Abstract
Objective
Accurate joint fluid quantification on MRI cannot simply rely on measuring the maximum fluid depth or using an ellipsoid approximation as this does not fully characterize the complex shape of a fluid-filled joint. As per the Outcome Measurement in Rheumatology (OMERACT) filter, we sought to evaluate the feasibility, reliability, and validity of a semi-automated supervised technique to quantify hip effusion volume.
Materials and methods
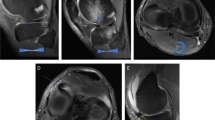
Ninety-three hip osteoarthritis patients were imaged with coronal short TI inversion recovery (STIR) and sagittal intermediate weighted fat-suppressed (IWFS) sequences at two time points (Fig. 1). Volumetric quantitative measurement (VQM) of joint fluid and measurement of the largest femoral neck fluid thickness (FTM) was performed using the custom MATLAB software. Self-reported Western Ontario and McMaster Universities Osteoarthritis Index (WOMAC) and clinical measures of pain, stiffness, and function were recorded.
Results
Inter-observer reliability was significantly higher for VQM than FTM (ICC = 0.96 vs. 0.85, p < 0.05). VQM and FTM correlated moderately (r = 0.76, p < 0.0001). There was significantly more articular fluid in symptomatic than asymptomatic hips at baseline (mean = 9.8 vs. 5.9 mL). Volumetric quantitative measurement generally displayed more frequent and stronger correlations to clinical parameters than FTM. Volumetric quantitative measurement required 3.9 min/hip vs. < 1 min/hip for femoral neck fluid thickness.
Conclusion
Volumetric quantitative measurement of joint effusion can serve as an MRI gold-standard, could apply to other joints and collections, and is highly suited to future automation.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Plotnikoff R, Karunamuni N, Lytvyak E, Penfold C, Schopflocher D, Imayama I, et al. Osteoarthritis prevalence and modifiable factors: a population study. BMC Public Health. 2015;15(1):1–10.
Shari Miura L, Bathon JM. Osteoarthritis in older adults. Journal of the American Geriatrics Society. 1998 (2):216.
Steer KJD, Bostick GP, Woodhouse LJ, Nguyen TT, Schankath A, Lambert RGW, et al. Can effusion-synovitis measured on ultrasound or MRI predict response to intra-articular steroid injection in hip osteoarthritis? Skelet Radiol. 2019;48(2):227–37.
Lai WC, Arshi A, Wang D, Seeger LL, Motamedi K, Levine BD, et al. Efficacy of intraarticular corticosteroid hip injections for osteoarthritis and subsequent surgery. Skelet Radiol. 2018;47(12):1635–40.
McCabe PS, Maricar N, Parkes MJ, Felson DT, O'Neill TW. The efficacy of intra-articular steroids in hip osteoarthritis: a systematic review. Osteoarthr Cartil. 2016;24(9):1509-17.
Leite VF, Daud Amadera JE, Buehler AM. Viscosupplementation for hip osteoarthritis: a systematic review and meta-analysis of the efficacy on pain and disability, and the occurrence of adverse events. Arch Phys Med Rehabil. 2018;99(3):574–83.
Damien L, Isabelle C-V, Jacqueline C, Anne-Christine R, Frédéric T, Astrid P-W, et al. Macroscopic and microscopic features of synovial membrane inflammation in the osteoarthritic knee: correlating magnetic resonance imaging findings with disease severity. Arthritis & Rheumatism. 2005 (11):3492.
Fernandez-Madrid F, Karvonen RL, Teitge RA, Miller PR, An T, Negendank WG. Synovial thickening detected by MR imaging in osteoarthritis of the knee confirmed by biopsy as synovitis. Magn Reson Imaging. 1995;13(2):177–83.
Atukorala I, Kwoh CK, Guermazi A, Roemer FW, Boudreau RM, Hannon MJ, et al. Synovitis in knee osteoarthritis: a precursor of disease? Ann Rheum Dis. 2016;75(2):390–5.
Dihlmann W, Tillmann B. Pericoxal fat stripes and the capsule of the hip joint. The anatomical-radiological correlations. Rofo: Fortschritte Auf Dem Gebiete Der Rontgenstrahlen Und Der Nuklearmedizin. 1992;156(5):411–4.
Bowerman JW, Sena JM, Chang R. The teardrop shadow of the pelvis; anatomy and clinical significance. Radiology. 1982;143(3):659–62.
Hall FM. Radiographic diagnosis and accuracy in knee joint effusions. Radiology. 1975;115(1):49–54.
Sudula SN. Imaging the hip joint in osteoarthritis: a place for ultrasound? Ultrasound (Leeds, England). 2016;24(2):111–8.
Roemer FW, Hunter DJ, Winterstein A, Li L, Kim YJ, Cibere J, et al. Hip Osteoarthritis MRI Scoring System (HOAMS): reliability and associations with radiographic and clinical findings. Osteoarthr Cartil. 2011;19(8):946–62.
Deseyne N, Conrozier T, Lellouche H, Maillet B, Weber U, Jaremko JL, et al. Hip Inflammation MRI Scoring System (HIMRISS) to predict response to hyaluronic acid injection in hip osteoarthritis. Joint Bone Spine. 2018;85(4):475–80.
Moss SG, Schweitzer ME, Jacobson JA, Brossmann J, Lombardi JV, Dellose SM, et al. Hip joint fluid: detection and distribution at MR imaging and US with cadaveric correlation. Radiology. 1998;208(1):43–8.
Wang X, Blizzard L, Jin X, Chen Z, Zhu Z, Han W, et al. Quantitative assessment of knee effusion-synovitis in older adults: association with knee structural abnormalities. Arthritis & Rheumatology (Hoboken, NJ). 2016;68(4):837–44.
Habib S, Guermazi A, Ozonoff A, Hayashi D, Crema M, Roemer F. MRI-based volumetric assessment of joint effusion in knee osteoarthritis using proton density-weighted fat-suppressed and T1-weighted contrast-enhanced fat-suppressed sequences. Skelet Radiol. 2011;40(12):1581–5.
Wang Y, Teichtahl AJ, Pelletier J, Abram F, Wluka AE, Hussain SM, et al. Knee effusion volume assessed by magnetic resonance imaging and progression of knee osteoarthritis: data from the osteoarthritis initiative. Rheumatology (Oxford, England). 2019;58(2):246–53.
Li W, Abram F, Pelletier J, Raynauld J, Dorais M, d'Anjou M, et al. Fully automated system for the quantification of human osteoarthritic knee joint effusion volume using magnetic resonance imaging. Arthritis research & therapy. 2010;12(5):R173.
Altman R, Alarcon G, Greenwald R, Hochberg M, Howell D, Ike R, et al. The American college of rheumatology criteria for the classification and reporting of osteoarthritis of the hip. Arthritis and rheumatism. 1991 (5):505.
Kersten P, White PJ, Tennant A. The visual analogue WOMAC 3.0 scale--internal validity and responsiveness of the VAS version. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2010;11:80.
Bellamy N, Buchanan WW, Goldsmith CH, Campbell J, Stitt LW. Validation study of WOMAC: a health status instrument for measuring clinically important patient relevant outcomes to antirheumatic drug therapy in patients with osteoarthritis of the hip or knee. J Rheumatol. 1988;15(12):1833–40.
Nilsdotter AK, Lohmander LS, Klässbo M, Roos EM. Hip disability and osteoarthritis outcome score (HOOS) – validity and responsiveness in total hip replacement. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2003;4(1):10.
Otsu N. A threshold selection method from gray-level histograms. IEEE Transactions on Systems, Man, and Cybernetics, Systems, Man and Cybernetics, IEEE Transactions on, IEEE Trans Syst, Man, Cybern. 1979 (1):62.
Guermazi A, Roemer FW, Crema MD, Englund M, Hayashi D. Imaging of non-osteochondral tissues in osteoarthritis. Osteoarthr Cartil. 2014;22(10):1590–605.
Rennesson-Rey B, Rat A, Chary-Valckenaere I, Bettembourg-Brault I, Juge N, Dintinger H, et al. Does joint effusion influence the clinical response to a single Hylan GF-20 injection for hip osteoarthritis? Joint Bone Spine. 2008;75(2):182–8.
Bierma-Zeinstra SMA, Bohnen AM, Verhaar JAN, Prins A, Ginai-Karamat AZ, Laméris JS. Sonography for hip joint effusion in adults with hip pain. Ann Rheum Dis. 2000;59(3):178–82.
Yen CH, Leung HB, Tse PY. Effects of hip joint position and intra-capsular volume on hip joint intra-capsular pressure: a human cadaveric model. J Orthop Surg Res. 2009;4:8.
Steer KJD, Bostick GP, Woodhouse LJ, Nguyen TT, Schankath A, Lambert RGW, et al. Can effusion-synovitis measured on ultrasound or MRI predict response to intra-articular steroid injection in hip osteoarthritis? Skelet Radiol. 2018;48(2):227–37.
Acknowledgments
We would like to acknowledge Dr. Abhilash Hareendranathan’s assistance in this manuscript.
Funding
The work was funded by the Alberta Health Services Chair in Diagnostic Imaging (currently held by Dr. Jaremko).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
Dr. Ramin Mandegaran is a medical advisor for ThinkSono. Dr. Robert GW Lambert provides consultation for CareArthritis, Image Analysis Group, and Parexel. All other authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Quinn-Laurin, V., Bostick, G.P., Thejeel, B. et al. Development of a technique for MRI gold-standard direct volumetric measurement of complex joint effusion, and validation at the hip. Skeletal Radiol 50, 781–787 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00256-020-03630-6
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00256-020-03630-6