Abstract
Background
Intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma (ICC) is hard to distinguish from inflammatory mass (IM) complicated with hepatolithiasis in clinical practice preoperatively. This study looked to develop and confirm the radiomics models to make a distinction between ICC with hepatolithiasis from IM and to compare the results of different contrast-enhanced computed tomography (CT) phase.
Methods
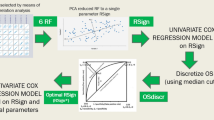
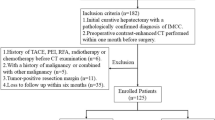
The models were developed in a training cohort of 110 patients from January 2005 to June 2020. Radiomics features were extracted from both arterial phase and portal venous phase contrast-enhanced computed tomography (CT) scans. The radiomics scores based on radiomics features, were built by logistic regression after using the least absolute shrinkage and selection operator (LASSO) method. The rad-scores of two contrast -enhanced CT phases and clinical features were incorporated into a novel model. The performance of the models were determined by theirs discrimination, calibration, and clinical usefulness. The models were externally validated in 35 consecutive patients.
Results
The radiomics signature comprised two features in arterial phase (training cohort, AUC = 0.809, sensitivity 0.700, specificity 0.848, and accuracy 0.774;validation cohort, AUC = 0.790, sensitivity 0.714, specificity 0.800, and accuracy 0.757) and three related features in portal venous phase (training cohort, AUC = 0.801, sensitivity 0.800, specificity 0.717, and accuracy 0.759; validation cohort, AUC = 0.830, sensitivity 0.700, specificity 0.750, and accuracy 0.775) showed significant association with ICC in both cohorts (P < 0.05).We also developed a model only based on clinical variables (training cohort, AUC = 0.778, sensitivity 0.567, specificity 0.891, and accuracy 0.729; validation cohort, AUC = 0.788, sensitivity 0.571, specificity 0.950, and accuracy 0.761). The radiomics-based model contained rad-score of two phases and two clinical factors (CEA and CA19-9) showed the best performance (training cohort, AUC = 0.864, sensitivity 0.867, specificity 0.804, and accuracy 0.836; validation cohort, AUC = 0.843, sensitivity 0.643, specificity 0.980, and accuracy 0.821).
Conclusions
Our radiomics-based models provided a diagnostic tool for differentiate intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma (ICC) from inflammatory mass (IM) with hepatolithiasis both in arterial phase and portal venous phase. To go a step further, the diagnostic accuracy will improved by a clinico-radiologic model.






Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- IHL-ICC:
-
Intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma (ICC) complicated by intrahepatic lithiasis (IHL)
- IHL-IM:
-
Inflammatory mass (IM) complicated by intrahepatic lithiasis (IHL)
- ICC:
-
Intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma
- IHL:
-
Intrahepatic lithiasis
- IM:
-
Inflammatory mass
- LASSO:
-
Least absolute shrinkage and selection operator
- DCA:
-
Decision curve analysis
- ROI:
-
Region of interest
- OR:
-
Odds ratios
- AUC:
-
Area under the curve
- H–L:
-
Hosmer–Lemeshow
- WMU:
-
Wenzhou Medical University
- CEA:
-
Carcinoembryonic antigen
- CA19-9:
-
Carbohydrate antigen 19-9
References
S. Rizvi, S.A. Khan, C.L. Hallemeier, R.K. Kelley, G.J. Gores, Cholangiocarcinoma - evolving concepts and therapeutic strategies, Nat Rev Clin Oncol 15(2) (2018) 95-111.
R. Wood, D.H. Brewster, L.A. Fraser, H. Brown, P.C. Hayes, O.J. Garden, Do increases in mortality from intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma reflect a genuine increase in risk? Insights from cancer registry data in Scotland, Eur J Cancer 39(14) (2003) 2087-92.
B. Sripa, C. Pairojkul, Cholangiocarcinoma: lessons from Thailand, Curr Opin Gastroenterol 24(3) (2008) 349-56.
Y. Shaib, H.B. El-Serag, The epidemiology of cholangiocarcinoma, Semin Liver Dis 24(2) (2004) 115-25.
I. Joo, J.M. Lee, J.H. Yoon, Imaging Diagnosis of Intrahepatic and Perihilar Cholangiocarcinoma: Recent Advances and Challenges, Radiology 288(1) (2018) 7-23.
T. Ben-Menachem, Risk factors for cholangiocarcinoma, Eur J Gastroen Hepat 19(8) (2007) 615-617.
G.L. Tyson, H.B. El-Serag, Risk factors for cholangiocarcinoma, Hepatology 54(1) (2011) 173-84.
T.Y. Lee, S.S. Lee, S.W. Jung, S.H. Jeon, S.C. Yun, H.C. Oh, S. Kwon, S.K. Lee, D.W. Seo, M.H. Kim, D.J. Suh, Hepatitis B virus infection and intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma in Korea: a case-control study, Am J Gastroenterol 103(7) (2008) 1716-20.
Y.M. Zhou, Z.F. Yin, J.M. Yang, B. Li, W.Y. Shao, F. Xu, Y.L. Wang, D.Q. Li, Risk factors for intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma: a case-control study in China, World J Gastroenterol 14(4) (2008) 632-5.
F. Donato, U. Gelatti, A. Tagger, M. Favret, M.L. Ribero, F. Callea, C. Martelli, A. Savio, P. Trevisi, G. Nardi, Intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma and hepatitis C and B virus infection, alcohol intake, and hepatolithiasis: a case-control study in Italy, Cancer Causes Control 12(10) (2001) 959-64.
H.J. Kim, J.S. Kim, S.J. Suh, B.J. Lee, J.J. Park, H.S. Lee, C.D. Kim, Y.T. Bak, Cholangiocarcinoma Risk as Long-term Outcome After Hepatic Resection in the Hepatolithiasis Patients, World J Surg 39(6) (2015) 1537-42.
S. Kubo, H. Kinoshita, K. Hirohashi, H. Hamba, Hepatolithiasis associated with cholangiocarcinoma, World J Surg 19(4) (1995) 637-41.
C.H. Su, Y.M. Shyr, W.Y. Lui, F.K. P'Eng, Hepatolithiasis associated with cholangiocarcinoma, Br J Surg 84(7) (1997) 969-73.
Y. Suzuki, T. Mori, M. Yokoyama, T. Nakazato, N. Abe, Y. Nakanuma, H. Tsubouchi, M. Sugiyama, Hepatolithiasis: analysis of Japanese nationwide surveys over a period of 40 years, J Hepatobiliary Pancreat Sci 21(9) (2014) 617-22.
M.F. Chen, Y.Y. Jan, C.S. Wang, L.B. Jeng, T.L. Hwang, S.C. Chen, Intrahepatic stones associated with cholangiocarcinoma, Am J Gastroenterol 84(4) (1989) 391-5.
T. Uenishi, H. Hamba, S. Takemura, K. Oba, M. Ogawa, T. Yamamoto, S. Tanaka, S. Kubo, Outcomes of hepatic resection for hepatolithiasis, Am J Surg 198(2) (2009) 199-202.
M.F. Chen, Y.Y. Jan, L.B. Jeng, T.L. Hwang, C.S. Wang, S.C. Chen, T.C. Chao, H.M. Chen, W.C. Lee, T.S. Yeh, Y.F. Lo, Intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma in Taiwan, J Hepatobiliary Pancreat Surg 6(2) (1999) 136-41.
M.F. Chen, Peripheral cholangiocarcinoma (cholangiocellular carcinoma): clinical features, diagnosis and treatment, J Gastroenterol Hepatol 14(12) (1999) 1144-9.
J. Bridgewater, P.R. Galle, S.A. Khan, J.M. Llovet, J.W. Park, T. Patel, T.M. Pawlik, G.J. Gores, Guidelines for the diagnosis and management of intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma, J Hepatol 60(6) (2014) 1268-89.
C. Valls, A. Guma, I. Puig, A. Sanchez, E. Andia, T. Serrano, J. Figueras, Intrahepatic peripheral cholangiocarcinoma: CT evaluation, Abdom Imaging 25(5) (2000) 490-6.
M. Iavarone, F. Piscaglia, S. Vavassori, M. Galassi, A. Sangiovanni, L. Venerandi, L.V. Forzenigo, R. Golfieri, L. Bolondi, M. Colombo, Contrast enhanced CT-scan to diagnose intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma in patients with cirrhosis, J Hepatol 58(6) (2013) 1188-93.
Y.T. Kim, J.S. Byun, J. Kim, Y.H. Jang, W.J. Lee, J.K. Ryu, S.W. Kim, Y.B. Yoon, C.Y. Kim, Factors predicting concurrent cholangiocarcinomas associated with hepatolithiasis, Hepatogastroenterology 50(49) (2003) 8-12.
A. Guglielmi, A. Ruzzenente, A. Valdegamberi, F. Bagante, S. Conci, A.D. Pinna, G. Ercolani, F. Giuliante, L. Capussotti, L. Aldrighetti, C. Iacono, Hepatolithiasis-associated cholangiocarcinoma: results from a multi-institutional national database on a case series of 23 patients, Eur J Surg Oncol 40(5) (2014) 567-575.
W. Liang, L. Xu, P. Yang, L. Zhang, D. Wan, Q. Huang, T. Niu, F. Chen, Novel Nomogram for Preoperative Prediction of Early Recurrence in Intrahepatic Cholangiocarcinoma, Front Oncol 8 (2018) 360.
X. Xu, H.L. Zhang, Q.P. Liu, S.W. Sun, J. Zhang, F.P. Zhu, G. Yang, X. Yan, Y.D. Zhang, X.S. Liu, Radiomic analysis of contrast-enhanced CT predicts microvascular invasion and outcome in hepatocellular carcinoma, J Hepatol 70(6) (2019) 1133-1144.
Y. Huang, Z. Liu, L. He, X. Chen, D. Pan, Z. Ma, C. Liang, J. Tian, C. Liang, Radiomics Signature: A Potential Biomarker for the Prediction of Disease-Free Survival in Early-Stage (I or II) Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer, Radiology 281(3) (2016) 947-957.
G.W. Ji, F.P. Zhu, Y.D. Zhang, X.S. Liu, F.Y. Wu, K. Wang, Y.X. Xia, Y.D. Zhang, W.J. Jiang, X.C. Li, X.H. Wang, A radiomics approach to predict lymph node metastasis and clinical outcome of intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma, Eur Radiol 29(7) (2019) 3725-3735.
M. Bogowicz, D. Vuong, M.W. Huellner, M. Pavic, N. Andratschke, H.S. Gabrys, M. Guckenberger, S. Tanadini-Lang, CT radiomics and PET radiomics: ready for clinical implementation?, Q J Nucl Med Mol Imaging 63(4) (2019) 355-370.
C.P. Smith, M. Czarniecki, S. Mehralivand, R. Stoyanova, P.L. Choyke, S. Harmon, B. Turkbey, Radiomics and radiogenomics of prostate cancer, Abdom Radiol (NY) 44(6) (2019) 2021-2029.
G. Chen, H. Yu, Y. Wang, C. Li, M. Zhou, Z. Yu, X. Zheng, X. Wu, Y. Shan, Q. Zhang, Q. Zeng, A novel nomogram for the prediction of intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma in patients with intrahepatic lithiasis complicated by imagiologically diagnosed mass, Cancer Manag Res 10 (2018) 847-856.
C. Nioche, F. Orlhac, S. Boughdad, S. Reuze, J. Goya-Outi, C. Robert, C. Pellot-Barakat, M. Soussan, F. Frouin, I. Buvat, LIFEx: A Freeware for Radiomic Feature Calculation in Multimodality Imaging to Accelerate Advances in the Characterization of Tumor Heterogeneity, Cancer Res 78(16) (2018) 4786-4789.
L. Chen, H. Wang, H. Zeng, Y. Zhang, X. Ma, Evaluation of CT-based radiomics signature and nomogram as prognostic markers in patients with laryngeal squamous cell carcinoma, Cancer Imaging 20(1) (2020) 28.
E.R. DeLong, D.M. DeLong, D.L. Clarke-Pearson, Comparing the areas under two or more correlated receiver operating characteristic curves: a nonparametric approach, Biometrics 44(3) (1988) 837-45.
M. Fitzgerald, B.R. Saville, R.J. Lewis, Decision curve analysis, JAMA 313(4) (2015) 409-10.
Y.Q. Huang, C.H. Liang, L. He, J. Tian, C.S. Liang, X. Chen, Z.L. Ma, Z.Y. Liu, Development and Validation of a Radiomics Nomogram for Preoperative Prediction of Lymph Node Metastasis in Colorectal Cancer, J Clin Oncol 34(18) (2016) 2157-64.
T. Fang, H. Wang, Y. Wang, X. Lin, Y. Cui, Z. Wang, Clinical Significance of Preoperative Serum CEA, CA125, and CA19-9 Levels in Predicting the Resectability of Cholangiocarcinoma, Dis Markers 2019 (2019) 6016931.
S.H. Loosen, C. Roderburg, K.L. Kauertz, A. Koch, M. Vucur, A.T. Schneider, M. Binnebosel, T.F. Ulmer, G. Lurje, W. Schoening, F. Tacke, C. Trautwein, T. Longerich, C.H. Dejong, U.P. Neumann, T. Luedde, CEA but not CA19-9 is an independent prognostic factor in patients undergoing resection of cholangiocarcinoma, Sci Rep 7(1) (2017) 16975.
V. Das, J. Kalita, M. Pal, Predictive and prognostic biomarkers in colorectal cancer: A systematic review of recent advances and challenges, Biomed Pharmacother 87 (2017) 8-19.
Y. Wang, J. Li, Y. Xia, R. Gong, K. Wang, Z. Yan, X. Wan, G. Liu, D. Wu, L. Shi, W. Lau, M. Wu, F. Shen, Prognostic nomogram for intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma after partial hepatectomy, J Clin Oncol 31(9) (2013) 1188-95.
K. Sasaki, G.A. Margonis, N. Andreatos, Q. Chen, C. Barbon, F. Bagante, M. Weiss, I. Popescu, H.P. Marques, L. Aldrighetti, S.K. Maithel, C. Pulitano, T.W. Bauer, F. Shen, G.A. Poultsides, O. Soubrane, G. Martel, B. Groot Koerkamp, A. Guglielmi, I. Endo, F.N. Aucejo, T.M. Pawlik, Serum tumor markers enhance the predictive power of the AJCC and LCSGJ staging systems in resectable intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma, HPB (Oxford) 20(10) (2018) 956–965.
H. Zhang, T. Yang, M. Wu, F. Shen, Intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma: Epidemiology, risk factors, diagnosis and surgical management, Cancer Lett 379(2) (2016) 198-205.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest to disclose.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Xue, B., Wu, S., Zhang, M. et al. A radiomic-based model of different contrast-enhanced CT phase for differentiate intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma from inflammatory mass with hepatolithiasis. Abdom Radiol 46, 3835–3844 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00261-021-03027-6
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00261-021-03027-6