Abstract.
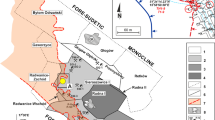
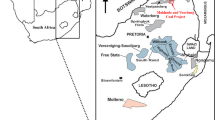
In northern France, the weathering and oxidation of pyrite-containing coal mine spoils can lead to sulphate enrichment of the underlying chalk aquifer. Two sites have been studied: in a free water-table zone and in a confined-aquifer zone. Solid-fraction analyses have shown a release of carbon and sulphur from the waste dump surfaces. The groundwater isotopic analysis (notably 34S) showed the existence of two sulphate sources (mine spoils and gypsum contained in Cenozoic formations). This study also saw evidence of bacterial sulphate reduction in the confined zone as a result of the release of carbon from mine spoils. The effects of acid mine drainage were the presence of secondary minerals as small jarosite dots (cm) present at depth, gypsum or ferrihydrite present on the bottom of temporary ponds, and an increase in sulphate content of groundwaters sampled downstream of the waste dumps. This acid mine drainage is buffered during its infiltration into the chalk aquifer. This is evidenced by the increase in magnesium, calcium, bicarbonate or strontium, resulting of carbonate digestion downstream of the sites. No significant leaching of metals, even those associated with the sulphide fraction, was seen at the two studied sites.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Electronic Publication
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Denimal, S., Tribovillard, N., Barbecot, F. et al. Leaching of coal-mine tips (Nord-Pas-de-Calais coal basin, France) and sulphate transfer to the chalk aquifer: example of acid mine drainage in a buffered environment. Env Geol 42, 966–981 (2002). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00254-002-0602-3
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00254-002-0602-3