, prevention and outcome of these infections.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Rawlings CE, Wilkins RH, Gallis HA, Goldner JL, Francis R (1983) Postoperative intervertebral disc space infection. Neurosurgery 13:371–376
Maiuri F, Iaconetta G, Gallicchio B, Manto A, Briganti F (1997) Spondylodiscitis: clinical and magnetic resonance diagnosis. Spine 22:1741–1746
Zink P-M, Frank AM, Trappe AE (1989) Prophylaxis of postoperative lumbar spondylodiscitis. Neurosurg Rev 1989:297–303
Fraser RD, Osti OL, Vernon-Roberts B (1987) Discitis after discography. J Bone Joint Surg Br 69:26–35
Nielsen VH, Iversen E, Ahlgren P (1990) Postoperative discitis radiology of progress and healing. Acta Radiol 31:559–563
Jimenez-Mejias ME, de Dios CJ, Sanchez-Lora FJ et al (1999) Postoperative spondylodiskitis: etiology, clinical findings, prognosis, and comparison with nonoperative pyogenic spondylodiskitis. Clin Infect Dis 29:339–345
Deyo RA, Cherkin DC, Loeser JD, Bigos SJ, Ciol MA (1992) Morbidity and mortality in association with operations on the lumbar spine. J Bone Joint Surg Am 74:536–543
El-Gindi S, Aref S, Salama M (1976) Infection of intervertebral discs after operation. J Bone Joint Surg Br 58:114–116
Silber JS, Anderson DG, Vaccaro AR, Anderson PA, McCormick P (2002) Management of postprocedural discitis. Spine J 2(4):279–287
Fang A, Hu S, Endres N, Bradford D (2005) Risk factors for infections after spinal surgery. Spine 30:1460–1465
Dufour V, Feydy A, Rillardon L et al (2005) Comparative study of postoperative and spontaneous pyogenic spondylodiscitis. Semin Arthritis Rheum 34:766–771
Sapkas GS, Mavrogenis AF, Mastrokalos DS, Papadopoulos E, Papagelopoulos EC, Papagelopoulos PJ (2006) Postoperative spine infection: a retrospective analysis of 21 patients. Eur J Orthop Surg Traumatol 16(4):322–326
Friedman BC, Simon GL (1987) Candida vertebral osteomyelitis: report of three cases and a review of the literature. Diagn Microbiol Infect Dis 8:31–36
Mawk JR, Ericksson DL, Chou SN et al (1983) Aspergillus infections of the lumbar disc spaces. Report of the three cases. J Neurosurg 58:270–274
Lotfinia I, Vahedi P (2010) Late-onset post-diskectomy tuberculosis at the same operated lumbar level: case report and review of literature. Eur Spine J 19(Suppl 2):S226–S232
Peters-Christodoulou MN, De Beer F, Bots G et al (1991) Treatment of postoperative Aspergillus fumigatus spondylodiskitis with itraconazole. Scand J Infect Dis 23:373–376
Parry M, Grant B, Yukna M et al (2001) Candida osteomyelitis and diskitis after spinal surgery: an outbreak that implicates artificial nail use. Clin Infect Dis 32:352–357
Chen F, Lü G, Kang Y et al (2006) Mucormycosis spondylodiscitis after lumbar disc puncture. Eur Spine J 15:370–376
Lenzi J, Agrillo A, Santoro A et al (2004) Postoperative spondylodiscitis from Aspergillus fumigatus in immunocompetent subjects. J Neurosurg Sci 48:81–85
Li J, Yan D, Duan L, Zhang Z, Zhu H, Zhang Z (2011) Percutaneous discectomy and drainage for postoperative intervertebral discitis. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg 131(2):173–178
Harris AE, Hennick C, Byers K, Welch WC (2005) Postoperative discitis due to Propionibacterium acnes: a case report and review of the literature. Surg Neurol 63(6):538–541
Hsieh MK, Chen LH, Niu CC, Fu TS, Lai PL, Chen WJ (2011) Postoperative anterior spondylodiscitis after posterior pedicle screw instrumentation. Spine J 11(1):24–29
Carmouche JJ, Molinari RW (2004) Epidural abscess and discitis complicating instrumented posterior lumbar interbody fusion: a case report. Spine 29(23):E542–E546
Kulkarni AG, Hee HT (2006) Adjacent level discitis after anterior cervical discectomy and fusion (ACDF): a case report. Eur Spine J 15(suppl 5):S559–S563
Jeon DW, Chang BS, Jeung UO, Lee SJ, Lee CK, Kim MS et al (2009) A case of postoperative tuberculous spondylitis with bizarre course. Clin Orth Surg 1:58–62
Kaplan ES (1973) Post-diskectomy tuberculous abscess. J Neurosurg 38:358–361
Almeida A (2005) Tuberculosis of the spine and spinal cord. Eur J Radiol 55:193–201
Tack KJ, Rhame FS, Brown B et al (1982) Aspergillus osteomyelitis: report of four cases and review of the literature. Am J Med 73:295–300
Kim KW, Ha KY, Kim MS et al (2008) Postoperative trichosporon asahii spondylodiscitis after open lumbar discectomy: a case report. Spine 33:E116–E120
Garcia-Vidal C, Cabellos C, Ayats J, Font F, Ferran E, Fernandez-Viladrich P (2009) Fungal postoperative spondylodiscitis due to Scedosporium prolificans. Spine J 9:e1–e7
Ozuna RM, Delamarter RB (1996) Pyogenic vertebral osteomyelitis ans postsurgical disc space infections. Orthop Clin North Am 27(1):87–94
Rohde V, Meyer B, Schaller C, Hassler WE (1998) Spondylodiscitis after lumbar discectomy. Spine 23:615–620
Bavinzski G, Schoeggl A, Trattnig S et al (2003) Microsurgical management of postoperative disc space infection. Neurosurg Rev 26:102–107
Schulitz KP, Assheuer J (1994) Discitis after procedures on the intervertebral disc. Spine 19:1172–1177
Fouquet B, Goupille P, Jattiot F et al (1992) Discitis after lumbar disc surgery. Features of « aseptic » and « septic » forms. Spine 17(3):356–358
Valls J, Ottolenghi CE, Schajowicz F (1948) Aspiration biopsy in diagnosis of lesions of vertebral bodies. J Am Med Assoc 136(6):276–382
Enoch DA, Cargill JS, Laing R et al (2008) Value of CT-guided biopsy in te diagnosis of septic discitis. J Clin Pathol 61(6):750–753
Staatz G, Adam GB, Keulers P, Vorwerk D, Gunther RW (1998) Spondylodisckitis abscesses: CT-guided percutaneous catheter drainage. Radiology 208(2):363–367
Gebhard JS, Brugman JL (1994) Percutaneous discectomy for the treatment of bacterial discitis. Spine 19(7):855–857
Haaker RG, Senkal M, Kilelich T, Kramer J (1997) Percutaneous lumbar discectomy in the treatment of lumbar discitis. Eur Spine J 6(2):98–101
Onik G (1996) Automated percutaneous biopsy in the diagnosis ans treatment of infectious discitis. Neurosurg Clin N Am 7(1):145–150
Berk RH, Yazici M, Atabey N, Ozdamar OS, Pabuccuoglu U, Alici E (1996) Detection of Mycobacterium tuberculosis in formaldehyde solution-fixed, paraffin-embedded tissue by polymerase chain reaction in Pott’s disease. Spine 21(17):1991–1995
Nikaido T, Ishibashi K, Otani K, Yabuki S, Konno S, Mori S et al (2007) Mycobacterium bovis BCG vertebral osteomyelitis after intravesical BCG therapy, diagnosed by PCR-based genomic deletion analysis. J Clin Microbiol 45(12):4085–4087
Ribeiro MA, Barouni AS, Augusto CJ, Augusto MV, Lopes MT, Salas CE (2007) PCR identification of Mycobacterium tuberculosis complex in a clinical sample from a patient with symptoms of tuberculous spondylodiscitis. Braz J Med Biol Res 40(1):1–4
Verettas D, Kazakos C, Tilkeridis C, Dermon A, Petrou H, Galanis V (2003) Polymerase chain reaction for the detection of Mycobacterium tuberculosis in synovial fluid, tissue samples, bone marrow aspirate and peripheral blood. Acta Orthop Belg 69(5):396–339
Khan IA, Vaccaro AR, Zlotolow DA (1999) Management of vertebral diskitis and osteomyelitis. Orthopedics 22:758–765
Wirtz DC, Genius I, Wildberger JE, Adam G, Zilkens KW, Niethard FU (2000) Diagnostic and therapeutic management of lumbar and thoracic sompdylodiscitis—an evaluation of 59 cases. Arch Orthop trauma Surg 120(5–6):245–251
Moon MS (2006) Development in the management of tuberculosis of the spine. Curr Orthop 20(2):132–140
Benli IT, Acaroglu E, Akalin S, Kis M, Duman E, Un A (2002) Anterior radical debridement and anterior instrumentation in tuberculosis spondylitis. Eur Spine J 12(2):224–234
Kumar R (2005) Spinal tuberculosis: with reference to the children of north India. Childs Nerv Syst 21:19–26
Calvosa G, Bonicoli E, Restuccia G, Mancusi G, Po F (2004) A single-stage posterior approach in the treatment of spinal tuberculosis: case report. J Orthop Traumatol 5(3):185–187
Iversen E, Nielsen VA, Hansen LG (1992) Prognosis in postoperative discitis. A retrospective study of 111 cases. Acta Orthop Scand 63(3):305–309
Luzzati R, Giacomazzi D, Danzi MC, Tacconi L, Concia E, Vento S (2009) Diagnosis, management and outcome of clinically-suspected spinal infection. J Infect 58(4):259–265
Viale P, Furlanut M, Scudeller L et al (2009) Treatment of pyogenic (non-tuberculous) spondylodiscitis with tailored high-dose lefloxacin plus rifampicin. Int J Antimicrob Agents 33(4):379–382
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gerometta, A., Bittan, F. & Rodriguez Olaverri, J.C. Postoperative spondilodiscitis. International Orthopaedics (SICOT) 36, 433–438 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00264-011-1442-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00264-011-1442-0