Abstract
Background
Postoperative intervertebral discitis occurs following spinal surgery. This study was done to evaluate the effect of percutaneous discectomy and drainage (PDD) for postoperative intervertebral discitis.
Methods
A retrospective study of postoperative intervertebral discitis treated by PDD procedures was conducted from January 1997 to June 2006. There were 34 patients (24 males, 10 females); 10 cases of after lumbar discectomy (L3–4 in 3 patients, L4–5 in 7 patients), 21 cases of after percutaneous lumbar discectomy (L3–4 in 7 patients, L4–5 in 14 patient), 2 cases of after percutaneous cervical discectomy (C5–6 in 1 patient, C6–7 in 1 patient), and 1 case of C5–6 after percutaneous cervical nucleoplasty.
Results
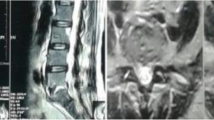
All patients tolerated the procedure well and there were 31 cases had followed up. VAS scores demonstrated statistically significant improvement after PDD when compared with preoperational values (P < 0.01). Elevated CRP and ESR values returned to normal range within 3–8 weeks. CRP and ESR values demonstrated statistically significant improvement after PDD when compared with preoperative values (P < 0.01). Biopsies of the disc were performed in all patients and pus was seen in 17 patients at the pathology levels. Inflammatory cells were observed nine cases (4 cases showed infiltration of lymphocytes and plasmacytes, 5 cases showed infiltrate of polymorphonuclear leucocytes). Cultures of disc and bone tissue showed 17 cases of sterile and 14 had positive culture. Spine X-rays films showed narrowed disc space in 29 cases, and bridging osteophytes were noted in 19 patients. Destructive and sclerotic changes of vertebral bodies with narrowing of disc spaces were observed in 14 patients.
Conclusions
The results show that PDD is a minimally invasive procedure for obtaining sufficient biopsy material for histological analysis and culture in cases of discitis, and has a good clinical outcome recommended for patients with early stage postoperative intervertebral discitis without neurologic deficit.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bavinzski G, Schoeggl A, Trattnig S et al (2003) Microsurgical management of postoperative disc space infection. Neurosurg Rev 26(2):102–107
Bozgeyik Z, Ozdemir H, Demirdag K, Ozden M, Sonmezgoz F, Ozgocmen S (2008) Clinical and MRI findings of Brucellar spondylodiscitis. Eur J Radiol 67(1):153–158
Connor PM, Darden BV (1993) Cervical discography complications and clinical efficacy. Spine 18(14):2035–2038
Dimar JR, Carreon LY, Glassman SD, Campbell MJ, Hartman MJ, Johnson JR (2004) Treatment of pyogenic vertebral osteomyelitis with anterior debridement and fusion followed by delayed posterior spinal fusion. Spine 29(3):326–332 discussion 332
Emery SE, Chan DP, Woodward HR (1989) Treatment of hematogenous pyogenic vertebral osteomyelitis with anterior debridement and primary bone grafting. Spine 14(3):284–291
Enoch DA, Cargill JS, Laing R, Herbert S, Corrah TW, Brown NM (2008) Value of CT-guided biopsy in the diagnosis of septic discitis. J Clin Pathol 61(6):750–753
Fouquet B, Goupille P, Jattiot F et al (1992) Discitis after lumbar disc surgery. Features of “aseptic” and “septic” forms. Spine 17(3):356–358
Gebhard JS, Brugman JL (1994) Percutaneous discectomy for the treatment of bacterial discitis. Spine 19(7):855–857
Haaker RG, Senkal M, Kielich T, Kramer J (1997) Percutaneous lumbar discectomy in the treatment of lumbar discitis. Eur Spine J 6(2):98–101
Hadjipavlou AG, Mader JT, Necessary JT, Muffoletto AJ (2000) Hematogenous pyogenic spinal infections and their surgical management. Spine 25(13):1668–1679
Heyde CE, Boehm H, El Saghir H, Tschoke SK, Kayser R (2006) Surgical treatment of spondylodiscitis in the cervical spine: a minimum 2-year follow-up. Eur Spine J 15(9):1380–1387
Iversen E, Nielsen VA, Hansen LG (1992) Prognosis in postoperative discitis. A retrospective study of 111 cases. Acta Orthop Scand 63(3):305–309
Kasperczyk A, Freyschmidt J (1994) Pustulotic arthroosteitis: spectrum of bone lesions with palmoplantar pustulosis. Radiology 191(1):207–211
Krodel A, Sturz H, Siebert CH (1991) Indications for and results of operative treatment of spondylitis and spondylodiscitis. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg 110(2):78–82
Li J, Yan DL, Zhang ZH (2008) Percutaneous cervical nucleoplasty in the treatment of cervical disc herniation. Eur Spine J 17(12):1664–1669
Luzzati R, Giacomazzi D, Danzi MC, Tacconi L, Concia E, Vento S (2009) Diagnosis, management and outcome of clinically-suspected spinal infection. J Infect 58(4):259–265
Macnab I (1971) Negative disc exploration. An analysis of the causes of nerve-root involvement in sixty-eight patients. J Bone Joint Surg Am 53(5):891–903
Nielsen VA, Iversen E, Ahlgren P (1990) Postoperative discitis. Radiology of progress and healing. Acta Radiol 31(6):559–563
Onik G (1996) Automated percutaneous biopsy in the diagnosis and treatment of infectious discitis. Neurosurg Clin N Am 7(1):145–150
Ozuna RM, Delamarter RB (1996) Pyogenic vertebral osteomyelitis and postsurgical disc space infections. Orthop Clin North Am 27(1):87–94
Rankine JJ, Barron DA, Robinson P, Millner PA, Dickson RA (2004) Therapeutic impact of percutaneous spinal biopsy in spinal infection. Postgrad Med J 80(948):607–609
Sharma SK, Jones JO, Zeballos PP, Irwin SA, Martin TW (2009) The prevention of discitis during discography. Spine 9(11):936–943
Staatz G, Adam GB, Keulers P, Vorwerk D, Gunther RW (1998) Spondylodiskitic abscesses: CT-guided percutaneous catheter drainage. Radiology 208(2):363–367
Tronnier V, Schneider R, Kunz U, Albert F, Oldenkott P (1992) Postoperative spondylodiscitis: results of a prospective study about the aetiology of spondylodiscitis after operation for lumbar disc herniation. Acta Neurochir (Wien) 117(3–4):149–152
Valls J, Ottolenghi CE, Schajowicz F (1948) Aspiration biopsy in diagnosis of lesions of vertebral bodies. J Am Med Assoc 136(6):376–382
Viale P, Furlanut M, Scudeller L et al (2009) Treatment of pyogenic (non-tuberculous) spondylodiscitis with tailored high-dose levofloxacin plus rifampicin. Int J Antimicrob Agents 33(4):379–382
Wirtz DC, Genius I, Wildberger JE, Adam G, Zilkens KW, Niethard FU (2000) Diagnostic and therapeutic management of lumbar and thoracic spondylodiscitis—an evaluation of 59 cases. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg 120(5–6):245–251
Zeidman SM, Thompson K, Ducker TB (1995) Complications of cervical discography: analysis of 4400 diagnostic disc injections. Neurosurgery 37(3):414–417
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, J., Yan, D., Duan, L. et al. Percutaneous discectomy and drainage for postoperative intervertebral discitis. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg 131, 173–178 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00402-010-1115-2
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00402-010-1115-2